| Citation: | Xu-xuan Ma, Li-E Gao, Zhong-bao Zhao, Xi-jie Chen, Hai-bing Li, 2021. Early Eocene leucocratic sill/dike swarms in the Gangdese belt, southern Xizang: Tectonic implications for Indo-Asian collision, China Geology, 4, 56-66. doi: 10.31035/cg2021019 |
Early Eocene leucocratic sill/dike swarms in the Gangdese belt, southern Xizang: Tectonic implications for Indo-Asian collision
-
Abstract
The timing of the initial Indo-Asian collision is a subject of debate for a long time. Besides, the magmatic trace of the collisional process is also unclear. In the present study, the authors report Early Eocene leucocratic sill/dike swarms in the northern edge of the Nymo intrusive complex of the Gangdese belt, southern Xizang. The Nymo intrusive complex was emplaced at ca. 50–47 Ma and surrounded by the metamorphosed Jurassic-aged Bima Formation volcano-sedimentary sequence along its northern side. At outcrops, the leucocratic sills/dikes intruded along or truncated the deformed foliations of the host Bima Formation, which has been subject to high-temperature amphibolite-facies metamorphism at ca. 50–47 Ma. Detailed cathodoluminescence image analyses reveal that the zircon grains of the leucocratic sills/dikes have core-mantle textures. The cores yield the Jurassic ages comparable to the protolith ages of the Bima Formation. In contrast, the mantles of zircon grains yield weighted mean ages of ca. 49–47 Ma, representing the crystallization timing of these leucocratic sills/dikes. The coeval ages for the Nymo intrusive complex, the high-temperature metamorphism, and the leucocratic sills/dikes indicate that a close relationship exists among them. The authors tentatively suggest that these leucocratic sills/dikes were generated from partial melting of the Jurassic-aged Bima Formation volcanic rocks, triggered by the high heat from the magma chamber of the Nymo intrusive complex. This Early Eocene tectono-thermal event of coeval magmatism, metamorphism and partial melting was most likely formed during the Indo-Asian collisional setting.
-
Keywords:
- Leucocratic sill/dike swarm /
- Early Eocene /
- Indo-Asian collision /
- Gangdese /
- Xizang /
- China
-

-
References
Aikman AB, Harrison TM, Ding L. 2008. Evidence for Early (>44 Ma) Himalayan Crustal Thickening, Tethyan Himalaya, southeastern Xizang. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 274, 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2008.06.038. Aitchison JC, Ali JR, Davis AM. 2007. When and where did India and Asia collide? Journal of Geophysical Research, 112, B05423. doi: 10.1029/2006jb004706. Ao SJ, Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Zhang JE, Zhang ZY, Yang L. 2018. Components and structures of the eastern Tethyan Himalayan Sequence in SW China: Not a passive margin shelf but a mélange accretionary prism. Geological Journal, 53, 2665–2689. doi: 10.1002/gj.3103. Carosi R, Montomoli C, Rubatto D, Visonà D. 2013. Leucogranite intruding the South Xizang Detachment in western Nepal: implications for exhumation models in the Himalayas. Terra Nova, 25, 478–489. doi: 10.1111/ter.12062. Chung SL, Chu MF, Zhang YQ, Xie YW, Lo CH, Lee TY, Lan CY, Li XH, Zhang Q, Wang YZ. 2005. Xizang tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism. Earth-Science Reviews, 68, 173–196. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.05.001. Cottle JM, Jessup MJ, Newell DL, Horstwood MSA, Noble SR, Parrish RR, Waters DJ, Searle MP. 2009. Geochronology of granulitized eclogite from the Ama Drime Massif: Implications for the tectonic evolution of the South Xizang Himalaya. Tectonics, 28, TC1002. doi: 10.1029/2008tc002256. Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C, Wang S. 1986. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central and southern Xizang: 39Ar-40Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamical significance. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 79, 281–302. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(86)90186-X. de Sigoyer J, Guillot S, Dick P. 2004. Exhumation of the ultrahigh-pressure Tso Morari unit in eastern Ladakh (NW Himalaya): A case study. Tectonics, 23, TC3003. doi: 10.1029/2002tc001492. Ding HX, Zhang ZM, Dong X, Tian ZL, Xiang H, Mu HC, Gou ZB, Shui XF, Li WC, Mao LJ. 2016. Early Eocene (ca. 50 Ma) collision of the Indian and Asian continents: Constraints from the North Himalayan metamorphic rocks, southeastern Xizang. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 435, 64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2015.12.006. Donaldson DG, Webb AAG, Menold CA, Kylander-Clark ARC, Hacker BR. 2013. Petrochronology of Himalayan ultrahigh-pressure eclogite. Geology, 41, 835–838. doi: 10.1130/g33699.1. Dong X, Zhang ZM, Klemd R, He ZY, Tian ZL. 2018. Late Cretaceous tectonothermal evolution of the southern Lhasa terrane, South Xizang: Consequence of a Mesozoic Andean-type orogeny. Tectonophysics, 730, 100–113. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.03.001. Dong X, Zhang ZM, Niu YL, Tian ZL, Zhang LL. 2020. Reworked Precambrian metamorphic basement of the Lhasa terrane, southern Xizang: Zircon/titanite U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and geochemistry. Precambrian Research, 336, 105496. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2019.105496. Gao LE, Zeng LS, Asimow PD. 2016. Contrasting geochemical signatures of fluid-absent versus fluid-fluxed melting of muscovite in metasedimentary sources: The Himalayan leucogranites. Geology, 45, 39–42. doi: 10.1130/G38336.1. Gao LE, Zeng LS, Xie KJ. 2012. Eocene high grade metamorphism and crustal anatexis in the North Himalaya Gneiss Domes, Southern Xizang. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57, 639–650. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4805-4. Guillot S, Mahéo G, de Sigoyer J, Hattori KH, Pêcher A. 2008. Tethyan and Indian subduction viewed from the Himalayan high- to ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks. Tectonophysics, 451, 225–241. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.059. Hu XM, Garzanti E, Moore T, Raffi I. 2015. Direct stratigraphic dating of India-Asia collision onset at the Selandian (middle Paleocene, 59 ±1 Ma). Geology, 43, 859–862. doi: 10.1130/g36872.1. Iaccarino S, Montomoli C, Carosi R, Massonne HJ, Langone A, Visonà D. 2015. Pressure-temperature-time-deformation path of kyanite-bearing migmatitic paragneiss in the Kali Gandaki valley (Central Nepal): Investigation of Late Eocene-Early Oligocene melting processes. Lithos, 231, 103–121. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.005. Ji WQ, Wu FY, Chung SL, Li JX, Liu CZ. 2009. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholith, southern Xizang. Chemical Geology, 262, 229–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.01.020. Ji WQ, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wang XC, Liu CZ, Li QL, Liu ZC, Liu XC, Wang JG. 2016. Eocene Neo-Tethyan slab breakoff constrained by 45 Ma oceanic island basalt–type magmatism in southern Xizang. Geology, 44, 283–286. doi: 10.1130/g37612.1. Kaneko Y, Katayama I, Yamamoto H, Misawa K, Rehman HU, Kausar AB, Shiraishi K. 2003. Timing of Himalayan ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism: Sinking rate and subduction angle of the Indian continental crust beneath Asia. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21, 589–599. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00466.x. Kang ZQ, Xu JF, Wilde SA, Feng ZH, Chen JL, Wang BD, Fu WC, Pan HB. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group Volcanic Rocks, Southern Lhasa Terrane: Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese Magmatic Arc. Lithos, 200–201, 157–168. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.04.019. Kohn MJ, Corrie SL. 2011. Preserved Zr-temperatures and U-Pb ages in high-grade metamorphic titanite: Evidence for a static hot channel in the Himalayan orogen. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 311, 136–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.09.008. Laskowski AK, Kapp P, Vervoort JD, Ding L. 2016. High-pressure Tethyan Himalaya rocks along the India-Asia suture zone in southern Xizang. Lithosphere, 8, 574–582. doi: 10.1130/l544.1. Lee HY, Chung SL, Lo CH, Ji JQ, Lee TY, Qian Q, Zhang Q. 2009. Eocene Neotethyan slab breakoff in southern Xizang inferred from the Linzizong volcanic record. Tectonophysics, 477, 20–35. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.031. Lee J, Whitehouse MJ. 2007. Onset of mid-crustal extensional flow in southern Xizang: Evidence from U/Pb zircon ages. Geology, 35, 45–48. doi: 10.1130/g22842a.1. Leech ML, Singh S, Jain AK, Klemperer SL, Manickavasagam RM. 2005. The onset of India-Asia continental collision: Early, steep subduction required by the timing of UHP metamorphism in the western Himalaya. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234, 83–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2005.02.038. Liu XC, Wu FY, Yu LJ, Liu ZC, Ji WQ, Wang JG. 2016. Emplacement age of leucogranite in the Kampa Dome, southern Xizang. Tectonophysics, 667, 163–175. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.001. Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG, Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257, 34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004. Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0: A Geochronological, Toolkit for Microsoft Excel Berkeley Geochronology Center. Berkeley Geochronology Center (special publication), 4, 1–71. Ma XX, Xu ZQ, Meert JG. 2016. Eocene slab breakoff of Neotethys as suggested by dioritic dykes in the Gangdese magmatic belt, southern Xizang. Lithos, 248–251, 55–65. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.01.008. Ma XX, Xu ZQ, Meert JG, Santosh M. 2017a. Early Jurassic intra-oceanic arc system of the Neotethys Ocean: Constraints from andesites in the Gangdese magmatic belt, south Xizang. Island Arc, e12202. doi: 10.1111/iar.12202. Ma XX, Meert JG, Xu ZQ, Zhao ZB. 2017b. Evidence of magma mixing identified in the Early Eocene Caina pluton from the Gangdese Batholith, southern Xizang. Lithos, 278–281, 126–139. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.01.020. Ma XX, Meert JG, Xu ZQ, Zhao ZB. 2018. The Jurassic Yeba Formation in the Gangdese arc of S. Xizang: Implications for upper plate extension in the Lhasa terranebet. International Geology Review, 1–23. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2018.1434835. Ma XX, Xu ZQ, Zhao ZB, Yi ZY. 2020a. Identification of a new source for the Triassic Langjiexue Group: Evidence from a gabbro-diorite complex in the Gangdese magmatic belt and zircon microstructures from sandstones in the Tethyan Himalaya, southern Xizang. Geosphere, 16, 407–434. doi: 10.1130/ges02154.1. Ma XX, Shi B, Xiong FH, Li HB. 2020b. Magma mixing of the Quxu batholith in the Gangdese belt, southern Xizang: Evidence from microstructure of hornblende in microgranular enclaves. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(10), 3063–3080 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.10.08. Ma XX, Xu ZQ, Meert JG, Tian ZL, Li HB. 2020c. Early Eocene high-flux magmatism and concurrent high-temperature metamorphism in the Gangdese belt, southern Xizang. GSA Bulletin. doi: 10.1130/B35770.1. Ma XX, Xu ZQ, Liu F, Zhao ZB, Li HB. 2021. Continental arc tempos and crustal thickening: A case study in the Gangdese arc, southern Xizang. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95, 107–123 (in Chinese with English abstract). Meng J, Wang CS, Zhao XX, Coe R, Li YL, Finn D. 2012. India-Asia collision was at 24 degrees N and 50 Ma: Palaeomagnetic proof from southernmost Asia. Scientific Reports, 2, 925. doi: 10.1038/srep00925. Meng YK, Xiong FH, Xu ZQ, Ma XX. 2019. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous mafic enclaves and their host granites in the Nyemo region of southern Xizang: Implications for the tectonic-magmatic evolution of the Central Gangdese Belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 176, 27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.01.041. Meng YK, Xu ZQ, Xu Y, Ma SW. 2018. Late Triassic granites from the Quxu batholith shedding a new light on the evolution of the Gangdese belt in Southern Xizang. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 92, 462–481. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13537. Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Deng JF, Dong GC, Zhou S, Guo TY, Zhang SQ, Wang LL. 2003. Response of volcanism to the India-Asia collision. Earth Science Frontiers, 10, 135–148 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mo XX, Dong GC, Zhao ZD, Guo TY, Wang LL, Chen T. 2005a. Timing of magma mixing in the Gangdise magmatic belt during the India-Asia collision: Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 79, 66–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2005.tb00868.x. Mo XX, Dong GC, Zhao ZD, Zhou S, Wang LL, Qiu RZ, Zhang FQ. 2005b. Spatial and temporal distribution and characteristics of granitoids in the Gangdese, Xizang and implication for crustal growth and evolution. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11, 281–290 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Zhou S, Dong GC, Liao ZL. 2007. On the timing of India-Asia continental collision. Geological Bulletin of China, 26, 1240–1244 (in Chinese with English abstract). Regis D, Warren CJ, Young D, Roberts NMW. 2014. Tectono-metamorphic evolution of the Jomolhari massif: Variations in timing of syn-collisional metamorphism across western Bhutan. Lithos, 190–191. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.01.001. Rubatto D, Chakraborty S, Dasgupta S. 2013. Timescales of crustal melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines (Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya) inferred from trace element-constrained monazite and zircon chronology. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165, 349–372. doi: 10.1007/s00410-012-0812-y. Tapponnier P, Xu ZQ, Roger F, Meyer B, Arnaud N, Wittlinger G, Yang JS. 2001. Oblique Stepwise Rise and Growth of the Xizang Plateau. Science, 294, 1671–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.105978. van Hinsbergen DJJ, Lippert PG, Li SH, Huang WT, Advokaat EL, Spakman W. 2019. Reconstructing Greater India: Paleogeographic, kinematic, and geodynamic perspectives. Tectonophysics, 760, 69–94. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.04.006. van Hinsbergen DJJ, Steinberger B, Doubrovine PV, Gassmöller R. 2011. Acceleration and deceleration of India-Asia convergence since the Cretaceous: Roles of mantle plumes and continental collision. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(B06101). doi:10.1029/2010JB008051. Wang C, Ding L, Zhang LY, Ding XL, Yue YH. 2019. Early Jurassic high-Mg andesites in the Quxu area, southern Lhasa terrane: Implications for magma evolution related to a slab rollback of the Neo-Tethyan Ocean. Geological Journal, 54, 2508–2524. doi: 10.1002/gj.3309. Wang Q, Zhu DC, Cawood PA, Zhao ZD, Liu SA, Chung SL, Zhang LL, Liu D, Zheng YC, Dai JG. 2015. Eocene magmatic processes and crustal thickening in southern Xizang: Insights from strongly fractionated ca. 43 Ma granites in the western Gangdese Batholith. Lithos, 239, 128–141. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.10.003. Wang YF, Zeng LS, Gao JH, Zhao LH, Gao LE, Shang Z. 2019. Along-arc variations in isotope and trace element compositions of Paleogene gabbroic rocks in the Gangdese batholith, southern Xizang. Lithos, 324–325, 877–892. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.11.036. Wen DR, Liu DY, Chung SL, Chu MF, Ji JQ, Zhang Q, Song B, Lee TY, Yeh MW, Lo CH. 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the Gangdese Batholith and implications for Neotethyan subduction in southern Xizang. Chemical Geology, 252, 191–201. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.03.003. Xu WC, Zhang HF, Luo BJ, Guo L, Yang H. 2015. Adakite-like geochemical signature produced by amphibole-dominated fractionation of arc magmas: An example from the Late Cretaceous magmatism in Gangdese belt, south Xizang. Lithos, 232, 197–210. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.001. Xu ZQ, Wang Q, Pêcher A, Liang FH, Qi XX, Cai ZH, Li HQ, Zeng LS, Cao H. 2013. Orogen-parallel ductile extension and extrusion of the Greater Himalaya in the late Oligocene and Miocene. Tectonics, 32, 191–215. doi: 10.1002/tect.20021. Yin A, Harrison TM. 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Xizang orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28, 211–280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211. Zeng LS, Gao LE, Xie KJ, Jing LZ. 2011. Mid-Eocene high Sr/Y granites in the Northern Himalayan Gneiss Domes: Melting thickened lower continental crust. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 303, 251–266. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2011.01.005. Zhang HF, Xu WC, Guo JQ, Zong KQ, Cai HM, Yuan HL. 2007. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic composition of deformed granite in the southern margin of the Gangdese belt, Xizang: Evidence for early Jurassic subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic slab. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23, 1347–1353 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang ZM, Dong X, Xiang H, He ZY, Liou JG. 2014. Metagabbros of the Gangdese arc root, south Xizang: Implications for the growth of continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143, 268–284. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.01.045. Zhang ZM, Xiang H, Dong X, Ding HX, He ZY. 2015. Long-lived high-temperature granulite-facies metamorphism in the Eastern Himalayan orogen, south Xizang. Lithos, 212–215, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.10.009. Zhang ZM, Zhao GC, Santosh M, Wang JL, Dong X, Liou JG. 2010. Two stages of granulite facies metamorphism in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, south Xizang: Petrology, zircon geochronology and implications for the subduction of Neo-Tethys and the Indian continent beneath Asia. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28, 719–733. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1314.2010.00885.x. Zhou LM, Wang R, Hou ZQ, Li C, Zhao H, Li XW, Qu WJ. 2018. Hot Paleocene-Eocene Gangdese arc: Growth of continental crust in southern Xizang. Gondwana Research, 62, 178–197. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2017.12.011. Zhu DC, Wang Q, Cawood PA, Zhao ZD, Mo XX. 2017. Raising the Gangdese Mountains in southern Xizang. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 122, 214–223. doi: 10.1002/2016jb013508. -
Access History

-
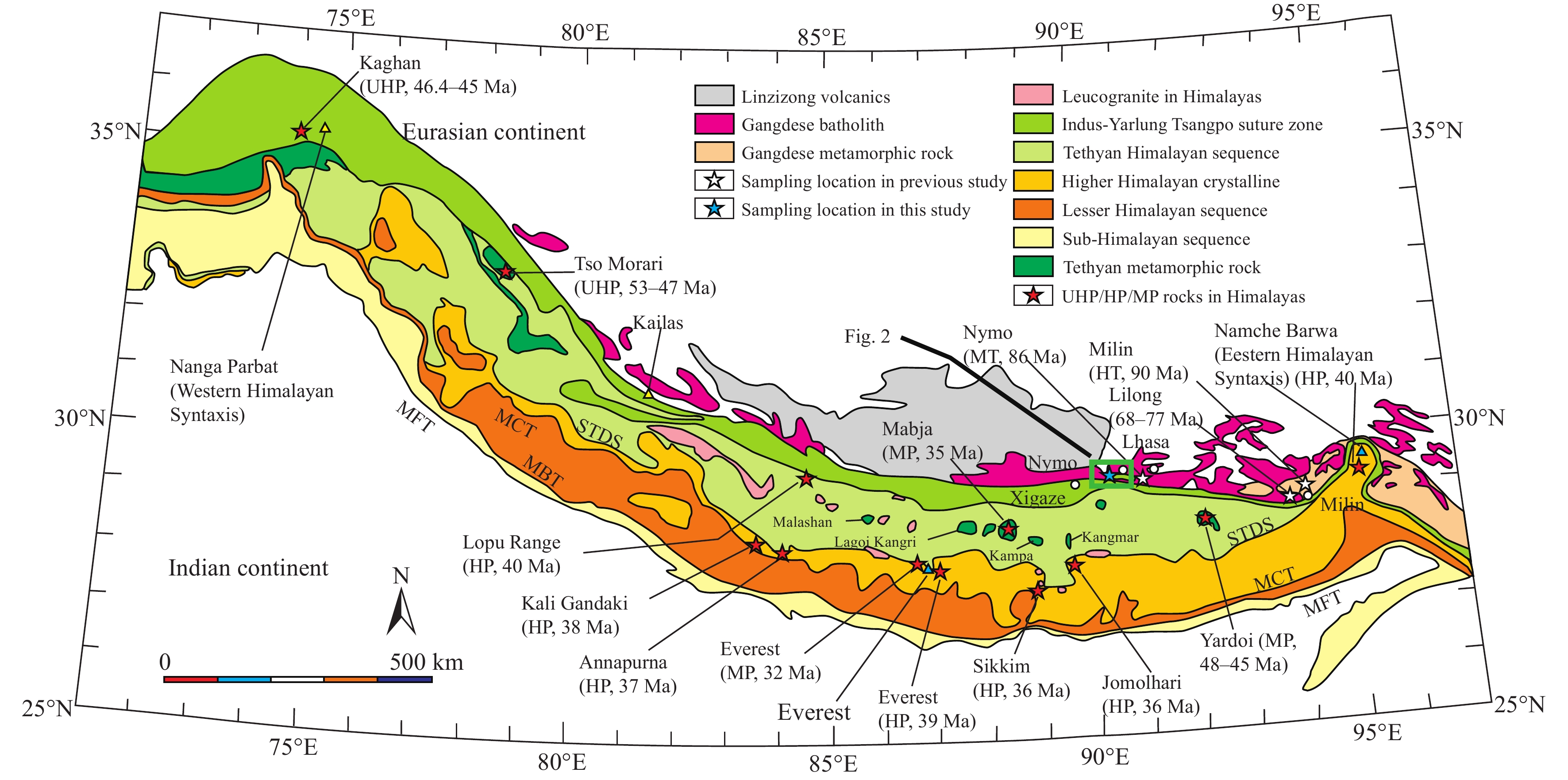
Figure 1.
Simplified geological map of southern Xizang showing Himalayan-Gangdese orogen (modified from Guillot S et al., 2008). Data in Himalaya: Annapurna (Kohn MJ and Corrie SL, 2011), Everest (Cottle JM et al., 2009), Jomolhari (Regis D et al., 2014), Kaghan (Kaneko Y et al., 2003), Kali Gandaki (Iaccarino S et al., 2015), Lopu Range (Laskowski AK et al., 2016), Mabja dome (Lee J and Whitehouse MJ, 2007), Namche Barwa (Zhang ZM et al., 2015), Sikkim (Rubatto D et al., 2013), Tso Morari (Donaldson DG et al., 2013), and Yardoi dome (Ding HX et al., 2016; Gao LE et al., 2012). Data in Gangdese: Lilong (Zhang ZM et al., 2014), Milin (Zhang ZM et al., 2010), and Nymo (Dong X et al., 2018). STDS–South Xizang Detachment System; MCT–Main Central Thrust; MBT–Main Boundary Thrust; MFT–Main Frontal Thrust; MP–median pressure; HP–high-pressure; UHP– ultrahigh-pressure; MT–median temperature; HT–high temperature.
-
Figure 2.
Simplified map for the central Gangdese belt, southern Xizang. Reported ages are collected from Dong X et al., 2018; Ji WQ et al., 2009; Ma XX et al., 2020a, 2020c; Meng YK et al., 2019; Mo XX et al., 2005a; Wang C et al., 2019; Wen DR et al., 2008; Xu WC et al., 2015; Zhang HF et al., 2007.
-
Figure 3.
Cross-section of the Nymo intrusive complex showing the leucocratic sill swarm. The ages of the ca. 178 Ma granite, ca. 47 Ma diorite, ca. 42 Ma dikes, and ca. 34 Ma granite are referred to Ji WQ et al., 2009; Ma XX et al., 2016, 2020c; Zhang HF et al., 2007.
-
Figure 4.
Field photos for the Nymo intrusive complex. a–deformed granite; b–undeformed diorite; c–garnet-biotite gneiss; d–plagioclase amphibolite; e–about 34 Ma granite; and f–leucocratic sill swarm within the amphibolitic rocks. Grt–garnet.
-
Figure 5.
Field photos for the studied leucocratic sills. a, b–leucocratic sill swarm; c–stoped block warped by the sill; d–leucocratic sill intruded along the deformed foliation; e–necking of the sill, and; f–leucocratic sill truncated the deformed foliation.
-
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs (cross-polarized light image) to illustrate petrographic features of the leucocratic sills (a, c, and e). Photomicrographs (plane-polarized light image) to illustrate petrographic features of the leucocratic sills (b, d, and f). Qtz–quartz; Bt–biotite; Pl–plagioclase; Mag–magnetite; Kfs–K-feldspar.
-
Figure 7.
Representative cathodoluminescence (CL) images of the zircon grains and the corresponding dating spots. The CL images were taken at Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences.
-
Figure 8.
U-Pb weighted mean ages of zircon grains from the leucocratic sills/dikes (a, c, e, and g) and field photos of sampling location (b, d, f, and h).
-
Figure 9.
Tentative cartoon showing the Early Eocene tectonic regime of the Indo-Asian collision and the relationship between the Nymo intrusive complex and the leucocratic sill/dike swarm.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:







