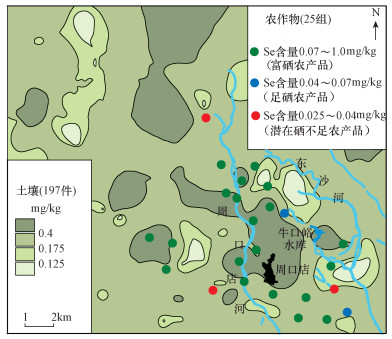
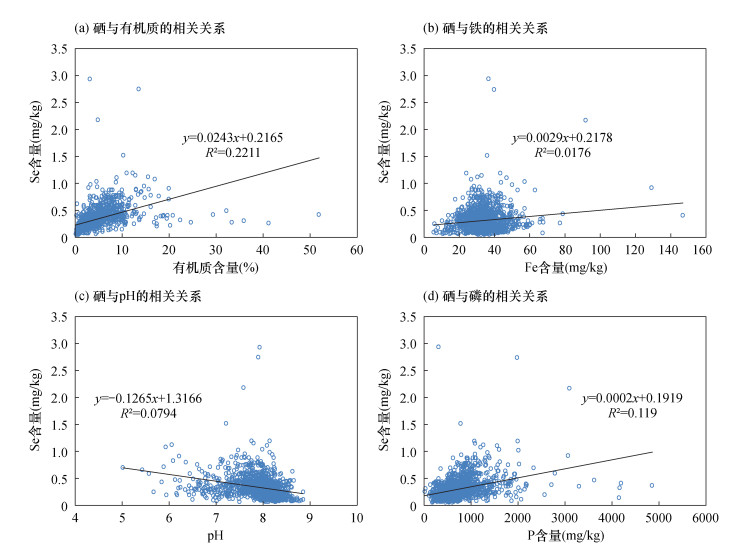
| [1] |
韩晓霞, 魏洪义.硒的营养生物学研究进展[J].南方农业学报, 2015, 46(10):1798-1804. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1798
CrossRef Google Scholar
Han X X, Wei H Y.Research progress in nutritional biology of selenium[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(10):1798-1804. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2015.10.1798
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Fordyce F.Selenium geochemistry and health[J].AMBIO:A Journal of the Human Environment, 2007, 36(1):94-97. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[94:SGAH]2.0.CO;2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
朱晓华, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等.川西高原天然剖面土壤硒的含量及分布特征[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(4):673-682.
Google Scholar
Zhu X H, Liu X D, Liu J C, et al.Contents and distributions characteristics of selenium in natural soil profile samples from the Western Sichuan plateau area[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(4):673-682.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Fordyce F M.Selenium Deficiency and Toxicity in the Environment[M]//Selinus O.Essentials of Medical Geology.2013: 375-416.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Yanai J, Mizuhara S, Yamada H.Soluble selenium content of agricultural soils in Japan and its determining factors with reference to soil type, land use and region[J].Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2015, 61(2):312-318. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2014.997147
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
李春生.开阳县硒资源农业开发利用研究[D].贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2000: 1-2.
Google Scholar
Li C S.Research on Development and Utilization of Selenium Resources in Agriculture of Kaiyang County[D].Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2000: 1-2.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
马迅, 宗良纲, 诸旭东, 等.江西丰城生态硒谷土壤硒有效性及其影响因素[J].安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(4):1588-1593.
Google Scholar
Ma X, Zong L G, Zhu X D, et al.Effectiveness and influential factors of soil selenium in selenium valley, Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(4):1588-1593.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
陈娟, 宋帅, 史雅娟, 等.富硒农业生产基地土壤硒资源空间分布特征及评价[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(12):2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
CrossRef Google Scholar
Chen J, Song S, Shi Y J, et al.Spatial distribution and assessment of selenium in soils of a Se-enrich agricultural production base[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12):2185-2190. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015040302
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
吴俊.福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176.
Google Scholar
Wu J.The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing factors[J].Chinese Geology, 2018, 45(6):1167-1176.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
蒋慧豪, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等.广东省普宁市土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J].现代地质, 2019, 33(1):161-168.
Google Scholar
Jiang H H, Luo J, Cai L M, et al.Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Puning City, Guangdong Province[J].Geoscience, 2019, 33(1):161-168.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
李福燕, 漆智平, 李许明.海口市农田土壤硒含量特征与农作物硒特征[J].土壤通报, 2016, 47(3):630-635.
Google Scholar
Li F Y, Qi Z P, Li X M.Survey and research of selenium contents in farmland soil and crops of Haikou[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3):630-635.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
陈锦平, 刘永贤, 潘丽萍, 等.浔郁平原不同作物的硒富集特征及其影响因素[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159.
Google Scholar
Chen J P, Liu Y X, Pan L P, et al.Selenium accumulation characteristics and influential factors of different crops in Xunyu Plain[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1155-1159.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
李海蓉, 杨林生, 谭见安, 等.我国地理环境硒缺乏与健康研究进展[J].生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):381-386.
Google Scholar
Li H R, Yang L S, Tan J A, et al.Progress on selenium deficiency in geographical environment and its health impacts in China[J].Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5):381-386.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等.北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):859-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Guo L, Yang Z F, Ruan Q H, et al.Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing Plain[J].Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):859-864. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
黄淇, 成杭新, 陈出新, 等.北京市房山区富硒土壤调查与评价[J].物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
Google Scholar
Huang Q, Cheng H X, Chen C X, et al.The investigation and evaluation of selenium-rich soil in Fangshan District of Beijing City[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Greco A D S, Sanjinez Argandona E J, Corazza M Z, et al.Use of chemometric tools for HG-AAS instrumental optimization in the determination of Se in nuts grown in Brazil[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(6):251-257.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
中国环境监测总站.中国土壤元素背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Google Scholar
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre.Background Values of Soil Elements in China[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
谭见安.环境生命元素与克山病:生态化学地理研究[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社, 1996.
Google Scholar
Tan J A.Environmental Life Elements and Keshan Disease:Eco-chemical Geography[M].Beijing:China Medical Science Press, 1996.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
邹辉, 王卉, 段碧辉, 等.恩施州宣恩地区富硒土壤硒含量特征及影响因素研究[J].资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):546-550.
Google Scholar
Zou H, Wang H, Duan B H, et al.Study on selenium contents characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Xuanen Area of Enshi and its influencing factors[J].Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4):546-550.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
曹容浩.福建省龙海市表层土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):282-288.
Google Scholar
Cao R H.Study on selenium content of surface soils in Longhai, Fujian and its influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):282-288.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
王秋爽, 罗杰, 蔡立梅, 等.广东省揭西县土壤硒的分布特征及影响因素研究[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1126-1133.
Google Scholar
Wang Q S, Luo J, Cai L M, et al.Distribution of soil selenium and its influential factors in Jiexi County, Guangdong Province[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1126-1133.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等.黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J].土壤学报, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274.
Google Scholar
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al.Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province, China[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
方金梅.福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(2):103-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Fang J M.Selenium speciation analysis and its transformation and enrichment in soils of Fuzhou City[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(2):103-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
周越, 吴文良, 孟凡乔, 等.土壤中硒含量、形态及有效性分析[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2014, 31(6):527-532.
Google Scholar
Zhou Y, Wu W L, Meng F Q, et al.Review on the content, specification of selenium and its availability in soils[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2014, 31(6):527-532.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183.
Google Scholar
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al.Selenium contents of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等.中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控与评价[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):273-281.
Google Scholar
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al.Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in Southern China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):273-281.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
严佳, 宗良纲, 杨旎, 等.不同pH条件和P-Se交互作用对茶园土壤Se(Ⅳ)吸附行为的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(5):935-942.
Google Scholar
Yan J, Zong L G, Yang N, et al.Effects of pH and phosphate on Se(Ⅳ) adsorption by tea garden soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(5):935-942.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
沈方科.土壤理化性质及磷硫水平对水稻吸收累积硒的影响[D].南宁: 广西大学, 2017.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10593-1018029104.htm
Google Scholar
Shen F K.Soil Factors, Sulfur and Phosphorus Fertilizations Affecting Selenium Accumulation in Paddy Rice[D].Nanning: Guangxi University, 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
严佳.磷-硒交互作用对茶园土壤硒吸附行为及有效性的影响[D].南京: 南京农业大学, 2014: 10-11.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10307-1016041793.htm
Google Scholar
Yan J.Effects of Interaction of Phosphorus-Selenium on the Adsorption Behavior and Availability of Selenium on Tea Garden Soil[D].Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014: 10-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
王鹏, 侯振安, 冶军, 等.磷和不同价态硒对小麦硒吸收转运的影响[J].新疆农业学报, 2018, 55(1):33-43.
Google Scholar
Wang P, Hou Z A, Ye J, et al.Effects of phosphorus and different valence selenium on the absorption and transport of selenium in wheat[J].Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(1):33-43.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
谭见安.中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M].北京:科学出版社, 1989.
Google Scholar
Tan J A.Atlas of Endemic Diseases and Environment of the People's Republic of China[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1989.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
李金峰, 聂兆君, 赵鹏, 等.土壤-植物系统中硒营养的研究进展[J].南方农业学报, 2016, 47(5):649-656. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.05.649
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li J F, Nie Z J, Zhao P, et al.Research progress on selenium nutrition in the soil-plant system[J].Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2016, 47(5):649-656. doi: 10.3969/j:issn.2095-1191.2016.05.649
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
朱薇, 杨守祥, 刘庆.影响植物富硒因素的研究进展[J].山东农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(4):636-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2016.04.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhu W, Yang S X, Liu Q.Advances of factors influencing selenium enrichment in plants[J].Journal of Shandong Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 47(4):636-640. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2324.2016.04.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
谭见安.地球环境与健康[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2004.
Google Scholar
Tan J A.Earth Environment and Health[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2004.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
夏卫平, 谭见安.中国一些岩类中硒的比较研究[J].环境科学学报, 1990, 10(2):125-131.
Google Scholar
Xia W P, Tan J A.A comparative study of selenium content in Chinese rocks[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1990, 10(2):125-131.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
廖启林, 任静华, 许伟伟, 等.江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802.
Google Scholar
Liao Q L, Ren J H, Xu W W, et al.Geological and geochemical background of Se-rich rice production in Yili area, Jiangsu Province[J].Geology in China, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
刘晓波, 张华, 金立新, 等.四川省屏山县土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J].环境化学, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017022101
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu X B, Zhang H, Jin L X, et al.Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in Pingshan of Sichuan Province[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10):2246-2252. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017022101
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
田欢.典型富硒区岩石-土壤-植物中硒的赋存状态及环境行为研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学, 2017: 30-31.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10491-1017740241.htm
Google Scholar
Tian H.The Occurrence State and Speciation of Selenium and Its Environmental Behaviors in Rock-Soil-Plant from Typical High-Se Areas[D].Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2017: 30-31.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
余涛, 杨忠芳, 王锐, 等.恩施典型富硒区土壤硒与其他元素组合特征及来源分析[J].土壤, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
Google Scholar
Yu T, Yang Z F, Wang R, et al.Characteristics and sources of soil selenium and other elements in typical high selenium soil area of Enshi[J].Soils, 2018, 50(6):1119-1125.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
郭跃品, 傅杨荣, 何玉生, 等.琼北火山岩区农田土壤重金属和硒含量评价及来源研究[J].安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(1):330-334.
Google Scholar
Guo Y P, Fu Y R, He Y S, et al.Evaluation and source analysis of the heavy metals and selenium in the farmland soils of volcanic area, north of Hainan Island[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(1):330-334.
Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
耿建梅, 王文斌, 温翠萍, 等.海南稻田土壤硒与重金属的含量、分布及其安全性[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(11):3477-3486.
Google Scholar
Geng J M, Wang W B, Wen C P, et al.Concentrations and distributions of selenium and heavy metals in Hainan paddy soil and assessment of ecological security[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(11):3477-3486.
Google Scholar
|





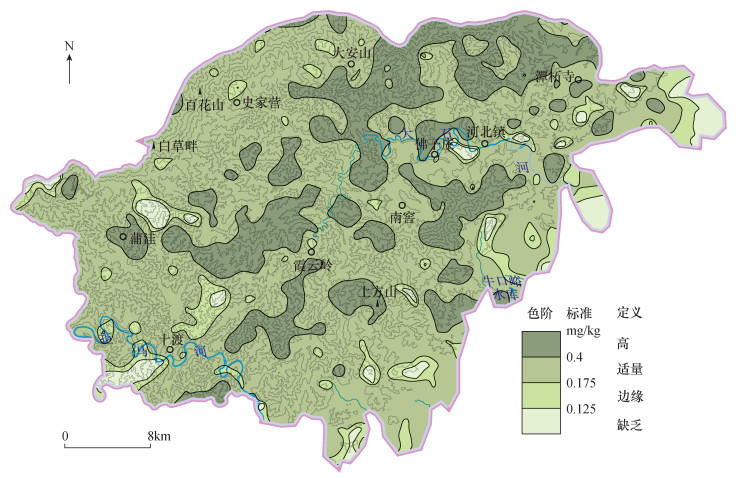

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: