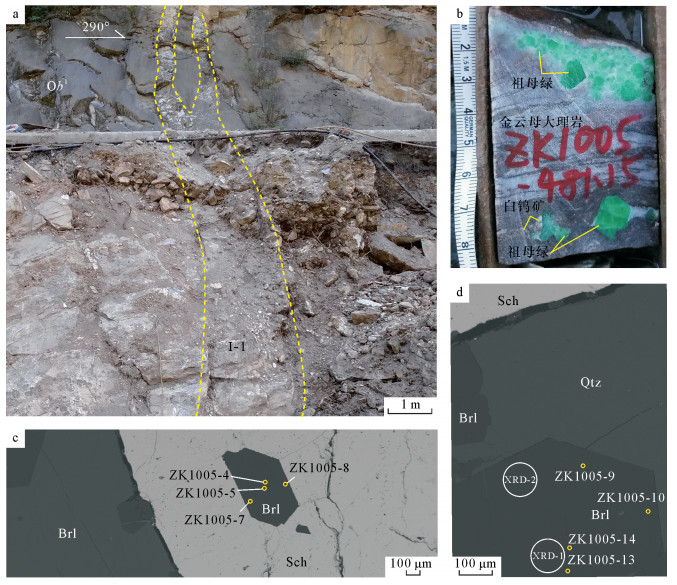
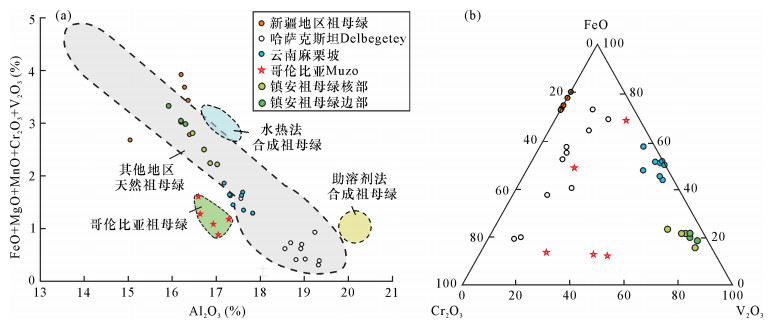
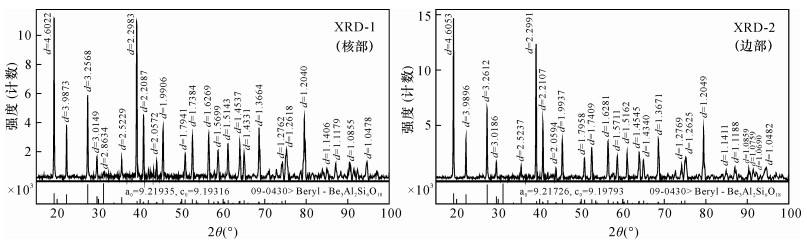
| [1] |
胡荣荣, 张世涛.祖母绿矿床研究现状[J].化工矿产地质, 2006, 28(4):234-240.
Google Scholar
Hu R R, Zhang S T.Current research situation of the world emerald deposits and the existing problems[J].Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2006, 28(4):234-240.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
胡荣荣, 张世涛.世界祖母绿矿床研究现状及存在问题[J].矿产与地质, 2007, 21(1):94-99.
Google Scholar
Hu R R, Zhang S T.Status of worldwide emerald deposit research and some problems[J].Mineral Resources and Geology, 2007, 21(1):94-99.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Gavrilenko E, Pérez B C, Bolibar R C, et al.Emeralds from the Delbegetey deposit (Kazakhstan):Mineralogical characteristics and fluid-inclusion study[J].Mineralogical Magazine, 2006, 70(2):159-173. doi: 10.1180/0026461067020321
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Ottaway T L, Wicks F J, Bryndzia L T, et al.Formation of the Muzo hydrothermal emerald deposit in Colombia[J].Nature, 1994, 369:552-554. doi: 10.1038/369552a0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Bragg W L, West J.The structure of beryl, Be3Al2Si6O18[J].Royal Society of London Proceedings, 1926, 111(759):691-714. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1926.0088
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
刘琰, 邓军, 孙岱生, 等.四川虎牙雪宝顶W-Sn-Be矿床矿物学标型特征及流体对矿物形态的影响[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2007, 32(1):75-81.
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Deng J, Sun D S, et al.Morphology and gensis typomorphism of minerals in W-Sn-Be deposit of Huya, Sichuan[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2007, 32(1):75-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
阮青锋, 张良钜, 张昌龙, 等.绿柱石的成因与特征的研究[J].矿产与地质, 2008, 22(3):265-269.
Google Scholar
Ruan Q F, Zhang L J, Zhang C L, et al.Genesis and characteristics of beryl[J].Mineral Resources & Geology, 2008, 22(3):265-269.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Garcí J M, Lastra A, Barriuso M T, et al.Origin of the different color of ruby and emerald[J].Physical Review B, 2005, 72(11):3104.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
钟倩, 廖宗廷, 周征宇, 等.水热法合成Paraíba色绿柱石的宝石学特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(6):1-7.
Google Scholar
Zhong Q, Liao Z T, Zhou Z Y, et al.Gemmological characteristics of hydrothermal synthetic paraíba-cloour beryl[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2016, 18(6):1-7.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
申柯娅.天然祖母绿与合成祖母绿的成分及红外吸收光谱研究[J].岩矿测试, 2011, 30(2):233-237.
Google Scholar
Shen K Y.Study on chemical compositions and infrared absorption spectra of natural and synthetic emeralds[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(2):233-237.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
梁婷.云南祖母绿的呈色机理初探[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2001, 3(4):21-24.
Google Scholar
Liang T.Study on coluration mechanism of emerald from Yunnan Province[J].Journal of Gems & Gemmology, 2001, 3(4):21-24.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
梁婷.祖母绿的红外光谱特征研究[J].长安大学学报(地球科学版), 2003, 25(2):10-13.
Google Scholar
Liang T.The study on infrared absorption pectroscopic characteristics of emeralds[J].Journal of Chang'an University (Earth Science Edition), 2003, 25(2):10-13.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
张文兰, 王汝成, 蔡淑月.超轻元素Be元素的电子探针定量分析——以绿柱石为例[J].电子显微学报, 2006(增刊1):293-294.
Google Scholar
Zhang W L, Wang R C, Cai S Y.Quantitative analysis of ultralight element Be by electron microprobe-Taking beryl as an example[J].Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2006(Supplement 1):293-294.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Liu J J, Zhai D G, Dai H Z, et al.Nanoscale character-ization of Au2Te grains from the Sandaowanzi gold deposit, Northeast China[J].The Canadian Mineralogist, 2017, 55(2):181-194. doi: 10.3749/canmin.1600077
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Uher P, Chudík P, Bačík P, et al.Beryl composition and evolution trends:An example from granitic pegmatites of the beryl-columbite subtype, Western Carpathians, Slovakia[J].Journal of Geosciences, 2010, 55(1):69-80.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Wang R C, Che X D, Zhang W L, et al.Geochemical evolution and late re-equilibration of Na-Cs-rich beryl from the Koktokay #3 pegmatite (Altai, NW China)[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 2009, 21(4):795-809. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1936
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Viana R R, Jordtevangelista H, Costa G M D, et al.Characterization of beryl (aquamarine variety) from pegmatites of Minas Gerais, Brazil[J].Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 2002, 29(10):668-679. doi: 10.1007/s00269-002-0278-y
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Evensen J M.Beryllium in silicic magmas and the origin of beryl-bearing pegmatites[J].Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry, 2002, 50(1):445-486.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Sabot B.Fluid inclusions in Ianapera emerald, Southern Madagasca[J].International Geology Review, 2005, 47(6):647-662. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.47.6.647
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Moore T P. Emeralds of the World[M]//Mineralogical Record. 2003: 10-23, 25-33, 74-78.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Groat L A, Giuliani G, Marshall D D, et al.Emerald deposits and occurrences:A review[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 34(1-2):87-112. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.09.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Groat L A, Marshall D D, Giuliani G, et al.Mineralogical and geochemical study of the Regal Ridge emerald showing, Southeastern Yukon[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 2002, 40(5):1313-1338. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.40.5.1313
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Cheilletz A, Féraud G, Giuliani G, et al.Time-pressure and temperature constraints on the formation of Colombian emeralds:An 40Ar/39Ar laser microprobe and fluid inclusion study[J].Economic Geology, 1994, 89:361-380. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.89.2.361
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
代鸿章, 王登红, 王成辉, 等.中央造山带秦巴地区发现石英脉型黑钨矿[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):559-560.
Google Scholar
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al.New discovery of quartz vein-type of wolframite ores in the Qinling-Daba area, Central Orogenic Belt, China[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):559-560.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
许乃岑, 沈加林, 张静.X射线衍射-X射线荧光光谱-电子探针等分析测试技术在玄武岩矿物鉴定中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(1):75-81.
Google Scholar
Xu N C, Shen J L, Zhang J.Application of X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence spectrometry and electron microprobe in the identification of basalt[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(1):75-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
刘永先, 范洪斌.云南祖母绿特征及开发利用初探[J].矿产综合利用, 1997(6):22-25.
Google Scholar
Liu Y X, Fan H B.A preliminary study on the characteristics and exploitation and utilization of emeralds in Yunnan[J].Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 1997(6):22-25.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝, 等.统矿物学(中册)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1982:155-156.
Google Scholar
Wang P, Pan Z L, Weng L B, et al.Systematic Mineralogy (Volume 2)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1982:155-156.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Aurisicchio C, Fioravanti G, Grubessi O, et al.Reappra-isal of the crystal chemistry of beryl[J].American Minealogist, 1988, 73:826-837.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
黄文清, 倪培, 水汀, 等.云南麻栗坡祖母绿的矿物学特征研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(1):103-109.
Google Scholar
Huang W Q, Ni P, Shui T, et al.Mineralogical characteristics of emerald from Malipo, Yunnan Province[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(1):103-109.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
任伟, 汪立今, 李甲平.电子探针和X射线衍射仪测定新疆祖母绿宝石[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(2):179-181.
Google Scholar
Ren W, Wang L J, Li J P. Detection of emerald from Xinjiang by electron probe microanalyzer and X-ray diffractometer[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2010, 29(2):179-181.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
JCPDS. International Center for Diffraction Data[Z]. [PDF#09-0430], 1988.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Schwartz D, Giuliani G.Emerald deposits:A review[J].Australian Gemmologist, 2001, 1:17-23.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Vapnik Y, Moroz I, Roth M, et al.Formation of emeralds at pegmatite-ultramafic contacts based on fluid inclusions in Kianjavato emerald, Mananjary deposits, Madagascar[J].Mineralogical Magazine, 2006, 70:141-158. doi: 10.1180/0026461067020320
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
汪立今, 彭雪峰, 李甲平, 等.新疆祖母绿(绿柱石)矿产出地质特征与找矿矿物学[J].矿物学报, 2011, 31(3):604-608.
Google Scholar
Wang L J, Peng X F, Li J P, et al.A study on basic geological characteristics and mineralogy of ore prospecting in Xinjiang emerald (beryl) deposit[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011, 31(3):604-608.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Wang C H, et al.Re-Os isotopic dating of a W-Be polymetallic deposit in the Southern Qinling Region, China[J].Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2018, 92(1):414-415. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2018.92.issue-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
刘茜. 陕西镇安钨矿床特征及成因研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1013270343.htm
Google Scholar
Liu Q. The Characterisitcs and Genesis of the Zhen'an W Deposit, Shannxi Province, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscinces (Beijing), 2013.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
盛继福, 王登红.中国矿产地质志·钨矿卷[M].北京:地质出版社(待出版), 2018.
Google Scholar
Sheng J F, Wang D H.China's Mineral Geology (Tungsten Ore Volume)[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2018(in press).
Google Scholar
|





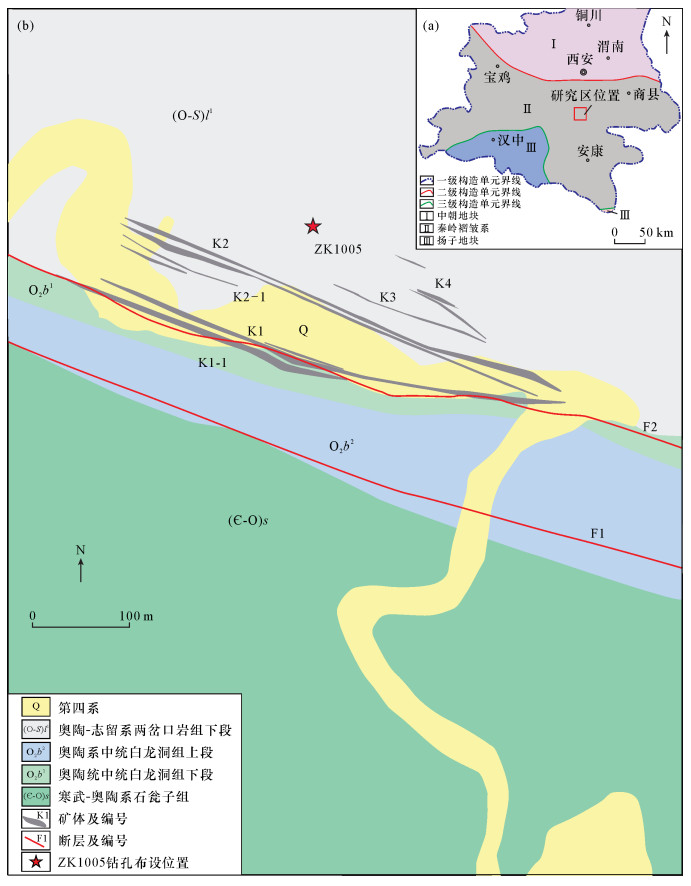

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: