| [1] |
李杰, 刘久臣, 汤奇峰, 等.川西高原地区水体中硒含量及分布特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2):183-192.
Google Scholar
Li J, Liu J C, Tang Q F, et al.Study of the content and distribution of selenium in water samples from the Western Sichuan Plateau and the incidence of Kaschin Beck disease[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2):183-192.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
王锐, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 等.富硒土壤硒生物有效性及影响因素研究[J].长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(7):1647-1654.
Google Scholar
Wang R, Yu T, Yang Z F, et al.Bioavailability of soil selenium and its influencing factors in selenium-enriched soil[J].Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(7):1647-1654.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
曹容浩.福建省龙海市表层土壤硒含量及影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):282-288.
Google Scholar
Cao R H.Study on selenium content of surface soils in Longhai, Fujian and its influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):282-288.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
杨琼, 侯青叶, 顾秋蓓, 等.广西武鸣县典型土壤剖面Se的地球化学特征及其影响因素研究[J].现代地质, 2016, 30(2):455-462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yang Q, Hou Q Y, Gu Q B, et al.Study of geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium[J].Geoscience, 2016, 30(2):455-462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.02.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Rayman M P, Sargent M, Infante H G.Food-chain selenium and human health:Emphasis on intake[J].The British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2).DOI:10.1017/S0007114508922522.
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
郭文慧, 刘庆, 史衍玺, 等.施硒对紫甘薯硒素累积及产量和品质的影响研究[J].中国粮油学报, 2016, 31(9):31-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.09.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Guo W H, Liu Q, Shi Y X, et al.Effects of applying selenium on the accumulation of selenium, yield, and quality of purple sweetpotato[J].Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2016, 31(9):31-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.09.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
穆婷婷, 杜慧玲, 景小兰, 等.外源硒对谷子产量因子及硒含量的影响[J].作物杂志, 2017, 14(1):73-78.
Google Scholar
Mu T T, Du H L, Jing X L, et al.Effects of exogenous selenium on yield components and selenium content in grain of foxtail millet[J].Crops, 2017, 14(1):73-78.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
谢邦廷, 贺灵, 江官军, 等.中国南方典型富硒区土壤硒有效性调控与评价[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(3):273-281.
Google Scholar
Xie B T, He L, Jiang G J, et al.Regulation and evaluation of selenium availability in Se-rich soils in Southern China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(3):273-281.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
谢珊妮, 宗良纲, 张琪惠, 等.3种改良剂对强酸性高硒茶园土壤硒有效性调控效果与机理[J].茶叶科学, 2017, 37(3):299-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2017.03.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
Xie S N, Zong L G, Zhang Q H, et al.Effects of three amendments on selenium availability of highly acidic and Se-rich soil in tea garden and their relative mechanisms[J].Journal of Tea Science, 2017, 37(3):299-307. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2017.03.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
廖桥, 彭博, 李碧雄.炉渣建材资源化利用现状[J].重庆建筑, 2018, 17(3):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9107.2018.03.53
CrossRef Google Scholar
Liao Q, Peng B, Li B X.A review of resource utilization of slag building material[J].Chongqing Architecture, 2018, 17(3):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9107.2018.03.53
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
杨慧, 刘立晶, 刘忠军, 等.我国农田化肥施用现状分析及建议[J].农机化研究, 2014, 36(9):260-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2014.09.059
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yang H, Liu L J, Liu Z J, et al.Analysis and suggestions of agricultural fertilizer application in China[J].Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(9):260-264. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2014.09.059
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
王怀臣, 冯雷雨, 陈银广.废物资源化制备生物质炭及其应用的研究进展[J].化工进展, 2012, 31(4):907-914.
Google Scholar
Wang H C, Feng L Y, Chen Y G.Advances in biochar production from wastes and its applications[J].Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(4):907-914.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
王晨晔, 陈艳, 郭占成, 等.以钢渣为原料合成Ca-Mg-Al-Fe层状双金属氢氧化物及其对甲基橙的吸附[J].过程工程学报, 2018, 18(3):570-574.
Google Scholar
Wang C Y, Chen Y, Guo Z C, et al.Preparation of Ca-Mg-Al-Fe layered double hydroxides using steel-making slag as raw material and its adsorption to methyl orange[J].The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018, 18(3):570-574.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
邓腾灏博, 谷海红, 仇荣亮.钢渣施用对多金属复合污染土壤的改良效果及水稻吸收重金属的影响[J].农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(3):455-460.
Google Scholar
Deng Teng H B, Gu H H, Qiu R L.Ameliorative effects of steel slag application on multi-metal contaminated soil and heavy metal uptake of rice[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(3):455-460.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
韩笑, 周越, 吴文良, 等.富硒土壤硒含量及其与土壤理化性状的关系——以江西丰城为例[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183.
Google Scholar
Han X, Zhou Y, Wu W L, et al.Selenium content of farmland soils and their relationship with main soil properties in Fengcheng, Jiangxi[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(6):1177-1183.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
李家熙, 张光弟.人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 2000.
Google Scholar
Li J X, Zhang G D.Characteristics and Prediction of Human Selenium Deficiency and Excess Geochemical Environment[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2000.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
诸旭东, 宗良纲, 马迅, 等.内源调控与外源补硒对红壤中硒有效性及水稻产量的影响[J].土壤通报, 2016, 47(2):398-404.
Google Scholar
Zhu X D, Zong L G, Ma X, et al.Effects of endogenous and exogenous regulation on effectiveness of selenium and rice yield in selenium enriched soil[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(2):398-404.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
瞿建国, 徐伯兴, 龚书椿.连续浸提技术测定土壤和沉积物中硒的形态[J].环境化学, 1997, 16(3):277-283.
Google Scholar
Qu J G, Xu B X, Gong S C.Sequential extraction techniques for determination of selenium speciation in soils and sediments[J].Environmental Chemistry, 1997, 16(3):277-283.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
贺攀红, 杨珍, 荣耀, 等.氢化物发生-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定铀矿地质样品中痕量硒[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(2):139-144.
Google Scholar
He P H, Yang Z, Rong Y, et al.Determination of trace selenium in uranium-bearing geological samples by hydride generation-inductively coupled plasma-optimal emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(2):139-144.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
陈再明, 陈宝梁, 周丹丹.水稻秸秆生物碳的结构特征及其对有机污染物的吸附性能[J].环境科学学报, 2013, 33(1):9-19.
Google Scholar
Chen Z M, Chen B L, Zhou D D.Composition and sorption properties of rice-straw derived biochars[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(1):9-19.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
赵世翔, 于小玲, 李忠徽, 等.不同温度制备的生物质炭对土壤有机碳及其组分的影响:对土壤活性有机碳的影响[J].环境科学, 2017, 38(1):333-342.
Google Scholar
Zhao S X, Yu X L, Li Z H, et al.Effects of biochar pyrolyzed at varying temperatures on soil organic carbon and its components:Influence on the soil active organic carbon[J].Environmental Science, 2017, 38(1):333-342.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
赵世翔, 于小玲, 李忠徽, 等.不同温度制备的生物质炭对土壤有机碳及其组分的影响:对土壤腐殖物质组成及性质的影响[J].环境科学, 2017, 38(2):769-782.
Google Scholar
Zhao S X, Yu X L, Li Z H, et al.Effects of biochar pyrolyzed at varying temperatures on soil organic carbon and its components:Influence on the composition and properties of humic substances[J].Environmental Science, 2017, 38(2):769-782.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Wang D, Xue M Y, Wang Y K, et al.Effects of straw amendment on selenium aging in soils mechanism and influential factors[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 657(20):871-881.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
袁金华, 徐仁扣.生物质炭对酸性土壤改良作用的研究进展[J].土壤, 2012, 44(4):541-547. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.04.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yuan J H, Xu R K.Research progress of amelioration effects of biochars on acid soils[J].Soil, 2012, 44(4):541-547. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9829.2012.04.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
韩学博.不同生物质炭对植烟土壤理化性状、重金属生物有效性及烤烟生长的影响[D].临安: 浙江农林大学, 2017.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10341-1017273810.htm
Google Scholar
Han X B.Effect of Different Biochars on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties, Heavy Metal Bioavailability and Tobacco Growth[D].Lin'an: Zhejiang Agriculture & Forestry University, 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
朱李俊, 刘国威, 王磊, 等.钢渣对稀土矿区酸性土壤的改良效果[J].安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(6):159-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.06.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhu L J, Liu G W, Wang L, et al.Improvement effect of steel slag on acid soil in rare earth mining area[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(6):159-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2016.06.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Kamei-Ishikawa N, Tagami K, Uchida S.Sorption kinetics of selenium on humic acid[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2007, 274(3):555-561. doi: 10.1007/s10967-006-6951-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
卢再亮, 李九玉, 徐仁扣.钢渣与生物质炭配合施用对红壤酸度的改良效果[J].土壤, 2013, 45(4):722-726.
Google Scholar
Lu Z L, Li J Y, Xu R K.Amelioration effects of steel slag combined with biochar on red soil acidity[J].Soil, 2013, 45(4):722-726.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
花莉, 金素素, 唐志刚.生物质炭输入对土壤CO2释放影响的研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2012, 40(11):6501-6503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.11.061
CrossRef Google Scholar
Hua L, Jin S S, Tang Z G.Effect of bio-charcoal on release of carbon dioxide in soil[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(11):6501-6503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2012.11.061
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
何振立, 杨肖娥, 祝军, 等.中国几种土壤中的有机态硒及其分布特征[J].环境科学学报, 1993, 13(3):281-287.
Google Scholar
He Z L, Yang X E, Zhu J, et al.Organic selenium and its distribution in soils[J].Journal of Environmental Science, 1993, 13(3):281-287.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
章海波, 骆永明, 吴龙华, 等.香港土壤研究Ⅱ.土壤硒的含量、分布及其影响因素[J].土壤学报, 2005, 42(3):404-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2005.03.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang H B, Luo Y M, Wu L H, et al.Hong Kong soil researches Ⅱ.Distribution and content of selenium in soils[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2005, 42(3):404-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2005.03.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
王文艳, 张丽萍, 刘俏.黄土高原小流域土壤阳离子交换量分布特征及影响因子[J].水土保持学报, 2012, 26(5):123-127.
Google Scholar
Wang W Y, Zhang L P, Liu Q.Distribution and affecting factors of soil cation exchange capacity in watershed of the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(5):123-127.
Google Scholar
|





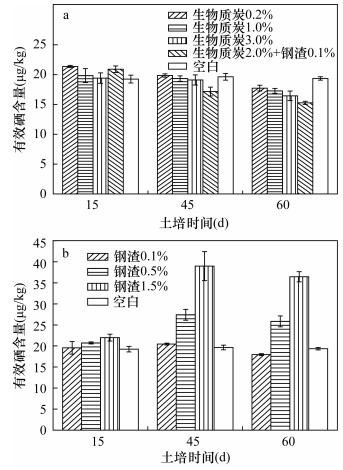

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: