| Citation: | Song Shu-hong, Nie Zhen-long, Geng Xin-xin, Shen Xue, Wang Zhe, Zhu Pu-cheng. 2023. Response of runoff to climate change in the area of runoff yield in upstream Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China: A case study of the Xiying River. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 11(1): 89-96. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2023.9280009 |
Response of runoff to climate change in the area of runoff yield in upstream Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China: A case study of the Xiying River
-
Abstract
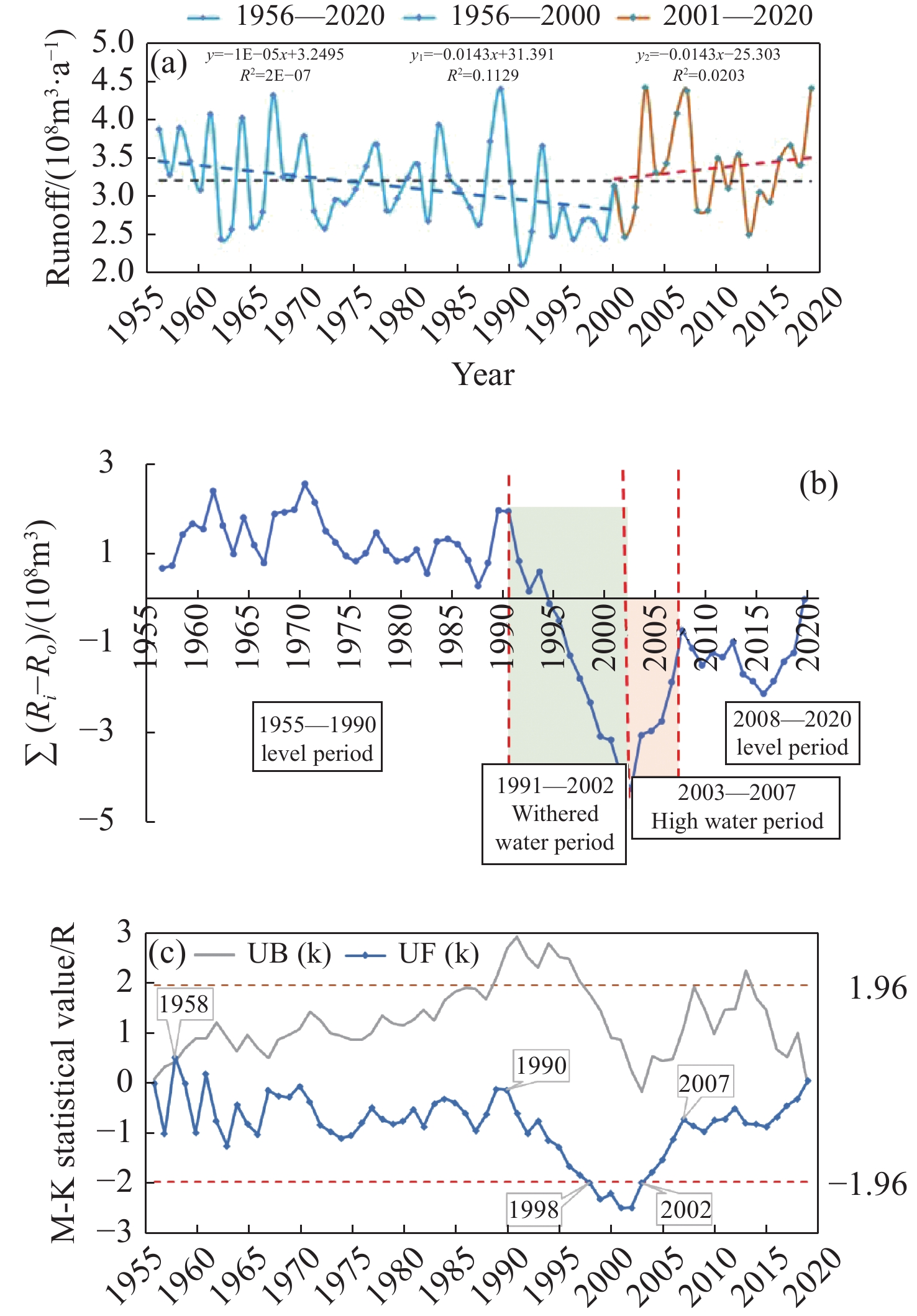
The objective of this study was to analyze the response of runoff in the area of runoff yield of the upstream Shiyang River basin to climate change and to promote sustainable development of regional water resources and ecological environment. As the biggest tributary of the Shiyang River, Xiying River is the only hydrological station (Jiutiaoling) that has provincial natural river and can achieve long time series monitoring data in the basin. The data obtained from this station is representative of natural conditions because it has little human activites. This study built a regression model through identifying the characteristics of runoff and climate change by using Mann-Kendall nonparametric statistical test, cumulative anomaly, and correlation analysis. The results show that the average annual runoff is 320.6 million m3/a with the coefficient of variation of 0.18 and shows slightly decrease during 1956–2020. It has a significant positive correlation the average annual precipitation (P<0.01). Runoff is sensitive to climate change, and the climate has becoming warm and wet and annual runoff has entering wet period from 2003. Compared to the earlier period (1955–2000), the increases of average annual temperature, precipitation and runoff in recent two decades were 15%, 9.3%, and 7.8%, respectively. Runoff in the Shiyang River is affected by temperature and precipitation among climate factors, and the simulation results of the runoff-climate response model (R = 0.0052P − 0.1589T + 2.373) indicate that higher temperature leads to a weakening of the ecological regulation of surface runoff in the flow-producing area.
-
Keywords:
- Runoff /
- Heating and wetting /
- Mann-Kendall test /
- Regression model /
- Ecological function
-

-
References
Blue Book on Climate Change in China 2020. China Meteorological News Press, 2020. (in Chinese) Bongaarts J. 2019. Intergovernmental panel on climate change special report on global warming of 1.5℃ Switzerland: IPCC 2018. Population & Development Review, 45(1): 251−252. Ding ZY, Ma JZ, Zhang BJ, et al. 2007. Analysis on the climate change in the Shiyang River Basin since regent 50 years. Arid Zone Research, 24(6): 779−784. (in Chinese) DOI:10.13866/j.azr.2007.06.009. Gao YP, Yao XJ, Liu SY, et al. 2019. Spatial-temporal variation of glacier resources in the Hexi interior from 1956 to 2017. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 41(6): 1313−1325. (in Chinese) DOI:10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2019.0054. Guo J, Wang N, Su XL. 2016. Response of runoff to climate change in upstream generation area of Shiyang River basin. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Nat. Sci. Ed. ), 44: 315(12): 211−218. DOI:10.13207/j.cnki.jnwafu.2016.12.029. IPCC. 2021. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In: Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Pirani A, et al. Jiang ZH, He JH, Li JP, et al. 2006. Northerly advancement characteristics of the East Asian summer monsoon with its interdecadal variations. Acta Geographica Sinica, 61(7): 675-686. (in Chinese) Doi: CNKI:SUN:DLXB.0.2006-07-001 Ji F, Wu ZH, Huang JP, et al. 2014. Evolution of land surface air temperature trend. Nature Climate Change, 4(6): 462−466. DOI:10.1038/nclimate2223. Lan YC, Hu XL, Ding HW, et al. 2014. Multiple time scales analysis of jump and variation of air temperature in mountain area of Hexi inland River Basin in the past more than 50 years. Mountain Research, 32(2): 163−170. (in Chinese) DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2014.02.005. Kahya E&S. Kalayci. 2004. Trend analysis of streamflow in Turkey. Journal of Hydrology, 289: 128−144. DOI:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.11.006. Kendall MG. 1990. Rank correlation methods. British Journal of Psychology, 25(1): 86−91. Lan YC, Kang ES, 2000. Changing trend and features of the runoff frommountain areas of some main rivers in the Hexi inland region, Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 22(2): 147-152. Li ZX, Li YG, Feng Q, et al. 2017. Contribution from cryosphere meltwater to runoff and its influence in Shiyang River Basin. Quaternary Sciences, 37(5): 1045−1054. (in Chinese) DOI:10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2017.05.12. Liu CZ. 2010. Some points of view on detection and attribution of observed changes in hydrological cycle under global warming. Climate Change Research, 6(05): 313−318. (in Chinese) Liu M, Nie ZL, Cao L, et al. 2021. Comprehensive evaluation on the ecological function of groundwater in the Shiyang River watershed. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(4): 326−340. DOI:10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.04.006. Ma HW, Wang NA. 2010. The response of runoff of Shiyang River Basin in mountain foot to climate change. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 24(01): 113−117. (in Chinese) DOI:10.13448/j.cnki.jalre.2010.01.003. Matin MA, Bourque CPA. 2015. Mountain-river runoff components and their role in the seasonal development of desert-oases in Northwest China. Journal of Arid Environment, 122(2015): 15−27. DOI:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2015.05.011. Pan BT, Cao B, Guan WJ. 2021. Changes of Ningchan No. 1 Glacier in Lenglongling, eastern Qilian Mountains from 2010 to 2020 based on observation. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 43(3): 864−873. (in Chinese) DOI:10.1017/jog.2017.70. Ren GY. 2007. Climate change and water resource in China. Beijing: Meteorology Press. (in Chinese) Savabi MR, Stockle CO. 2001. Modeling the possible impact of increased CO2 and temperature on soil water balance, crop yield and soil erosion. Environmental Modeling & Software, 16(7): 631−640. DOI:10.1016/S1364-8152(01)00038-X. Shen DJ, Liu CM. 1998. Hydrological and water resources responses to climatic change a review. Geographica Research, 17(04): 435−443. (in Chinese) Shi YF, Shen YP, Kang E, et al. 2007. Recent and future climate change in northwest China. Climate Change, 80(3/4): 379−393. (in Chinese) Song SH, Xie Y, Nie ZL, et al. 2022. A solid reservoir that gradually dries up—The melting of glaciers in the Shiyang River Basin. Scientific and Cultural Popularization of Natural Resources, 0(2): 32−35. (in Chinese) Song C, Liu M, Dong QY, et al. 2022. Variation characteristics of CO2 in a newly-excavated soil profile, Chinese Loess Plateau: Excavation-induced ancient soil organic carbon decomposition. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 10(1): 19−32. DOI:10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2022.01.003. Sun MP, Liu SY, Yao XJ, et al. 2018. Glacier changes in the Qilian Mountains in the past half-century: Based on the revised First and Second Chinese Glacier Inventory. Journal of Geographical Science, 28(02): 206−220. DOI:10.1007/s11442-018-1468-y. Wei FY. 2007. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Technology. Beijing: Meteorological Press. China. (in Chinese) Xu QY, Guo H, Yin XZ, et al. 2007. Climate evolution in the Shiyang River Basin of China since 10 ka BP. Journal of glaciology and geocryology, 29(4): 617−625. (in Chinese) Zhang SQ, Gao X, Zhang XW. 2015. Glacial runoff likely reached peak in the Mountainous areas of the Shiyang River basin. Journal of Mountain Science, 12(2): 382−395. DOI:10.1007/s11629-014-3077-2. Zhang F, Chen QM, SU JJ, et al. 2017. Tree-ring recorded of the drought variability in the northwest monsoon marginal, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 39(2): 245−251. (in Chinese) DOI:10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2017.0028. Zhang XF, Shu Q, Li C. 2012. Rules of runoff variation of Yark and River in recent 48 years. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 26(1): 93−97. (in Chinese) DOI:10.1007/s11783-011-0280-z. Zhou JJ, Huang JM, Xi Z, et al. 2020. Changes of extreme temperature and its influencing factors in Shiyang River Basin, Northwest China. Atmosphere, 11(11): 1171. Zhou JJ, Shi W, Shi PJ, et al. 2012. Characteristics of mountainous runoff and its responses to climate change in the upper reaches of Shiyang river basin during 1956-2009. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 48(1): 27−34. (in Chinese) DOI:10.1109/ICMSS.2011.5998949. Zuo HC, Lyu SH, Hu YJ. 2004. Variations trend of yearly mean air temperature and precipitation in China in the last 50 years. Plateau Meteorology, 23(2): 238−224. (in Chinese) -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Schematic map of the study area
-
Figure 2.
(a) Runoff variation in the Xiying River runoff yield area; (b) Cumulative anomaly; (c) M-k characteristics curve (1956–2020)
-
Figure 3.
The types of land uses in the Xiying River runoff yield area (1975–2018)
-
Figure 4.
Xiying River runoff yield area: (a) Temperature change process; (b) cumulative anomaly; (c) M-k characteristics (1956–2020) curve
-
Figure 5.
Xiying River runoff yield area: (a) Precipitation change process; (b) Cumulative anomaly; (c) M-k characteristics (1956–2020) curve





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: