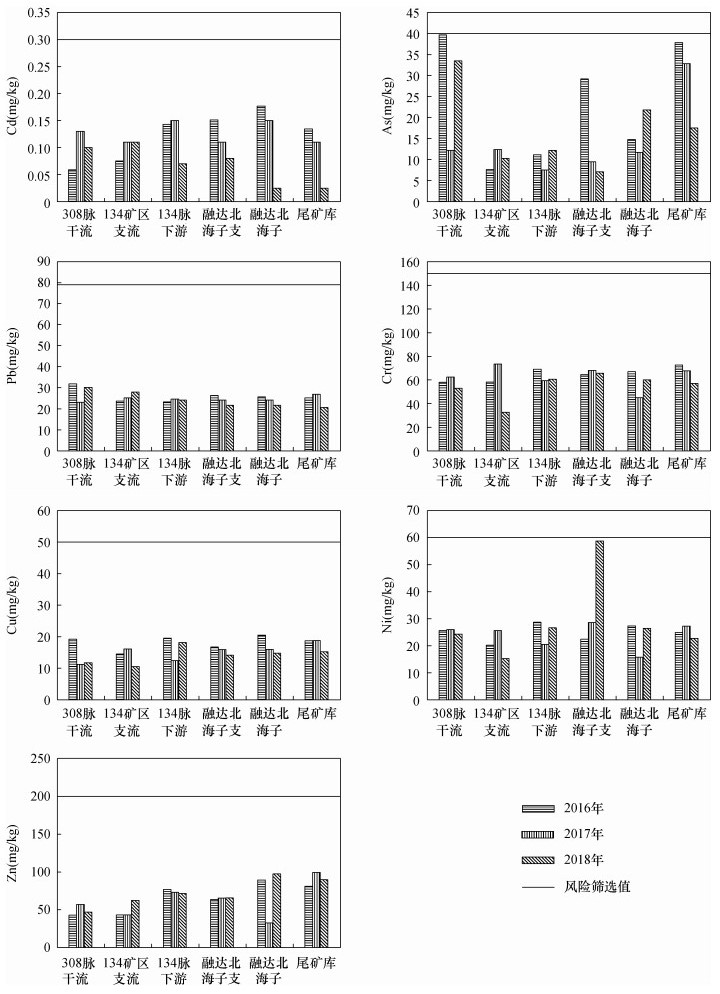
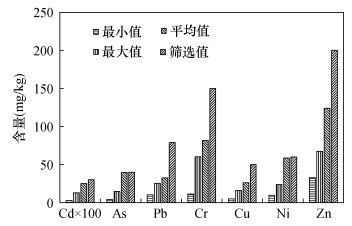
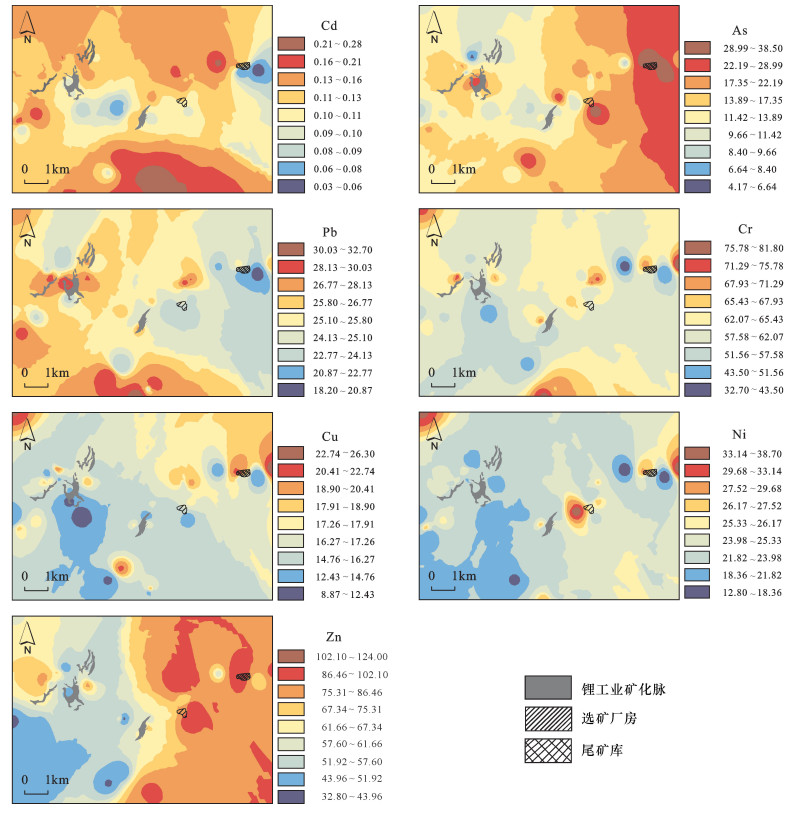
| [1] |
余广学, 张金震, 王烨, 等.郑州市土壤重金属污染状况和质量评价[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(3):340-345.
Google Scholar
Yu G X, Zhang J Z, Wang Y, et al.Investigation and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soil from Zhengzhou City[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(3):340-345.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
郑喜珅, 鲁安怀, 高翔, 等.土壤中重金属污染现状与防治方法[J].土壤与环境, 2002, 11(1):79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2002.01.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zheng X S, Lu A H, Gao X, et al.Contamination of heavy metals in soil present situation and method[J].Soil and Environmental Science, 2002, 11(1):79-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2002.01.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
刘勇, 岳玲玲, 李晋昌.太原市土壤重金属污染及其潜在生态风险评价[J].环境科学学报, 2011, 31(6):1285-1293.
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Yue L L, Li J C.Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and its potential ecological risk to the soil in Taiyuan, China[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(6):1285-1293.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Fernández C J, Barba B C, GonzáLez I, et al.Heavy metal pollution in soils around the abandoned mine sites of the Iberian Pyrite Belt (Southwest Spain)[J].Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2009, 200(1-4):211-226. doi: 10.1007/s11270-008-9905-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
徐友宁, 张江华, 柯海玲, 等.矿业活动区农田土壤重金属累积风险的评判方法——以小秦岭金矿区为例[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1097-1105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Xu Y N, Zhang J H, Ke H L, et al.An assessment method for heavy metal cumulative risk on farmland soil in the mining area:A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold mining area[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(8):1097-1105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
陈小敏, 朱保虎, 杨文, 等.密云水库上游金矿区土壤重金属空间分布、来源及污染评价[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(12):2248-2256. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015071601
CrossRef Google Scholar
Chen X M, Zhu B H, Yang W, et al.Sources, spatial distribution and contamination assessments of heavy metals in gold mine area soils of Miyun Reservoir upstream, Beijing, China[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(12):2248-2256. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2015.12.2015071601
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Candeias C, Melo R, Ávila P F, et al.Heavy metal pollution in mine-soil-plant system in S.Francisco de Assis-Panasqueira mine (Portugal)[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 44(12):12-26.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
常玉虎, 赵元艺, 曹冲, 等.德兴铜矿区主要流域内环境介质中重金属含量特征与健康风险评价[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(5):889-908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.05.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Chang Y H, Zhao Y Y, Cao C, et al.Characteristics of heavy metals content and assessment of health risk in different environment media in the Dexing copper mining area[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(5):889-908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.05.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
毛香菊, 马亚梦, 邹安华, 等.内蒙古草原某铜钼矿区土壤重金属污染特征研究[J].环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(6):156-161.
Google Scholar
Mao X J, Ma Y M, Zou A H, et al.Characteristics of heavy metals in soils from a copper-molybdenum mining area of grassland in Inner Mongolia[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 39(6):156-161.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
兰砥中, 雷鸣, 周爽, 等.湘南某铅锌矿区周围农业土壤中重金属污染及其潜在风险评价[J].环境化学, 2014, 33(8):1307-1313.
Google Scholar
Lan D Z, Lei M, Zhou S, et al.Heavy metals pollution and potential ecological risk in soils around Pb/Zn mine area in Hunan Province[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2014, 33(8):1307-1313.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
余志, 陈凤, 张军方, 等.锌冶炼区菜地土壤和蔬菜重金属污染状况及风险评价[J].中国环境科学, 2019, 39(5):2086-2094. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yu Z, Chen F, Zhang J F, et al.Contamination and risk of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from zinc smelting area[J].China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(5):2086-2094. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
金晓丹, 罗栋源, 马华菊, 等.广西某铅锌矿区土壤镉、铅、砷形态分布对水稻重金属的影响[J].西南农业学报, 2018, 31(6):1293-1299.
Google Scholar
Jin X D, Luo D Y, Ma H J, et al.Effect of soil Cd, Pb, As and their fractions distribution on corresponding heavy metals in rice surrounding lead-zinc mines in Guangxi Province[J].Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Science, 2018, 31(6):1293-1299.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
邢奕, 司艳晓, 洪晨, 等.铁矿区重金属污染对土壤微生物群落变化的影响[J].环境科学研究, 2013, 26(11):1201-1211.
Google Scholar
Xing Y, Si Y X, Hong C, et al.Impact of long term heavy metal pollution on microbial community in iron mine soil[J].Research of Environmental Science, 2013, 26(11):1201-1211.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
唐文杰, 黄江波, 余谦, 等.锰矿区农作物重金属含量及健康风险评价[J].环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(增刊1):464-473.
Google Scholar
Tang W J, Huang J B, Yu Q, et al.Analysis on the content of heavy metal in the food crop sand assessment on human health risk of manganese mine[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38(Suppplement 1):464-473.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
刘胜洪, 张雅君, 杨妙贤, 等.稀土尾矿区土壤重金属污染与优势植物累积特征[J].生态环境学报, 2014, 23(6):1042-1045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.06.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liu S H, Zhang Y J, Yang M X, et al.Heavy metal contamination of soil and concentration of dominant plants in rare earth mine tailing area[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(6):1042-1045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.06.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
徐狮.离子型稀土矿原地浸矿土壤重金属迁移转化规律研究[D].南昌: 江西理工大学, 2017.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10407-1017223392.htm
Google Scholar
Xu S.Study on Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals in in-situ Leaching Soil of Ionic Rare Earth Ore[D].Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Claveria R J R, Perez T R, Perez R E C, et al.The identification of indigenous Cu and As metallophytes in the Lepanto Cu-Au mine, Luzon, Philippines[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2019, 191(3):185. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7278-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
陈璐, 文方, 程艳, 等.铅锌尾矿库周边土壤重金属污染特征及环境风险[J].中国环境监测, 2017, 33(1):82-87.
Google Scholar
Chen L, Wen F, Cheng Y, et al.Study on contamination characteristics and environmental risk of heavy metals in the soils around Pb-Zn tailings reservoir[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(1):82-87.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
王登红, 王瑞江, 付小方, 等.对能源金属矿产资源基地调查评价基本问题的探讨——以四川甲基卡大型锂矿基地为例[J].地球学报, 2016, 37(4):471-480. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.04.09
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang D H, Wang R J, Fu X F, et al.A discussion on the major problems related to geological investigation and assessment for energy metal resources base:A case study of the Jiajika large lithium mineral resource base[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(4):471-480. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.04.09
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
王登红, 孙艳, 刘喜方, 等.锂能源金属矿产深部探测技术方法与找矿方向[J].中国地质调查, 2018, 5(1):1-9.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Sun Y, Liu X F, et al.Deep exploration technology and prospecting direction for lithium energy metal[J].Geological Survey of China, 2018, 5(1):1-9.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
王登红, 吴西顺.21世纪的能源金属——锂的奥秘[J].国土资源科普与文化, 2017(4):22-27.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Wu X S.Energy metals in the 21st century:The mystery of lithium[J].Land Resources Science and Culture, 2017(4):22-27.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
王登红, 付小方.四川甲基卡外围锂矿找矿取得突破[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):987. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang D H, Fu X F.A breakthrough in the prospecting of lithium deposits in the periphery of Sichuan Jiajika[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6):987. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.06.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
王登红, 刘丽君, 侯江龙, 等.初论甲基卡式稀有金属矿床"五层楼+地下室"勘查模型[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(5):1-7.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Liu L J, Hou J L, et al.A preliminary review of the application of "Five levels+Basement" model for Jiajika-style rare metal deposits[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(5):1-7.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
刘丽君, 付小方, 王登红, 等.甲基卡式稀有金属矿床的地质特征与成矿规律[J].矿床地质, 2015, 34(6):1187-1198.
Google Scholar
Liu L J, Fu X F, Wang D H, et al.Geological characteristics and metallogeny of Jiajika style rare metal deposits[J].Mineral Deposit, 2015, 34(6):1187-1198.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
付小方, 袁蔺平, 王登红, 等.四川甲基卡矿田新三号稀有金属矿脉的成矿特征与勘查模型[J].矿床地质, 2015, 34(6):1172-1186.
Google Scholar
Fu X F, Yuan L P, Wang D H, et al.Mineralization characteristics and prospecting model of newly discovered X03 rare metal vein in Jiajika orefield, Sichuan[J].Mineral Deposit, 2015, 34(6):1172-1186.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
鲁照玲, 胡红云, 姚洪.土壤中重金属元素电感耦合等离子体质谱定量分析方法的研究[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(2):241-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.02.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
Lu Z L, Hu H Y, Yao H.Study on quantitative analysis method for several heavy metals in soil sample by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(2):241-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.02.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
苏荣, 王晓飞, 洪欣, 等.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤中10种重金属元素[J].现代化工, 2015, 35(1):175-177.
Google Scholar
Su R, Wang X F, Hong X, et al.Determination of 10 elements in soil by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with microwave digestion[J].Modern Chemical Industry, 2015, 35(1):175-177.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
李自强, 李小英, 钟琦, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定土壤重金属普查样品中铬铜镉铅的关键环节研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1):37-41.
Google Scholar
Li Z Q, Li X Y, Zhong Q, et al.Determination of Cr, Cu, Cd and Pb in soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry for an investigation of heavy metal pollution[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1):37-41.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
国家环境保护局.中国元素土壤背景值[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Google Scholar
National Environmental Protection Agency.Background Value of Elements in Chinese Soil[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1990.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
贾婷, 贾洋洋, 余淑娟, 等.闽东某钼矿周边农田土壤钼和重金属的污染状况[J].中国环境监测, 2015, 31(1):45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Jia T, Jia Y Y, Yu S J, et al.Pollution of molybdenum and heavy metals of the soils and rice near a molybdenum mining site in Eastern Fujian[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(1):45-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
王斐, 黄益宗, 王小玲, 等.江西钨矿周边土壤重金属生态风险评价:不同评价方法的比较[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(2):225-233.
Google Scholar
Wang F, Huang Y Z, Wang X L, et al.Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surrounding soils of tungsten ores:Comparison of different evaluation methods[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(2):225-233.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
卓静, 朱延年.秦岭主脊区年降水量空间插值最优方法研究[J].干旱区地理, 2017, 40(3):555-563.
Google Scholar
Zhuo J, Zhu Y N.Spatial interpolation methods of annual average precipitation on Qinling Mountains[J].Arid Land Geography, 2017, 40(3):555-563.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
贾悦, 崔宁博, 魏新平, 等.基于反距离权重法的长江流域参考作物蒸散量算法适用性评价[J].农业工程学报, 2016, 32(6):130-138.
Google Scholar
Jia Y, Cui N B, Wei X P, et al.Applicability evaluation of different algorithm for reference crop evapotrans-piration in Yangtze River Basin based on inverse distance weighted method[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32(6):130-138.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
李凯, 赵华甫, 吴克宁, 等.土壤重金属Cd污染指数的适宜插值方法和合理采样数量研究[J].土壤通报, 2016, 47(5):1056-1064.
Google Scholar
Li K, Zhao H F, Wu K N, et al.Suitable interpolation method and reasonable sampling quantity of Cd pollution index in soil[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(5):1056-1064.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
解恒燕, 张深远, 侯善策, 等.降水量空间插值方法在小样本区域的比较研究[J].水土保持研究, 2018, 25(3):117-121.
Google Scholar
Xie H Y, Zhang S Y, Hou S C, et al.Comparison research on rainfall interpolation methods in small sample areas[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(3):117-121.
Google Scholar
|





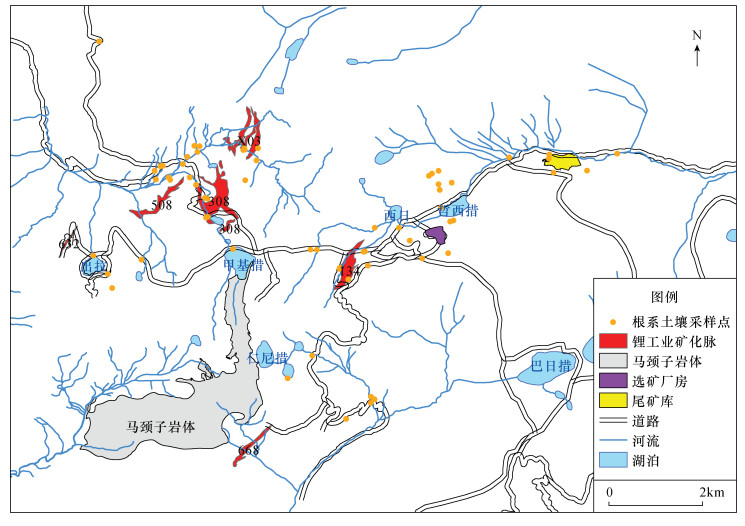

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: