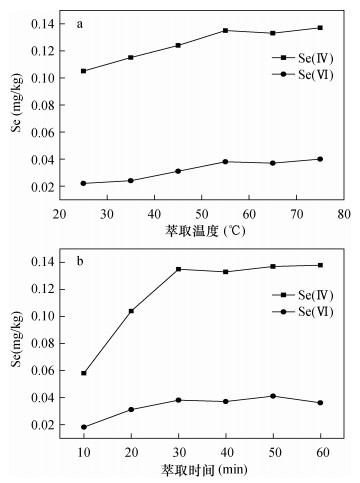
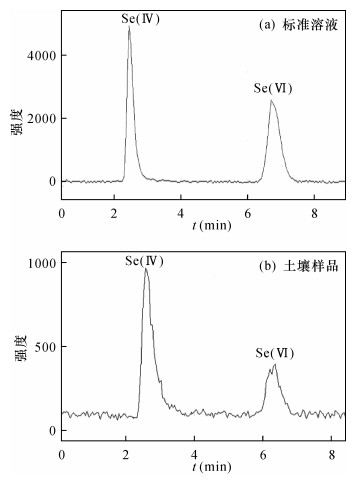
| [1] |
Kápolna E, Fodor P.Speciation analysis of selenium enriched green onions (allium fistulosum) by HPLC-ICP-MS[J].Microchemical Journal, 2006, 84(1):56-62.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
王丙涛, 谢丽琪, 林燕奎, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱联用检测食品中的五种硒形态[J].色谱, 2011, 29(3):223-227.
Google Scholar
Wang B T, Xie L Q, Lin Y K, et al.Determination of selenium species in food by high performance liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2011, 29(3):223-227.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Uden P C, Boakye H T, Kahakachchi C, et al.Selective detection and identification of Se containing compounds-Review and recent developments[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1050(1):85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.05.077
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
王欣, 幸苑娜, 陈泽勇, 等.高效液相色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法检测富硒食品中6种硒形态[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(11):1669-1674.
Google Scholar
Wang X, Xing Y N, Chen Z Y, et al.Determination of 6 selenium species in selenium-enriched food by hyphenated technique of high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(11):1669-1674.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Dumont E, Vanhaecke F, Cornelis R.Selenium speciation from food source to metabolites:A critical review[J].Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2006, 385(7):1304-1323.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Połatajko A, Jakubowski N, Szpunar J.State of the art report of selenium speciation in biological samples[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(7):639-654. doi: 10.1039/B605654G
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
邱建华, 王秋泉, 黄本立.硒形态分析研究进展[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2006, 26(9):1692-1701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2006.09.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
Qiu J H, Wang Q Q, Huang B L.New approaches to selenium speciation[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2006, 26(9):1692-1701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2006.09.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
B'Hymer C, Caruso J A.Selenium speciation analysis using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1114(1):1. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.02.063
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Ogra Y, Anan Y.Selenometabolomics:Identification of selenometabolites and specification of their biological significance by complementary use of elemental and molecular mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2009, 24(11):1477-1488. doi: 10.1039/b910235c
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Rayman M P.Food-chain selenium and human health:Emphasis on intake[J].British Journal of Nutrition, 2008, 100(2):254-268.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Antanaitis A, Lubyte J, Antanaitis S, et al.Selenium con-centration dependence on soil properties[J].Journal of Food, Agriculture & Environment, 2008, 6(1):163-167.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Muchowski P.Assessing the speciation and the bioge-ochemical processes affecting the mobility of selenium from a geological repository of radioactive wastes to the biosphere[J].Analysis, 1998, 26(5):193-197.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Abrams M M, Burau R G, Zasoski R J.Organic selenium distribution in selected California soils[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1990, 54(4):979-982. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1990.03615995005400040007x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Zhang Y, Moore J N.Selenium fractionation and spe-ciation in a wetland system[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(8):2613-2619.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Masscheleyn P H, Delaune R D, Patrick W H J.Trans-formations of selenium as affected by sediment oxidation-reduction potential and pH[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1990, 24(1):91-96.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Masscheleyn P H, Delaune R D, Patrick W H.Arsenic and selenium chemistry as affected by sediment redox potential and pH[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 1991, 20(3):522-527.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
方金梅.福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(2):28-32.
Google Scholar
Fang J M.Selenium speciation analysis and its transformation and enrichment in soils of Fuzhou city[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(2):28-32.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
徐强, 迟凤琴, 匡恩俊, 等.基于通径分析的土壤性质与硒形态的关系——以黑龙江省主要类型土壤为例[J].土壤, 2016, 48(5):992-999.
Google Scholar
Xu Q, Chi F Q, Kuang E J, et al.Relationship between soil physico-chemical properties and selenium species based on path analysis[J].Soils, 2016, 48(5):992-999.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Favorito J E, Luxton T P, Eick M J, et al.Selenium speciation in phosphate mine soils and evaluation of a sequential extraction procedure using XAFS[J].Environmental Pollution, 2017, 229:911-921. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.07.071
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
耿建梅, 王文斌, 罗丹, 等.不同浸提剂对海南稻田土壤有效硒浸提效果比较[J].土壤, 2010, 42(4):624-629.
Google Scholar
Geng J M, Wang W B, Luo D, et al.Comparative studies on effects of several extractants on available selenium of paddy soils in Hainan[J].Soils, 2010, 42(4):624-629.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
温国灿, 黄艳, 郭永玲, 等.酸性土壤有效硒提取条件优化的研究[J].农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(5):1996-2000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.05.079
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wen G C, Huang Y, Guo Y L, et al.Optimal conditions of extraction method for available selenium in acid soils[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2007, 26(5):1996-2000. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2007.05.079
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Wright M T, Parker D R, Amrhein C.Critical evaluation of the ability of sequential extraction procedures to quantify discrete forms of selenium in sediments and soils[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(20):4709-4716.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Stroud J L, McGrath S P, Zhao F J.Selenium speciation in soil extracts using LC-ICP-MS[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 92(2):222-236. doi: 10.1080/03067310903111661
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Zhang Y, Jr W T F.Determination of selenium frac-tionation and speciation in wetland sediments by parallel extraction[J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2003, 83(4):315-326. doi: 10.1080/0306731031000076850
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Bujdoš M, Kubová J, Streško V.Problems of selenium fractionation in soils rich in organic matter[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2000, 408(1):103-109.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
薛超群, 郭敏.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定土壤样品中不同价态的硒[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):980-984. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
Xue C Q, Guo M.Analysis of different valence states of selenium in geological samples by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):980-984. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
彭岚, 谈明光, 李玉兰, 等.微波辅助萃取-液质联用技术测底泥砷、硒的化学形态[J].分析试验室, 2006, 25(5):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2006.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Peng L, Tan M G, Li Y L, et al.Simultaneous speciation of arsenic and selenium by high-performance liquid chromatography on-line with inductively coupled plasma collision cell mass spectrometry in sediment samples[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Laboratory, 2006, 25(5):10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2006.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Hsieh Y J, Jiang S J.Determination of selenium com-pounds in food supplements using reversed-phase liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectro-metry[J].Microchemical Journal, 2013, 110(9):1-7.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Zheng J, Ohata M, Furuta N, et al.Speciation of selenium compounds with ion-pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry as element-specific detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2000, 874(1):55-64. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00077-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: