| [1] |
Zhang W, Lentz D R, Charnley B E.Petrogeochemical assessment of rock units and identification of alteration/mineralization indicators using portable X-ray fluorescence measurements:Applications to the Fire Tower Zone (W-Mo-Bi) and the North Zone (Sn-Zn-In), Mount Pleasant deposit, New Brunswick, Canada[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 177:61-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.02.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Liao S, Tao C, Li H, et al.Use of portable X-ray fluorescence in the analysis of surficial sediments in the exploration of hydrothermal vents on the Southwest Indian Ridge[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(7):66-76. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-1085-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Ribeiro B T, Silva S H G, Silva E A, et al.Portable X-ray fluorescence (pXRF) applications in tropical soil science[J].Ciência E Agrotecnologia, 2017, 41(3):245-254. doi: 10.1590/1413-70542017413000117
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
黄阳晓.对比等离子发射光谱法/原子荧光法探讨便携式X射线荧光光谱法在测定土壤重金属中的应用[J].广东化工, 2016, 43(13):261-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2016.13.127
CrossRef Google Scholar
Huang Y X.Compared with plasma emission spectrometry, atomic fluorescence method to investigate the portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in determination of the application of the soil heavy metal[J].Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2016, 43(13):261-263. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2016.13.127
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
王豹, 余建新, 黄标, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱仪快速监测重金属土壤环境质量[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2015, 35(6):1735-1740.
Google Scholar
Wang B, Yu J X, Huang B, et al.Fast monitoring soil environmental qualities of heavy metal by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(6):1735-1740.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
廖学亮, 程大伟, 周超, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱法检测大米中的镉[J].粮食与饲料工业, 2014(9):62-65.
Google Scholar
Liao X L, Cheng D W, Zhou C, et al.Determination of cadmium in rice by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J].Cereal & Feed Industry, 2014(9):62-65.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
耿志旺, 乐健, 杨永健.便携式X射线荧光光谱仪快速鉴别硫熏八角[J].食品安全质量检测学报, 2017, 8(6):2277-2281.
Google Scholar
Geng Z W, Le J, Yang Y J.Rapid screening of sulfur fumigated star anises by field-portable X-ray fluorescence[J].Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2017, 8(6):2277-2281.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
聂黎行, 张烨, 朱俐, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱快速无损分析牛黄清心丸(局方)中汞、砷含量及均匀度[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(10):3225-3228.
Google Scholar
Ni L X, Zhang Y, Zhu L, et al.Fast and nondestructive analysis of content of mercury and arsenic and homogeneity of Niuhuang Qingxin pills by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(10):3225-3228.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
蒋小良, 兰丽丽, 叶丽贞, 等.便携式能量色散X射线荧光光谱法快速检测玩具中5种元素[J].皮革与化工, 2016, 33(6):12-14.
Google Scholar
Jiang X L, Lan L L, Ye L Z, et al.Rapid determination of 5 elements in toys by portable energy dispersion X-ray flourescence spectrometry[J].Leather and Chemicals, 2016, 33(6):12-14.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Arne D C, Mackie R A, Jones S A.The use of property-scale portable X-ray fluorescence data in gold exploration:Advantages and limitations[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2014, 14(3):233-244. doi: 10.1144/geochem2013-233
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Sarala P.Comparison of different portable XRF methods for determining till geochemistry[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2016, 16(3-4):181-192. doi: 10.1144/geochem2012-162
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
le Vaillant M, Barnes S J, Fisher L, et al.Use and calibration of portable X-ray fluorescence analysers:Application to lithogeochemical exploration for komatiite-hosted nickel sulphide deposits[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2014, 14(3):199-209. doi: 10.1144/geochem2012-166
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
李向超.便携式X射线荧光光谱仪现场测定地质样品中钛[J].冶金分析, 2014, 34(4):32-36.
Google Scholar
Li X C.On-site determination of titanium in geological samples by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(4):32-36.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Uvarova Y A, Gazley M F, Cleverley J S, et al.Representative, high-spatial resolution geochemistry from diamond drill fines (powders):An example from Brukunga, Adelaide, South Australia[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 170:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Young K E, Evans C A, Hodges K V, et al.A review of the handheld X-ray fluorescence spectrometer as a tool for field geologic investigations on Earth and in planetary surface exploration[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2016, 72:77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.07.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Hall G E M, McClenaghan M B, Page L.Application of portable XRF to the direct analysis of till samples from various deposit types in Canada[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2016, 16(1):62-84. doi: 10.1144/geochem2015-371
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
杨桂兰, 商照聪, 李良君, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱法在土壤重金属快速检测中的应用[J].应用化工, 2016, 45(8):1586-1591.
Google Scholar
Yang G L, Shang Z C, Li L J, et al.Application of portable-XRF spectrometry for rapid determination of common heavy metals in soil[J].Applied Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(8):1586-1591.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
邝荣禧, 胡文友, 何跃, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱法(PXRF)在矿区农田土壤重金属快速检测中的应用研究[J].土壤, 2015, 47(3):589-595.
Google Scholar
Kuang R X, Hu W Y, He Y, et al.Application of portable X-ray fluorescence (PXRF) for rapid analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soils around mining area[J].Soils, 2015, 47(3):589-595.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
冉景, 王德建, 王灿, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱法与原子吸收/原子荧光法测定土壤重金属的对比研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2014, 34(11):3113-3118. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)11-3113-06
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ran J, Wang D J, Wang C, et al.Comparison of soil heavy metals determined by AAS/AFS and portable X-ray fluorescense analysis[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(11):3113-3118. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)11-3113-06
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
杨帆, 郝志红, 刘华忠, 等.便携式能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪在新疆东天山浅钻化探异常查证中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6):665-671.
Google Scholar
Yang F, Hao Z H, Liu H Z, et al.Application of Minipal 4 portable energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer in the verification of geochemical anomaly delineated by shallow hole drill core in Eastern Tianshan[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(6):665-671.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
龙灵利, 王京彬, 王玉往, 等.东天山卡拉塔格矿集区赋矿火山岩地层时代探讨——SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J].矿产勘查, 2016, 7(1):31-37.
Google Scholar
Long L L, Wang J B, Wang Y W, et al.Discussion on the age of ore-host volcanic strata in the Kalatage ore concentration area, Eastern Tianshan:Evidence from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating[J].Mineral Exploration, 2016, 7(1):31-37.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
于明杰, 王京彬, 毛启贵, 等.东天山卡拉塔格地区梅岭铜(金)矿床M1号矿体黄铁矿热电性特征及其地质意义[J].矿产勘查, 2016, 7(1):149-156.
Google Scholar
Yu M J, Wang J B, Mao Q G, et al.Pyroelectricitical characteristics of pyrite from the No.M1 orebody in Meiling copper-gold deposit and its geological significance in the Kalatage area, Eastern Tianshan[J].Mineral Exploration, 2016, 7(1):149-156.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
于明杰. 东天山卡拉塔格矿集区梅岭铜锌(金)矿床成矿作用[D]: 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.http: //cdmd. cnki. com. cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1016184117. htm
Google Scholar
Yu M J. Metellogeneses in Relation to the Meiling Cu-Zn (Au) Deposit in the Kalatage Ore Concentration Area, Eastern Tianshan Mountain, Xinjiang, NW China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Zhu Y, Weindorf D C, Zhang W.Characterizing soils using a portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer:1.Soil texture[J].Geoderma, 2011, 167-168(Supplement C):167-177.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
马德锡, 杨进, 陈孝强, 等.便携式X荧光仪在多金属矿区的应用[J].物探与化探, 2013, 37(1):63-66. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2013.1.11
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ma D X, Yang J, Chen X Q, et al.The application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument to the polymetallic ore district[J].Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(1):63-66. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2013.1.11
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Fisher L, Gazley M F, Baensch A, et al.Resolution of geochemical and lithostratigraphic complexity:A workflow for application of portable X-ray fluorescence to mineral exploration[J].Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2014, 14(2):149-159. doi: 10.1144/geochem2012-158
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
董天宇, 王海江, Yunger J A, 等.便携式X射线荧光光谱仪实验室异位检测法的实用性研究[J].土壤, 2017, 49(4):853-857.
Google Scholar
Dong T Y, Wang H J, Yunger J A, et al.Practicality validation of portable X-ray fluorescence for ex-situ measuring soil heavy metals in laboratory[J].Soils, 2017, 49(4):853-857.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Gazley M F, Bonnett L C, Fisher L A, et al.A workflow for exploration sampling in regolith-dominated terranes using portable X-ray fluorescence:Comparison with laboratory data and a case study[J].Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017, 64(7):903-917. doi: 10.1080/08120099.2017.1367721
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





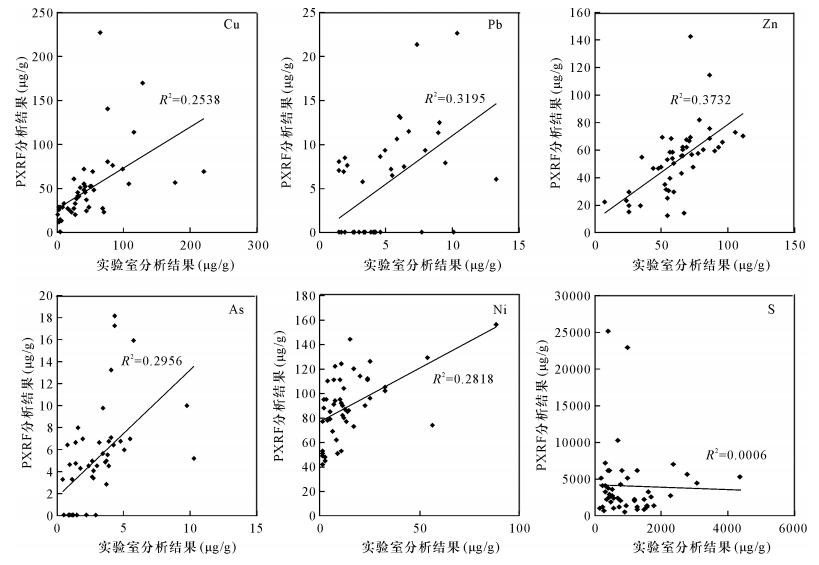

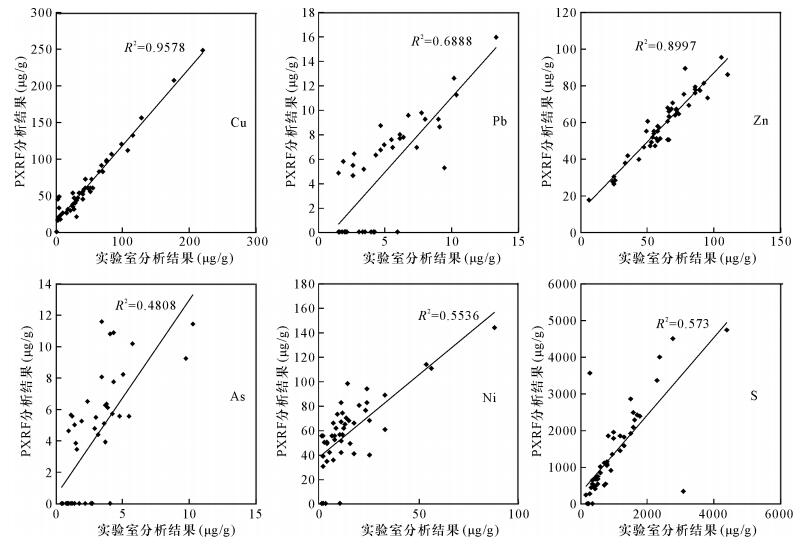
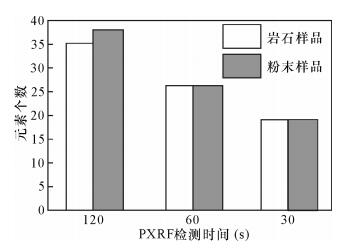
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: