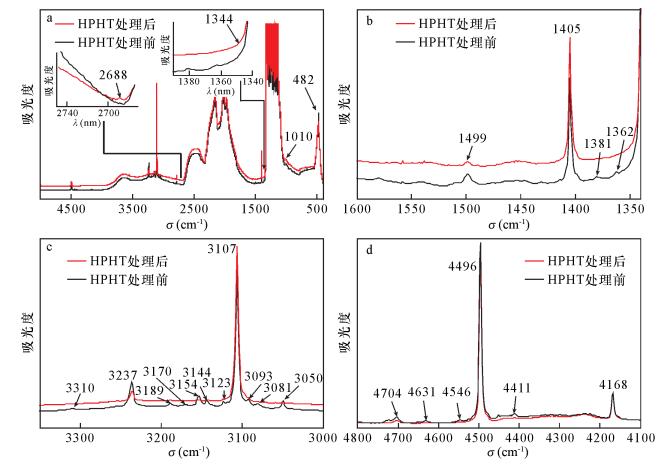
| [1] |
宋中华, 魏华, 田晶. 钻石辨假[B]. 北京: 文化出版社, 2017.
Google Scholar
Song Z H, Wei H, Tian J. Identification of Diamonds[B]. Beijing: Cultural Development Press, 2017.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Fritsch E, Hainschwang T, Massi L, et al.Hydrogen-related optical centers in natural diamond-An update[J].New Diamond and Frontier Carbon Technology, 2007, 17(2):63-89.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Bangert U, Barnes R, Gass M H, et al.Vacancy clusters, dislocations and brown colouration in diamond[J].Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2009, 21, 364208. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/21/36/364208
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Dobrinets I A, Vins V G, Zaitsev A M.HPHT-treated Diamonds[M].Springer Press, 2013.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Fisher D, Spits R A.Sectroscopic evidence of GE POL HPHT-treated natural type Ⅱa diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 2000, 36(1):42-49.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Reinitz I M, Buerki P R, Shigley J E, et al.Identification of HPHT-treated yellow to green diamonds[J].Gems & Gemology, 2000, 36(2):128-137.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Smith C P, Bosshart G, Ponahlo J, et al.GE POL diamond:Before and after[J].Gems & Gemology, 2000, 36(3):192-215.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Hounsome L S. Investigations on the Origin of Brown Colouration in Diamond[D]. 2007.http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.439873
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Hainschwang T.HPHT treatment of different classes of type Ⅰ brown diamond[J].Journal of Gemmology, 2005, 29(5/6):261-273.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Fisher D.Brown diamonds and high pressure high tem-perature treatment[J].Lithos, 2009, 112(Supplement):619-624.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Breeding C M, Shigley J E.The 'TYPE' classification system of diamonds and importance in gemology[J].Gems & Gemology, 2009, 45(2):96-111.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Howell D, Griffin W L, Piazolo S, et al.A spectroscopic and carbon-isotope study of mixed-habit diamonds impurity characteristics and growth environment[J].American Mineralogist, 2013, 98:66-77. doi: 10.2138/am.2013.4179
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Smit K V, Shirey S B, Stern R A, et al.Diamond growth from C-H-N-O recycled fluids in the Zimbabwe lithosphere:Evidence from CH4 micro-inclusions and δ13C-δ15N-N content in Marange mixed-habit diamonds[J].Lithos, 2016, doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.03.015.
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Hainschwang T, Notari F, Vadaszi E.The Rhodesian star:An exceptional asteriated diamond[J].The Journal of Gemmology, 2014, 34(4):306-315.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Zaitsev A M, Wang W, Moe K S, et al.Spectroscopic studies of yellow nitrogen-doped CVD diamonds[J].Diamond and Related Materials, 2016, 68:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.06.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Zaitsev A M.Optical Properties of Diamond-A Data Handbook[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag Press, 2001.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Hainschwang T, Fritsch E, Massi L, et al.The C center isolated nitrogen-related infrared absorption at 2688cm-1:Perfect harmony in diamond[J].Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2012, 79(5):737-743. doi: 10.1007/s10812-012-9664-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Collins A T, Connor A, Ly C, et al.High-temperature annealing of optical centers in type-Ⅰ diamond[J].Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 97:083517-1-10. doi: 10.1063/1.1866501
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Goss J P, Briddon P R, Hill V, et al.Identification of the structure of the 3107cm-1 H-related defect in diamond[J].Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter, 2014, 26:1-6.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Collins A T.Colour centres in diamond[J].Journal of Gemmology, 1982, 18:37-75. doi: 10.15506/JoG.1982.18.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Wang W Y, Mose T M.Gem quality CVD synthetic dia-monds from Gemesis[J].Gems & Gemology, 2011, 71(3):227-228.
Google Scholar
|





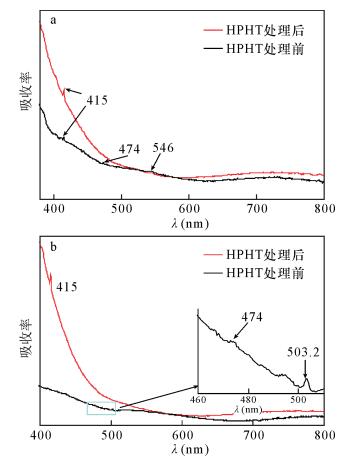

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: