| Citation: | Huai-sheng Zhang, Wu-tian Cai, Feng Guo, Chao Bian, Fu-dong Liu, Lei Zhang, Jin-wei Liu, Miao Zhao, 2023. Microbial community composition and environmental response characteristics of typical brackish groundwater in the North China Plain, China Geology, 6, 383-394. doi: 10.31035/cg2022073 |
Microbial community composition and environmental response characteristics of typical brackish groundwater in the North China Plain
-
Abstract
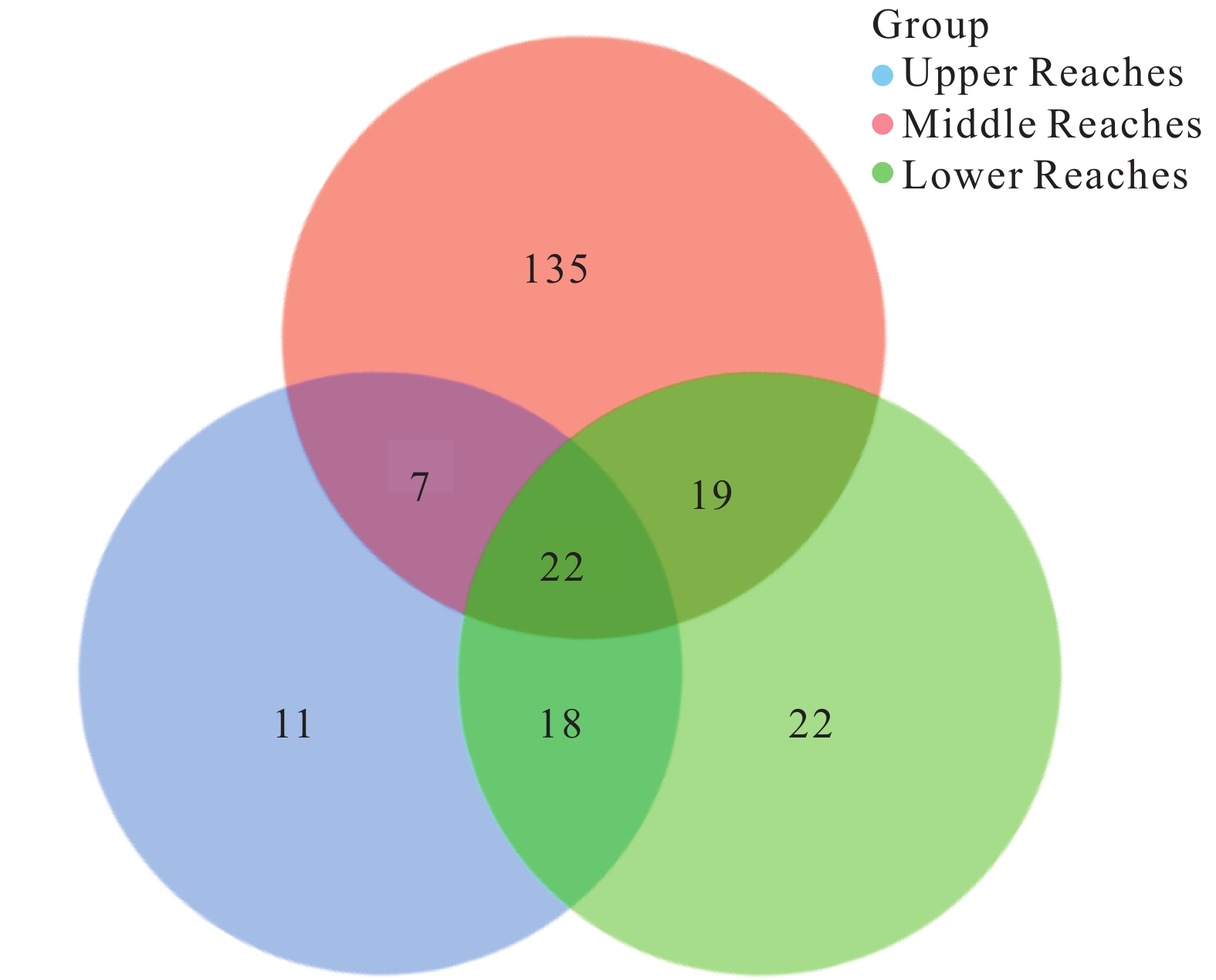
To reveal the microbial community composition of regional shallow porous brackish groundwater and its response characteristics to groundwater environment, the first and second aquifers in Taocheng District, Hengshui City were selected, and 10 groundwater source samples were collected for hydrochemical analysis and microbial 16S RNA gene V4–V5 regional sequencing. The results showed that the shallow brackish groundwater in the study area is weakly alkaline and has high ion content. The hydrochemical types are SO4·Cl-Na·Mg type and HCO3·Cl-Na·Mg type as a whole. The spatial zonation of the abundance and diversity of groundwater microorganisms is obvious. The number of endemic bacteria in groundwater from upstream, midstream to downstream is 11, 135 and 22 respectively, with a total of 22 bacteria. Proteobacteria is the most dominant in groundwater level (38.82%–86.88%), and there are obvious differences in different sections. At the genus level, the main dominant species in each group and sample are Pseudomonas and Hydrogenophaga. In terms of composition difference, Pseudohongiella, Pseudorhodobacter and Limnohabitans are the representatives of UR, MR and LR. On the whole, the composition of flora in groundwater in the study area is sensitive and closely related to hydrochemical processes. Species abundance is affected by alkaline and high salinity environmental indicators, while species diversity is related to depth and dissolved oxygen in weak reduction environment.
-

-
References
Chen Z, Li Y, Peng Y, Mironov V, Chen J, Jin H. 2022. Feasibility of sewage sludge and food waste aerobic co-composting: Physicochemical properties, microbial community structures, and contradiction between microbial metabolic activity and safety risks. Science of the Total Environment, 825. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154047. Chen ZY, Zhang ZW, Zhang TN, Zhou SL, Zhang YR, Dong WJ, Yu MH, Zhang YF, Zhang JF. 2022. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and driving factors of denitrification bacterial community structure from landscape water in Hebei province: taking Shijiazhuang as example. Environmental Science, 43(2), 813–825 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202104341. Delmont TO, Quince C, Shaiber A, Esen CÖ, Lee TMS, Rappé SM, MacLellan SL, Lücker S; Eren AM. 2018. Nitrogen-fixing populations of planctomycetes and proteobacteria are abundant in surface ocean metagenomes. Nature Microbiology, 3(8), 963–963. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0209-4. Fuge R. 2019. Fluorine in the environment, a review of its sources and geochemistry. Applied Geochemistry, 100, 393–406. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.016. Hao QY, Xu XT, Zhang XB, Zhou L. 2020. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of high-fluorine shallow groundwater in Yanggu area of the northwestern Shandong, China. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 42(5), 668–677 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2020.04033. Hou JL, Nie C, Perumal V, Xiao X, Wang FP. 2018. Metabolic analysis of epsilonproteobacteria genomes reconstructed from the deep sea hydrothermal vent chimney based on metagenomic technology. Microbiology Bulletin, 45(9), 1843–1852 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.180100. Huang Z, Kong F, Li Y, Xu G, Wang S. 2020. Advanced treatment of effluent from municipal wastewater treatment plant by strengthened ecological floating bed. Bioresource Technology, 309, 123358. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123358. Lerm S, Westphal A, Miethling-Graff R, Alawi M, Seibt A, Wolfgramm M, Würdemann H. 2013. Thermal effects on microbial composition and microbiologically induced corrosion and mineral precipitation affecting operation of a geothermal plant in a deep saline aquifer. Extremophiles, 17(2), 311–327. doi: 10.1007/s00792-013-0518-8. Li S, Cheng JM, Li MM, Cui LH. 2016. Water quality characteristics and evolution of groundwater system influenced by human exploitation activity in Hengshui area. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science and Technology, 14(3), 55–61,100 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2016.03.010. Liu B, Wang S, Kong X, Liu X. 2019. Soil matric potential and salt transport in response to different irrigated lands and soil heterogeneity in the North China Plain. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(12), 3982–3993. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02331-5. Liu SY and Wang HQ. 2016. Dynamic assessment of pollution risk of groundwater source area in northern China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 4(2), 79–89. Liu YC, Zhang ZJ, Zhao XY, Wen MT, Cao SW, Li YS. 2021. Arsenic contamination caused by roxarsone transformation with spatiotemporal variation of microbial community structure in a column experiment. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(4), 304–316. doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.04.004. Mossa AW, Dickinson MJ, West HM, Young SD, Crout NMJ. 2017. The response of soil microbial diversity and abundance to long-term application of biosolids. Environmental Pollution, 224, 16–25. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.056. Negoro S, Kato K, Fujiyama K, Okada H. 1995. The nylon oligomer biodegradation system of Flavobacterium and Pseudomonas. Biodegradation, 5(3‒4), 185‒194. doi:10.1007/bf00696459 Ning Z, Cai PP, Zhang M, Guo C, He Z. 2019. Abnormally low dissolved inorganic carbon in petroleum contaminated groundwater caused by microbiological geochemistry. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(4), 1140–1147 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2018.0410. Qi JF, TIAN MK, CHI XC, WANG CZ. 2016. Research on ground fissure origins and mechanisms in Hebei Plain, PR China. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 4(2), 188–196. Qian Y, Zhang Z, Fei Y, Chen J, Zhang F, Wang Z. 2014. Sustainable exploitable potential of shallow groundwater in the North China Plain. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 22(8), 890–897 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.140704. Qu JY, Tong M, Yuan SH. 2021. Effect and Mechanism of Fe(II) Oxygenation on activities of iron and manganese cycling functional microbes. Earth Science, 46(2), 632–641 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.029. Robinson M, Liam R, Anna P, Jan P, Nathan K. 2017. Comparison of the predictive performance and interpretability of random forest and linear models on benchmark datasets. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 57(8), 1773–1792. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00753. Sakihara TS, Dudley BD, Mackenzie RA, Beets JP. 2015. Endemic grazers control benthic microalgal growth in a eutrophic tropical brackish ecosystem. Marine Ecology Progress, 519, 29–45. doi: 10.3354/meps11099. Shapiro B, Hoehler TM, Jin Q. 2018. Integrating genome-scale metabolic models into the prediction of microbial kinetics in natural environments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 242, 102–122. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.047. Shi ZQ, Hu SW, Lin JY, Liu TX, Li XM, Li FB. 2020. Quantifying microbially mediated kinetics of ferrihydrite transformation and arsenic reduction: role of the arsenate-reducing gene expression pattern. Environmental Science and Technology, 54(11), 6621–6631 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b07137. Sun QL. 2016. Studies on the environmental and symbiotic microorganisms in the hydrothermal field of the Okinawa Trough. Beijing, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ph. D thesis, 1‒85 (in Chinese with English abstract). Valsala R, Govindarajan SK. 2019. Co-colloidal BTEX and microbial transport in a saturated porous system: numerical modeling and sensitivity analysis. Transport in Porous Media, 127(2), 269–294. doi: 10.1007/s11242-018-1191-2. Zhang HS, Cai WT, Bian C, Liu JW. 2021. Hydrochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of shallow high-flourine groundwater in Taocheng District, Hengshui City. Science Technology and Engineering, 21(24), 93–100 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.24.013. Zhang L, Zhang C, Lian K, Ke D, Xie T, Liu C. 2021. River restoration changes distributions of antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and microbial community. Science of the Total Environment, 788, 147873. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147873. Zhang ZG, He JT, Wang L, Peng C. 2018. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of deep groundwater in Hengshui area. Geoscience, 32(3), 565–573 (in Chinese with English abstract). -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Geographical location and distribution of sampling points.
-
Figure 2.
Geological profile and hydrological characteristics of the study area.
-
Figure 3.
Piper diagram of water type analysis based on the ionic composition.
-
Figure 4.
Box chart of Alpha index of groundwater microbial community in brackish groundwater.
-
Figure 5.
The phylum and genus composition of the groundwater microbial community in brackish groundwater.
-
Figure 6.
Venn of brackish groundwater samples on genus level.
-
Figure 7.
Distribution of common genera of brackish groundwater samples.
-
Figure 8.
Principal coordinate analysis of brackish groundwater samples at genus level.
-
Figure 9.
Heat map of community structure of brackish groundwater samples on genus level.
-
Figure 10.
RDA analysis on relationship between environmental factors and bacterial phyla.
-
Figure 11.
RDA analysis on relationship between environmental factors and bacterial genera





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: