| Citation: | She-ming Chen, Fu-tian Liu, Zhuo Zhang, Qian Zhang, Wei Wang, 2021. Changes of groundwater flow field of Luanhe River Delta under the human activities and its impact on the ecological environment in the past 30 years, China Geology, 4, 455-462. doi: 10.31035/cg2021060 |
Changes of groundwater flow field of Luanhe River Delta under the human activities and its impact on the ecological environment in the past 30 years
-
Abstract
The Luanhe River Delta is located in the center of the Circum-Bohai Sea Economic Zone. It enjoys rapid economic and social development while suffering relatively water scarcity. The overexploitation of groundwater in the Luanhe River Delta in recent years has caused the continuous drop of groundwater level and serious environmental and geological problems. This study systematically analyzes the evolution characteristics of the population, economy, and groundwater exploitation in the Luanhe River Delta and summarizes the change patterns of the groundwater flow regime in different aquifers in the Luanhe River Delta according to previous water resource assessment data as well as the latest groundwater survey results. Through comparison of major source/sink terms and groundwater resources, the study reveals the impacts of human activities on the groundwater resources and ecological environment in the study area over the past 30 years from 1990 to 2020. The results are as follows. The average annual drop rate of shallow groundwater and the deep groundwater in the centers of depression cones is 0.4 m and 1.64 m, respectively in the Luanhe River Delta in the past 30 years. The depression cones of shallow and deep groundwater in the study area cover an area of 545.32 km² and 548.79 km², respectively, accounting for more than 10% of the total area of the Luanhe River Delta. Overexploitation of groundwater has further aggravated land subsidence. As a result, two large-scale subsidence centers have formed, with a maximum subsidence rate of up to 120 mm/a. The drop of groundwater level has induced some ecological problems in the Luanhe River Delta area, such as the zero flow and water quality deterioration of rivers and continuous shrinkage of natural wetlands and water. Meanwhile, the proportion of natural wetland area to the total wetland area has been decreased from 99% to 8% and the water area from 1776 km² to 263 km². These results will provide data for groundwater overexploitation control, land subsidence prevention, and ecological restoration in plains and provide services for water resources management and national land space planning.
-

-
References
Bao K, Liu JL, You XG, Shi X, Meng B. 2017. A new comprehensive ecological risk index for risk assessment on Luanhe River, China. Environmental Geochemistry & Health, 40(5), 1965–1978. doi: 10.1007/s10653-017-9978-6. Chen P, Ma Z, Wang W, Shi PX, Meng LS, Du D. 2014. Ground water contamination assessment in the Luanhe River Delta. Geological Survey and Research, 37(2), 115–122 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen WH. 1999. Groundwater in Hebei. Beijing, Seismological Press, 121‒345 (in Chinese). Cheng MH, Jiao XY, Guo WH, Wang SF, Pan YC, Zhang H, Sang HH. 2020. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of irrigation water requirement for main crops in the plain area of Hebei Province. Irrigation and Drainage, 69(5), 1051–1062. doi: 10.1002/ird.2489. Cui XT, Wang XQ, Liu B. 2020. The characteristics of heavy metal pollution in surface dust in Tangshan, a heavily industrialized city in North China, and an assessment of associated health risks. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 210, 106432. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106432. Dang XZ, Gao MS, Wen Z, Jakada H, Hou GH, Liu S. 2020. Evolutionary process of saline groundwater influenced by palaeo-seawater trapped in coastal deltas: A case study in Luanhe River Delta, China. Estuarine, 244, 106894. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106894. Department of Water Resources of Hebei Province. 2001–2019. Hebei Water Resources Bulletin (in Chinese). Du D. 2007. Analysis of Groundwater Pollution and Trend in the Luanhe Delta Area. Xi’an, Ph.D thesis,1–30 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du SP. 2020. Preliminary research on water resources optimal allocation of Tangshan City. Haihe Water Resources, (6), 23–24 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo LL, Zhang J, Li YR, McLennan J. 2021. Experimental and numerical investigation of the influence of groundwater flow on the borehole heat exchanger performance: A case study from Tangshan, China. Energy and Buildings, 248, 111199. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111199. Haihe River Water Conservancy Commission of Ministry of Water Resources. 1993. Luanhe Chronicle. Shijiazhuang, Hebei People’s Publishing House, 1‒306 (in Chinese). Hao H, Gao B, Wang J, Zhou H, Zhu C. 2012. Distribution characteristic and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Luanhe River. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 31(6), 1000–1005. doi: 10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z. Huang W, Ma W, Liu XB. Zhang JM. 2021. Numerical study of hydrodynamics and water quality in Qinhuangdao coastal waters, China: Implication for pollutant loadings management. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 26, 63–76. doi: 10.1007/s10666-020-09715-9. Jones J, Jones CE, Bekaert DPS. 2021. Value of InSAR for monitoring land subsidence to support water management in the San Joaquin valley, California. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 4, 1–7. doi: 10.1111/1752-1688.12942. Kang XN, Yin P, Liu JQ. 2016. Variations in water and sediment discharges of mediam and small rivers and their response to human activities: A case study on the Luan river. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, (6), 1–6 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li JZ, Feng P. 2007. Runoff variations in the Luanhe River Basin during 1956‒2002. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 17(3), 339–350. doi: 10.1007/s11442-007-0339-8. Li SX. 1994. The Luanhe deltaic region-a treasured land awaiting to be comprehensive by developed. Resources Science, (1), 67–69 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lin TY. 2020. Thinking on water environment management and protection in the Luanhe River basin. Water Resources Development and Management, (1), 14–17 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu K. 2010. Study on current situation of soil and water loss in Tangshan section of the middle and lower reaches of Luanhe River. China Water Resources, (10), 28–29 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu Y, Lu CM, Ma R. 2019. Discriminant analysis on iron ion provenance in groundwater, eastern Hebei Plain. Geological Survey and Research, 42(2), 135–142 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu SB, Zhang XL, Tang Y. 2020. Evolutionary analysis on structural characteristics of water resource system in basins of Northern China. Sustainable Development, 28(4), 800–812. Lu XP, Wang G, Chen N, Liu SH. 2014. Hydrological effects of water resources development and its eco-environmental response in Luanhe River Basin. Environmental Protection Science, 40(1), 18–21 (in Chinese with English abstract). National Bureau of Statistics of China. 1995. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing, 1–85. Wang YX, Li JZ, Feng P, Hu R. 2016. Analysis of drought characteristics over Luanhe River basin using the joint deficit index. Journal of water and climate change, 7(2), 340–352. Shi Y, Han ZY, Xu Y, Zhou BT, Wu J. 2019. Future changes of climate extremes in Xiongan New Area and Jing-Jin-Ji district based on high resolution (6.25 km) combined statistical and dynamical downscaling datasets. Climate Change Research, 15(2), 140‒149. Tian HL. 2011. The Dynamic Analysis of the Modern Luanhe River Delta. Shijiazhuang, Hebei Normal University, Master thesis, 1‒77 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tian Y, Jiang Y, Liu Q, Dong MY, Xu DX, Liu Y, Xu X. 2019. Using a water quality index to assess the water quality of the upper and middle streams of the Luanhe River, northern China. Science of The Total Environment, 667(2), 142–151. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.356. Wang YJ, Zhai JQ, Song LC. 2021. Waterlogging risk assessment of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration in the past 60 years. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 145, 1039–1051. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-162526/v. Xu J, Renaud FG, Barrett B. 2021. Modelling land system evolution and dynamics of terrestrial carbon stocks in the Luanhe River Basin, China: a scenario analysis of trade-offs and synergies between sustainable development goals. Sustainability Science, 1–23. doi: 10.1007/s11625-021-01004-y. Yan J, Liu C, Li X. 2015. Hydrological impacts of climate change simulated by HIMS Models in the Luanhe River Basin, north China. Water Resources Management, 29(4), 1365–1384. Yan XL, Bao ZX, Zhang JY, Wang GQ, He RM, Liu CS. 2020. Quantifying contributions of climate change and local human activities to runoff decline in the upper reaches of the Luanhe River basin. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 28, 67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jher.2018.11.002. Zhang BC. 2013. Analysis of water consumption change trend in Hebei Province. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, (z2), 24–26 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang YF, Li FX. 1983. The characteristics of material component and the material resources in Huanghe river and luanhe river. Marine Sciences, 7(3), 16–18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang ZJ. 2009. Investigation and Evaluation on Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater in North China Plain. Beijing, Geological Publishing House, 1–55 (in Chinese). Zhao Y, Wang CL, Yang JQ, Bi J. 2021. Coupling model of groundwater and land subsidence and simulation of emergency water supply in Ningbo urban area, China. Journal of Hydrology, 594(8), 125956. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125956. Zhao YF. 2019. Analysis on the development and utilization degree and existing problems of water resources in Qinhuangdao city. Ground Water, 41(1), 184–186 (in Chinese with English abstract). -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Landform types of Luanhe River Delta, North China.
-
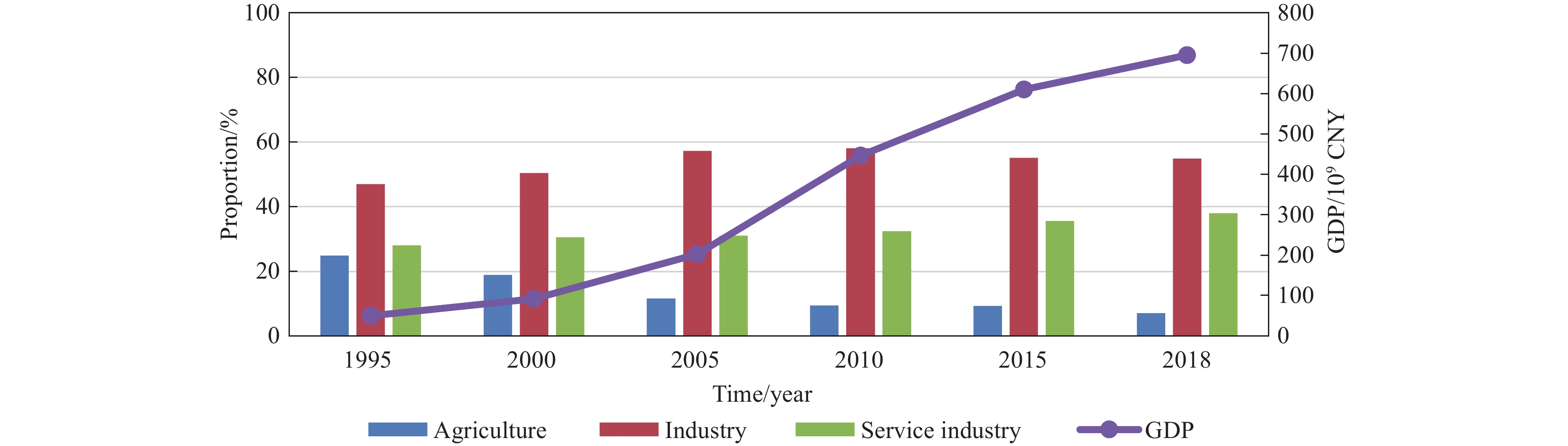
Figure 2.
Agriculture, industry, service industry, and GDP of Tangshan City, Hebei Province from 1995 to 2018.
-
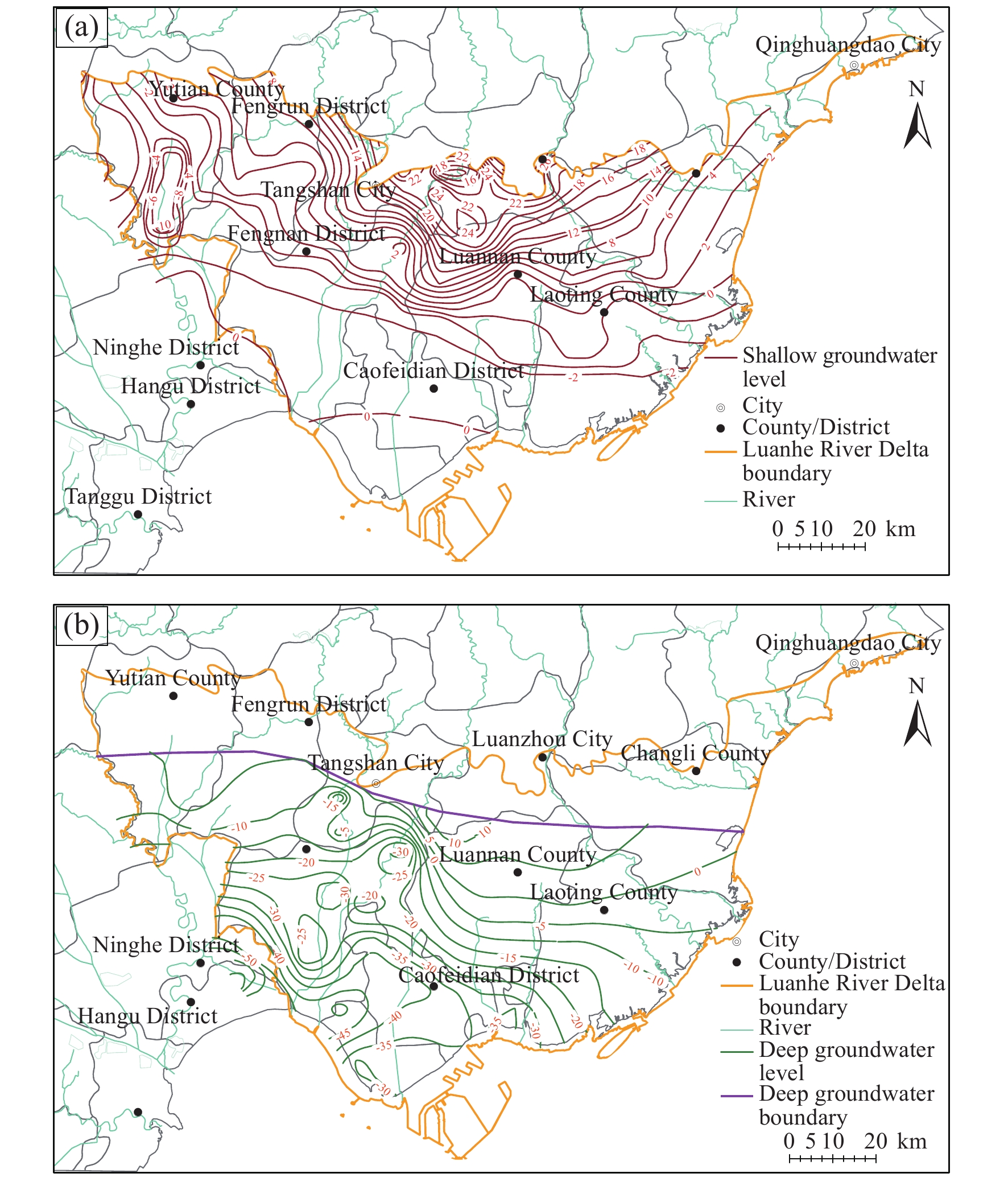
Figure 3.
Groundwater flow regime in Luanhe River Delta in June 2005 (a‒shallow groundwater; b‒deep groundwater).
-
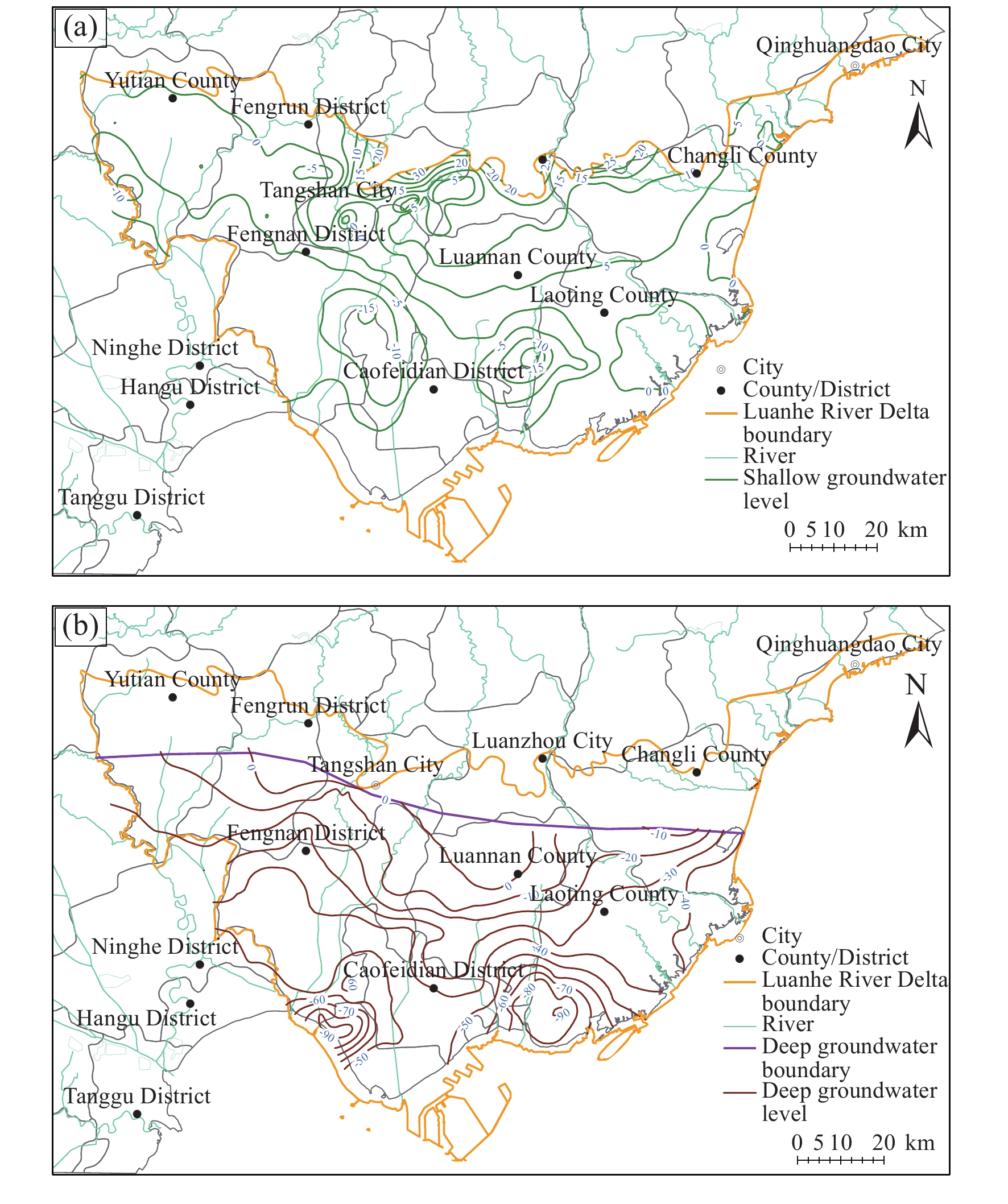
Figure 4.
Groundwater flow regime in Luanhe River Delta in June 2020 (a‒shallow groundwater; b‒deep groundwater).
-
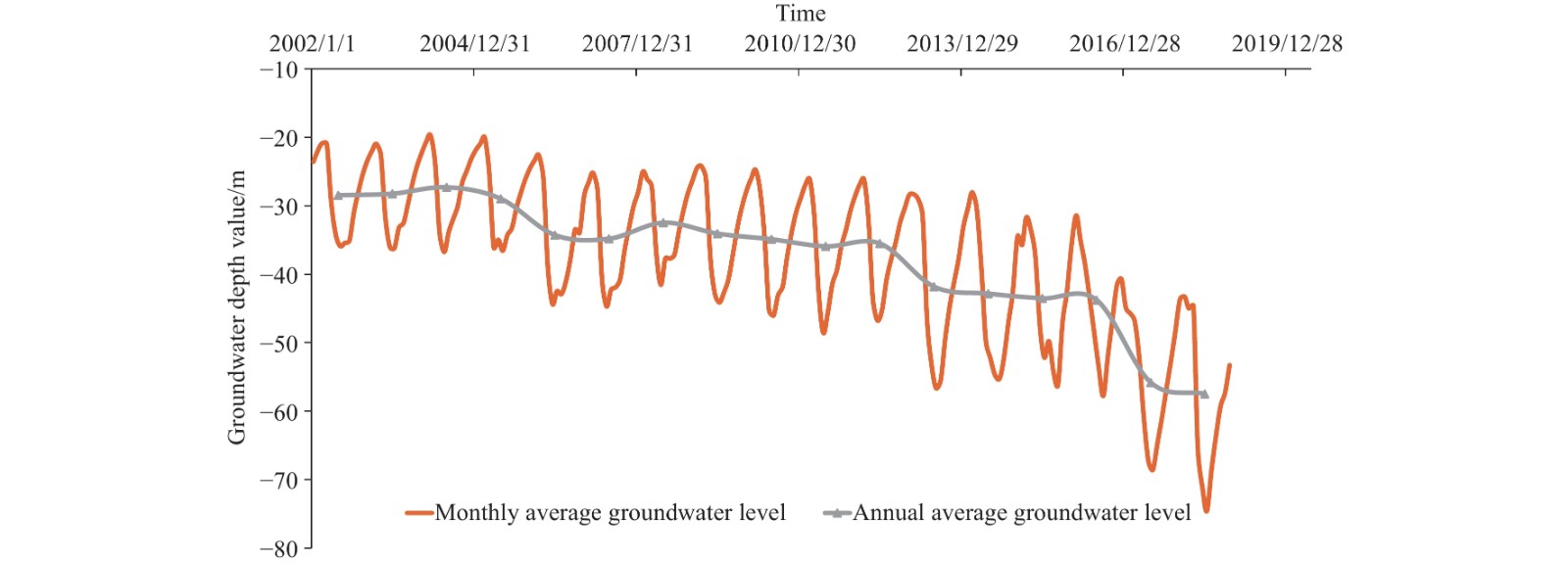
Figure 5.
The variation curve of deep groundwater level in Caofeidian area, Hebei Province.
-
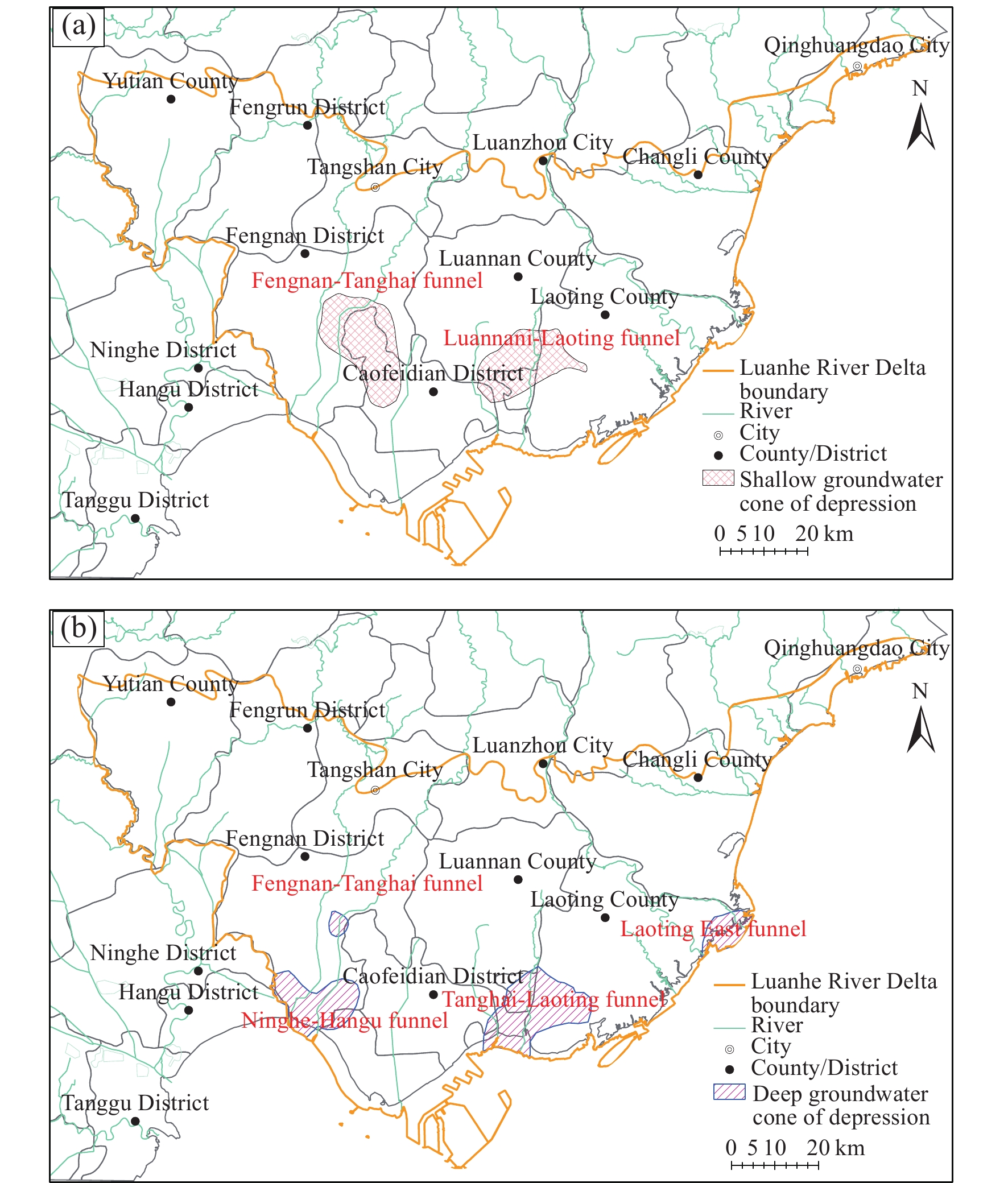
Figure 6.
Distribution position of groundwater funnels in 2020 (a‒shallow groundwater; b‒deep groundwater).
-
Figure 7.
Contour maps of land subsidence rate in the Luanhe River Delta (a-2010; b-2014; c-2018).





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: