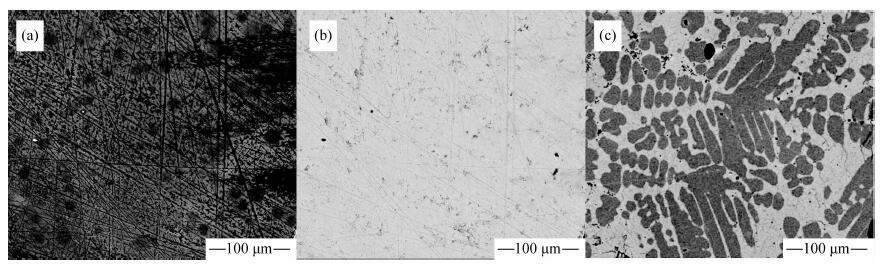
| [1] |
Axelsson M D, Rodushkin I. Determination of major and trace elements in sphalerite using laser ablation double focusing sector field ICP-MS [J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2001,72(2):81-89. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(00)00166-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Houghton J, Shanks W, Seyfried W. Massive sulfide deposition and trace element remobilization in the Middle Valley sediment-hosted hydrothermal system, northern Juan de Fuca Rdge [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004,68(13):2863-2873. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.12.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, Pring A, Skinner W, Shimizu M, Danyushevsky L, Saini-Eidukat B, Melcher F. Trace and minor elements in sphalerite:A LA-ICPMS study [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009,73(16): 4761-4791. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.05.045
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
周涛发,张乐骏,袁峰,范裕, Cook D R. 安徽铜陵新桥Cu-Au-S矿床黄铁矿微量元素LA-ICP-MS原位测定及其对矿床成因的制约[J].地学前缘, 2010,17(2):306-319.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Piña R, Gervilla F, Barnes S J, Ortega L, Lunar R. Distribution of platinum-group and chalcophile elements in the Aguablanca Ni-Cu sulfide deposit (SW Spain): Evidence from a LA-ICP-MS study [J].Chemical Geology, 2012,302: 61-75.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Bockrath C, Ballhaus C, Holzheid A. Fractionation of the platinum-group elements during mantle melting [J].Science, 2004,305(5692): 1951-1953. doi: 10.1126/science.1100160
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Lorand J P, Luguet A, Alard O, Bezos A, Meisel T. Abundance and distribution of platinum-group elements in orogenic lherzolites; a case study in a Fontete Rouge lherzolite (French Pyrénées) [J].Chemical Geology, 2008,248(3): 174-194.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Lorand J P, Luguet A, Alard O. Platinum-group element systematics and petrogenetic processing of the continental upper mantle: A review [J].Lithos, 2013,164-167: 2-21. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Alard O. Nonchondritic distribution of the highly sider-ophile elements in mantle sulfides [J].Nature, 2000,407: 891-894. doi: 10.1038/35038049
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
McDonald I. Development of sulphide standards for the in-situ analysis of platinum-group elements by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)[C]//10th Intern Platinum Symp, 2005: 468-471.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Jarvis K E, Williams J G, Parry S J, Bertalan E. Quantitative determination of the platinum-group elements and gold using NiS fire assay with laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS ) [J].Chemical Geology, 1995,124(1 2): 37-46.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Norman M, Robinson P, Clark D. Major-and trace-element analysis of sulfide ores by laser-ablation ICP-MS, solution ICP-MS, and XRF: New data on international materials [J].The Canadian Mineralogist, 2003,41: 293-305. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.41.2.293
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Barnes S J, Cox R A, Zientek M L. Platinum-group element, gold, silver and base metal distribution in compositionally zoned sulfide droplets from the Medvezky Creek Mine, Noril′sk, Russia [J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006,152(2): 187-200. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0100-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Godel B, Barnes S J. Platinum-group elements in sulfide minerals and the whole rocks of the J-M Reef (Stillwater Complex): Implication for the formation of the reef [J].Chemical Geology, 2008(248): 272-294.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Wilson S A, Ridley W I, Koenig A E. Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique [J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2002,17(4): 406-409. doi: 10.1039/B108787H
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser C C, Ballhaus C, Berndt J, Stotternée P V, Meisel T. Synthesis of PGE sulfide standards for laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) [J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007,154(5): 607-617. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0212-x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
袁继海,詹秀春,范晨子,赵令浩,孙冬阳,贾泽荣,胡明月,蒯丽君. 玻璃标样结合硫内标归一定量技术在激光剥蚀-等离子体质谱分析硫化物矿物中的应用[J].分析化学, 2012,40(2): 201-207.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
袁继海,詹秀春,樊兴涛,胡明月. 硫化物矿物中痕量元素的激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱微区分析进展 [J].岩矿测试, 2011,30(2): 121-130.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Perkins W T, Pearce N J G, Westgate J A. The development of laser ablation ICP-MS and calibration strategies: Examples from the analysis of trace elements in volcanic glass shards and sulfide minerals [J].Geostandards Newsletter, 1997,21: 175-190. doi: 10.1111/ggr.1997.21.issue-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Figueiredo A M, Enzweiler J, Sarkis J E, Jorge A P, Shibuya E. NAA and UV laser ablation ICP-MS for platinum group elements and gold determination in NiS fire assay buttons: A comparison between two methods [J].Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 2000,244(3): 623-625. doi: 10.1023/A:1006725618998
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Gros M, Lorand J P, Luguet A. Analysis of platinum group elements and gold in geological materials using NiS fire assay and Te coprecipitation; the NiS dissolution step revisited [J]. Chemical Geology, 2002,185(3): 179-190.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Sylvester P, Cabri L, Tubrett M, McMahon G, Laflamme J, Peregoedova A. Synthesis and evaluation of a fused pyrrhotite standard reference material for platinum group element and gold analysis by laser ablation-ICPMS[C]//10th International Platinum Symposium. Finland: Geological Survey of Finland, 2005: 16-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Wang X, Zeng Z, Yin X, Wang X. Study on the constituents of nickel sulfide assay button [J].Precious Metals, 2007,28(4): 45-49.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Q/GD 008—2002,岩石、土壤、水系沉积物中铂族元素的锍镍试金-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定[S].
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Sylvester P. A practical guide to platinumgroup element analysis of sulphides by laser ablation ICPMS[M].Toronto: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2001: 203-211.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Shibuya E K, Sarkis J E S, Enzweiler J, Jorge A P S, Figueiredo A M G. Determination of platinum group elements and gold in geological materials using an ultraviolet laser ablation high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric technique [J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1998,13(9): 941-944. doi: 10.1039/a801477i
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





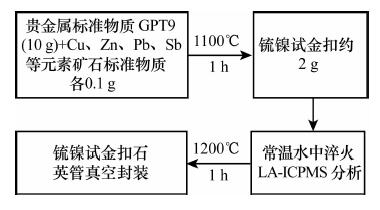

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: