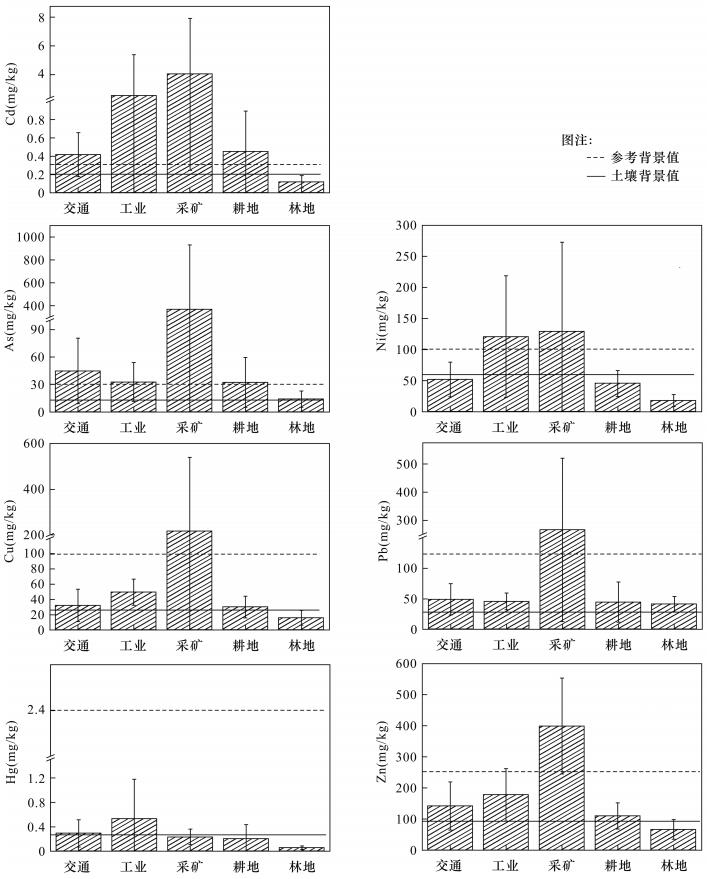
| [1] |
燕婷, 刘恩峰, 张恩楼, 等.抚仙湖沉积物重金属时空变化与人为污染评价[J].湖泊科学, 2016, 28(1):50-58.
Google Scholar
Yan T, Liu E F, Zhang E L, et al.The spatio-temporal variations of heavy metals in the sediment of Fuxian Lake and the contamination assessment[J].Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(1):50-58.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
李春芳, 曹见飞, 吕建树, 等.不同土地利用类型土壤重金属生态风险与人体健康风险[J].环境科学, 2018, 39(12):1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.12.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li C F, Cao J F, Lü J S, et al.Ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in different land use types and evaluation of human health[J].Environment Science, 2018, 39(12):1-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2018.12.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
安婧, 宫晓双, 陈宏伟, 等.沈抚灌区农田土壤重金属污染时空变化特征及生态健康风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(1):37-44.
Google Scholar
An J, Gong X S, Chen H W, et al.Temporal and spatial characteristics and health risk assessments of heavy metal pollution in soils of Shenfu irrigation area[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(1):37-44.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
张军, 董洁, 梁青芳, 等.宝鸡城区土壤重金属空间分布特征及生态风险评价[J].干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(10):100-106.
Google Scholar
Zhang J, Dong J, Liang Q F, et al.Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of Baoji city[J].Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2018, 32(10):100-106.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Cheng H X, Li M, Zhao C D, et al.Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 157:15-26. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.05.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
张倩, 陈宗娟, 彭昌盛, 等.大港工业区土壤重金属污染及生态风险评价[J].环境科学, 2015, 36(11):4232-4240.
Google Scholar
Zhang Q, Chen Z J, Peng C S, et al.Heavy metals pollution in topsiol from Dagang industry area and its ecological risk assessment[J].Environment Science, 2015, 36(11):4232-4240.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
张晗, 靳青文, 黄仁龙, 等.大宝山矿区农田土壤重金属污染及其植物累积特征[J].土壤, 2017, 49(1):141-149.
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Jin Q W, Huang R L, et al.Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils and bioaccumulation in plants of Dabaoshan mine[J].Soils, 2017, 49(1):141-149.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
郑堃, 任宗玲, 覃小泉, 等.韶关工矿区水稻土和稻米中重金属污染状况及风险评价[J].农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5):915-925.
Google Scholar
Zheng K, Ren Z L, Qin X Q, et al.Status and risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in paddy soil and rice grains from the industrial and mining area of Shaoguan, Guangdong Province[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5):915-925.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
陈莹, 陈炳辉, 邹琦, 等.粤北大宝山AMD水-表层沉积物的重金属分布特征及其影响因素[J].环境科学学报, 2018, 38(1):133-141.
Google Scholar
Chen Y, Chen B H, Zou Q, et al.Distribution and influencing factors of heavy metals in water-sediments in Dabaoshan mine, Northern Guangdong Province[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(1):133-141.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
朱爱萍, 陈建耀, 江涛, 等.北江流域横石河-翁江沿岸土壤重金属污染特征分析[J].中国环境科学, 2015, 35(2):506-515.
Google Scholar
Zhu A P, Chen J Y, Jiang T, et al.Characteristics analysis of heavy metal pollution in soil alongside Hengshihe and Wengjiang River in Beijiang Basin[J].China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(2):506-515.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
付善明, 肖方, 宿文姬, 等.基于模糊数学的广东大宝山矿横石河下游土壤重金属元素污染评价[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1140-1146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
Fu S M, Xiao F, Su W J, et al.The evaluation of heavy metals pollution in soils of the lower reaches of the Hengshi River within the Dabaoshan mining area based on fuzzy mathematics[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(8):1140-1146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
宿文姬, 徐友宁, 凡生, 等.广东大宝山矿区横石河沿岸水土重金属分布规律及其累积风险[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(8):1231-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
Su W J, Xu Y N, Fan S, et al.The distribution regularity and accumulation risk of heavy metals in water and soil along the Hengshi River in the Dabaoshan mining area, Guangdong Province[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(8):1231-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.08.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Hakanson L.An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-A sediment ecological approach[J].Water Research, 1980, 14(8):975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
潘佑民, 杨国治.湖南土壤背景值及研究方法[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 1988:159-233.
Google Scholar
Pan Y M, Yang G Z.Soil Background Values and Research Methods in Hunan[M].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press, 1988:159-233.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等.日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J].地理学报, 2012, 67(7):971-984.
Google Scholar
Lü J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y, et al.Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao city[J].Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(7):971-984.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Wilding L P.Spatial Variability:Its Documentation, Accommodation and Implication to Soil Surveys[M].Wageningen:PUDOC Publishers, 1985:166-194.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
郭伟, 孙文惠, 赵仁鑫, 等.呼和浩特市不同功能区土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(4):1561-1567.
Google Scholar
Guo W, Sun W H, Zhao R X, et al.Characteristics and evaluation of soil pollution by heavy metal in different functional zones of Hohhot[J].Environment Science, 2013, 34(4):1561-1567.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
刘亚纳, 朱书法, 魏学锋, 等.河南洛阳市不同功能区土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J].环境科学, 2016, 37(6):2322-2328.
Google Scholar
Liu Y N, Zhu S F, Wei X F, et al.Assessment and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in soil of different functional areas in Luoyang[J].Environment Science, 2016, 37(6):2322-2328.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
马啸, 左锐, 王金生, 等.沈阳浑河冲积扇土壤的重金属空间分布特征及来源[J].环境科学研究, 2014, 27(11):1298-1305.
Google Scholar
Ma X, Zuo R, Wang J S, et al.Spatial distribution and source of heavy metal in soils from alluvial and diluvial fan of Hun River in Shenyang[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(11):1298-1305.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
周妍姿, 王钧, 曾辉, 等.内蒙古土壤重金属的空间异质性及污染特征[J].生态环境学报, 2015, 24(8):1381-1387.
Google Scholar
Zhou Y Z, Wang J, Zeng H, et al.Spatial characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution in Inner Mongolia, China[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(8):1381-1387.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
李睿, 吴艳宏, 邴海健, 等.青藏高原东麓贡嘎山东坡土壤中Pb的来源解析[J].环境科学研究, 2015, 28(9):1439-1448.
Google Scholar
Li R, Wu Y H, Bing H J, et al.Source identification of lead in soils on the eastern slope of Gongga Mountain, Eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(9):1439-1448.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
李清良, 吴倩, 高进波, 等.基于小流域尺度的土壤重金属分布与土地利用相关性研究——以厦门市坂头水库流域为例[J].生态学报, 2015, 35(16):5486-5494.
Google Scholar
Li Q L, Wu Q, Gao J B, et al.Distribution of heavy metals in topsoils affected by land use patterns at a small watershed scale:A case study in the Bantou Reservoir watershed in Xiamen, China[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(16):5486-5494.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
刘德鸿, 王发园, 周文利, 等.洛阳市不同功能区道路灰尘重金属污染及潜在生态风险[J].环境科学, 2012, 33(1):253-259.
Google Scholar
Liu D H, Wang F Y, Zhou W L, et al.Heavy metal pollution in street dusts from different functional zones of Luoyang city and its potential ecological risk[J].Environment Science, 2012, 33(1):253-259.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
张一修, 王济, 秦樊鑫, 等.贵阳市道路灰尘和土壤重金属来源识别比较[J].环境科学学报, 2012, 32(1):204-212.
Google Scholar
Zhang Y X, Wang J, Qin F X, et al.Comparison of sources of metals in roda-dust and soil in Guiyang[J].Acta Scientiae Ciecumstantiae, 2012, 32(1):204-212.
Google Scholar
|





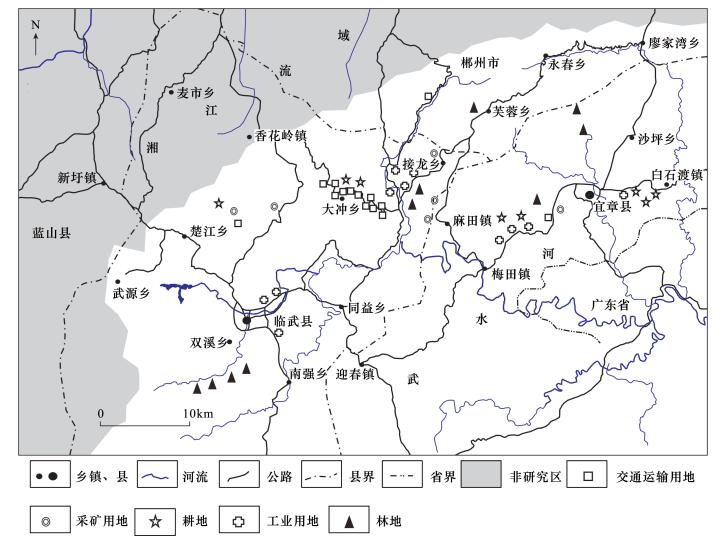

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: