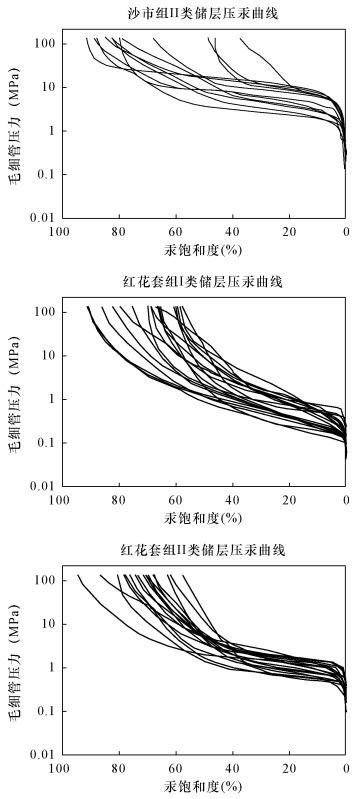
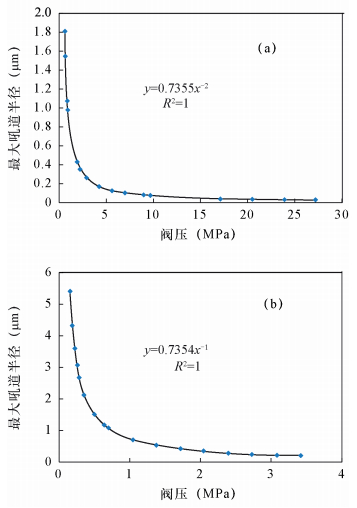
| [1] |
肖佃师, 卢双舫, 陆正元, 等.联合核磁共振和恒速压汞方法测定致密砂岩孔喉结构[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(6):961-970.
Google Scholar
Xiao D S, Lu S F, Lu Z Y, et al.Combining nuclear magnetic resonance and rate-controlled porosimetry to probe the pore-throat structure of tight sandstones[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(6):961-970.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
操应长, 葸克来, 朱如凯, 等.松辽盆地南部泉四段扶余油层致密砂岩储层微观孔喉结构特征[J].中国石油大学学报 (自然科学版), 2015, 39(5):7-17.
Google Scholar
Cao Y C, Xi K L, Zhu R K, et al.Microscopic porethroat characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs in Fuyu Layer of the fourth member of Quantou Formation in Southern Songliao basin[J].Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science), 2015, 39(5):7-17.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Yao Y B, Liu D M.Comparison of low-field NMR and mercury intrusion porosimetry in characterizing pore size distribution of coals[J].Fuel, 2012, 95(1):152-158.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Clarkson C R, Jensen J L, Pedersen P K, et al.Innovative methods for flow-unit and pore-structure analysis in a tight siltstone and shale gas reservoir[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(2):355-374. doi: 10.1306/05181110171
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
李爱芬, 任晓霞, 王桂娟, 等.核磁共振研究致密砂岩孔隙结构的方法及应用[J].中国石油大学学报 (自然科学版), 2015, 39(6):92-98.
Google Scholar
Li A F, Ren X X, Wang G J, et al.Characterization of pore structure of low permeability reservoirs using a nuclear magnetic resonance method[J].Journal of China University of Petroleum (Natural Science), 2015, 39(6):92-98.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
窦文超, 刘洛夫, 吴康军, 等.基于压汞实验研究低渗储层孔隙结构及其对渗透率的影响——以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部三叠系延长组长7储层为例[J].地质论评, 2016, 62(2):502-511.
Google Scholar
Dou W C, Liu L F, Wu K J, et al.Pore structure characteristics and its effect on permeability by mercury injection measurement:An example from Triassic Chang-7 reservoir, Southwest Ordos basin[J].Geological Review, 2016, 62(2):502-511.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Torabi A, Fossen H, Braathen A.Insight into petrophy-sical properties of deformed sandstone reservoirs[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(4):619-637. doi: 10.1306/10031212040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等.高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J].天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3):450-455.
Google Scholar
Yang F, Ning Z F, Kong D T, et al.Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3):450-455.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
陈生蓉, 帅琴, 高强, 等.基于扫描电镜-氮气吸脱附和压汞法的页岩孔隙结构研究[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6):636-642.
Google Scholar
Chen S R, Shuai Q, Gao Q, et al.Analysis of the pore structure of shale in Ordos Basin by SEM with nitrogen gas adsorption-desorption[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(6):636-642.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.应用氩离子抛光-扫描电镜方法研究四川九老洞组页岩微观孔隙特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(3):278-285.
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Characterization of pore structures of Jiulaodong Formation shale in the Sichuan basin by SEM with Ar-ion milling[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(3):278-285.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
刘亚伟, 张士万, 刘涛, 等.深层天然卤水特征及成因探讨——以江陵凹陷深层天然卤水研究为例[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(6):1291-1299.
Google Scholar
Liu Y W, Zhang S W, Liu T, et al.Tentative discussion on features and genesis of deep natural brine:A case study of deep natural brine in Jiangling Depression[J].Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(6):1291-1299.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
马黎春, 黄华, 张连元, 等.湖北潜江凹陷古近系深层富钾卤水矿床特征及成因[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(11):2114-2121.
Google Scholar
Ma L C, Huang H, Zhang L Y, et al.Characteristics of paleogene deep potassium rich brines in the Qianjiang Depression, Hubei Province[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(11):2114-2121.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Lowenstein T K, Risacher F.Closed basin brine evolution and the influence of Ca-Cl inflow waters:Death valley and Bristol dry lake California, Qaidam basin, China, and Salar de Atacama, Chile[J].Aquatic Geochemistry, 2009(15):71-94.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Nishio Y, Okamura K, Tanimizu M, et al.Lithium and strontium isotopic systematics of waters around Ontake volcano, Japan:Implications for deep-seated fluids and earthquake swarms[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(3-4):567-576.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
潘源敦, 刘成林, 徐海明.湖北江陵凹陷深层高温富钾卤水特征及其成因探讨[J].化工矿产地质, 2011, 33(2):65-72.
Google Scholar
Pan Y D, Liu C L, Xu H M.Characteristics and genesis of deep high temperature potassium rich brine in Jiangling sag, Hubei[J].Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2011, 33(2):65-72.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
易积正.江陵凹陷梅槐桥地区第三系新沟咀组下段沉积相及砂体分布研究[J].矿物岩石, 2010, 30(3):77-82.
Google Scholar
Yi J Z.Research of sedimentary facies of lower Ex in Meihuaiqiao area, Jiangling Sag[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 30(3):77-82.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Roberto A, Sandstone V S.Carbonate petroleum reservoirs:A global perspective on porosity-depth and porosity-permeability relationships:Discussion[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(5):807-810. doi: 10.1306/09140505131
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
邸世祥.中国碎屑岩储集层的孔隙结构[M].西安:西北大学出版社, 1991.
Google Scholar
Di S X.Pore Structure of Clastic Reservoir in China[M].Xi'an:Northwestern University Press, 1991.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
王国亭, 何东博, 李易隆, 等.吐哈盆地巴喀气田八道湾组致密砂岩储层分析及孔隙度演化定量模拟[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(11):1847-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang G T, He D B, Li Y L, et al.Tight sandstone reservoir analysis and porosity-evolution quantitative simulation of the Badaowan Formation in the Baka gas field, Turpan-Hami basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(11):1847-1856. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.11.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
王培春, 李兴丽, 张琳琳, 等.利用常规测井物性曲线重构毛细管压力曲线[J].测井技术, 2012, 36 (1):33-36.
Google Scholar
Wang P C, Li X L, Zhang L L, et al.The capillary pressure curve reconstruction based on conventional log physical properties[J].Well Logging Technology, 2012, 36(1):33-36.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
赖锦, 王贵文, 柴毓, 等.致密砂岩储层孔隙结构成因机理分析及定量评价——以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长8油层组为例[J].地质学报, 2014, 88(11):2119-2130.
Google Scholar
Lai J, Wang G W, Chai Y, et al.Mechanism analysis and quantitative assessment of pore structure for tight sandstone reservoirs:An example from Chang 8 oil layer in the Jiyuan area of Ordos basin[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11):2119-2130.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
王国仓, 孙敏卓, 王鹏, 等.柴北缘马北8号构造下干柴沟组下段砂岩储层特征[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(2):242-248.
Google Scholar
Wang G C, Sun M Z, Wang P, et al.Characteristics of the lower part of the Xiaganchaigou Formation in the Maber-Ⅷ structure in the Northern margin, Qaidam basin[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2):242-248.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
石媛媛, 洪才均, 房晓璐, 等.塔里木盆地库东—轮台地区苏维依组Ⅱ砂组沉积储层特征[J].石油实验地质, 2014, 36(4):422-427. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201404422
CrossRef Google Scholar
Shi Y Y, Hong C J, Fang X L, et al.Sedimentary reservoir characteristics of sandstone team Ⅱ of Suweiyi Formation in Kudong—Luntai area, Tarim basin[J].Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2014, 36(4):422-427. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201404422
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
赵姗姗, 张哨楠, 万友利.塔中顺托果勒低隆区柯坪塔格组长石溶蚀及对储层的影响[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(3):293-299. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503293
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhao S S, Zhang S N, Wan Y L.Feldspar dissolution and its effect on reservoir in Kepingtage Formation, Shuntuoguole low uplift, Central Tarim basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(3):293-299. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503293
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
秦勇, 申建, 王宝文, 等.深部煤层气成藏效应及其耦合关系[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(1):48-54. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Qin Y, Shen J, Wang B W, et al.Accumulation effects and coupling relationship of deep coalbed methane[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1):48-54. doi: 10.7623/syxb201201006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
成志刚, 罗少成, 杜支文, 等.基于储层孔喉特征参数计算致密砂岩渗透率的新方法[J].测井技术, 2014, 38(2):185-189.
Google Scholar
Cheng Z G, Luo S C, Du Z W, et al.The method to calculate tight sandstone reservoir permeability using pore throat characteristic parameters[J].Well Logging Technology, 2014, 38(2):185-189.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
徐丽, 王轶平, 段毅, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地南梁地区长4+5油层组储层特征[J].岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(4):34-39.
Google Scholar
Xu L, Wang Y P, Duan Y, et al.Reservoir characteristics of Chang 4+5 oil reservoir set in Nanliang area, Ordos basin[J].Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(4):34-39.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
李百强, 邱雅洁, 李洋, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区长9储层微观孔隙结构特征[J].西安石油大学学报 (自然科学版), 2015, 30(5):10-15.
Google Scholar
Li B Q, Qiu Y J, Li Y, et al.Micro pore structure characteristics of Chang 9 reservoir in Huaqing area, Ordos basin[J].Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science), 2015, 30(5):10-15.
Google Scholar
|





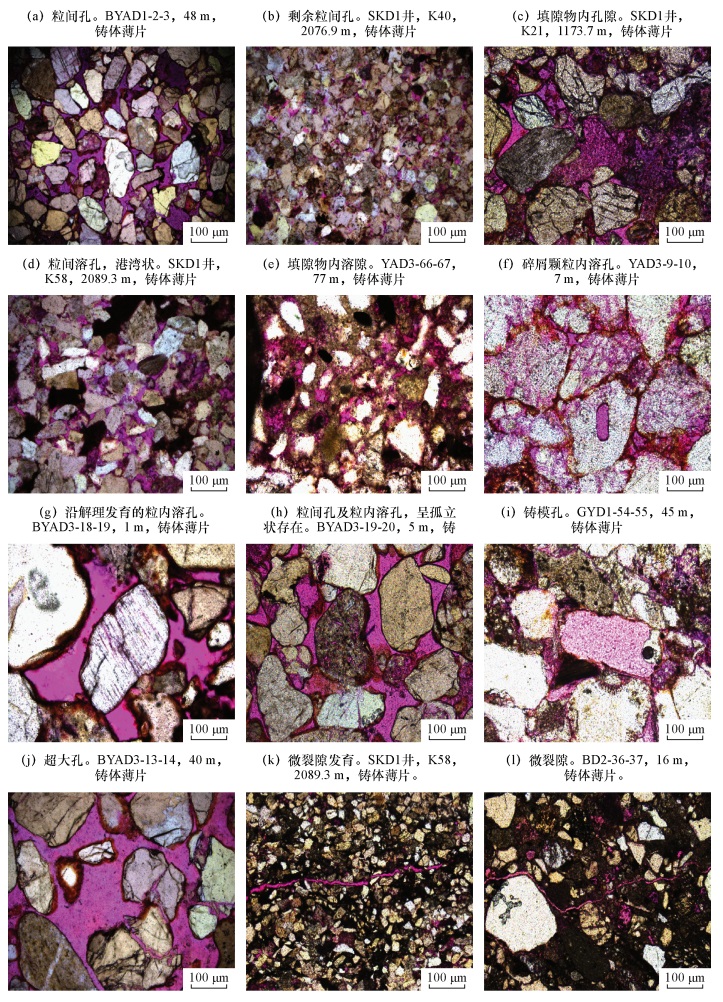

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: