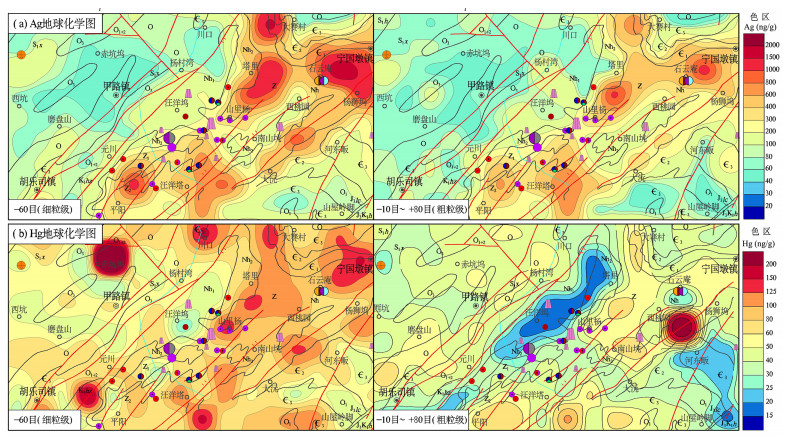
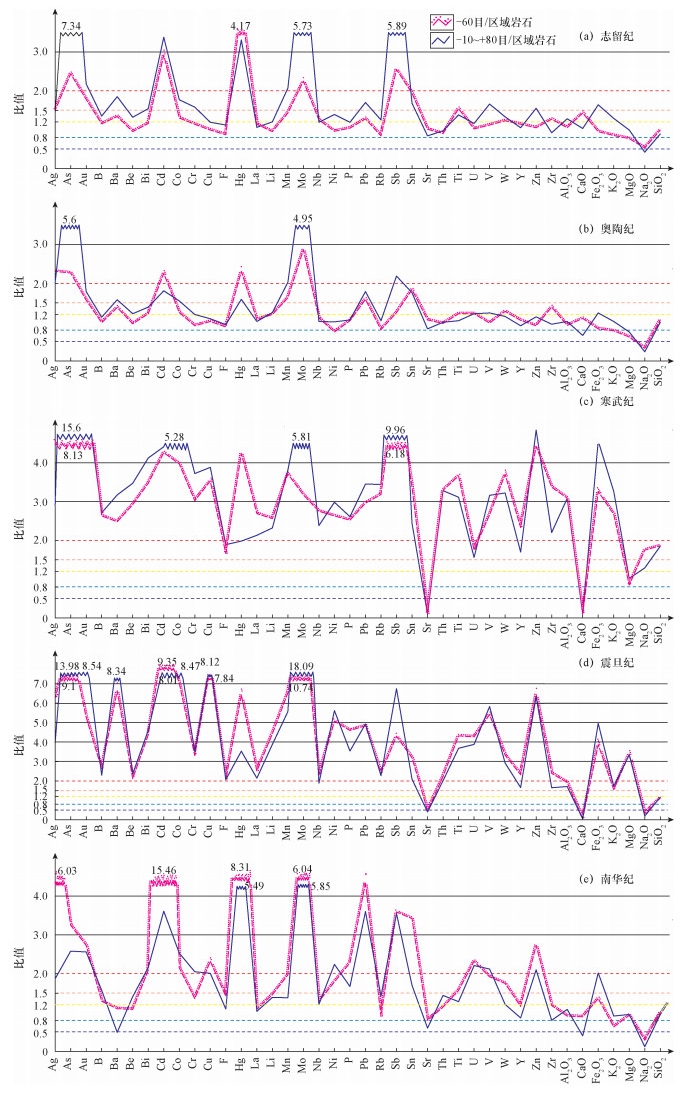
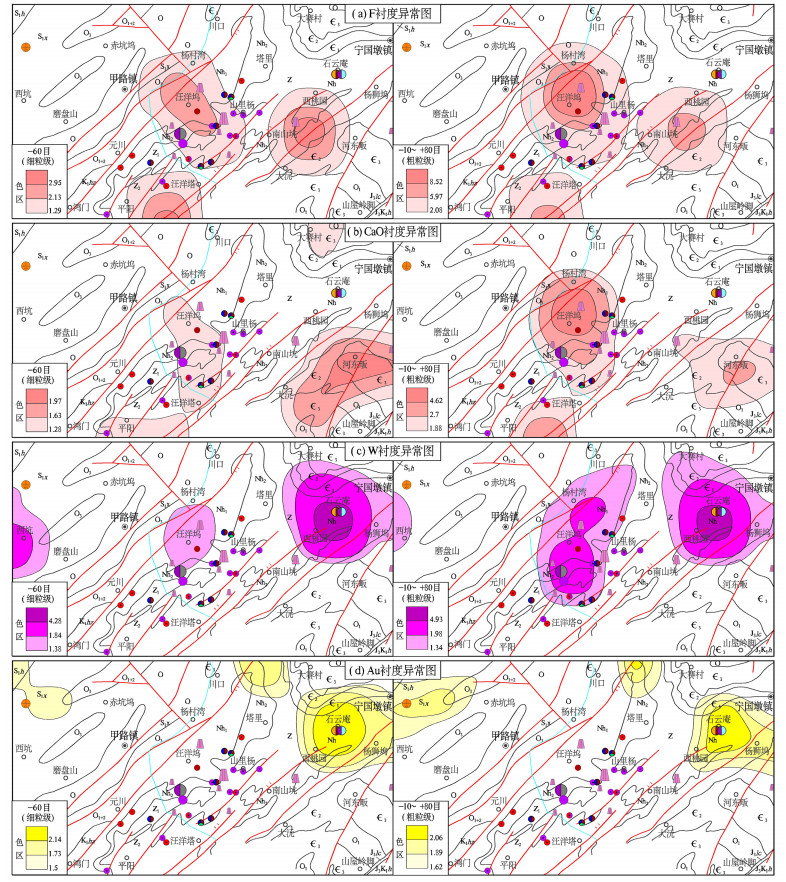
| [1] |
向运川, 任天祥, 牟绪赞, 等.化探资料应用技术要求[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010.
Google Scholar
Xiang Y C, Ren T X, Mou X Z, et al.Application and Technical Requirements of Geochemical Materials[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2010.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
迟清华, 鄢明才.应用地球化学元素丰度手册[M].北京:地质出版社, 2007.
Google Scholar
Chi Q H, Yan M C.Application of Geochemical Element Abundance Data Handbook[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2007.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
冷福荣, 李志强.1:20万区域化探方法核心技术"取样粒级"的讨论[J].物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):678-685.
Google Scholar
Leng F R, Li Z Q.A discussion on the "sampling grade", a key technology in 1:200000 regional geochemical exploration[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(6):678-685.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
禹斌, 李惠, 张国义, 等.不同地球化学景观区的化探方法及实例[J].地质找矿论丛, 2005, 12(3):182-186.
Google Scholar
Yu B, Li H, Zhang G Y, et al.Geochemical exploration at various landscapes and the examples[J].Geological Prospecting Series, 2005, 12(3):182-186.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
贾玉杰, 龚庆杰, 韩东昱, 等.化探方法技术之取样粒度研究——以豫西牛头沟金矿1:5万化探普查为例[J].地质与勘探, 2013, 49(5):928-938.
Google Scholar
Jia Y J, Gong Q J, Han D Y, et al.Sample granularity of soils and stream sediments in geochemical surveys:A case study of the Niutougou gold deposit, Xiong' erShan gold mine in Western Hennan Province[J].Geology and Exploration, 2013, 49(5):928-938.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
郭玉生.元素的赋存状态、样品粒度、取样量对试样代表性的影响[J].岩矿测试, 1987, 6(2):147-150.
Google Scholar
Guo Y S.Effect of elemental occurrence phases, sample size and sampling mass on sample's representation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1987, 6(2):147-150.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
沈莽庭, 徐鸣, 姚春彦, 等.巴西巴伊亚州阿巴伊拉地区水系沉积物采样粒级方法试验[J].地质找矿论丛, 2015, 30(3):392-399. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Shen M T, Xu M, Yao C Y, et al.Grain size test for sampling media from river sediments in Arbari area, Bahia state, Brazil[J].Geological Prospecting Series, 2015, 30(3):392-399. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
张华, 张玉领, 史新民.河北围场幅1:20万区域化探方法技术讨论[J].物探与化探, 2004, 28(1):35-38.
Google Scholar
Zhang H, Zhang Y L, Shi X M.A discussion on methods and techniques for 1:200000 geochemical exploration in Weichang sheet, Hebei Province[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 28(1):35-38.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
魏印涛, 邱成贵, 张斌, 等.区域化探方法试验探讨——以胶东半岛莱阳幅1:20万水系沉积物测量为例[J].山东国土资源, 2015, 31(12):54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.12.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wei Y T, Qiu C G, Zhang B, et al.Study on regional geochemical sampling method-setting stream sediment survey of Laiyang map with the scale of 1:200000 in Jiaodong Peninsula as an example[J].Shandong Land and Resources, 2015, 31(12):54-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.12.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Gong Q J, Deng J, Wang C M, et al.Element behaviors due to rock weathering and its implication to geochemical anomaly recognition:A case study on Linglong biotite granite in Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 128:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
王会峰, 彭立华, 安兴, 等.森林沼泽区区域化探新旧方法技术应用效果对比[J].物探与化探, 2008, 32(5):502-508.
Google Scholar
Wang H F, Peng L H, An X, et al.The preparation of geochemical speciation certified reference materials for main soil types of China[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(5):502-508.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Wang X, Xu S, Zhang B, et al. Deep-penetrating geochemistry for sandstone-type uranium deposits in the Turpan-Hami Basin, North-Western China[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(12):2238-2246. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.08.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
徐永利, 郑有业, 徐广东, 等.青海省大柴旦双口山荒漠戈壁景观区1:5万水系沉积物测量采样方法技术研究[J].西北地质, 2012, 45(1):307-316.
Google Scholar
Xu Y L, Zheng Y Y, Xu G D, et al.Study on sampling methods for 1:50000 stream sediment geochemical survey in the Go-bi desert landscape area of Shuangkoushan, Dachaidan, Qinghai Province[J].Northwestern Geology, 2012, 45(1):307-316.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
康明, 岑况, 吴悦斌, 等.北山戈壁荒漠景观1:5万地球化学测量方法研究[J].地质与勘探, 2004, 40(3):64-68.
Google Scholar
Kang M, Cen K, Wu Y B, et al.1:50000 geochemical prospecting methods and techniques in GoBi desert landscape in the Beishan area, Northwestern China[J].Geology and Exploration, 2004, 40(3):64-68.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
杨帆, 孔牧, 刘华忠, 等.北山干旱荒漠戈壁残山景观1:5万地球化学勘查方法技术的选择[J].物探与化探, 2011, 35(3):308-312.
Google Scholar
Yang F, Kong M, Liu H Z, et al.The choice of methods and technologies for 1:50000 geochemical exploration in Beishan arid desert GoBi relict mountain landscape[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(3):308-312.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
冯治汉, 徐家乐.甘肃省景观地球化学特征及区域化探工作方法研究[J].地质与勘探, 2003, 39(6):2-5.
Google Scholar
Feng Z H, Xu J L.Landscape geochemistry features and working methods of regional geochemistry in Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2003, 39(6):2-5.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
程志中, 王学求, 谢学锦, 等.黑龙江森林沼泽区超低密度地球化学调查采样介质对比[J].物探与化探, 2005, 29(3):201-204.
Google Scholar
Cheng Z Z, Wang X Q, Xie X J, et al.A comparison of sampling media in ultra-low density geochemical investigation in the forest-swamp area of Heilongjiang Province[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(3):201-204.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
贾先巧, 张丽春, 任利民, 等.矿区及外围土壤地球化学测量采样深度与粒度方法试验——以江西省九江市城门山铜矿为例[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(7):963-969.
Google Scholar
Jia X Q, Zhang C L, Ren L M, et al.Examination of sampling depth and granularity on geochemical soil survey at mining and external areas—Taking the Chengmenshan copper mine, Jiujiang city, Jiangxi Province, China as an Example[J].Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(7):963-969.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
席明杰, 马生明, 赵波, 等.西藏羊八井—青龙地区水系沉积物元素背景值及分布特征[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(1):81-89.
Google Scholar
Xi M J, Ma S M, Zhao B, et al.The background values and distribution characteristics of stream sediments in the Yangbajain—Qinglong region, Tibet[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(1):81-89.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
周向辉, 侯光久.大兴安岭水系沉积物采样介质粒级段对圈定元素异常的影响[J].资源环境与工程, 2008, 22(6):569-576.
Google Scholar
Zhou X H, Hou G J.Effect of different mesh of stream sediment sampling media in Daxinganling to delineate element anomalies[J].Resources Environment & Engineering, 2008, 22(6):569-576.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Rose A W, Hawkes H E, Webb J S.Geochemistry in Mineral Exploration[M].London:Academic Press, 1979.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Xu R T.The study on geochemical technology for mineral exploration in the Arid Gobi desert terrain, Beishan mountains area, Gansu[R].Beijing:China University of Geosciences, 2006.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
陈富荣.安徽宁墩地区金钨地球化学异常找矿远景[J].物探与化探, 2010, 34(2):150-153.
Google Scholar
Chen F R.Ore-search prospects of gold and tungsten geochemical anomalies in Ningdun area, Anhui Province[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(2):150-153.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
佟依坤, 龚庆杰, 韩东昱, 等.化探技术之成矿指示元素组合研究——以豫西牛头沟金矿为例[J].地质与勘探, 2014, 50(4):712-724.
Google Scholar
Tong Y K, Gong Q J, Han D Y, et al.Indicator element association in geochemical surveys:A case study of the Niutougou gold deposit in Western Henan Province[J].Geology and Exploration, 2014, 50(4):712-724.
Google Scholar
|





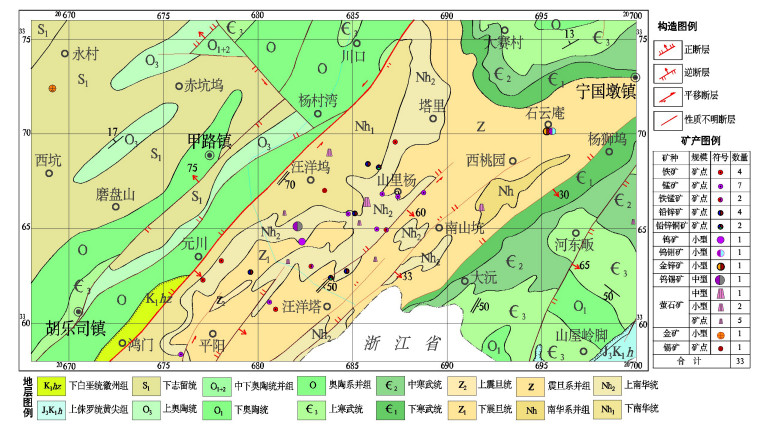

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: