Zhen-kun WANG, Hong JIN, Xue-jun LI, Chi ZHANG, Xin SUN, Tao BIAN, Yu-qing MO, Qiang LUO. Study on Migration of Lead and Admium in the Port Environment and Model building[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5): 753-758.
| Citation: |
Zhen-kun WANG, Hong JIN, Xue-jun LI, Chi ZHANG, Xin SUN, Tao BIAN, Yu-qing MO, Qiang LUO. Study on Migration of Lead and Admium in the Port Environment and Model building[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(5): 753-758.
|
Study on Migration of Lead and Admium in the Port Environment and Model building
-
1.
Chemicals, Minerals and Metallic Materials Inspection Center, Tianjin Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau, Tianjin 300456, China
-
2.
Tianjin Inspection and Test Development Service Co., Ltd, Tianjin 300456, China
-
Abstract
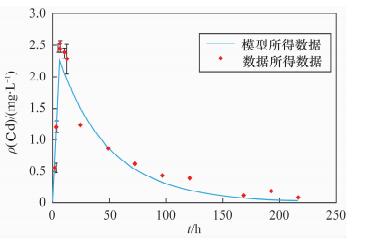
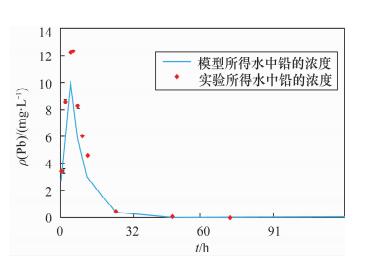
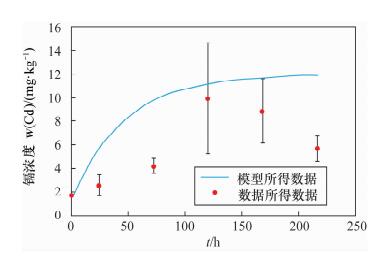
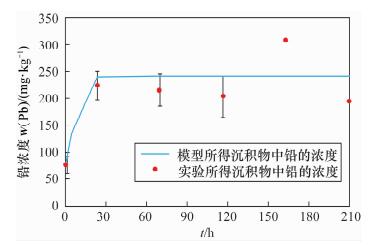
Based on field research at port mineral yard, leaching of heavy metals as an important port soil, water pollution cannot be ignored. The rules of typical pollutants were simulated by the micro-universe model. In this study, the soil and water samples from 7 heavy metals storage yards of Tianjin Port have been investigated, revealing high Cd pollution in soil. Aquatic microcosm was used to simulate the chemical behavior of lead and cadmium in Tianjin port, and the internal transportation law was found by using the fugacity-based multimedia environmental mathematical model. The results of the model and experiment were consistent, showing that this model is suitable. The results of the model suggest that 61% of the cadmium in the system was sunk into sediment, the rest flowing out with water, and 99% of the lead was sunk into sediment, showing that for cadmium and lead, settling was the main transport process in the aquatic environment, especially for lead. The impact of minerals stored in the open areas is significant, and should be stored in containers without any direct contact with rain. Also, the pollution channel should be kept closed.
-

-
References
| [1] |
张培玉.渤海湾近岸海域底栖动物生态学与环境质量评价研究[D].山东:中国海洋大学,2005.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Mackay D, Finizio A, Bidleman T.Octanolair partition coefficient as a predictor of partitioning of semivolatile organic chemicals to aerosols [J].Atmospheric Environ-ment,1997,31(7):2289-2296.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Mackay D, Mirlam D.Application of the QWASI (Quantitative Water Air Sediment Interaction) fugacity model to the dynamics of organic and inorganic chemicals in lakes [J].Chemosphere, 1989, 18: 1343-1365. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(89)90027-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
郑建平.海河河口生态需水量研究[J].海河大学学报:自然科学版,2005(3): 518-521.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
王振坤.邻苯二甲酸酯类化合物在海河河口水环境中行为研究[D].天津:天津大学, 2006.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
陈少峰.天津港港池水交换与生态堤岸设计研究[D].天津:天津大学, 2011.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
陈瑜.铅和镉在水生微宇宙中的分布特征[D].长春:吉林大学, 2009.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
吴昊.重金属模型——三峡库区水域典型重金属化学行为的多介质环境模型研究与应用[D].重庆:重庆大学, 2007.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Donald M, Diamond M, Lorna C.A model of the exchange of inorganic chemicals between water and sediments [J].Environmental Science & Technology, 1990, 24: 713-722.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Donald M, Salle Y.A quantitative water, air, sediment interaction (QWASI) fugacity model for describing the fate of chemicals in lakes [J].Chemosphere, 1983, 12: 981-997. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(83)90251-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Donald M, Diamond M, Donald P.Development of a mass balance model of the fate of 17 chemicals in the bay of Quinte [J].Journal of Great Lakes Research, 1994, 20: 643-666. doi: 10.1016/S0380-1330(94)71184-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Diamond M.Development of a fugacity/aquivalence model of mercury dynamics in lakes [J].Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 1999, 111: 337-357. doi: 10.1023/A:1005062316518
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Diamond M, Helen L L. Loadings, dynamics and re-sponse time of seven metals in Hamilton harbor: Results of a mass balance study [J].Water Quality, 1996, 3: 623-641.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Helen L L, Diamond M, Donald M.Application of the QWASI fugacity/aquivalence model to assessing sources and fate of contaminants in Hamilton harbour [J].Journal of Great Lakes Research, 1993, 19: 582-602. doi: 10.1016/S0380-1330(93)71243-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Donald M. Multimedia Environmental Models: The Fugacity Approach [M].Albany: Lewis Publishers, 2001.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
迟杰,张玄.DDTs在海河干流市区段沉积物/水间迁移行为研究[J].环境科学, 2009,30(8):2376-2380.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
王振坤.进出口资源性矿产品港口环境风险模型研究报告[D].天津:天津出入境检验检疫局, 2012.
Google Scholar
|
-
-
Access History







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: