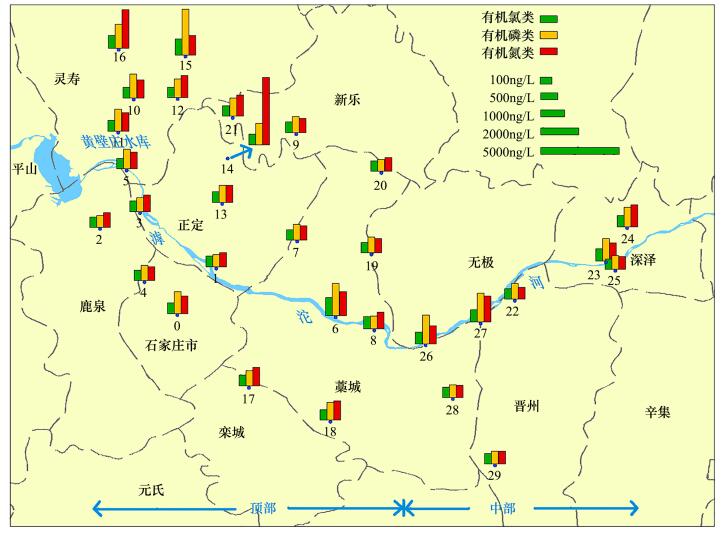
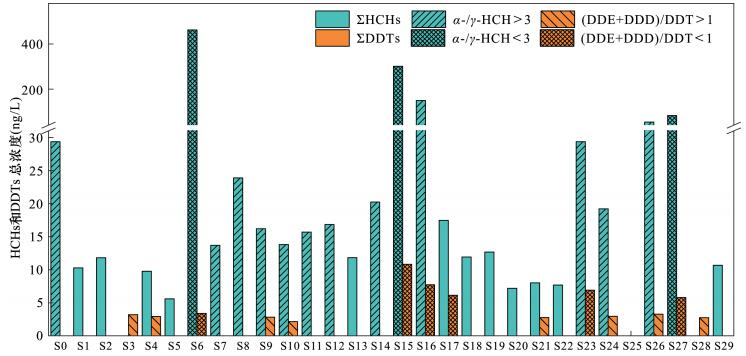
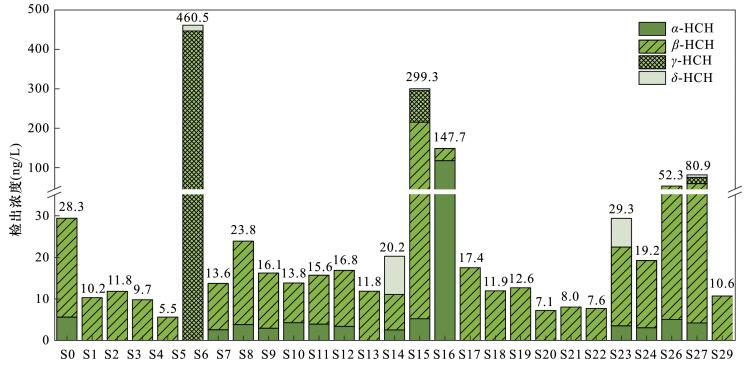
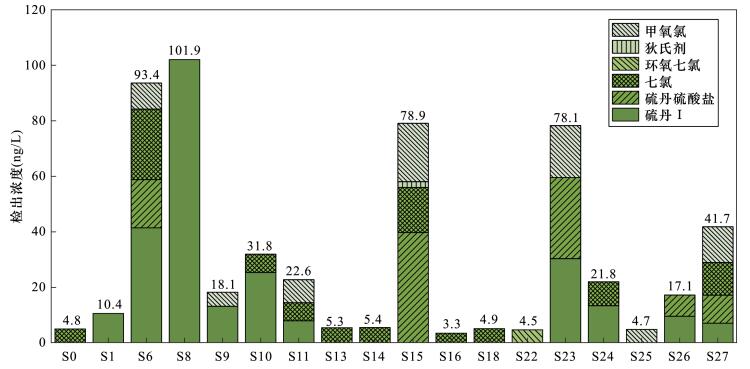
| [1] |
Zheng S L, Chen B, Qiu X Y, et al.Distribution and risk assessment of 82 pesticides in Jiulong River and estuary in South China[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 144:1177-1192. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.09.050
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
陈卫平, 彭程伟, 杨阳, 等.北京市地下水有机氯和有机磷农药健康风险评价[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(1):117-122.
Google Scholar
Chen W P, Peng C W, Yang Y, et al.Health risk evaluation of organochlorine and organophosphorous pesticides in groundwater in Beijing[J].Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1):117-122.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Grung M, Yan L, Hua Z, et al.Pesticide levels and envi-ronmental risk in aquatic environments in China-A review[J].Environment International, 2015, 81:87-97. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.04.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
王灿灿, 陈旭, 冯剑丰, 等.有机氯农药在东方白鹳组织里的浓度[J].中国环境科学, 2016, 36(9):2807-2814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.09.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang C C, Chen X, Feng J F, et al.The concentration of OCPs in the tissue of oriental white stork[J].China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(9):2807-2814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.09.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Li Y Y, Niu J F, Shen Z Y, et al.Spatial and seasonal distribution of organochlorine pesticides in the sediments of the Yangtze Estuary[J].Chemosphere, 2014, 114(22):233-240.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Rissato S R, Galhiane M S, Ximenes V F, et al.Organo-chlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in soil and water samples in the Northeastern part of Sao Paulo State, Brazil[J].Chemosphere, 2006, 65(11):1949-1958. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Liu J, Qi S H, Yao J, et al.Contamination characteristics of organochlorine pesticides in multimatrix sampling of the Hanjiang River Basin, Southeast China[J].Chemosphere, 2016, 163:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
王未, 黄从建, 张满成, 等.我国区域性水体农药污染现状研究分析[J].环境保护科学, 2013, 39(5):5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.05.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang W, Huang C J, Zhang M C, et al.Study on status of regional water pollution by pesticides in China[J].Environmental Protection Science, 2013, 39(5):5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2013.05.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
王建伟, 张彩香, 潘真真, 等.江汉平原地下水中有机磷农药的分布特征及影响因素[J].中国环境科学, 2016, 36(10):3089-3098. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.10.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang J W, Zhang C X, Pan Z Z, et al.Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of organophosphorus pesticides in Jianghan plain groundwater[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(10):3089-3098. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.10.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Wu C F, Luo Y M, Gui T, et al.Characteristics and potential health hazards of organochlorine pesticides in shallow groundwater of two cities in the Yangtze River Delta[J].CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2014, 42(7):923-931. doi: 10.1002/clen.v42.7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Navarrete I A, Tee K A M, Unson J R S, et al.Organo-chlorine pesticide residues in surface water and groundwater along Pampanga River, Philippines[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2018, 190(5):289. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-6680-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Chaza C, Sopheak N, Mariam H, et al.Assessment of pe-sticide contamination in Akkar groundwater, Northern Lebanon[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2017, 25(1-4):1-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
刘琰, 乔肖翠, 江秋枫, 等.滹沱河冲洪积扇地下水硝酸盐含量的空间分布特征及影响因素[J].农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(5):947-954.
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Qiao X C, Jiang Q F, et al.Spatial distribution and influencing factors of nitrate content in groundwater of alluvial-pluvial fan of Hutuo River[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(5):947-954.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
史入宇, 崔亚莉, 赵婕, 等.滹沱河地区地下水适宜水位研究[J].水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(2):36-41.
Google Scholar
Shi R Y, Cui Y L, Zhao J, et al.A study of the suitable groundwater level of the Hutuo River area[J].Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(2):36-41.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
茹淑华, 张国印, 孙世友, 等.河北省地下水硝酸盐污染总体状况及时空变异规律[J].农业资源与环境学报, 2013, 35(5):48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.05.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ru S H, Zhang G Y, Sun S Y, et al.Status of the contamination and spatial-temporal variations of nitrate in groundwater of Heibei Province, China[J].Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2013, 35(5):48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2013.05.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
白雪媛.地下水中82种农药测试方法开发与应用[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1017125836.htm
Google Scholar
Bai X Y.Development and Application for Test Method of 82 Kinds of Pesticides in Groundwater[D].Beijing: China University of Geoscience (Beijing), 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
贺红武.有机磷农药产业的现状与发展趋势[J].世界农药, 2008, 30(6):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2008.06.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
He H W.Current situation and development trend of organophosphorus pesticide industry[J].World Pesticides, 2008, 30(6):29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6485.2008.06.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
高秋生, 焦立新, 杨柳, 等.白洋淀典型持久性有机污染物污染特征与风险评估[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(4):1616-1627.
Google Scholar
Gao Q S, Jiao L X, Yang L, et al.Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of typical persistent organic pollutants in Baiyangdian Lake[J].Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4):1616-1627.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
刘翠翠, 何洁妮, 仇雁翎, 等.黄浦江水相中有机氯农药的污染特征分析[J].环境化学, 2017, 36(4):849-857.
Google Scholar
Liu C C, He J N, Qiu Y L, et al.Pollution status analysis of organochlorine pesticides in Huangpu River water[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(4):849-857.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
WalkerK, Vallero D A, Lewis R G.Factors influencing the distribution of lindane and other hexa-chlorocy-clohexanes in the environment[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1999, 33(24):4373-4378.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
张文静.三氯杀螨醇生产过程中的DDT环境排放研究[J].安全与环境学报, 2012, 12(2):130-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2012.02.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang W J.DDT release in the dicofol production process[J].Journal of Safety and Environment, 2012, 12(2):130-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6094.2012.02.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Qiu X H, Zhu T, Yao B, et al.Contribution of dicofol to the current DDT pollution in China[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(12):4385-4390.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Bhalerao T S, Puranik P R.Biodegradation of organochlo-rine pesticide, endosulfan, by a fungal soil isolate, Aspergillus Niger[J].International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2007, 59(4):315-321.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Fujii Y, Ito Y, Harada K H, et al.Comparative survey of levels of chlorinated cyclodiene pesticides in breast milk from some cities of China, Korea and Japan[J].Chemosphere, 2012, 89(4):452-457. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.098
CrossRef Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: