| Citation: | Zhen Wang, Hua-ming Guo, Hai-yan Liu, Wei-min Zhang, 2023. Source, migration, distribution, toxicological effects and remediation technologies of arsenic in groundwater in China, China Geology, 6, 476-493. doi: 10.31035/cg2022086 |
Source, migration, distribution, toxicological effects and remediation technologies of arsenic in groundwater in China
-
Abstract
Groundwater with high arsenic (As) content seriously threatens human life and health. Drinking high-As groundwater for a long time will lead to various pathological changes such as skin cancer, liver cancer, and kidney cancer. High-As groundwater has become one of the most serious environmental geological problems in China and even internationally. This paper aims to systematically summarize the sources, migration, distribution, toxicological effects, and treatment techniques of As in natural groundwater in China based on a large number of literature surveys. High-As groundwater in China is mainly distributed in the inland basins in arid and semi-arid environments and the alluvial and lacustrine aquifers in river deltas in humid environments, which are in neutral to weakly alkaline and strongly reducing environments. The content of As in groundwater varies widely, and As(III) is the main form. The main mechanism of the formation of high-As groundwater in China is the reduced dissolution of Fe and Mn oxides under the action of organic matter and primary microorganisms, alkaline environment, intense evaporation and concentration, long-term water-rock interaction, and slow groundwater velocity, which promote the continuous migration and enrichment of As in groundwater. There are obvious differences in the toxicity of different forms of As. The toxic of As(III) is far more than As(V), which is considered to be more toxic than methyl arsenate (MMA) and dimethyl arsenate (DMA). Inorganic As entering the body is metabolized through a combination of methylation (detoxification) and reduction (activation) and catalyzed by a series of methyltransferases and reductases. At present, remediation methods for high-As groundwater mainly include ion exchange technology, membrane filtration technology, biological treatment technology, nanocomposite adsorption technology, electrochemical technology, and so on. All the above remediation methods still have certain limitations, and it is urgent to develop treatment materials and technical means with stronger As removal performance and sustainability. With the joint efforts of scientists and governments of various countries in the future, this worldwide problem of drinking-water As poisoning will be solved as soon as possible. This paper systematically summarizes and discusses the hot research results of natural high-As groundwater, which could provide a reference for the related research of high-As groundwater in China and even the world.
-

-
References
Ahmed S, Akhtar E, Roy A, Von Ehrenstein OS, Vahter M, Wagatsuma Y, Raqib R. 2017. Arsenic exposure alters lung function and airway inflammation in children: A cohort study in rural Bangladesh. Environment International, 101, 108–116. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.01.014. Alexander LF, Justin HD, Samantha CY, Roya B. 2017. The Effect of a Receding Saline Lake (The Salton Sea) on Airborne Particulate Matter Composition. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(15), 8283–8292. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b01773. Alsulaili A, Al-Harbi M, Elsayed K. 2020. The influence of household filter types on quality of drinking water. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 143, 204–211. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.06.051. An Y, Li CC, Deng YH. 2015. Current conditions of researches in arsenic-induced oxidative stress. Foreign Medical Sciences (Section of Medgeography), 36(3), 165–173 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8883.2015.03.001. Anawar HM, Akai J, Sakugawa H. 2004. Mobilization of arsenic from subsurface sediments by effect of bicarbonate ions in groundwater. Chemosphere, 54(6), 753–762. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.08.030. Asere TG, Stevens CV, Laing GD. 2019. Use of (modified) natural adsorbents for arsenic remediation: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 676, 706–720. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.237. Ashraf S, Siddiqa A, Shahida S, Qaisar S. 2019. Titanium-based nanocomposite materials for arsenic removal from water: A review. Heliyon, 5(5), 1577–1584. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01577. Besold J, Kumar N, Scheinost AC, Pacheco JL, Fendorf S. 2019. Antimonite Complexation with Thiol and Carboxyl/Phenol Groups of Peat Organic Matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(9), 5005–5015. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b00495. Bhattacharjee P, Banerjee M, Giri AK. 2013. Role of genomic instability in arsenic induced carcinogenicity: A review. Environment International, 53, 29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2012.12.004. Bhattacharya P, Welch AH, Stollenwerk KG, McLaughlin MJ, Bundschuh J, Panaullah G. 2007. Arsenic in the environment: Biology and Chemistry. Science of the Total Environmental, 379, 109–120. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.02.037. Bhowmick S, Pramanik S, Singh P, Mondal P, Nriagu J. 2017. Arsenic in groundwater of West Bengal, India: A review of human health risks and assessment of possible intervention options. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 148–169. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.216. Birkle P, Bundschuh J, Sracek O. 2010. Mechanisms of arsenic enrichment in geothermal and petroleum reservoirs fluids in Mexico. Water Research, 44(19), 5605–5617. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.05.046. Brauner EV, Nordsborg RB, Andersen ZJ, Tjønneland A, Loft S, Raaschou-Nielsen O. 2014. Long-term exposure to low-level arsenic in drinking water and diabetes incidence: A prospective study of the Diet, Cancer and Health Cohort. Environmental Health Perspectives, 122(10), 1059–1065. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408198. Cai LM, Xu ZC, Bao P, He M, Dou L, Chen LG, Zhou YZ, Zhu YG. 2015. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source of arsenic and heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunde, Southeast China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 148, 189–195. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.09.010. Cao WG, Wang YY, Ren Y, Fei YH, Li JC, Li ZY, Zhang D, Shuai GY. 2022. Status and progress of treatment technologies for arsenic-containing groundwater. Geology in China, 49(05), 1408–1426 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen ASC, Wang L, Sorg TJ, Lytle DA. 2020. Removing arsenic and co-occurring contaminants from drinking water by full-scale ion exchange and point-of-use/point-of-entry reverse osmosis systems. Water Research, 172, 115455. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115455. Choong TSY, Chuah TG, Robiah Y, Gregory-Koay FL, Azni I. 2007. Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: An overview. Desalination, 217 (1–3), 139–166. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.015. Cohen SM, Arnold LL, Eldan M, Lewis AS, Beck BD. 2006. Methylated arsenicals: The implications of metabolism and carcinogenicity studies in rodents to human risk assessment. Critical Reviews in Toxicology, 36, 99–133. doi: 10.1080/10408440500534230. Dai SF, Ren D, Tang Y, Yue M, Hao LM. 2005. Concentration and distribution of elements in Late Permian coals from western Guizhou Province, China. International Journal of Coal Geology, 61(1), 119–137.doi. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2004.07.003. Dai XY, Li P, Tu J, Zhang R, Wei DZ, Li B, Wang YH, Jiang Z. 2018. Evidence of arsenic mobilization mediated by an indigenous iron reducing bacterium from high arsenic groundwater aquifer in Hetao Basin of Inner Mongolia, China. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 128, 22–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.05.012. Das N, Giri A, Chakraborty S, Bhattacharjee P. 2016. Association of single nucleotide polymorphism with arsenic-induced skin lesions and genetic damage in exposed population of West Bengal, India. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 809, 50–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02548.x. Deng YM, Wang YX, Ma T, Yang H, He J. 2011. Arsenic associations in sediments from shallow aquifers of northwestern Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(8), 2001–2011. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1020-1. Dixit S, Hering JG. 2003. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto Fe oxide minerals, implications for arsenic mobility. Environmental Science and Technology, 37(18), 4182–4189. doi: 10.1021/es030309t. Dong YH, Ma T, Li JL, Liu Y. 2018. Arsenic releasing from poly-metallic sulfide deposits at Hetao Plain, China. Geochemistry International, 56(12), 1179–1188. doi: 10.1134/S001670291812011X. Duan YH, Gan YQ, Wang YX, Liu CX, Yu K, Deng YM, Zhao K, Dong CJ. 2017. Arsenic speciation in aquifer sediment under varying groundwater regime and redox conditions at Jianghan Plain of Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 608, 992–1000. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.011. Edmunds WM, Ahmed KM, Whitehead PG. 2015. A review of arsenic and its impacts in groundwater of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta, Bangladesh. Environmental Science:Processes and Impacts, 17(6), 1032–1046. doi: 10.1039/c4em00673a. Evans HA, Wu Y, Seshadri R, Cheetham AK. 2020. Perovskite-related ReO3-type structures. Nature Reviews Materials, 5, 196–213. doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0160-x. Ferrario D, Collotta A, Carfi M, Bowe G, Vahter M, Hartung T, Gribaldo L. 2009. Arsenic induces telomerase expression and maintains telomere length in human cord blood cells. Toxicology, 260(1–3), 132–141. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2009.03.019. Figoli A, Fuoco I, Apollaro C, Chabane M, Mancuso R, Gabriele B, De Rosa R, Vespasiano G, Barca D, Criscuoli A. 2020. Arsenic-contaminated groundwaters remediation by nanofiltration. Separation and Purification Technology, 238, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116461. Ding ZH, Zheng BS, Long JP, Belkin HE, Finkelman RB, Chen CG, Zhou DX, Zhou YS. 2001. Geological and geochemical characteristics of high arsenic coals from endemic arsenosis areas in southwestern Guizhou Province, China. Applied Geochemistry, 16, 1353–1360. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00049-X. Gao CR, Liu WB, Liu B, Li JF, Li F. 2010. Modes of occurrence of arsenic in Quaternary sediments of the Hetao Plain. Geology in China, 37(3), 760–770 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.032. Gao ZP, Jia YF, Guo HM, Zhang D, Zhao B. 2020. Quantifying geochemical processes of arsenic mobility in groundwater from an inland basin using a reactive transport model. Water Resources Research, 56(2), 1–15. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025492. Gao ZP, Weng HC, Guo HM. 2021. Unraveling influences of nitrogen cycling on arsenic enrichment in groundwater from the hetao basin using geochemical and multi-isotopic approaches. Journal of Hydrology, 595(47), 125981. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125981. Goswami R, Kumar M, Biyani N, Shea PJ. 2020. Arsenic exposure and perception of health risk due to groundwater contamination in Majuli (River Island), Assam, India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(2), 443–460. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00373-9. Guo HM, Guo Q, Jia YF, Liu ZY, Jiang YX. 2013. Chemical characteristics and geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater in different regions of China. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 35(3), 83–96 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo HM, Li XM, Xiu W, He W, Cao YS, Zhang D, Wang A. 2019. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, P. R. China. Journal of Hydrology, 571, 448–459. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.01.076. Guo HM, Jia YF, Wanty RB, Jiang YX, Zhao WG, Xiu W, Shen JX, Li Y, Cao YS, Wu Y, Zhang D, Wei C, Zhang YL, Cao WG, Fosterf A. 2015. Contrasting distributions of groundwater arsenic and uranium in the western Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia: Implication for origins and fate controls. Science of the Total Environment, 541, 1172–1190. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.018. Guo HM, Tang XH, Yang SZ. 2008. Effect of indigenous bacteria on geochemical behavior of arsenic in aquifer sediments from the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia: Evidence from sediment incubation. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3267–3277. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2008.07.010. Guo HM, Wen DG, Liu ZY, Jia YF, Guo Q. 2014. A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes. Applied Geochemistry, 41(1), 196–217. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.12.016. Guo HM, Zhang B, Yang SZ, Stüben D, Norra S, Wang JJ. 2009. Role of colloidal particles for hydrogeochemistry in As-affected aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Geochemical Journal, 2009,43(4), 227–234. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0020. Guo HM, Zhang Y, Xing LN, Jia YF. 2012. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the Shahai town of the Hetao basin, Inner Mongolia. Applied Geochemistry, 27(11), 2187–2196. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2012.01.016. Guo Q, Wang Y, Liu W. 2007. Major hydrogeochemical processes in the two reservoirs of the Yangbajing geothermal field, Xizang, China. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 166(3–4), 255–268. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2007.08.004. Guo QH, Cao YW, Li JX, hang XB, Wang YX. 2015. Natural attenuation of geothermal arsenic from Yangbajain power plant discharge in the Zangbo River, Xizang, China. Applied Geochemistry, 62, 164–170. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2015.01.017. Han Y, Zhang HM, Zhang YF, Zhang X. 2017. Distribution regularity, origin and quality division of high arsenic, fluorine and iodine contents in groundwater in Datong Basin. Geological Survey of China, 4(1), 57–68 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2017.01.09. Harvey CF, Ashfaque KN, Yu W, Badruzzaman ABM, Ali MA, Oates PM, Michael HA, Neumann RB, Beckie R, Islam S. 2006. Groundwater dynamics and arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Chemical Geology, 228(1–3), 112–136. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.025. Hayakawa T, Kobayashi Y, Cui X, Hirano S. 2005. A new metabolic pathway of arsenite: Arsenic-glutathione complexes are substrates for human arsenic methyltransferase Cyt 19. Archives of Toxicology, 79, 183–191. doi: 10.1007/s00204-004-0620-x. Hayati B, Maleki A, Najafi F, Gharibi F, McKay G, Gupta VK, Puttaiah SH, Marzban N. 2018. Heavy metal adsorption using PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 346, 258–270. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.172. He B, Liang L, Jiang G. 2002. Distributions of arsenic and selenium in selected Chinese coal mines. Science of the Total Environment, 296, 19–26. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01136-6. He XD, Li PY, Wu JH, Wei MJ, Ren XF, Wang D. 2020. Poor groundwater quality and high potential health risks in the Datong Basin, northern China: Research from published data. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2020,43(2), 791–812. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00520-7. Hong HJ, Yang JS, Kim BK, Yang JW. 2011. Arsenic removal behavior by Fe-Al binary oxide: Thermodynamic and kinetic study. Separation Science and Technology, 46(16), 2531–2538. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2011.598205. Hong YS, Song KH, Chung JY. 2014. Health effects of chronic arsenic exposure. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health, 47(5), 245–252. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.14.035. Ilgen AG, Rychagov SN, Trainor TP. 2011. Arsenic speciation and transport associated with the release of spent geothermal fluids in mutnovsky field (Kamchatka, Russia). Chemical geology, 288(3/4), 115–132. doi: org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.07.010. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). 2004. Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 84. WHO, Lyon, France, 61–96. Jia YF, Guo HM, Xi BD, Jiang YH, Zhang Z, Yuan RX, Yi WX, Xue XL. 2017. Sources of groundwater salinity and potential impact on arsenic mobility in the western Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Science of the Total Environment, 601–602(1), 691–702. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.196. Jia YF, Xi BD, Jiang YH, Guo HM, Yang Y, Lian XY, Han SB. 2018. Distribution, formation and human-induced evolution of geogenic contaminated groundwater in China: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 643, 967–993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.201. Jian M, Liu B, Zhang G, Liu R, Zhang X. 2015. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles. Colloid Surface A, 465, 67–76. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.10.023. Jiang J, Kappler A. 2008. Kinetics of microbial and chemical reduction of humic substances: Implications for electron shuttling. Environmental Science and Technology, 42(10), 3563–3569. doi: 10.1021/es7023803. Kan R, Zhong R, Liu J, Wu ZG, Peng CY, Chen H, Fu XM. 2022. Research progress in nephrotoxicity and prevention of arsenic trioxide. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2, 177–180 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2022.02.005. Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H. 2005. Removal of Arsenic(III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valentiron. Environmental Science and Technology, 39(5), 1291–1298. doi: 10.1021/es048991u. Kanematsu M, Young TM, Fukushi K, Green PG, Darby JL. 2013. Arsenic(III, V) adsorption on a goethite-based adsorbent in the presence of major co-existing ions: Modeling competitive adsorption consistent with spectroscopic and molecular evidence. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 106(1), 404–428. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.09.055. Kersten M, Vlasova N. 2009. Arsenite adsorption on goethite at elevated temperatures. Applied Geochemistry, 24(1), 32–43. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2008.10.004. Kim K, Moon JT, Kim SH, Ko KS. 2009. Importance of surface geologic condition in regulating As concentration of groundwater in the alluvial plain. Chemosphere, 77(4), 478–484. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.053. Kligerman AD, Tennant AH. 2007. Insights into the carcinogenic mode of action of arsenic. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222(3), 281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.10.006. Kumar I, Ranjan P, Quaff AR. 2020. Cost-effective synthesis and characterization of CuO NPs as a nanosize adsorbent for As(III) remediation in synthetic arsenic-contaminated water. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 18(2), 1131–1140. doi: 10.1007/s40201-020-00532-6. Kumar S, Kumar V, Saini RK, Pant N, Singh R, Singh A, Kumar S, Singh S, Yadav BK, Krishan G, Raj A, Maurya NS, Kumar M. 2021. Floodplains landforms, clay deposition and irrigation return flow govern arsenic occurrence, prevalence and mobilization: A geochemical and isotopic study of the mid-Gangetic floodplains. Environmental Research, 201, 111516. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111516. Kuo YC, Lo YS, Guo HR. 2017. Lung cancer associated with arsenic ingestion: Cell-type specificity and dose response. Epidemiology, 28(1), 106–112. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000743. Lang XJ, Lin WJ, Liu ZM, Xing LX, Wang GL. 2016. Hydrochemical characteristics of geothermal water in Guide Basin. Earth Sciences:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 41(10), 1–12 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2016.509. Langner HW, Jackson CR, Mcdermott TR, Inskeep WP. 2001. Rapid oxidation of arsenite in a hot spring ecosystem, Yellowstone National Park. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(16), 3302–3309. doi: 10.1021/es0105562. Lawson M, Polya DA, Boyce AJ, Bryant C, Ballentine CJ. 2016. Tracing organic matter composition and distribution and its role on arsenic release in shallow Cambodian groundwaters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 178, 160–177. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.01.010. Li B, Zhao CJ, Li PY, Yuan Y. 2013. BCR speciation analysis of arsenic in contaminated soil in arsenic mining area. Journal of Yunnan University of Nationalities (Natural Sciences Edition), 22(5), 330–333 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8513.2013.05.006. Li JX, Wang YX, Xie XJ, Zhang LP, Guo W. 2013. Hydrogeochemistry of high iodine groundwater: A case study at the Datong Basin, northern China. Environmental Sciences:Processes and Impacts, 15(4), 848–859. doi: 10.1039/c3em30841c. Liao TQ, Xi YH, Zhang LB, Li J. 2020. Removal of toxic arsenic (As(Ⅲ)) from industrial wastewater by ultrasonic enhanced zero-valent lead combined with CuSO4. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 408(1), 124464. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124464. Liao Y, Ma T, Chen LZ, Tian CY, Shi JJ. 2013. Hydrochemistry of high-arsenic thermal groundwater of low-temperature in the Guide basin in Qinghai, China. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 40(4), 121–126 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu LH, Qiao Q, Tan WF, Sun XC, Liu CS, Dang Z, Qiu GH. 2021. Arsenic detoxification by iron-manganese nodules under electrochemically controlled redox: Mechanism and application. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403, 123912. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123912. Liu YC, Zhang ZJ, Zhao XY, Wen MT, Cao SW, Li YS. 2021. Arsenic contamination caused by roxarsone transformation with spatiotemporal variation of microbial community structure in a column experiment. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(4), 304–316. doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.04.004. Maji SK, Pal A, Pal T, Adak A. 2007. Adsorption thermos dynamics of arsenic on laterite soil. Journal of Surface Science and Technology, 22 (3–4), 161–176. doi: 10.18311/JSST/2007/1930. Martinson CA, Reddy KJ. 2009. Adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) by cupric oxide nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 336(2), 406–411. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.04.075. Massoudinejad M, Ghaderpoori M, Shahsavani A, Jafari A, Kamarehie B, Ghaderpoury A, Amini MM. 2018. Ethylenediamine-functionalized cubic ZIF-8 for arsenic adsorption from aqueous solution: Modeling, isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 255, 263–268. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2018.01.163. Matthijs B, Breukelen BMV, Stuyfzand PJ. 2013. Temperature-induced impacts on groundwater quality and arsenic mobility in anoxic aquifer sediments used for both drinking water and shallow geothermal energy production. Water Research, 47(14), 5088–5100. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.05.049. Mazumder DNG, Chakraborty AK, Ghose A, Gupta JD, Chattopadhyay N. 1988. Chronic arsenic toxicity from drinking tubewell water in rural West Bengal. Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 9(1), 379–401. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.09.050188.002115. McArthur JM, Ghosal U, Sikdar PK, Ball JD. 2016. Arsenic in groundwater: The deep late pleistocene aquifers of the western bengal basin. Environmental Science and Technology, 50(7), 3469–3476. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02477. Mochizuki H. 2019. Arsenic neurotoxicity in humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3418–3428. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143418. Mukherjee A, Verma S, Gupta S, Henke KR, Bhattacharya P. 2014. Influence of tectonics, sedimentation and aqueous flow cycles on the origin of global groundwater arsenic: Paradigms from three continents. Journal of Hydrology, 518(1), 284–299. doi: 10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2013.10.044. Naranmandura H, Suzuki N, Suzuki KT. 2006. Trivalent arsenicals are bound to proteins during reductive methylation. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 19, 1010–1018. doi: 10.1021/tx060053f. Narayan VM, Adejoro O, Schwartz I, Ziegelmann M, Elliott S, Konety BR. 2018. The prevalence and impact of urinary marker testing in patients with bladder cancer. Journal of Urology, 199(1), 74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.08.097. Negrea A, Lupa L, Ciopec M, Lazau R, Muntean C, Negrea P. 2010. Adsorption of As(III) ions onto iron-containing waste ludge. Adsorption Science and Technology, 28(6), 467–484. doi: 10.1260/0263-6174.28.6.467. Nicolli HB, García JW, Falcón CM, Smedley PL. 2012. Mobilization of arsenic and other trace element of health concern in groundwater from the Salí River Basin, Tucumán Province, Argentina. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 34(2), 251–262. doi: 10.1007/s10653-011-9429-8. Nriagu J, Xi C, Siddique A, Vincent A, Shomar B. 2018. Influence of household water filters on bacteria growth and trace metals in tap water of Doha, Qatar. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–17. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26529-8. Orosun MM. 2021. Assessment of arsenic and its associated health risks due to mining activities in parts of North-central Nigeria: Probabilistic approach using Monte Carlo. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412(1), 125262. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.12526. Oyarzun R, Lillo J, Higueras P, Oyarzún J, Maturana H. 2004. Strong arsenic enrichment in sediments from the Elqui watershed, Northern Chile: industrial (gold mining at El Indio–Tambo district) vs. geologic processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 84(2), 53–64. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2004.03.002. Park KS, Ni Z, Côté AP, Choi JY, Huang R, UribeRomo FJ, Chae HK, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM. 2006. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(27), 10186–10191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0602439103. Pascua CS, Minato M, Yokoyama S, Sato T. 2007. Uptake of dissolved arsenic during the retrieval of silica frospent geothermal brine. Geothermics, 36(3), 230–242. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2007.03.001. Pei J, Fan WH, Dong ZM. 2018. The effects of inorganic arsenic on accumulation and detoxification by GSH/GST in tilapia liver. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 13(6), 107–114 (in Chinese with English abstract). Pi KF, Wang YX, Xie XJ, Ma T, Su CL, Liu YQ. 2017. Role of sulfur redox cycling on arsenic mobilization in aquifers of Datong Basin, northern China. Applied Geochemistry, 77, 31–43. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2016.05.019. Polizzotto ML, Kocar BD, Benner SG, Sampson M, Fendorf S. 2008. Near-surface wetland sediments as a source of arsenic release to ground water in Asia. Nature, 454(7203), 505–508. doi: 10.1038/nature07093. Polizzotto ML, Lineberger EM, Matteson AR, Neumann RB, Badruzzaman ABM, Alic MA. 2013. Arsenic transport in irrigation water across rice-field soils in Bangladesh. Environmental Pollution, 179, 210–217. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.04.025. Qiao JT, Li XM, Li FB. 2017. Roles of different active metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from arsenic-contaminated paddy soil amended with biochar. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 344(15), 958–967. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.025. Qiao W, Guo HM, He C, Shi Q, Xing SP, Gao ZP. 2021. Identification of processes mobilizing organic molecules and arsenic in geothermal confined groundwater from Pliocene aquifers. Water Research, (10), 117140. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117140. Rahman A, Rahaman H. 2018. Contamination of arsenic, manganese and coliform bacteria in groundwater at Kushtia District, Bangladesh: Human health vulnerabilities Acta Geologica Sinica. Journal of Water and Health, 16(5), 782–795. doi: 10.2166/wh.2018.057. Raml R, Goessler W, Traar P. 2005. Novel thioarsenic metabolites in human urine after ingestion of an arsenosugar, 2', 3'-dihydroxypropyl 5-deoxy-5-dimethylarsinoyl-beta-D-riboside. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 18(9), 1444–1450. doi: 10.1021/tx050111h. Rathi BS, Kumar PS, Ponprasath R, Rohan K, Jahnavi N. 2021. An effective separation of toxic arsenic from aquatic environment using electrochemical ion exchange process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 412(8), 125240. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125240. Rivera-Núñez Z, Linder AM, Chen B, Nriagu JO. 2011. Low-level determination of six arsenic species in urine by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-ICP-MS). Analytical Methods, 3(5), 1122–1129. doi: 10.1039/c0ay00601g. Roh T, Steinmaus C, Marshall G, Ferreccio C, Liaw J, Smith AH. 2018. Age at exposure to arsenic in water and mortality 30–40 years after exposure cessation. American Journal of Epidemiology, 187(11), 2297–2305. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy159. Romero L, Alonso H, Campano P, Fanfani L, Farago M. 2003. Arsenic enrichment in waters and sediments of the Rio Loa (Second Region, Chile). Applied Geochemistry, 18(9), 1399–1416. Romero L, Alonso H, Campano P, Fanfani L, Cidu R, Dadea C, Keegan T, Thornton I, Farago M. 2003. Arsenic enrichment in waters and sediments of the Rio Loa (Second Region, Chile). Applied Geochemistry, 18(9), 1399–1416. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00059-3. Rudnick RL, Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust. In: The Crust, Vol. 4, Treatise on Geochemistry. Rudnick RL (Eds.), Holland HD, Turekian KK (Ex. eds.). Elsevier Science Ltd., Amsterdam, 1–51. Sadler R, Olszowy H, Shaw G, Biltoft R, Connell D. 1994. Soil and water contamination by arsenic from a tannery waste. Water, Air, Soil and Pollution, 78, 189–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00475677. Sarkar A, Paul B. 2016. The global menace of arsenic and its conventional remediation –A critical review. Chemosphere, 158, 37–49. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.043. Saunders JA, Lee MK, Shamsudduha M, Dhakal P, Uddin A, Chowdury MT, Ahmed KM. 2008. Geochemistry and mineralogy of arsenic in (natural) anaerobic groundwaters. Applied Geochemistry, 23(11), 3205–3214. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.07.002. Scheiber L, Ayora C, Vázquez-Suñé E, Cendón DI, Soler A, Baquero JC. 2016. Origin of high ammonium, arsenic and boron concentrations in the proximity of a mine: Natural vs. anthropogenic processes. Science of the Total Environmental, 541, 655–666. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.098. Schmidt SA, Gukelberger E, Hermann M, Fiedler F, Großmann B, Hoinkis J, Ghosh A, Chatterjeec D, Bundschuhd J. 2016. Pilot study on arsenic removal from groundwater using a small-scale reverse osmosis system towards sustainable drinking water production. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 318, 671–678. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.005. Scholz C, Wieder T, Stärck L, Essmann F, Schulze-Osthoff K, Daniel PT. 2005. Arsenic trioxide triggers a regulated form of caspase-independent necrotic cell death via the mitochondrial death pathway. Oncogene, 24(11), 1904–1911. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208233. Sharma VK, Sohn M. 2009. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environment International, 35(4), 743–759. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2009.01.005. Shi WJ, Song WJ, Zheng JL, Luo Y, Qile G, Lü SJ, Lü XM, Zhou B, Lü CW, He J. 2021. Factors and pathways regulating the release and transformation of arsenic mediated by reduction processes of dissimilated iron and sulfate. Science of the Total Environment, 768, 144697. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144697. Simmons SF. 2000. Hydrothermal Minerals and Precious Metals in the Broadlands-Ohaaki Geothermal System: Implications for Understanding Low-Sulfidation Epithermal Environments. Economic Geology, 95(5), 971–999. doi: 10.2113/95.5.971. Singh R, Singh S, Parihar P, Singh VP, Prasad SM. 2015. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 247–270. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.009. Sinha D, Prasad P. 2020. Health effects inflicted by chronic low-level arsenic contamination in groundwater: A global public health challenge. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 40(1), 87–131. doi: 10.1002/jat.3823. Slotnick MJ, Nriagu JO. 2006. Validity of human nails as a biomarker of arsenic and selenium exposure: A review. Environmental Research, 102, 125–139. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2005.12.001. Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG. 2002. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5. Smith AH, Marshall G, Roh T, Ferreccio C, Liaw J, Steinmaus C. 2018. Lung, bladder, and kidney cancer mortality 40 years after arsenic exposure reduction. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 110(3), 241–249. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx201. Stuckey JW, Schaefer MV, Kocar BD, Benner SG, Fendorf S. 2016. Arsenic release metabolically limited to permanently water-saturated soil in Mekong Delta. Nature Geoscience, 9(1), 70–76. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2589. Souza ACM, De Almeida MG, Pestana IA, De Souza CMM. 2019. Arsenic exposure and effects in humans: A mini-review in Brazil. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 76(3), 357–365. doi: 10.1007/s00244-018-00586-6. Sun Y, Lan JR, Chen XH, Du YG, Ye HP, Du DY, Li J, Hou HB. 2021. Impacts of external organic carbon on arsenic release in aquifer of Jianghan plain, central China. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 5, 1343–1354. doi: 10.1021/acsearthspacechem.0c00358. Sun ZX, Zhang W, Hu BQ, Pan TY. 2006. Heat flow and geothermal field in the Qinshui Basin. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(1), 123–128. doi: 10.1002/CJG2.819. Tang XC, Wang GL, Ma Y, Zhang DL, Liu Z, Zhao X, Cheng TJ. 2020. Geological model of heat source and accumulation for geothermal anomalies in the Gonghe basin, northeastern Xizang Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(7), 1–14 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2020221. Takenaka T, Furuya S. 2008. Geochemical model of the Takigami geothermal system, northeast Kyushu, Japan. Geochemical Journal, 25(4), 267–281. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.25.267. Thomas DJ. 2007. Molecular processes in cellular arsenic metabolism. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222, 365–373. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.02.007. Wan P, Yuan M, Yu X, Zhang Z, Deng B. 2020. Arsenate removal by reactive mixed matrix PVDF hollow fiber membranes with UIO-66 metal organic frameworks. Chemical Engineering Journal, 382, 122921. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122921. Wang B, Côté AP, Furukawa H, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM. 2008. Colossal cages in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks as selective carbon dioxide reservoirs. Nature, 453(7192), 207–211. doi: 10.1038/nature06900. Wang Y, Wang S, Xu P, Liu C, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhang C, Ge Y. 2015. Review of arsenic speciation, toxicity and metabolism in microalgae. Reviews in Environmental Science and Biotechnology, 14(3), 427–451. doi: 10.1007/s11157-015-9371-9. Wang YX, Shvartsev SL, Su CL. 2009. Genesis of arsenic/fluoride-enriched soda water: A case study at Datong, northern China. Applied Geochemistry, 24(4), 641–649. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.12.015. Wang Z, Guo HM, Xiu W, Wang J, Shen MM. 2018. High arsenic groundwater in the Guide basin, northwestern China: Distribution and genesis mechanisms. Science of the Total Environment, 640–641, 194–206. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.2559. Williams M. 2001. Arsenic in mine waters: An international study. Environmental Geology, 40, 267–278. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142062. Xiao XY, Chen TB, Liao XY. 2008. Regional distribution of arsenic contained minerals and arsenic pollution in China. Geographical Research, 27(1), 201–212. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2008.01.022. Xie XJ, Ellis A, Wang YX, Xie ZM, Duan MY, Su CL. 2009. Geochemistry of redox-sensitive elements and sulfur isotopes in the high arsenic groundwater system of Datong Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3823–3835. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.041. Xie YX, Miyamato H, Kondo M, Koga H, Zhang A, Ohmichi M, Inaba Y, Chiba M. 2001. Element concentrations in urine of patients suffering from chronic arsenic poisoning. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine, 193, 229–235. doi: 10.1620/tjem.193.229. Xie XJ, Wang YX, Li JX, Yu Q, Wu Y, Su CL, Duan MY. 2015. Effect of irrigation on Fe(III)-SO42- redox cycling and arsenic mobilization in shallow groundwater from the Datong basin, China: Evidence from hydrochemical monitoring and modeling. Journal of Hydrology, 523, 128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.035. Xie ZM, Wang J, Wei XF, Li F, Chen MN, Wang J, Gao B. 2018. Interactions between arsenic adsorption/desorption and indigenous bacterial activity in shallow high arsenic aquifer sediments from the Jianghan Plain, central China. Science of the Total Environment, 644, 382–388. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.377. Xing SP, Guo HM, Zhang LZ, Wang Z, Sun XM. 2022. Silicate weathering contributed to arsenic enrichment in geotherm-affected groundwater in Pliocene aquifers of the Guide basin, China. Journal of Hydrology, 606, 12744. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127444. Xu NZ, Gong JS, Tan MJ, Ye YH, Zhou K, Zhu CF, Shu LC, Meng D. 2021. Hydrogeochemical processes and potential exposure risk high-arsenic groundwater in Huaihe River Basin, China. Geology in China, 48(5), 1418–1428 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.12029/gc20210508. Xue XM, Yan Y, Xiong C, Raber G, Francesconi K, Pan T, Ye J, Zhu YG. 2017. Arsenic biotransformation by a cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. Environmental Pollution, 228, 111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.005. Yang YJ, Yuan XF, Deng YM, Xie XJ, Wang YX. 2020. Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter in high arsenic shallow groundwater systems. Journal of Hydrology, 589, 125120. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125120. Ye J, Rensing C, Rosen BP, Zhu YG. 2012. Arsenic biomethylation by photosynthetic organisms. Trends in Plant Science, 17(3), 155–162. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.12.003. You YJ, Liang YZ, Peng SM, Lan S, Lu GN, Feng XH, Shi ZQ. 2019. Modeling coupled kinetics of arsenic adsorption/desorption and oxidation in ferrihydrite-Mn(II)/manganese (oxyhydr) oxides systems. Chemosphere, 244, 125517. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125517. Yu Q, Wang YX, Xie XJ, Currell M, Pi KF, Yu M. 2015. Effects of short-term flooding on arsenic transport in groundwater system: A case study of the Datong Basin. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 158, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.05.015. Zhang HY, Guan XJ, Mao GY, Zhang Z, Guo XJ. 2016. Progress and trend of metabonomics in arsenic poisoning. Zhejiang Journal of Preventive Medicine, 28(6), 591–593. doi: 10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2016.06.013. Zhang JY, Sun GB, Wang M, Sun XB. 2016. Research advances on cardiac toxicity of arsenic trioxide. Chinese Pharmacology Bulletin, 32(9), 1194–1198 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.09.003. Zhang W, Qi LJ, Ning JY, Gao S, Li GJ. 2021. Health hazard assessment of arsenic. Journal of Toxicology, 35(5), 367–372 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16421/j.cnki.1002-3127.2021.05.002. Zhang Y, Zhou T, Liu YQ, Song Y, Yang L. 2019. Research progress on DNA methylation in arsenic-induced atherosclerosis. Journal of Hangzhou Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 18(3), 280–284 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-232X.2019.03.010. Zhang YF, Li SH, Zheng LR, Chen JG, Zheng Y. 2017. Evaluation of arsenic sorption and mobility in stream sediment and hot spring deposit in three drainages of the Xizang Plateau. Applied Geochemistry, 77, 89–101. doi: 10.1016/J.APGEOCHEM.2016.04.006. Zhang Z, Guo HM, Han SB, Gao ZP, Niu XT. 2022a. Controls of Geochemical and Hydrogeochemical Factors on Arsenic Mobility in the Hetao Basin, China. Groundwater, 13230. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113455. Zhang Z, Guo HM, Han SB, Niu XT. 2022b. Occurrence characteristics of arsenic in sediments and its control to arsenic enrichment in groundwater: A case study of Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Geology in China (in Chinese with English abstract). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20221031.0948.002.html. Zhang Z, Guo HM, Liu S, Weng HC, Han SB, Gao ZP. 2020. Mechanisms of groundwater arsenic variations induced by extraction in the western Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Hydrology, (583), 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124599. . Zhao Z, Meng Y, Yuan Q, Wang Y, Luan F. 2021. Microbial mobilization of arsenic from iron-bearing clay mineral through iron, arsenate, and simultaneous iron-arsenate reduction pathways. Science of the Total Environment, 763, 144613. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144613. Zheng Z, Sheng B, Ma C, Zhang H, Gao C, Su F, Xu P. 2012. Relative catalytic efficiency of ldhL- and ldhD- encoded products is crucial for optical purity of lactic acid produced by lactobacillus strains. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(9), 3480–3483. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00058-12. Zhu F, Yang M, Luo ZX, Yu RL, Hu GR, Yan Y. 2020. Bioaccumulation and biotransformation of arsenic in Leptolyngbya boryana. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(24), 29993–30000. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09294-y. -
Access History

-
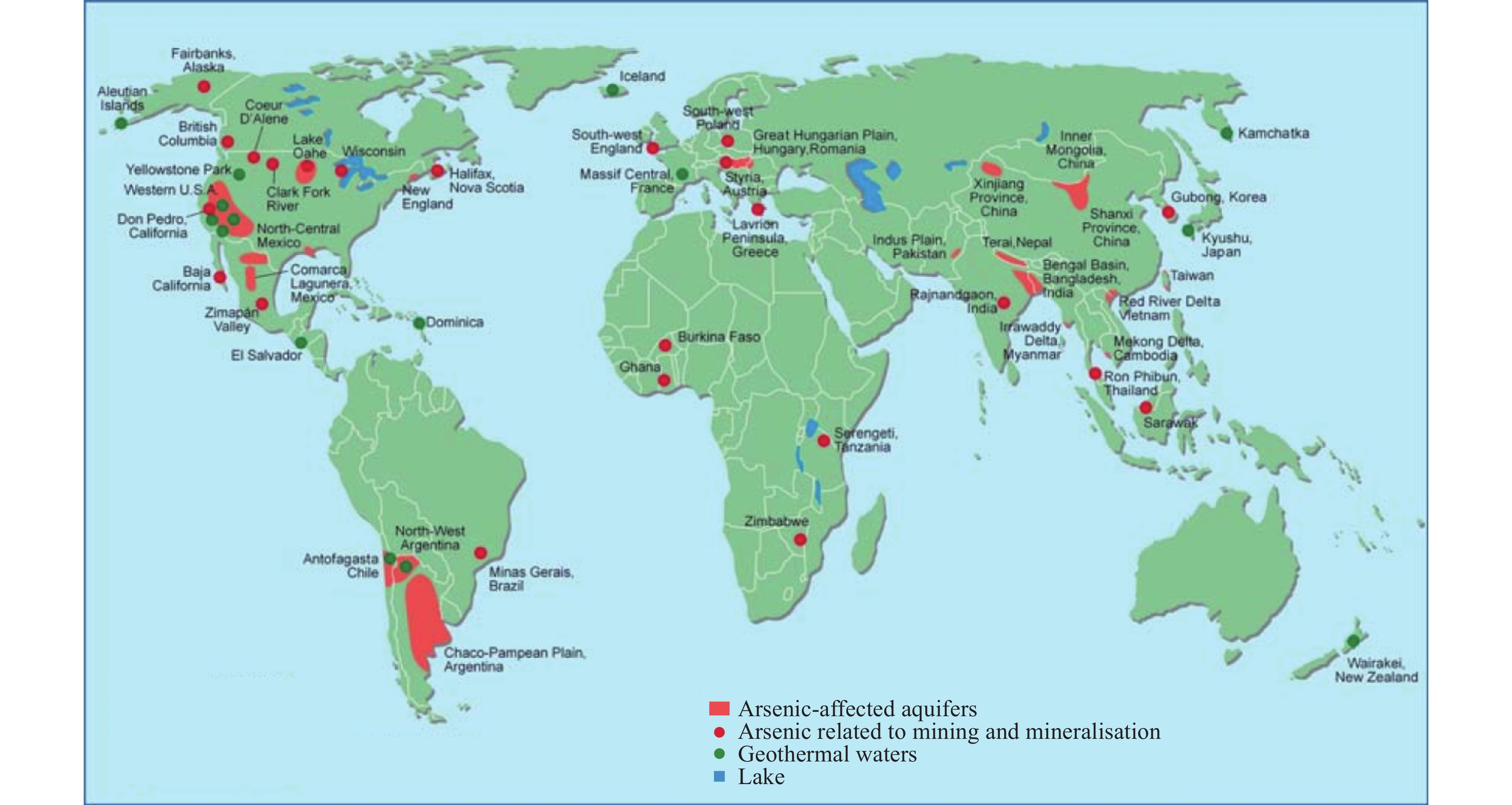
Figure 1.
Global distribution of high As groundwater (modified from Smedley PL et al., 2002).
-
Figure 2.
Key processes of arsenic migration in natural groundwater systems.
-
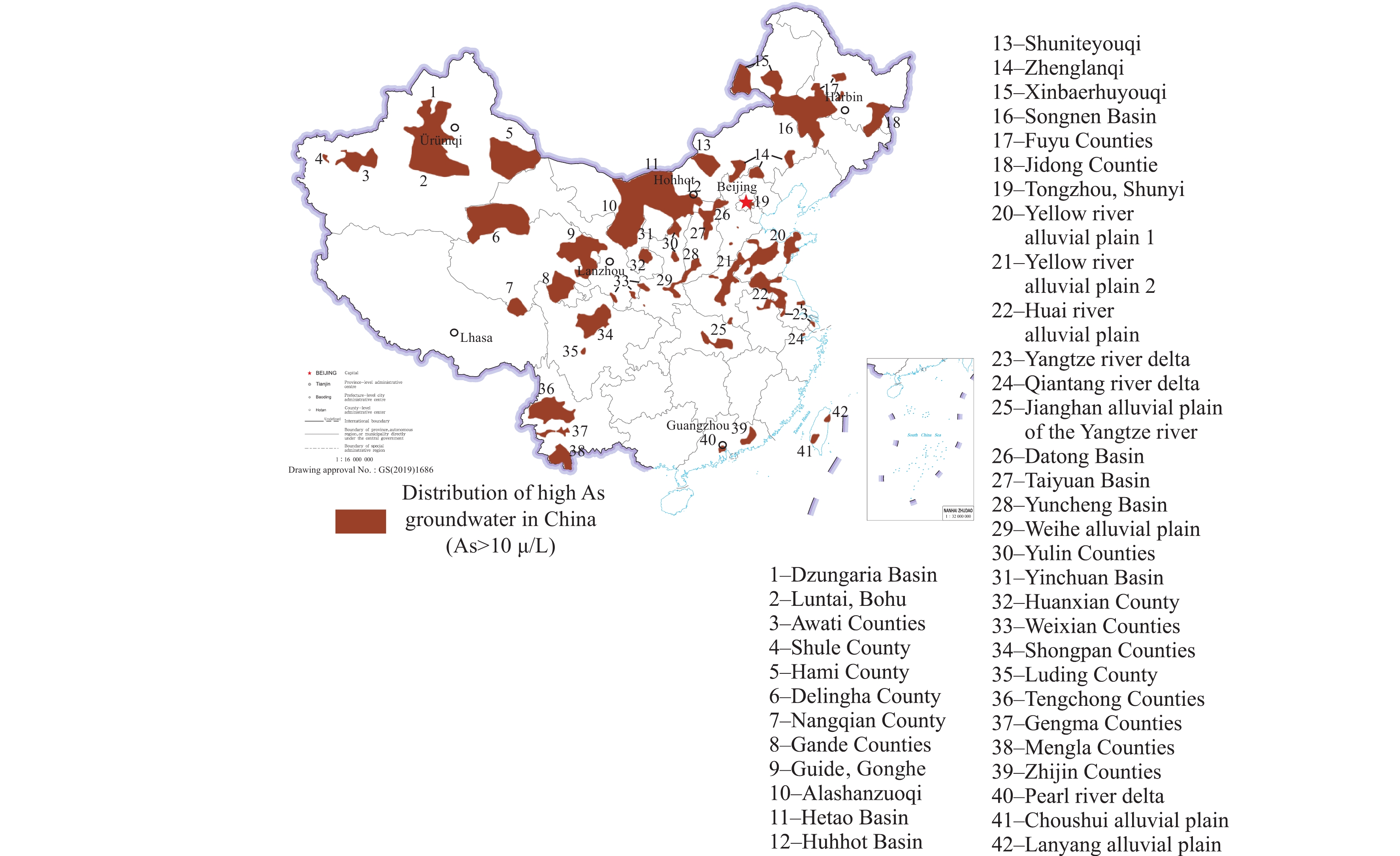
Figure 3.
High-arsenic groundwater distribution map in China (modified from Guo HM et al., 2014).
-
Figure 4.
Metabolic pathway of arsenic (modified from Bhowmick S et al., 2017). MMA‒methyl arsenate; DMA‒dimethyl hypoarsenic acid; GSH‒glutathione; AS3MT‒As(III) methyltransferase; ATG‒As triglutathione; MADG‒monomethyl As diglutathione; DMAG‒dimethyl As glutathione; SAM‒active adenosine methionine; MA‒monomethyl As; DMA‒dimethyl As.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: