| Citation: | Tian-wen Liu, Cheng Hu, Qing Wang, Jun Li, Kun Huang, Zhi-hua Chen, Ting-ting Shi, 2020. Conversion relationship of rainfall-soil moisture-groundwater in Quaternary thick cohesive soil in Jianghan Plain, Hubei Province, China, China Geology, 3, 462-472. doi: 10.31035/cg2020053 |
Conversion relationship of rainfall-soil moisture-groundwater in Quaternary thick cohesive soil in Jianghan Plain, Hubei Province, China
-
Abstract
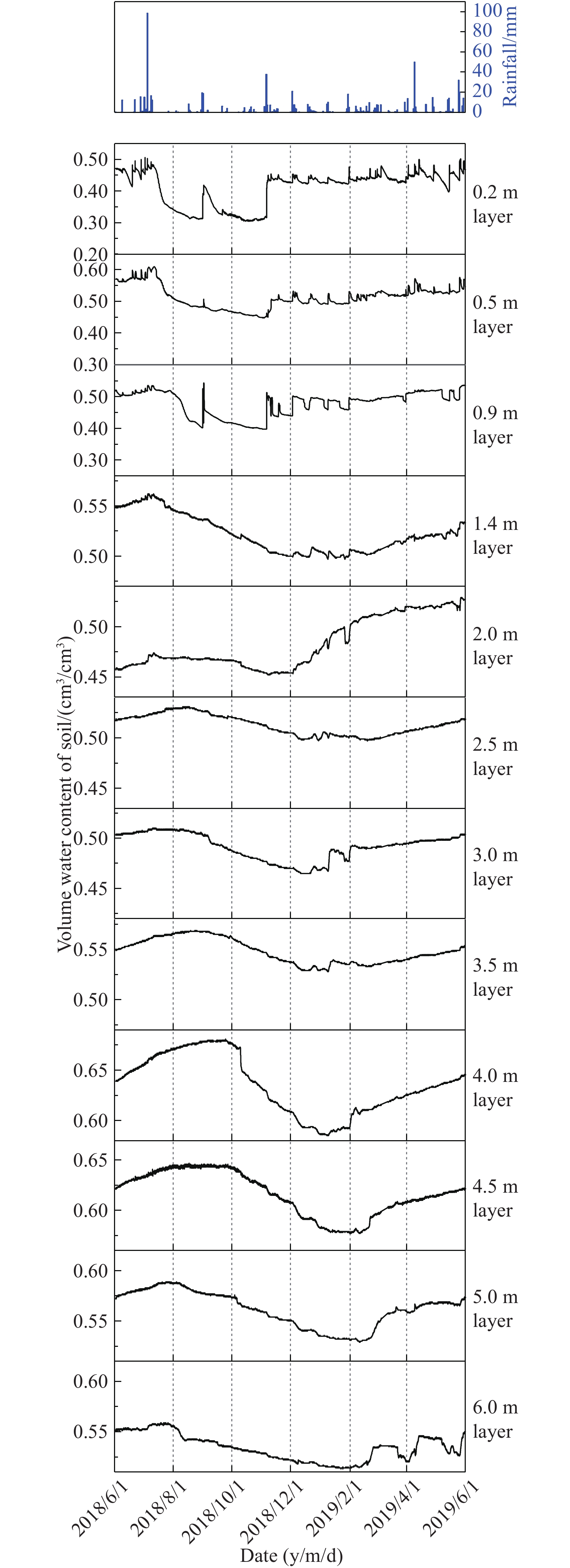
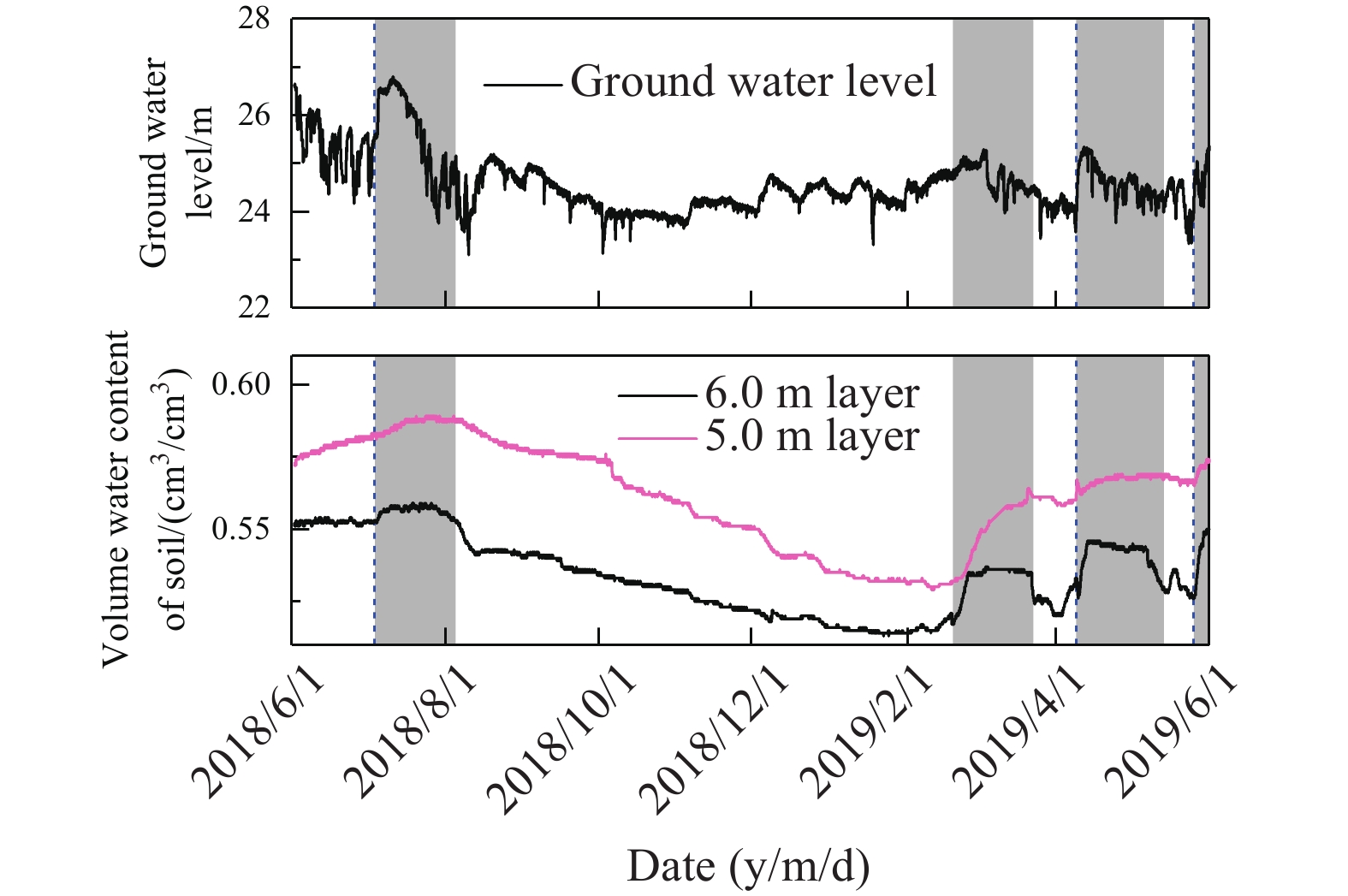
The scientific field test site of rainfall-soil moisture-groundwater conversion in Dabie Mountain Area–Jianghan Plain is located in the northern region of the Jianghan Plain, the transition zone between the Dabie Mountain Area and Jianghan Plain. It’s a great field test site to study the material and energy exchange among rainfall, soil moisture, and groundwater of the Earth’s critical zone in subtropical monsoon climate plain areas. This paper analyzed the connection between rainfall and volume water content (VWC) of soil at different depths of several soil profiles, and the dynamic feature of groundwater was discussed, which reveals the rainfall infiltration recharge of Quaternary Upper Pleistocene strata. The results show that the Quaternary Upper Pleistocene aquifer groundwater accepts a little direct rainfall recharge, while the lateral recharge is the main supplement source. There were 75 effective rainfall events among 120 rainfall events during the monitoring period, with an accumulated amount of 672.9 mm, and the percentages of effective rainfall amount and duration time were 62.50% and 91.56%, respectively. The max evaporation depth at the upper part in Quaternary cohesive soil was no less than 1.4 m. The soil profile was divided into four zones: (1) The sensitive zone of rainfall infiltration within 1.4 m, where the material and energy exchange frequently near the interface between atmosphere and soil; (2) the buffer zone of rainfall infiltration between 1.4 m and 3.5 m; (3) the migration zone of rainfall infiltration between 3.5 m and 5.0 m; and (4) the rainfall infiltration and groundwater level co-influenced zone below 5.0 m. The results revealed the reaction of soil moisture and groundwater to rainfall in the area covered by cohesive soil under humid climate in Earth’s critical zone, which is of great theoretical and practical significance for groundwater resources evaluation and development, groundwater environmental protection, ecological environmental improvement, drought disaster prevention, and flood disaster prevention in subtropical monsoon climate plain areas.
-

-
References
[1] Brewer PE, Calderon F, Vigil M, Von Fischer JC. 2018. Impacts of moisture, soil respiration, and agricultural practices on methanogenesis in upland soils as measured with stable isotope pool dilution. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 127, 239–251. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.09.014 [2] Brinkmann N, Seeger S, Weiler M, Buchmann N, Eugster W, Kahmen A. 2018. Employing stable isotopes to determine the residence times of soil water and the temporal origin of water taken up by Fagus sylvatica and Picea abies in a temperate forest. New Phytologist, 219(4), 1300–1313. doi: 10.1111/nph.15255 [3] Chang W, Huang K, Hu C, Wang Q, Wang NT. 2019. Characteristics of the aquifer structure and groundwater conversion model in the northeastern Yunying Basin. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 46(5), 9–15+23 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.05.02. [4] Che CW, Zhang MJ, Argiriou AA, Wang SJ, Du QQ, Zhao PP, Ma ZZ. 2019. The stable isotopic composition of different water bodies at the soil-plant-atmosphere continuum (SPAC) of the Western Loess Plateau, China. Water, 11(9). doi: 10.3390/w11091742. [5] Chen SN, He JT, Jin AF, Wei YX. 2010. Distribution characteristics of PAHs in soil profiles of different irrigation areas. Environmental Science & Technology, 33(10), 10–14+63 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2010.10. 003. [6] Chen SY, Guo YZ, Zheng YX, Wang JS. 2012. Impart of rainfall on soil moisture in Gansu arid agricultural regions. Journal of Desert Research, 32(1), 155–162 (in Chinese with English abstract). [7] Chen W, Li QH, Yu SW, Liu HQ. 2017. Hydrochemical characteristics and ion sources of groundwater in Fangcheng district, Guangxi. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 32(1), 162–168 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3701.2017.02.007. [8] Cremer CJM, Neuweiler I, Bechtold M, Vanderborght J. 2016. Solute transport in heterogeneous soil with time-dependent boundary conditions. Vadose Zone Journal, 15(6). doi: 10.2136/vzj2015.11.0144. [9] Deng QJ, Tang ZH. 2014. Soil-groundwater geological environment integrated monitoring and evaluation in Jianghan Plain. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 41(4), 131–135+142 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665. 2014.04.028. [10] Gazis C, Feng XH. 2004. A stable isotope study of soil water: Evidence for mixing and preferential flow paths. Geoderma, 119(1–2), 97–111. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7061(03)00243-X [11] Gomez I, Caselles V, Estrela MJ, Sanchez JM, Rubio E, Miro JJ. 2018. Improved meteorology and surface fluxes in mesoscale modelling using adjusted initial vertical soil moisture profiles. Atmospheric Research, 213, 523–536. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2018.06.020 [12] Haverd V, Cuntz M, Leuning R, Keith H. 2007. Air and biomass heat storage fluxes in a forest canopy: Calculation within a soil vegetation atmosphere transfer model. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 147(3–4), 125–139. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2007.07.006 [13] He MN, Tong YP, Wang YQ, Lu YD, Zhao YL. 2017. A case study on the effects of micro-topography and rainfall events on 0–5 m soil moisture at a slope of the Loess Plateau. Journal of Earth Environment, 8(4), 357–366 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7515/JEE201704008. [14] Hu MY, Wang Q, Chen ZH, Hu C. 2018. Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of shallow groundwater in the north area of Yunying Basin. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 25(5), 9–14 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13578/ j.cnki.issn.1671-1556. 2018.05.002. [15] Huang H, Chen ZH, Wang T, Xiang CJ, Zhang L, Zhou GM, Sun BT, Wang Y. 2019. Nitrate distribution and dynamics as indicators to characterize karst groundwater flow in a mined mineral deposit in southwestern China. Hydrogeology Journal, 27, 2077–2089. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-01987-0 [16] Huo SY, Jin MG, Liang X, Li X, Hao HB. 2020. Estimating impacts of water-table depth on groundwater evaporation and recharge using lysimeter measurement data and bromide tracer. Hydrogeology Journal, 28(3), 955–971. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-02098-6 [17] Kafaei R, Arfaeinia H, Savari A, Mahmoodi M, Rezaei M, Rayani M, Ramavandi B. 2020. Organochlorine pesticides contamination in agricultural soils of southern Iran. Chemosphere, 240, 124–983. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124983 [18] Li FD, Song XF, Tang CY, Liu CM, Yu JJ, Zhang WJ. 2007. Tracing infiltration and recharge using stable isotope in Taihang Mt., North China. Environmental Geology, 53(3), 687–696. doi: 10.1007/s00254-007-0683-0 [19] Li JQ, Ma T, Deng YM, Du Y, Wang ZQ, Jiang YH. 2019. Progresses on monitoring network construction of Earth’s Critical Zone in Jianghan Plain. Geological Survey of China, 6(5), 115–123 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2019.05. 13. [20] Lin D, Jin MG, Ma B, Wang BG. 2014. Characteristics of infiltration recharge at thickening vadose zone using soil hydraulic parameters. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geoscience), 39(6), 760–768 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.071. [21] Liu FF, Mao XS, Zhang JX, Wu Q, Li YY, Xu C. 2020. Isothermal diffusion of water vapor in unsaturated soils based on Fick’s second law. Journal of Central South University, 27(7), 2017–2031. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4427-6 [22] Liu LC, Chen HH, Yang Y, Wang JS. 2009. The effects of sedimentary environment and human activity on shallow groundwater quality in Suxichan area. Geology in China, 36(4), 915–919 (in Chinese with English abstract). [23] Liu TW, Pan Y, Hu C, Wang Q, Chen ZH, Shi TT. 2020. Tracing infiltration and recharge of thick silt by using D, 18O isotopes of soil moisture in Xiaogan, Hubei and its ecological effects. Geology in China (in Chinese with English abstract). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200806.1544.008.html. [24] Liu XR, Wang Q, Chen ZH, Hu C. 2019. Study on groundwater conversion relationship in Piedmont Plain based on robust Regression-De-Trend fluctuation analysis. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 26(5), 17–24 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2019.05.003. [25] Ma B, Liang X, Liu SH, Jin MG, Nimmo JR, Li J. 2017. Evaluation of diffuse and preferential flow pathways of infiltrated precipitation and irrigation using oxygen and hydrogen isotopes. Hydrogeology Journal, 25(3), 675–688. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1525-5 [26] Meng SH, Fei YH, Zhang ZJ, Qian Y, Li YS. 2011. Groundwater vulnerability assessment of North China Plain. Geology in China, 38(6), 1607–1613 (in Chinese with English abstract). [27] National Research Council. 2001. Basic Research Opportunities in Earth Sciences. Washington DC, National Academies Press, 35–45. [28] Pang ZH, Huang TM, Yang S, Yuan LJ. 2018. The potential of the unsaturated zone in groundwater recharge in arid and semiarid areas. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(1), 51–61 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2018.01.006. [29] Qian Z, Mao Y, Xiong S, Peng B, Liu W, Liu HF, Qi SH. 2020. Historical residues of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a flood sediment profile from the Longwang Cave in Yichang, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 196, 110–542. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110542 [30] Ren R, Ma JJ, Cheng QY, Zheng LJ, Guo XH, Sun XH. 2017. Modeling coupled water and heat transport in the root zone of winter wheat under non-isothermal conditions. Water, 9(4). doi: 10.3390/w9040290. [31] Shao W, Coenders-Gerrits M, Judge J, Zeng YJ, Su Y. 2018. The impact of non-isothermal soil moisture transport on evaporation fluxes in a maize cropland. Journal of Hydrology, 561, 833–847. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.04.033 [32] Song XF, Wang SQ, Xiao GQ, Wang ZM, Liu X, Wang P. 2009. A study of soil water movement combining soil water potential with stable isotopes at two sites of shallow groundwater areas in the North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 23(9), 1376–1388. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7267 [33] Sprenger M, Tetzlaff D, Soulsby C. 2017. Soil water stable isotopes reveal evaporation dynamics at the soil-plant-atmosphere interface of the critical zone. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 21(7), 3839–3858. doi: 10.5194/hess-21-3839-2017 [34] Sun FQ, Yin LH, Wang XY, Ma HY, Zhang J, Dong JQ, He SJ. 2017. Determination of vertical infiltration recharge of groundwater in the thick unsaturated zone of Sangong River Basin, Xinjiang. Geology in China, 44(5), 913–923 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.12029/gc20170506. [35] Sun J. 1992. Leakage and sticky soil storage related to the evaluation of deep level pore water resource. Geology of Anhui, 2(3), 46–50 (in Chinese with English abstract). [36] Wan HL, Bian JM, Zhang H, Li YH. 2021. Assessment of future climate change impacts on water-heat-salt migration in unsaturated frozen soil using Coup Model. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 15(10), . doi: 10.1007/s11783-020-1302-5 [37] Wang XJ, Piao XY, Chen J, Hu JD, Xu FL, Tao S. 2006. Organochlorine pesticides in soil profiles from Tianjin, China. Chemosphere, 64(9), 1514–1520. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.052 [38] Xiao DA, Wang SJ. 2009. Comments on the progress and direction in soil moisture research. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 18(3), 1182–1188 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2009.03.054. [39] Xu YD, Wang JK, Gao XD, Zhang YL. 2018. Application of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope techniques on soil moisture research: A Review. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 32(3), 1–9+15 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb. 2018.03.001. [40] Yang J, Xiao TY, Li HB, Wang QR. 2018. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of the NO3-N concentration in groundwater in Jianghan Plain. China Environmental Science, 38(2), 710–718 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19674/j. cnki.issn1000-6923.2018.0084. [41] Yang JF. 1999. A review on water exchange through interface between groundwater, soil moisture or atmospheric water. Advances in Water Science, 10(2), 84–90 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.1999.02.016. [42] Yuan RQ, Song XF, Han DM, Zhang YH, Zhang L, Zhang B, Yu YL. 2012. Rate and historical change of direct recharge from precipitation constrained by unsaturated zone profiles of chloride and oxygen-18 in dry river bed of North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 26(9), 1291–1301. doi: 10.1002/hyp.8207 [43] Zhang CX, Liao XP, Li JL, Xu L, Liu M, Du B, Wang YX. 2013. Influence of long-term sewage irrigation on the distribution of organochlorine pesticides in soil-groundwater systems. Chemosphere, 92(4), 337–343. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.020 [44] Zhang GL, Zhu YG, Shao MG. 2019. Understanding sustainability of soil and water resources in a critical zone perspective. Science China Earth Sciences, 62, 1716–1718. doi: 10.1007/s11430-019-9368-7 [45] Zhang JX, Wang X, Wang YK, Jing SS, Dong JG, Wang ZT. 2017. Regularities of rainfall infiltration and water migration in woodland drying soil in the Loess Hilly Region. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(3), 231–238 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2017.03.039. [46] Zhao DJ, Liu ZP, Xiong QH. 2007. The vulnerability evaluation for groundwater pollution in Jianghan Plain. Resources Environment & Engineering, (S1), 64–67 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16536/j.cnki.issn.1671-1211.2007.s1.029. [47] Zhao J, Chen ZH, Wang T, Xiang CJ, Luo MM, Yuan HX. 2019. Control of contaminant transport caused by open-air heavy metal slag in Zhehai, Southwest China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(3). doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030443. [48] Zhao Y, Ling DS, Wang YL, Huang B, Wang HL. 2016. Study on a calibration equation for soil water content in field tests using time domain reflectometry. Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE A (Applied Physics & Engineering), 17(3), 240–252. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1500065 [49] Zhu HY, Jia ZF, Li PC, Liu XH. 2014. Transport mode of soil moisture in arid areas considering air effect. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 45(12), 126–138 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2014.12.020. -
Access History

-
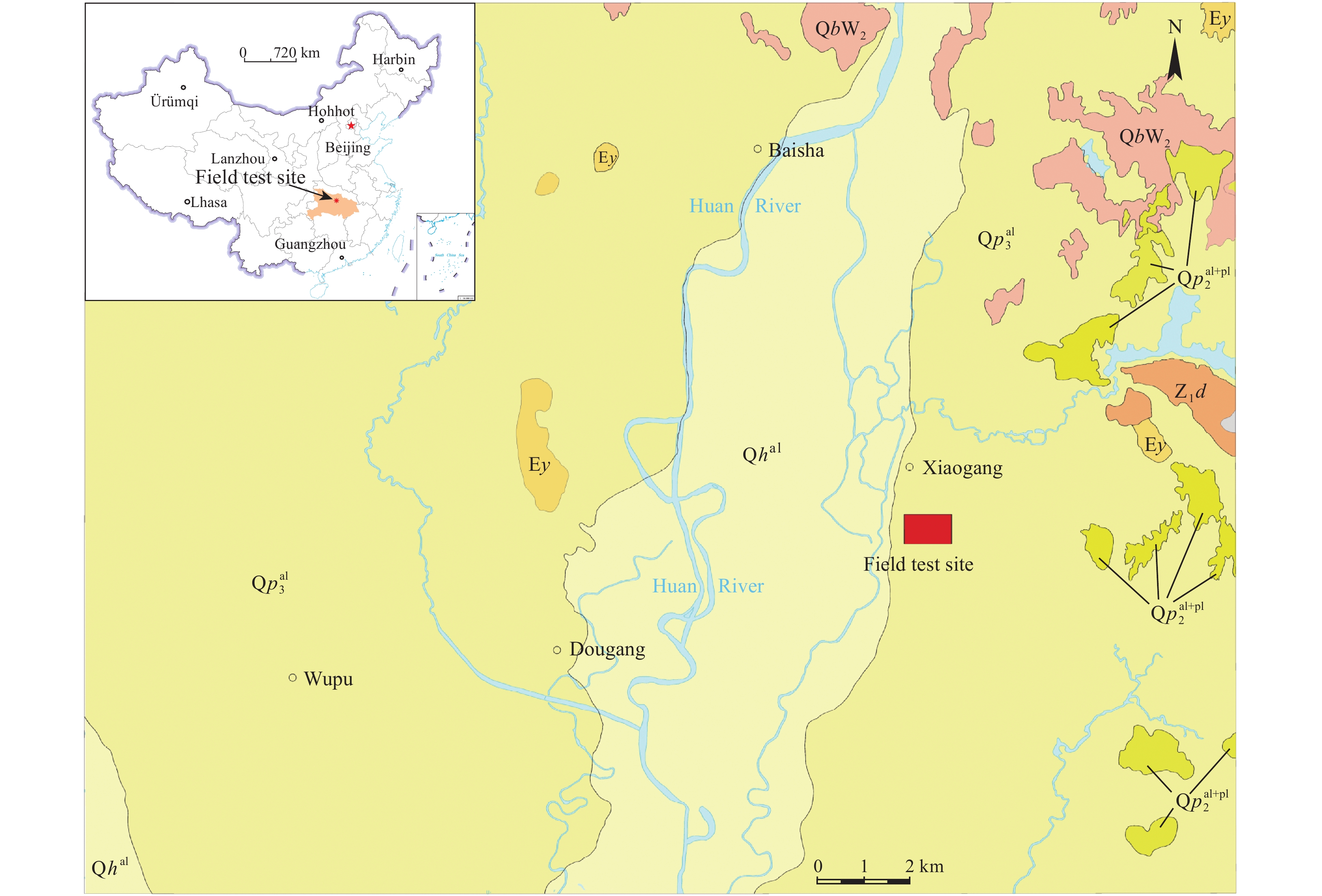
Figure 1.
Regional geological sketch map and the location of the field test site. The symbols in the figure are shown in Table 1.
-
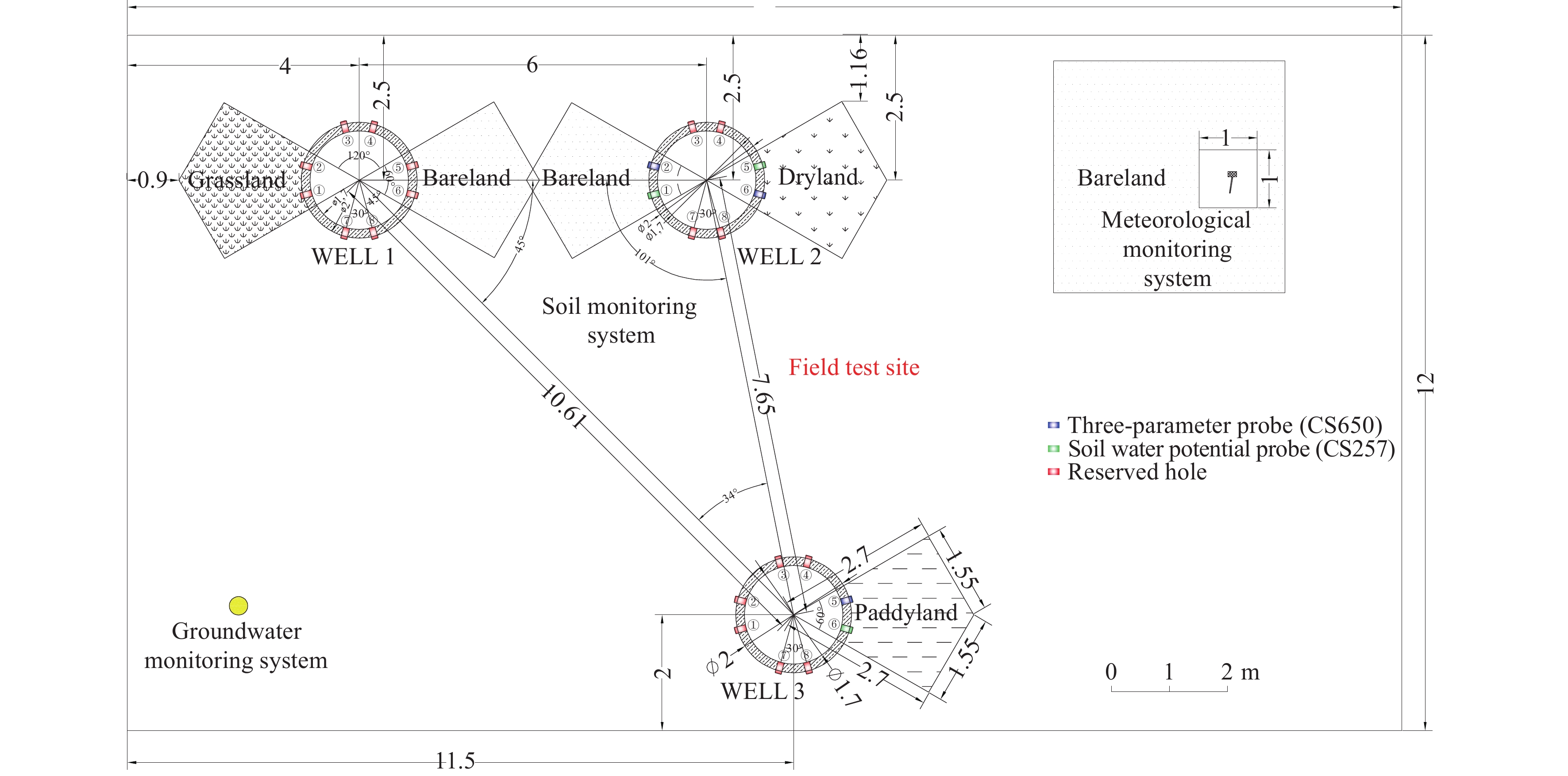
Figure 2.
The schematic plan of the field test site.
-
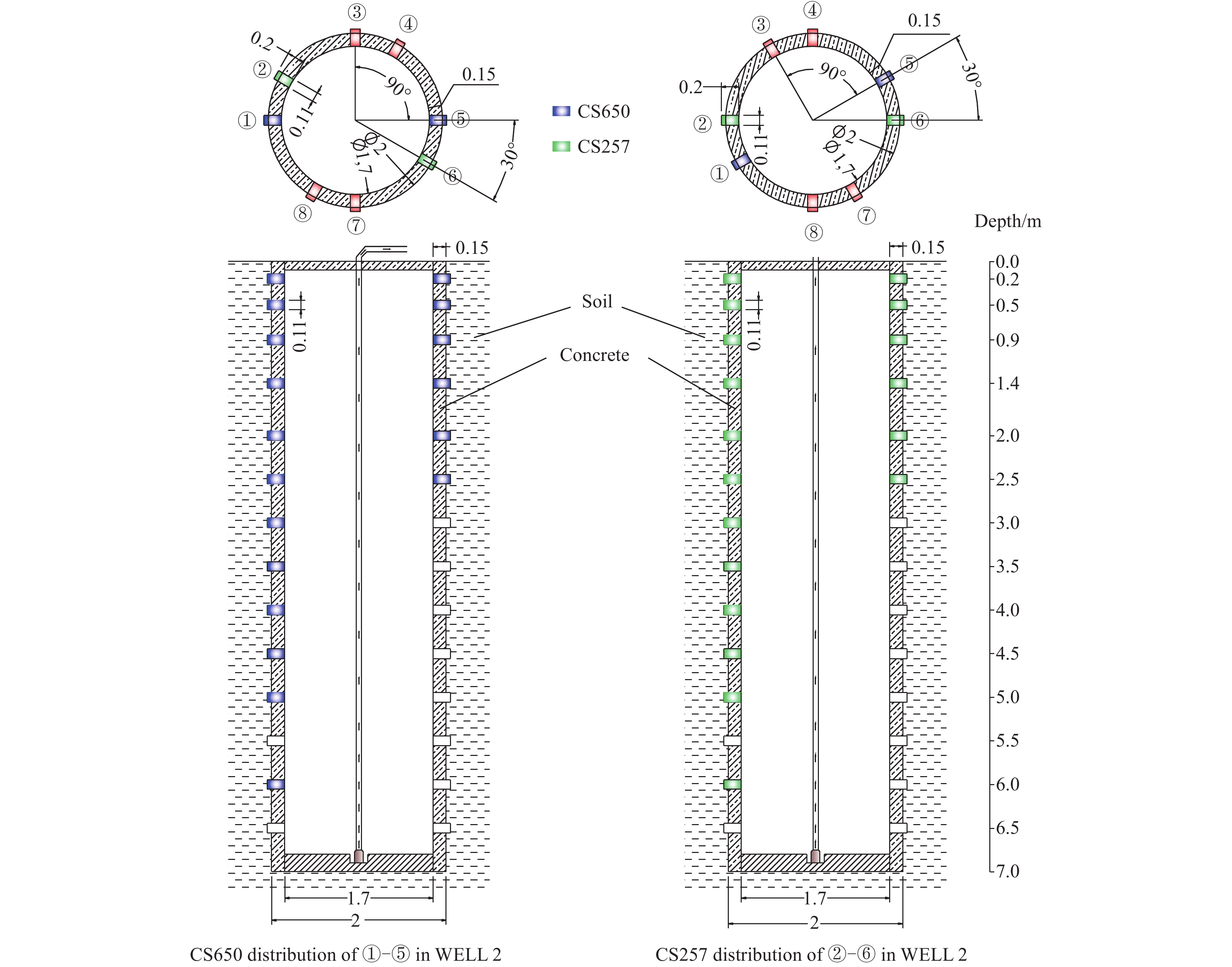
Figure 3.
Equipment layout plan of monitoring profile in WELL 2.
-
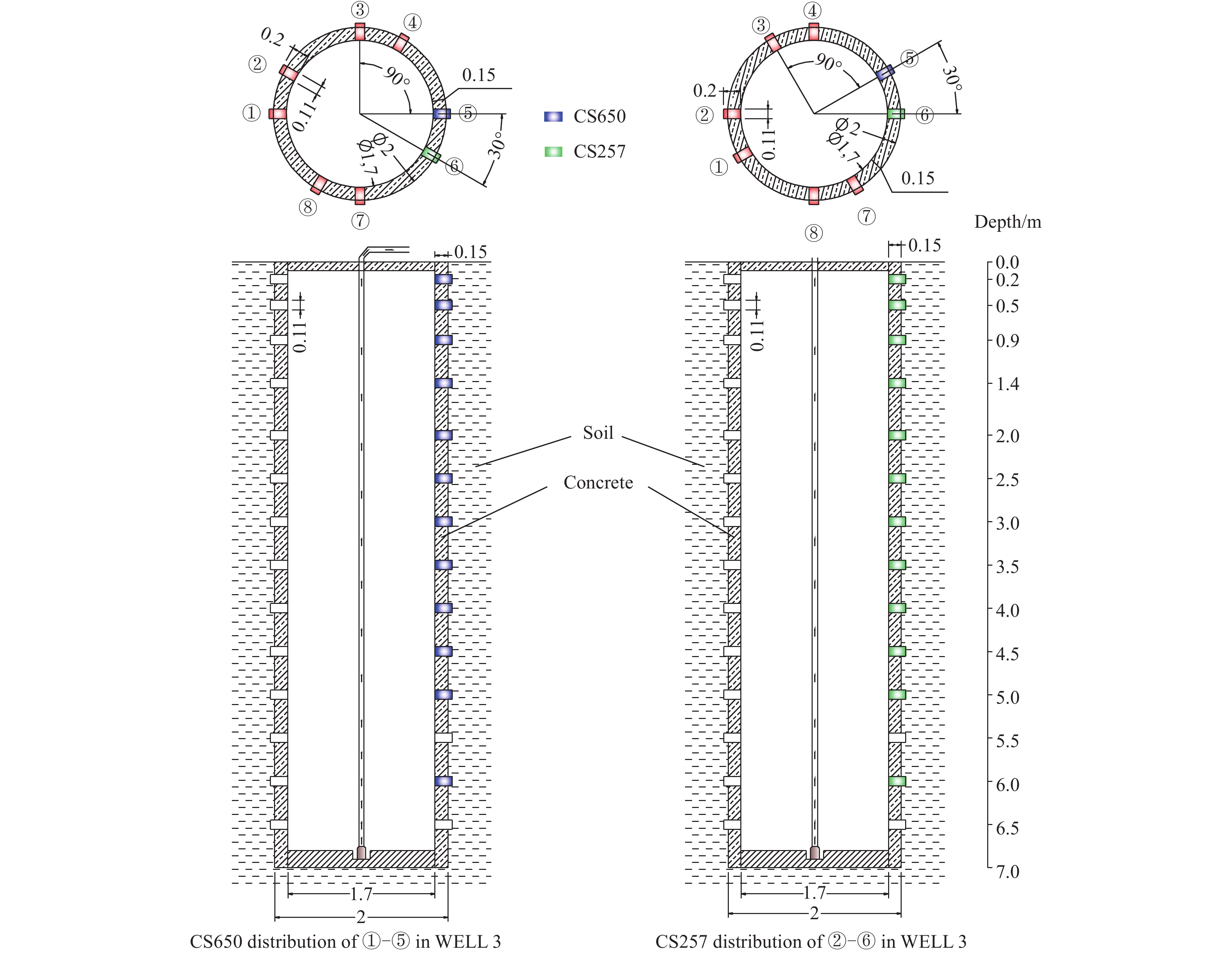
Figure 4.
Equipment layout plan of monitoring profile in WELL 3.
-
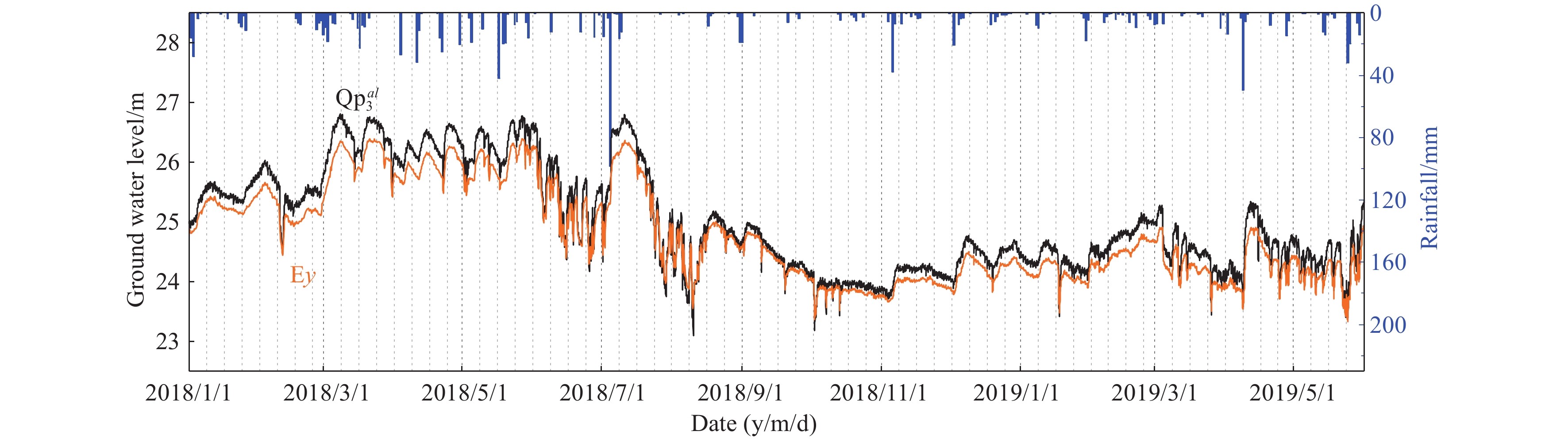
Figure 5.
Dynamic diagram of rainfall and groundwater levels.
-
Figure 6.
Dynamic diagram of rainfall and soil VWC in the profile 3E.
-
Figure 7.
Dynamic diagram of rainfall and soil water potential in the profile 3E.
-
Figure 8.
Dynamic diagram of soil VWC (5.0m, 6.0m) and groundwater.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: