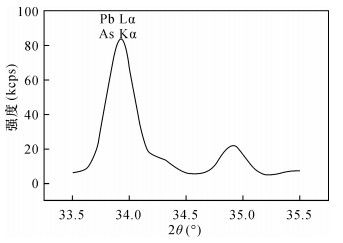
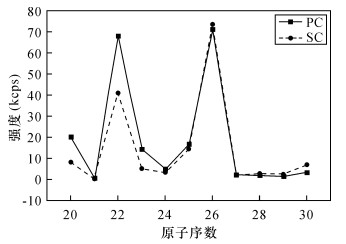
| [1] |
Owoade O K, Olise F S, Olaniyi H B, et al.Model esti-mated uncertainties in the calibration of a total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometer using single-element standards[J].X-Ray Spectrometry, 2010, 35(4):249-252.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Manninen S.Compton scattering:Present status and fu-ture[J].Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2000, 61(3):335-340. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3697(99)00312-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Nie H, Chettle D, Stronach I, et al.A study of MDL improvement for the in vivo measurement of lead in bone[J].Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, 2004, 213:579-583. doi: 10.1016/S0168-583X(03)01675-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
于波, 严志远, 杨乐山, 等.X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤和水系沉积物中碳和氮等36个主次痕量元素[J].岩矿测试, 2006, 25(1):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.01.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yu B, Yan Z Y, Yang L S, et al.Determination of 36 major, minor and trace elements in soil and stream sediment samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2006, 25(1):74-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.01.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
徐海, 刘琦, 王龙山.X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤样品中碳氮硫氯等31种组分[J].岩矿测试, 2007, 26(6):490-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.06.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
Xu H, Liu Q, Wang L S.Determination of 31 components in soil samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(6):490-492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.06.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
张勤, 樊守忠, 潘宴山, 等.X射线荧光光谱法测定多目标地球化学调查样品中主次痕量组分[J].岩矿测试, 2004, 23(1):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2004.01.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang Q, Fan S Z, Pan Y S, et al.Determination of 25 major, minor and trace elements in geochemical exploration samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2004, 23(1):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2004.01.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Luo L, Chettle D R, Nie H, et al.Curve fitting using a genetic algorithm for the X-ray fluorescence measurement of lead in bone[J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2006, 269(2):325-329. doi: 10.1007/s10967-006-0386-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
岩石矿物分析编委会.岩石矿物分析(第四版 第一分册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2011:605-622.
Google Scholar
The Editorial Committee of Rock and Mineral Analysis.Rock and Mineral Analysis (Fourth Edition:VolumeⅠ)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2011:605-622.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
王祎亚, 詹秀春, 樊兴涛, 等.粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法测定地质样品中痕量硫的矿物效应佐证实验及其应用[J].冶金分析, 2010, 30(1):7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2010.01.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang Y Y, Zhan X C, Fan X T, et al.Experimental evidence of mineralogical effects on the determination of trace sulfur in geological samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with pressed powder pellet sample preparation and its application[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2010, 30(1):7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2010.01.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
王晓红, 何红蓼, 王毅民, 等.超细样品的地质分析应用[J].分析测试学报, 2010, 29(6):578-583.
Google Scholar
Wang X H, He H L, Wang Y M, et al.Geological techniques using ultrafine samples[J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2010, 29(6):578-583.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
陈静, 高志军, 陈冲科, 等.X射线荧光光谱法分析地质样品的应用技巧[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1):91-98.
Google Scholar
Chen J, Gao Z J, Chen C K, et al.Application skills on determination of geological sample by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1):91-98.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
郑存江.地质标准物质不确定度评估方法初探[J].岩矿测试, 2005, 24(4):284-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.04.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zheng C J.Primary investigation for evaluation of uncertainty of geological reference materials[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(4):284-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2005.04.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
张荣, 张玉钧, 章炜, 等.土壤重金属铅元素的X射线荧光光谱测量分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2013, 33(2):554-557. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)02-0554-04
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang R, Zhang Y J, Zhang W, et al.Spectrometry and analysis of lead in soil using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2013, 33(2):554-557. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2013)02-0554-04
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Rousseau R M.Corrections for matrix effects in X-ray fluorescence analysis-A tutorial[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2006, 61(7):759-777. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.06.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
胡波, 武晓梅, 余韬, 等.X射线荧光光谱仪的发展及应用[J].核电子学与探测技术, 2015(7):695-702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2015.07.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
Hu B, Wu X M, Yu T, et al.The development and application of X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J].Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology, 2015(7):695-702. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2015.07.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
周国兴, 赵恩好, 岳明新, 等.X射线荧光光谱仪及其分析技术的发展[J].当代化工, 2013(8):1169-1172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2013.08.047
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhou G X, Zhao E H, Yue M X, et al.Development of X-ray fluorescence spectrometer and its analysis technology[J].Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2013(8):1169-1172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2013.08.047
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
罗立强, 詹秀春, 李国会.X射线荧光光谱仪[M].北京:化学出版社, 2008:162-165.
Google Scholar
Luo L Q, Zhan X C, Li G H.X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2008:162-165.
Google Scholar
|





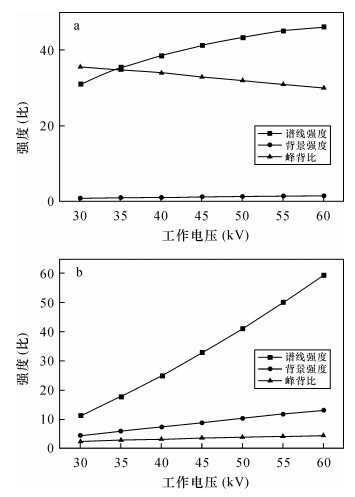

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: