| Citation: | Li Hui, Han Zhan-tao, Deng Qiang, Ma Chun-xiao, Kong Xiang-ke. 2023. Assessing the effectiveness of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles produced by green tea for Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater remediation. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 11(1): 55-67. doi: 10.26599/JGSE.2023.9280006 |
Assessing the effectiveness of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles produced by green tea for Cr(VI)-contaminated groundwater remediation
-
Abstract
Nanoscale zero-valent iron particles (NZVI) produced by using green tea (GT) extract as a reductant can remove Cr(VI) from water effectively, which can be utilized in groundwater remediation. In order to define the reaction mechanism and removal effect in the aquifer, in this study, GT-NZVI particles were prepared and measured by some characterization methods to define their surface performance, and then batch and one-dimensional experiments were carried out to reveal the reaction properties of GT-NZVI and Cr(VI) in groundwater. The results showed that the prepared GT-NZVI particles were regular spherical with a diameter of 10–20 nm, which could disperse in water stably. The main component of GT-NZVI was α-Fe with superficial polyphenols as a stabilizer. GT-NZVI suspension had good ability to reduce the Cr(VI) to Cr(III) in water. When the concentration of GT-NZVI was 1 g/L, the removal efficiency of Cr(VI) with an initial concentration of 100 mg/L reached 92.8% in 1 h reaction. In column tests, GT-NZVI passed through the natural sand column successfully with an average outflow percentage of 71.2%. The simulated in-situ reaction zone (IRZ) with GT-NZVI was used to remediate Cr(VI) contaminated groundwater. The outflow concentration of Cr(VI) kept in 0.14–0.32 mg/L corresponding to the outflow rate below 0.32% within 15 days, and the removal efficiency of Cr(VI) by IRZ with GT-NZVI decreased with the increase of aquifer medium particle size, groundwater flow rate and ionic strength. Most of Cr(III) as reduzate was adsorbed or immobilized on the surface or in the lattice of GT-NZVI, which indicated effective immobilization for chromium.
-
Keywords:
- Nanoscale iron particles /
- Green tea /
- Hexavalent chromium /
- Groundwater remediation
-

-
References
Badmus KO, Coetsee-Hugo E, Swart H, et al. 2018. Synthesis and characterisation of stable and efficient nano zero valent iron. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25: 23667−23684. DOI:10.1007/s11356-018-2119-7. Bhattacharya M, Shriwastav A, Bhole S, et al. 2020. Processes governing chromium contamination of groundwater and soil from a chromium waste source. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 4(1): 35−49. DOI:10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00223. Ceballos E, Dubny S, Othax N, et al. 2021. Assessment of human health risk of chromium and nitrate pollution in groundwater and soil of the Matanza-Riachuelo River Basin, Argentina. Exposure and Health, 13: 323−336. DOI:10.1007/s12403-021-00386-9. Cheng X, Wang S, Xu N, et al. 2022. Enhanced transport and chromium remediation of nano-zero valent iron modified by tea polyphenol extracts and carboxymethyl cellulose in water–soil media. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 22: 196−207. DOI:10.1007/s11368-021-03072-0. Chrysochoou M, Ferreira D, Johnston CP. 2010. Calcium polysulfide treatment of Cr contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1-3): 650−657. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.052. Deng Q, Li H, Han ZT, et al. 2019. Study on the removal efficiency of nano-sized iron produced by green tea reduction on Cr(VI) in simulated groundwater. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science and Technology, 17(1): 130−137. (in Chinese) Deng Y, Zhang Q, Zhang Q, et al. 2020. Arsenate removal from underground water by polystyrene-confined hydrated ferric oxide (HFO) nanoparticles: Effect of humic acid. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 27: 6861−6871. DOI:10.1007/s11356-019-07282-5. Duan W, Chen G, Chen C, et al. 2017. Electrochemical removal of hexavalent chromium using electrically conducting carbon nanotube/polymer composite ultrafltration membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 531: 160−171. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.02.050. Fazlzadeh M, Rahmani K, Zarei A, et al. 2016. A novel green synthesis of zero valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) using three plant extracts and their efficient application for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Advanced Powder Technology, 28(1): 122−130. DOI:10.1016/j.apt.2016.09.003. Fei YH, Liu YC, Li YS, et al. 2022. Prospect of groundwater pollution remediation methods and technologies in China. Geology in China, 49(2): 420−434. (in Chinese) Gao YQ. 2018. Preparation of green nano-zero-valent iron material and its application in the restoration of Cr(VI) in groundwater. MS Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology. (in Chinese) Han PL. 2022. Experimental study on in situ reactive zone remediation of Cr(VI) contaminated groundwater by sulfidated micron zero valent iron stabilized with xanthan gum. MS. thesis. Changchun: Jilin University. (in Chinese) Han ZT, Ma CX, Lv XL, et al. 2015. A method and application for preparing nanoscale zerovalent iron suspension by using green tea. CN201510262113.3. (in Chinese) Hoag G E. 2009. Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 19(45): 8671−8677. DOI:10.1039/B909148C. Hong M,Han X, Wang Q, et al. 2018. Removal effect and influencing factors of Cr(Ⅵ) in simulated groundwater by sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(6): 1821−1830. DOI:10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20180029. Huang QX, Zhang QL, Li N, et al. 2013. Preparation, characterization and adsorption of modified waste tea by FeOOH. Laboratory Science, 16(1): 45−49. (in Chinese) Jhim TS, Galo MV, Ana RJ. 2020. Migration of total chromium and chloride anion in the Rocha River used for estimating degradation of agricultural soil quality at the Thiu Rancho zone. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 8(3): 223−229. DOI:10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2020.03.003. Ju YW, Huang C, Sun C, et al. 2018. Nanogeology in China: A review. China Geology, 1: 286−303. DOI:10.31035/cg2018020. Kim EJ, Kim JH, Chang YS, et al. 2014. Effects of metal ions on the reactivity and corrosion electrochemistry of Fe/FeS nanoparticles. Environmental Science and Technology, 48(7): 4002−4011. DOI:10.1021/es405622d. Kim K, Choi W. 2011. Enhanced redox conversion of chromate and arsenite in ice. Environmental Science Technology, 45(6): 2202−2208. DOI:10.1021/es103513u. Li H, Han ZT, Ma CX, et al. 2015: Comparison of 1, 2, 3-Trichloropropane reduction and oxidation by nanoscale zero-valent iron, zinc and activated persulfate. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 3(2): 156-163. Li H, Zhao YS, Han ZT, et al. 2015. Transport of sourose-modified nanaoscale zero-valent iron in saturated porous media: Role of media size, injection rate and input concentration. Water Science and Technology, 72(9): 1463−1470. DOI:10.2166/wst.2015.308. Li YC, Jin ZH, Li TL. 2011. Silica fume supported FeO nanoparticles for removal of hexavalent chromium and enhanced transport in water and soil. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 39(7): 1211−1217. (in Chinese) Li ZH, Xu SY, Xiao GH, et al. 2019. Removal of hexavalent chromium from groundwater using sodium alginate dispersed nano zero-valent iron. Journal of Environmental Management, 244: 33−39. DOI:10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.130. Liang W, Zhou NQ, Dai CM, et al. 2021. Study of diclofenac removal by the application of combined zero-valent iron and calcium peroxide nanoparticles in groundwater. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(3): 171−180. DOI:10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.03.001. Liao Y, Min X, Yang Z, et al. 2014. Assessment of the stability of chromium in remedied soils by pannonibacter phragmitetus BB and its risk to groundwater. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 14: 1098−1106. DOI:10.1007/s11368-014-0860-1. Liu Y. 2018. Green synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles by eucalyptus leaf and used to remove Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. MS. thesis. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University. (in Chinese) Liu Y, Lowry GV. 2006. Effect of particle age (FeO content) and solution pH on NZVI reactivity: H2 evolution and TCE dechlorination. Environmental Science and Technology, 40(19): 6085−6090. DOI:10.1021/es060685o. Miretzky P, Cirelli AF. 2010. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180(1-3): 1−19. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.04.060. Mystrioti C, Xanthopoulou TD, Papassiopi N, et al. 2015. Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Science of the Total Environment, 539(405): 105−113. DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.091. Njagi EC, Huang H, Stafford L, et al. 2010. Biosynthesis of iron and silver nanoparticles at room temperature using aqueous sorghum bran extracts. Langmuir, 27(1): 264−271. DOI:10.1021/la103190n. Orozco AF, Velimirovic M, Tosco T, et al. 2015. Monitoring the injection of microscale zerovalent iron particles for groundwater remediation by means of complex electrical conductivity imaging. Environmental Science and Technology, 49(9): 5593−5600. DOI:10.1021/acs.est.5b00208. Papassiopi N, Vaxevanidou K, Christou C, et al. 2014. Synthesis, characterization and stability of Cr(III) and Fe(III) hydroxides. Journal of Hazardous Material, 264: 490−497. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.058. Sanchez I, Stuber F, Font J, et al. 2007. Elimination of phenol and aromatic compounds by zero valent iron and EDTA at low temperature and atmospheric pressure. Chemosphere, 68(2): 338−344. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.059. Shahwan T, Abu Sirriah S, Nairat M, et al. 2011. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172(1): 258−266. DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.103. Sofija SP, Dejan MK, Snezana PM, et al. 2016. Removal of As(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using “green” zero-valent iron nanoparticles produced by oak, mulberry and cherry leaf extracts. Ecological Engineering, 90: 42−49. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.01.083. Truskewycz A, Shukla R, Ball AS. 2016. Iron nanoparticles synthesized using green tea extracts for the fenton-like degradation of concentrated dye mixtures at elevated temperatures. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 4(4): 4409−4417. DOI:10.1016/j.jece.2016.10.008. Wang B, Zhu C, Ai D, et al. 2021. Activation of persulfate by green nano-zero-valent iron-loaded biochar for the removal of p-nitrophenol: Performance, mechanism and variables effects. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 417: 126106−126114. DOI:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126106. Wang JY. 2020. Study on the migration mechanism of GT-n ZVI in groundwater aquifer and its remediation efficiency of Cr(Ⅵ) pollution. MS. thesis. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology. Wang RX, Li MZ, Liu T, et al. 2022. Encapsulating carbon-coated nano zero-valent iron particles wit h biomass-derived carbon aerogel for efficient uranium extraction from uranium-containing wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 364: 132654−132662. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132654. Wang T, Lin JJ, Chen ZL, et al. 2014. Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. Journal of Cleaner Production, 83: 413−419. DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.07.006. Wang XY, Wang AQ, Ma J, et al. 2017. Facile green synthesis of functional nanoscale zero-valent iron and studied of its activity toward ultrasound-enhanced decolorization of cationic dyes. Chemosphere, 166: 80−88. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.056. Zhang XL, Zhang SY, Feng JW. 2012. Preparation of nano-iron for removing Cr(VI) from wastewaters. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 6(9): 3167−3168. (in Chinese) Zhao LZ. 2020. Study on the remediation of hexavalent chromium contaminated groumdwater witu in-situ reaction zone of carboxymethyl cellulose modified sulfidated nano zerovalent iron. Ph. D. thesis. Changchun: Jilin University. (in Chinese) Zhao Z, An H, Lin J, et al. 2019. Progress on the photocatalytic reduction removal of chromium contamination. The Chemical Record, 19: 873−882. DOI:10.1002/TCR.201800153. -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the column experimental setup
-
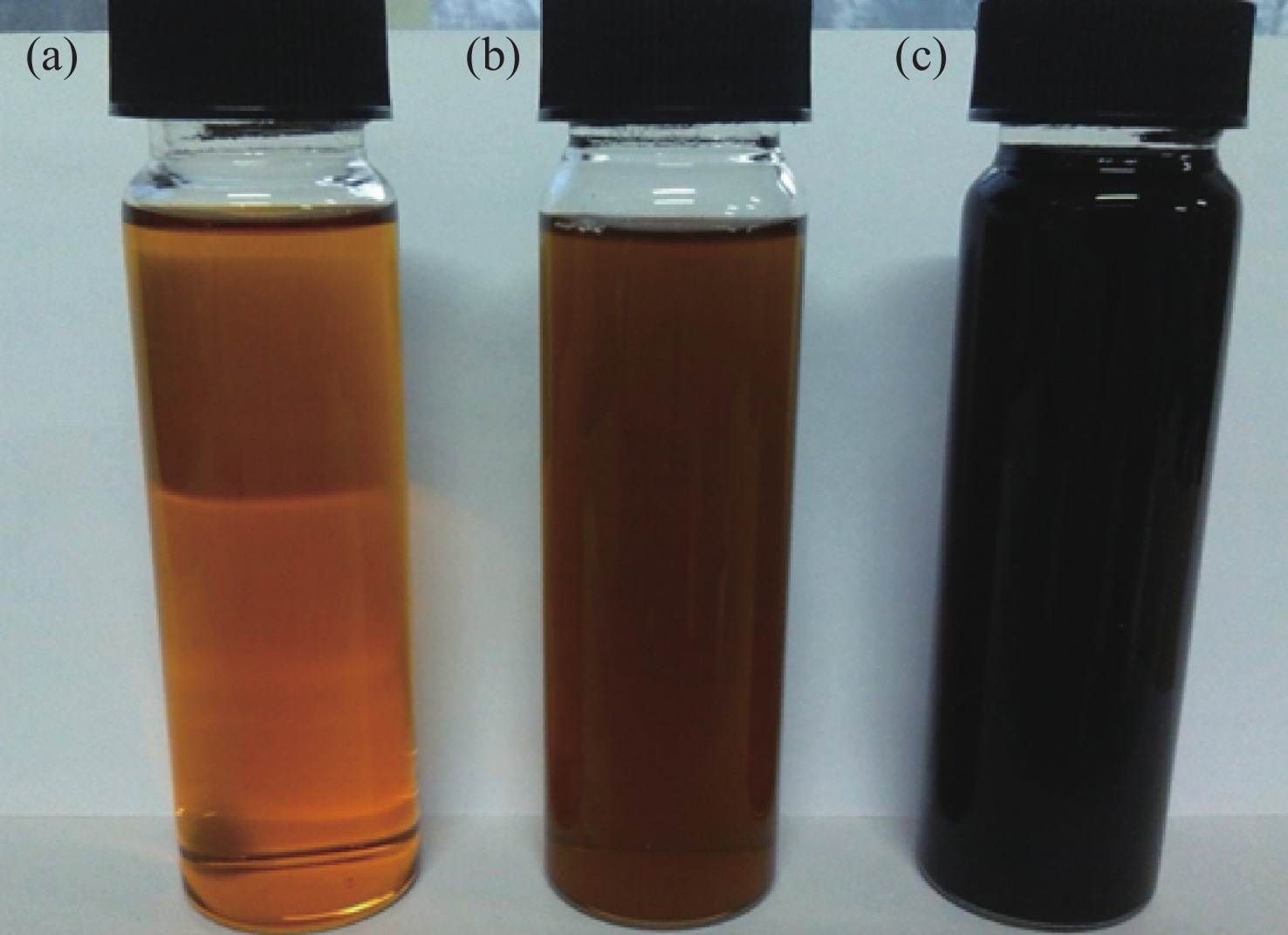
Figure 2.
The characteristic colours of FeCl3 solution, GT extracts and GT-NZVI suspension: (a) Initial FeCl3 solution (b) Green Tea (c) GT-NZVI suspension
-
Figure 3.
TEM image of GT-NZVI
-
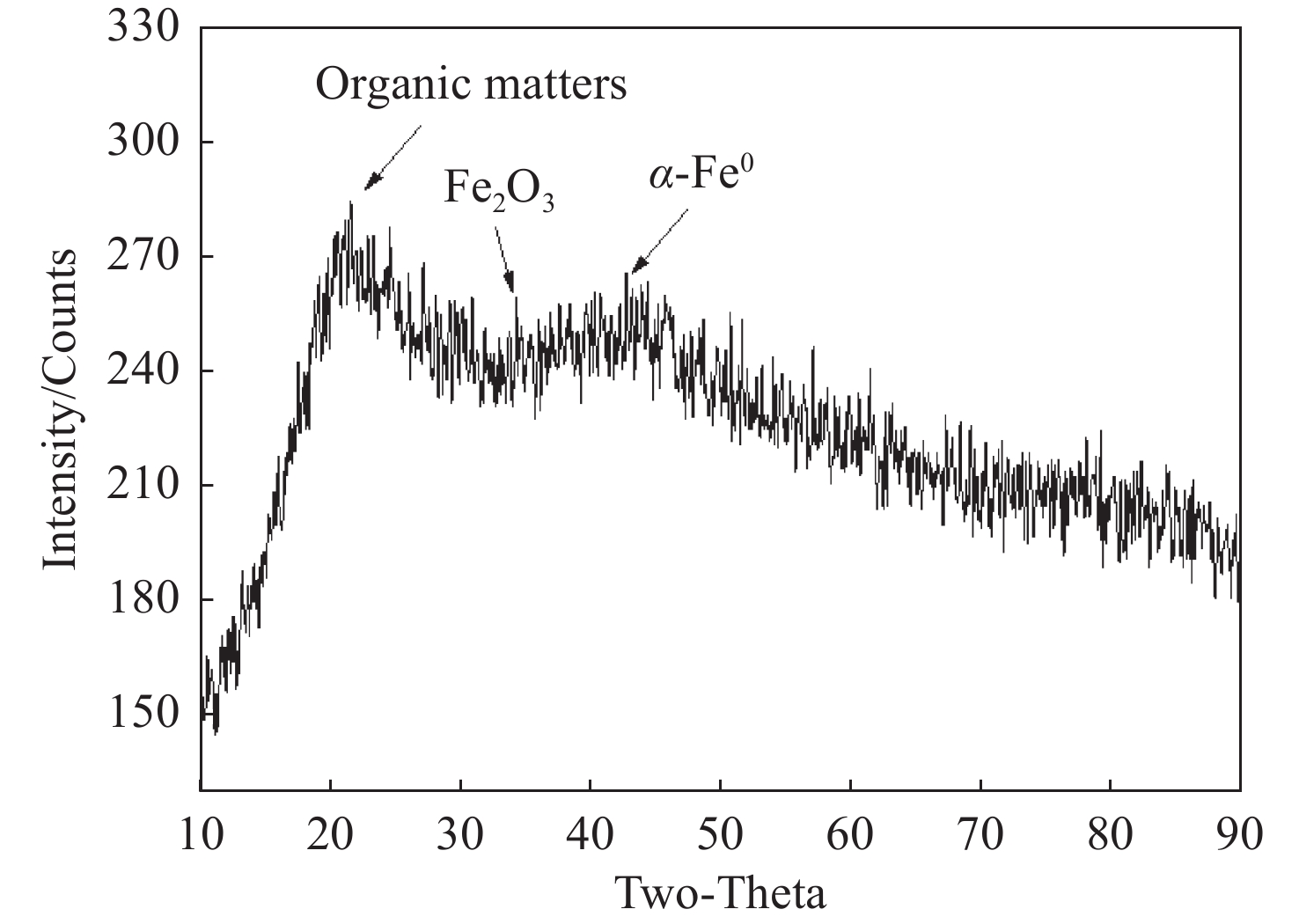
Figure 4.
XRD pattern of GT-NZVI
-
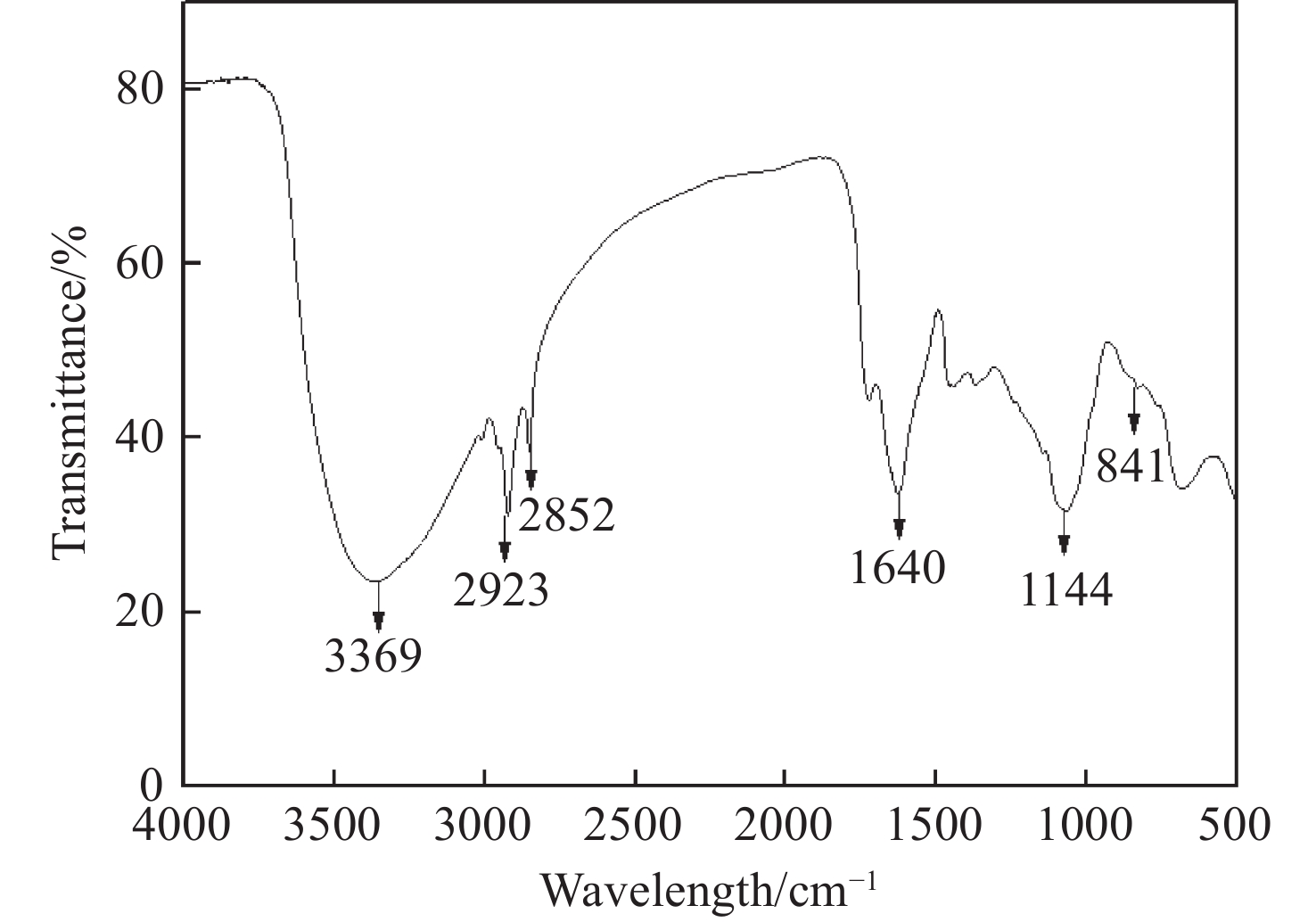
Figure 5.
FTIR spectrum of GT-NZVI
-
Figure 6.
Effects of polyphenols and GT-NZVI on the removal of Cr (VI)
-
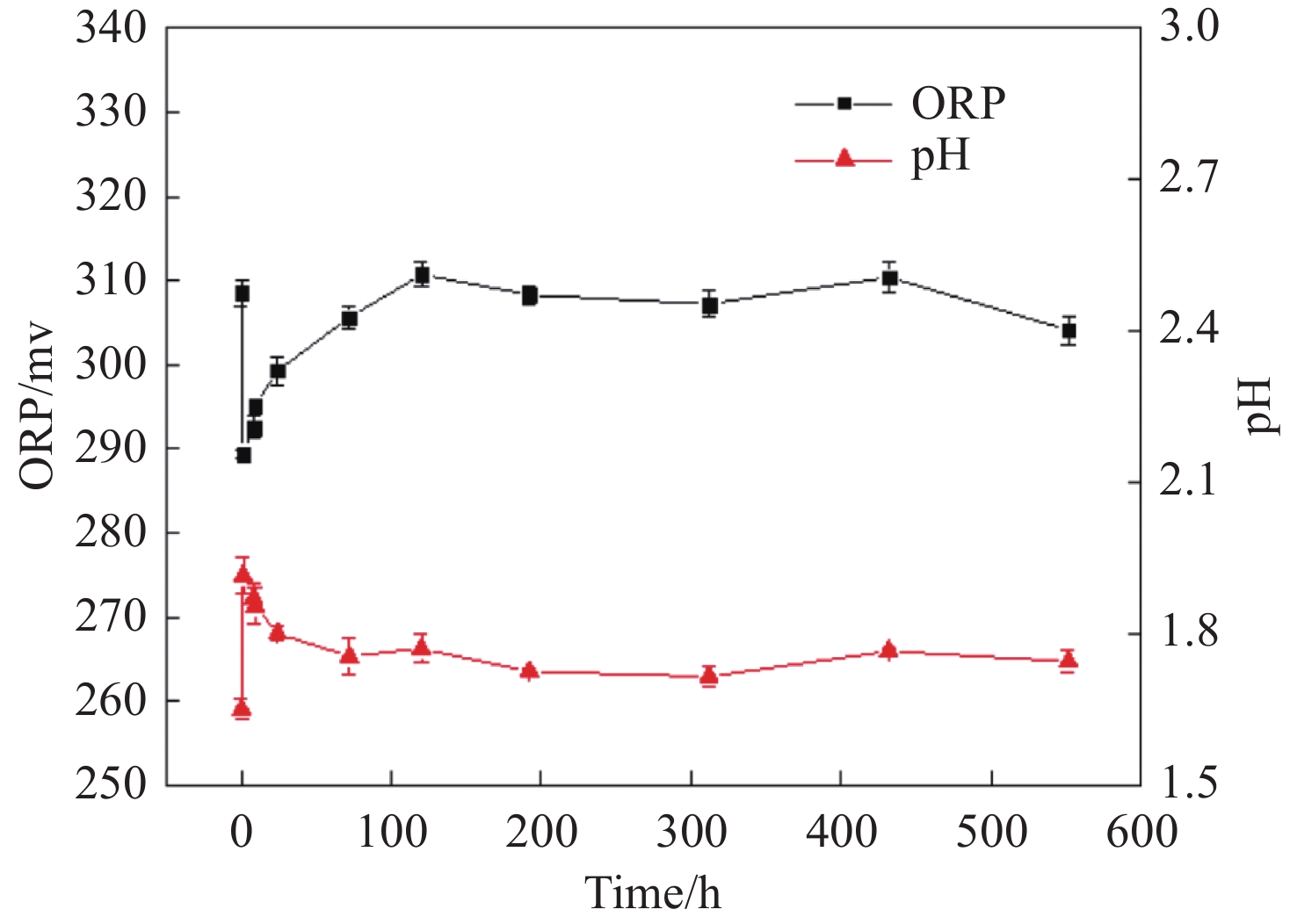
Figure 7.
pH and ORP changes in the reaction solution during the reaction
-
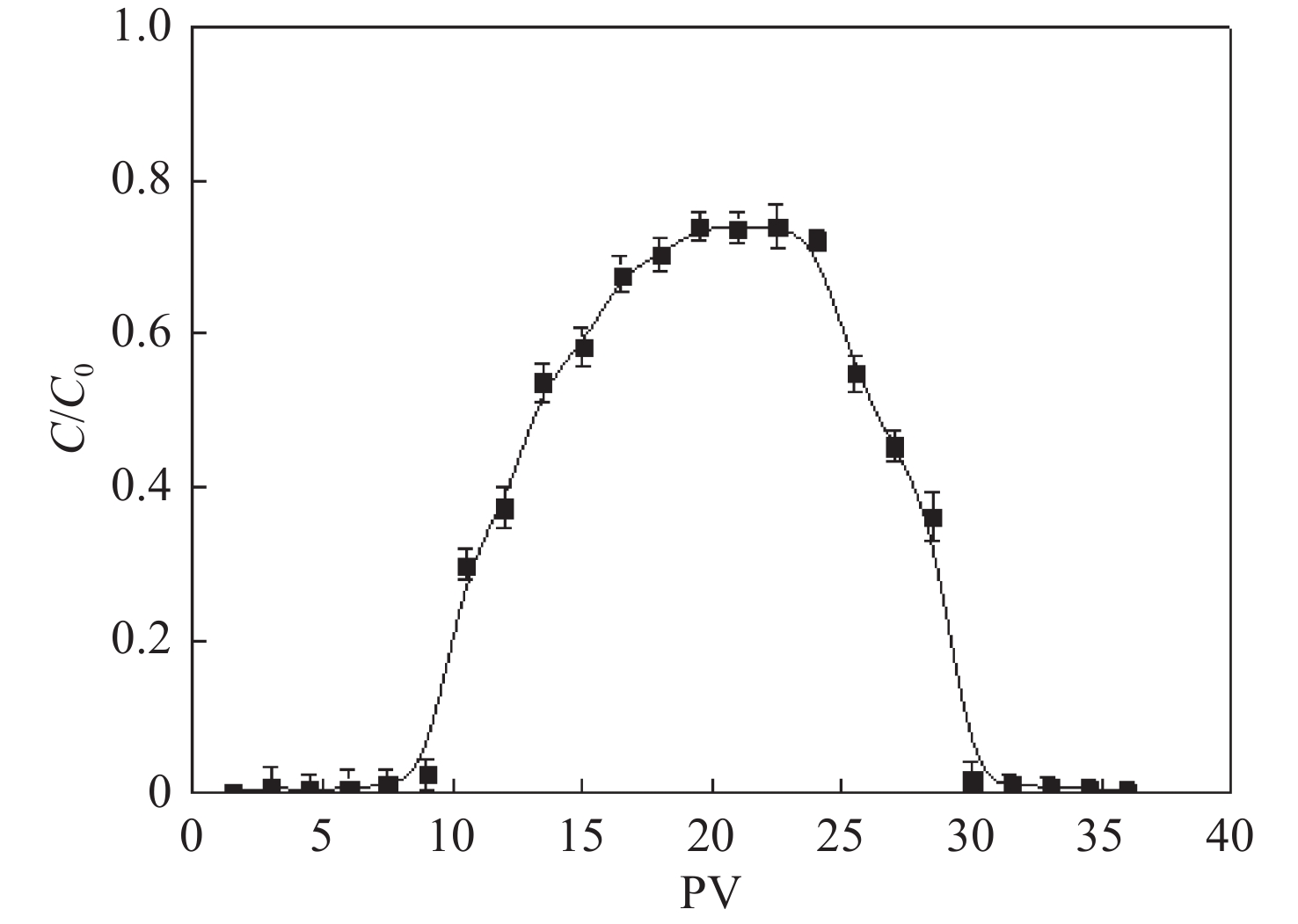
Figure 8.
The breakthrough curve of GT-NZVI in natural sand
-
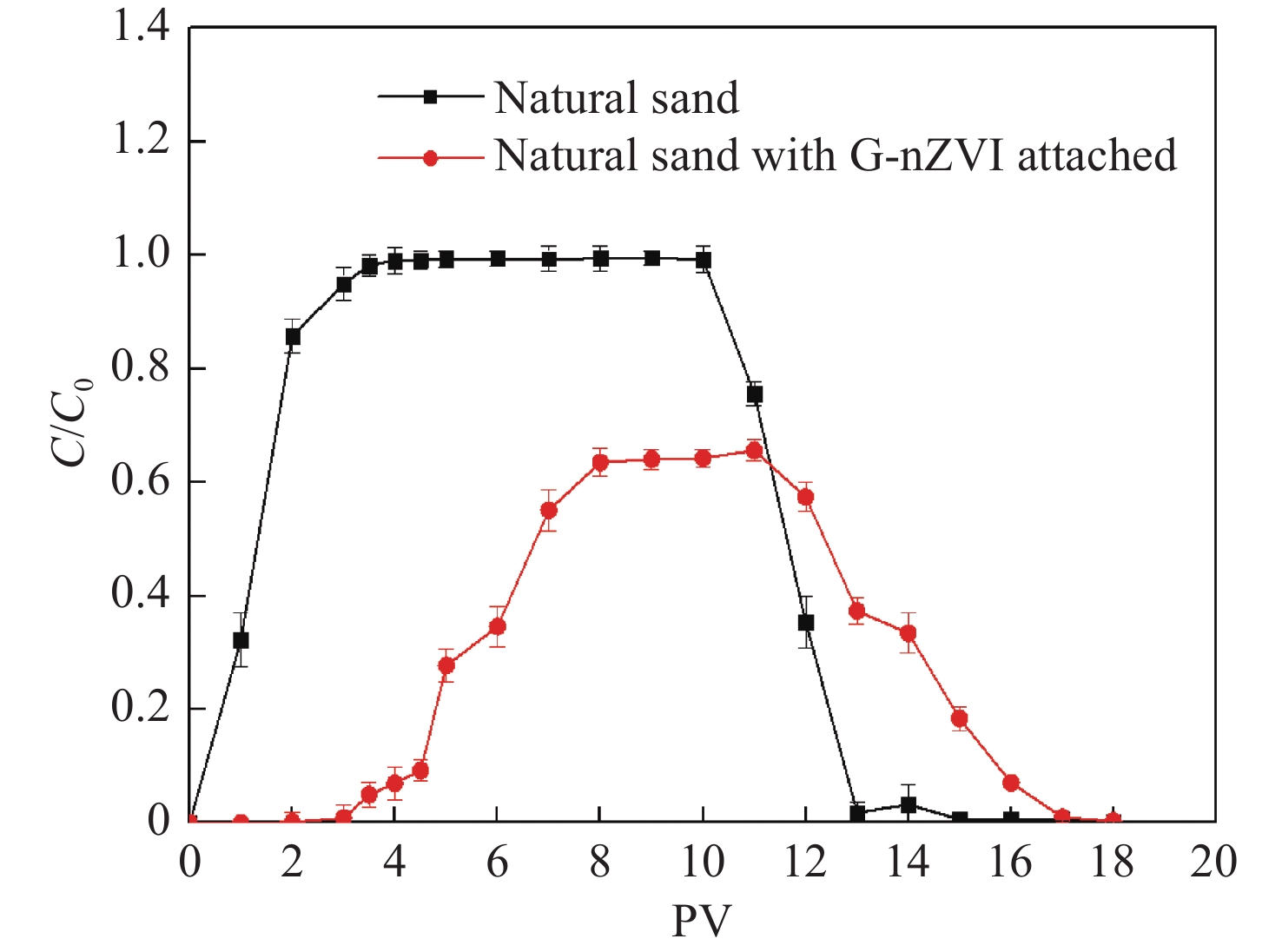
Figure 9.
Breakthrough curves of Cr(Ⅵ) in sand column
-
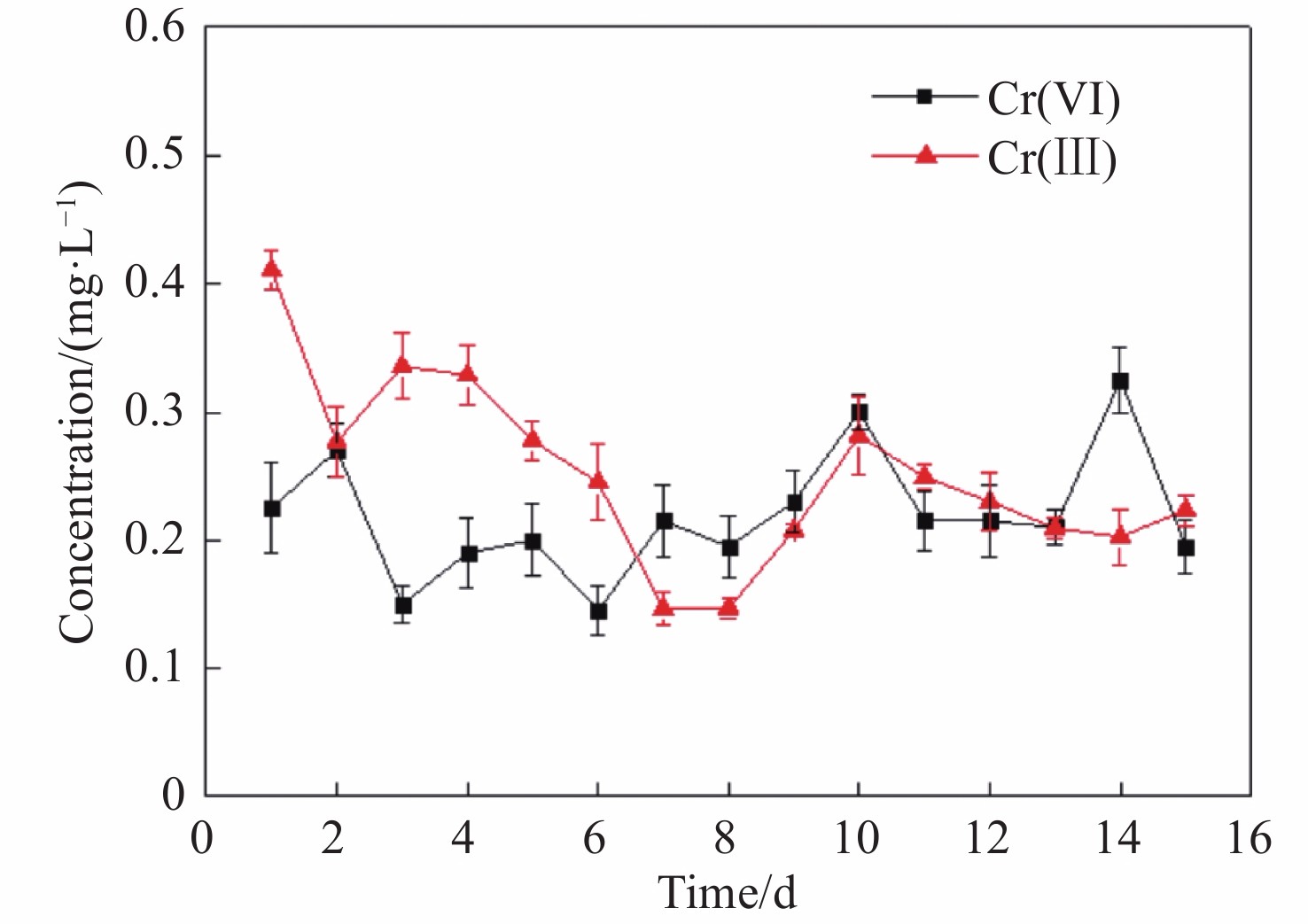
Figure 10.
Eluting concentration of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) in IRZ with GT-NZVI
-
Figure 11.
Influence of medium size (a), groundwater flow rate (b) and ionic strength (c) on Cr(VI) reduction in IRZ with GT-NZVI
-
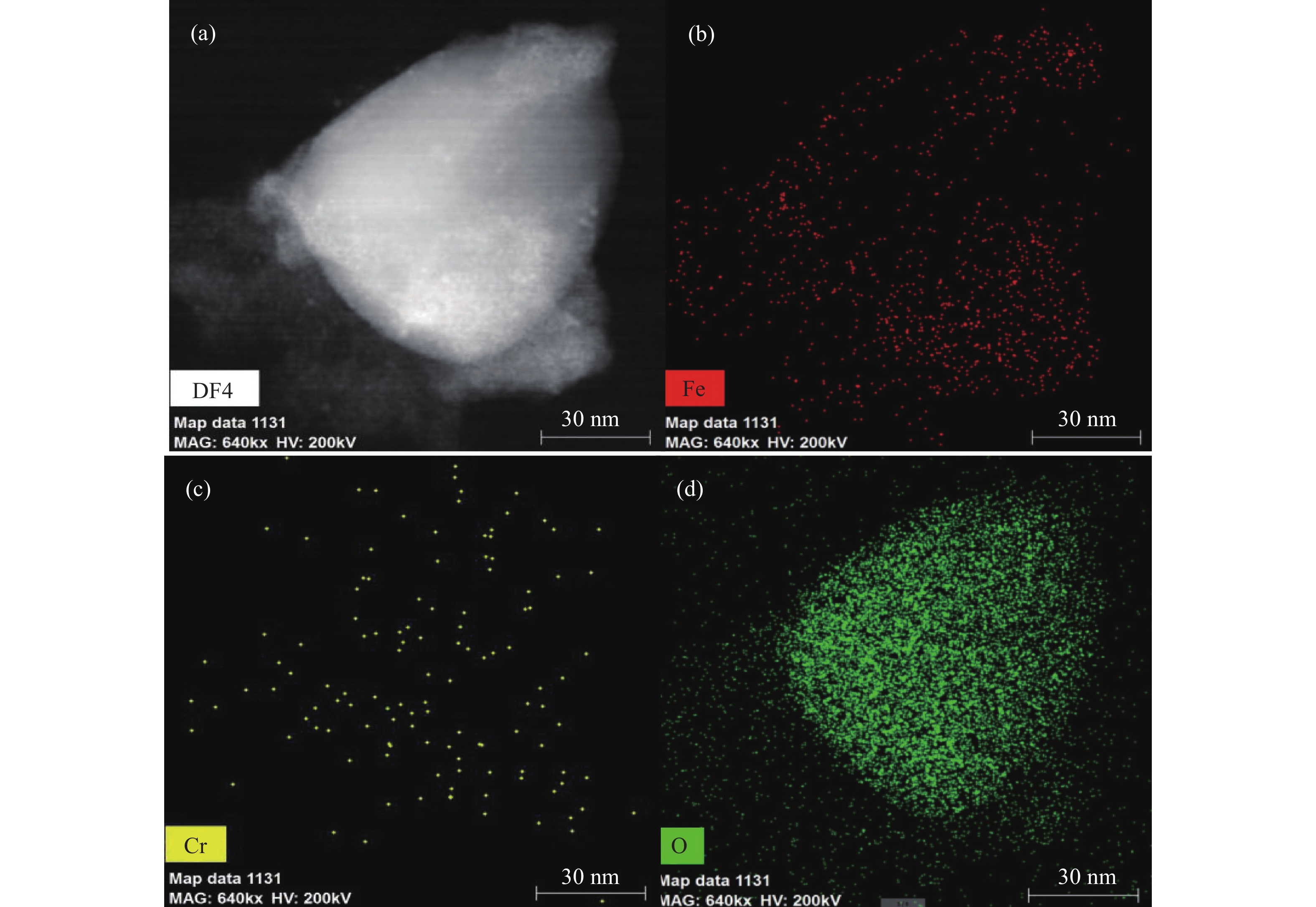
Figure 12.
Cs-corrected STEM image of GT-NZVI and distribution of elements





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: