| Citation: | Zhang Han, Chen Zong-yu, Tang Chang-yuan. 2021. Quantifying groundwater recharge and discharge for the middle reach of Heihe River of China using isotope mass balance method. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 9(3): 225-232. doi: 10.19637/j.cnki.2305-7068.2021.03.005 |
Quantifying groundwater recharge and discharge for the middle reach of Heihe River of China using isotope mass balance method
-
Abstract
Quantifying the inflow and outflow of groundwater is essential to understand the interaction between surface water and groundwater. It is difficult to determine these elements in relation to groundwater recharge and discharge to the river, because they cannot be directly measured through site specific study. The methods of isotope mass balance combining with water budget were used to quantify the groundwater recharge from and discharge to the Heihe River, northwest China. The mean isotope ratios of monthly monitoring data for one hydrological year were selected to be the isotope rations of end members in isotope mass balance. The results from the isotope mass balance analysis, incorporating with the 35-year hydrological data, suggest that about 0.464×109 m3/a of runoff flowing out Qilian Mountains is contributed to groundwater recharge (about 28% inflow of the Heihe River), while about 1.163×109 m3/a of runoff is discharged from groundwater in the middle reach of the river, which accounts for about 46% of river runoff in the basin. The analysis offers a unique, broad scale studies and provides valuable insight into surface water-groundwater interaction in arid area.
-
Keywords:
- Arid region /
- Stable isotopes /
- Water budget /
- Surface water-ground water interaction
-

-
References
[1] Bocanegra E, Quiroz Londoño OMQ, Martínez DE, et al. 2013. Quantification of the water balance and hydrogeological processes of groundwater–lake interactions in the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68(8): 2347-2357. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1916-4 [2] Chen MX. 1997. The water resources related with Quaternary basin system in arid area of Northwest China. Quaternary Sciences, 16: 97-104. (in Chinese) [3] Chen RS, Kang ES, Yang JP, et al. 2003. Simulation of water resources transformation in the midstream area of the Hei river basin. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 25: 566-573. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00073-0 [4] Chen ZY, Wan L, Nie ZL, et al. 2006. Estimating groundwater exchange with the Heihe River using isotope mass balance approaches. Congress of International Association of Hydrogeologists. (in Chinese) [5] Craig H, Gordon LI. 1965. Deuterium and oxygen-18 variations in the ocean and marine atmosphere. In: Stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures. Edited by: Tongiorgi E. Lab. de Geologia Nucleare, Pisa, Italy: 9-130. [6] Fan XP. 1991. Characteristics of the stream-aquifer systems and rational utilization of water resources in the Heihe River. Gansu Geol, 12: 1-16. (in Chinese) [7] Gao QZ. 1991. Development and utilization of water resources in the Heihe River catchment. Gansu Science and Technology Press, Lanzhou: 205. (in Chinese) [8] Gibson JJ, Edwards TWD, Prowse TD. 1999. Pan-derived isotopic composition of atmospheric water vapour and its variability in northern Canada. Journal of Hydrology, 217: 55-74. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00015-3 [9] Gibson JJ, Birks SJ, Yi Y, et al. 2016. Stable isotope mass balance of fifty lakes in central Alberta: Assessing the role of water balance parameters in determining trophic status and lake level. Journal of Hydrology Regional Studies, 6: 13-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrh.2016.01.034 [10] Gonfiantini R. 1986. Environmental isotopes in lake studies. New York: Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry, vol.2, The Terrestrial Environment, B: 113-168. [11] Krabbenhoft DP, Bowser CJ, Anderson MP, et al. 1990. Estimating groundwater exchange with lakes 1. The stable isotope mass balance method. Water Resources Research, 26: 2445-2453. doi: 10.1029/WR026i010p02445 [12] Lan YC, Kang ES, Zhang JS, et al. 2002. Study on the water resources and its rational development and utilization in Heihe River basin. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 38: 108-114. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1080/12265080208422884 [13] Li WP, Kang WD, et al. 2011. Optimization model for regulation and utilization of water resources in typical arid inland basin in Northwest China: A case study of Heihe River Basin. Geological Publishing House: 362. (in Chinese) [14] Majoube M. 1971. Fractionnement en oxygene-18 et en deuterium entre l’eau et sa vapeur. Journal of Chemisty and Physics, 197: 1423-1436. doi: 10.1051/jcp/1971681423 [15] Sacks LA. 2002. Estimating ground-water inflow to lakes in central Florida using the isotope mass-balance approach. USA: Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 02-4192: 59. [16] Sacks LA, Swancar A, Lee TM. 1998. Estimating ground-water exchange with lakes using water-budget and chemical mass-balance approaches for ten lakes in ridge areas of Polk and Highlands counties, Florida. USA: Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 98-4133: 52. [17] Sacks LA, Lee TM, Swancar A. 2013. The suitability of a simplified isotope-balance approach to quantify transient groundwater–lake interactions over a decade with climatic extremes. Journal of Hydrology, 519: 3042-3053. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.12.012 [18] Shi JA, Wang XB, Wang Q, et al. 1999. Evidences from helium isotope for groundwater supplement, Circulation and mixing − Taking the Shiyanghe and Heihe river basins as an example. Acta Sedimentalogica Sinica 17 supp: 815-819. (in Chinese) [19] Su C, Cheng ZS, Zheng ZX, et al. 2019. Groundwater age and renewability in the north of Muling-Xingkai plain. Geology in China, 46(2): 328-336. (in Chinese) [20] Turner JV. 1984. The water balance of a small lake using stable isotopes and tritium. Journal of Hydrology, 70: 199-220. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(84)90122-7 [21] Wang GX, Cheng GD. 1999. Land desertification status and developing trend in the Hei River basin. J Des Res, 19: 368-374. (in Chinese) [22] Wang J, Meng JJ. 2008. Characteristics and tendencies of annual runoff variations in the Heihe River basin during the past 60 years. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 28(1): 83-88. [23] Wu YQ, Wen X, Zhang Y. 2004. Analysis of the exchange of groundwater and river water by using Radon-222 in the middle Heihe Basin of northwestern China. Environmental Geology, 45: 647-653. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0914-y [24] Zhang JS, Kang ES, Lan YC, et al. 2001. Studies of the transformation between surface water and groundwater and the utilization ratio of water resources in Hexi region. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 23: 375-382. (in Chinese) [25] Zhang YH, Wu YQ, Ding JQ, et al. 2005. Exchange of groundwater and river water in a basin of the middle Heihe river by using δ18O. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 27: 106-110. (in Chinese) -
Access History

-
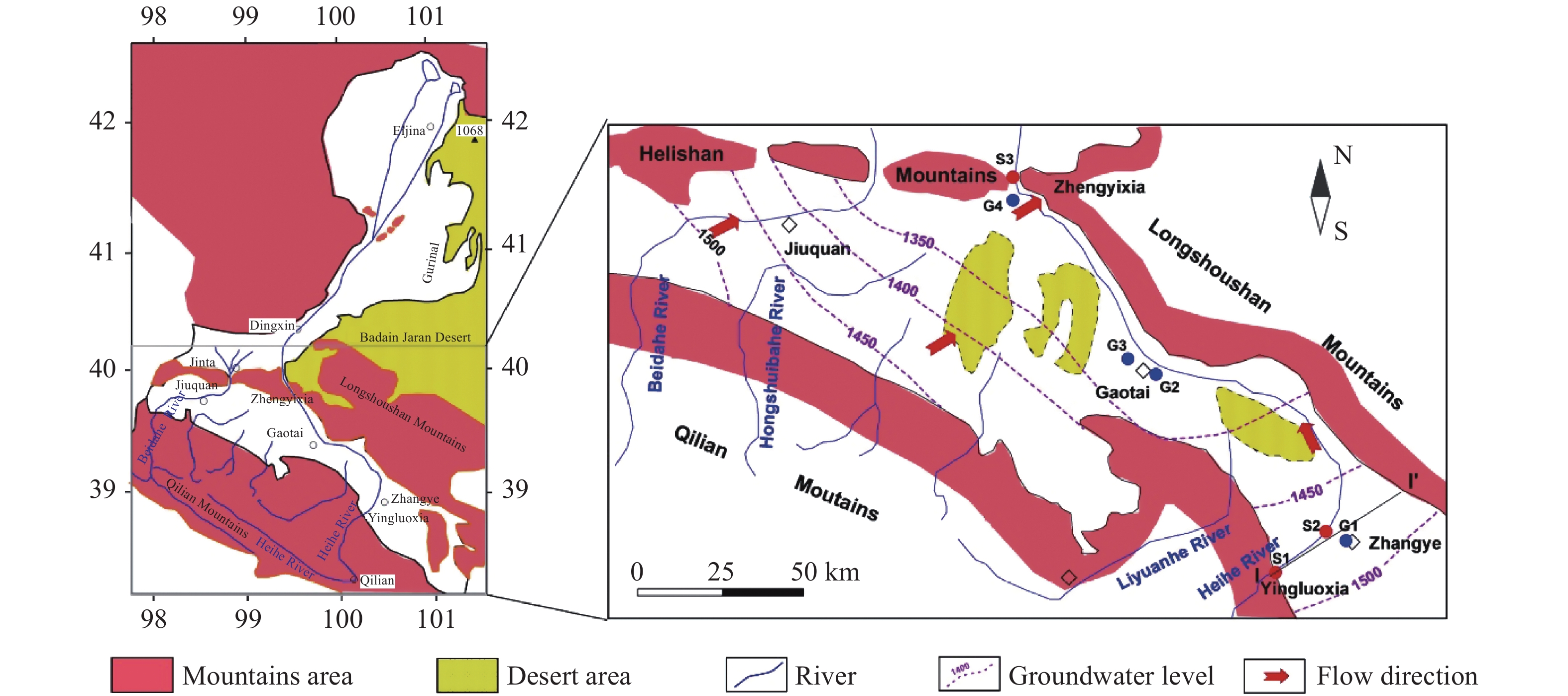
Figure 1.
The Heihe River catchment and study area
-
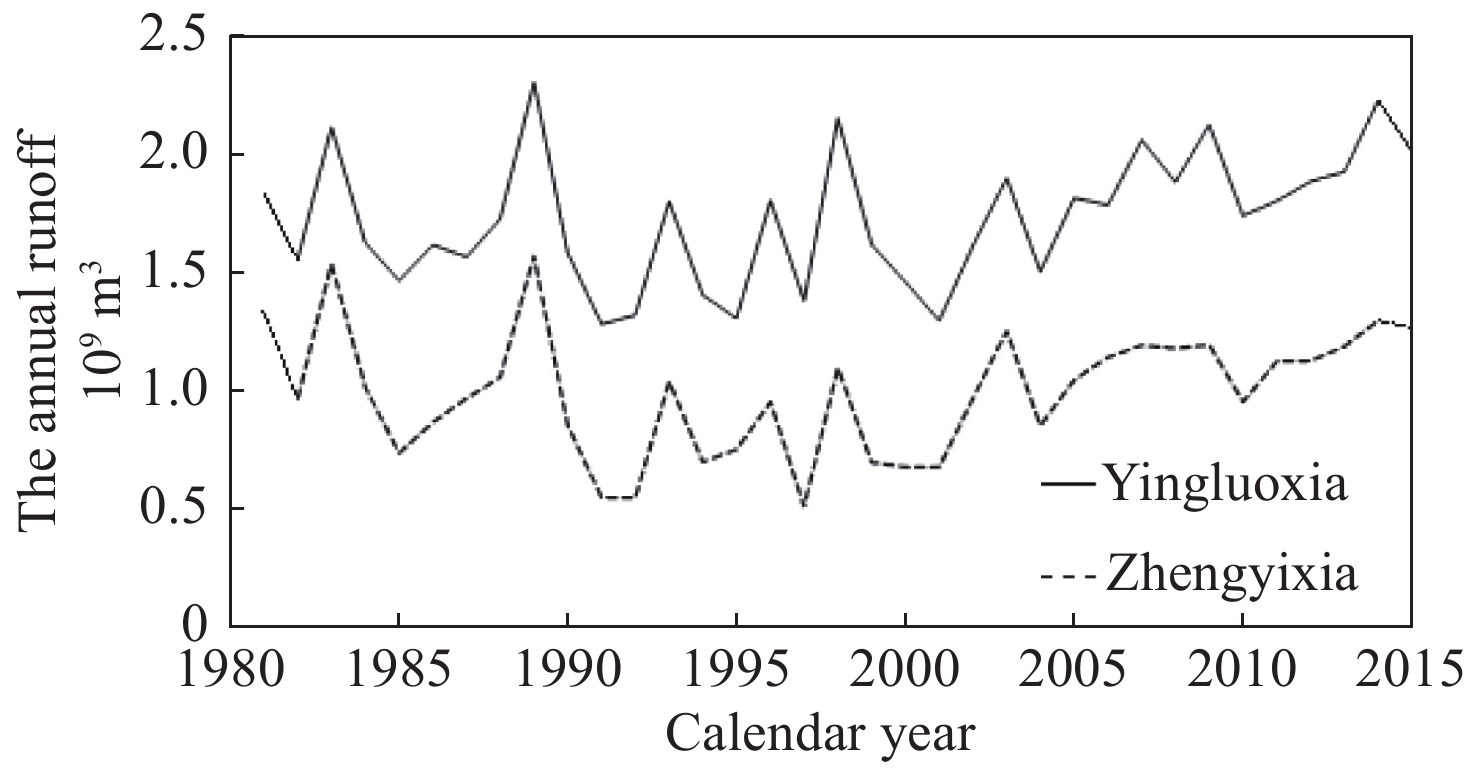
Figure 2.
The annual runoff at the gauging station of Yingluoxia and Zhengyixia (Data from Zhangye hydrological and Water Resources Survey Bureau)
-
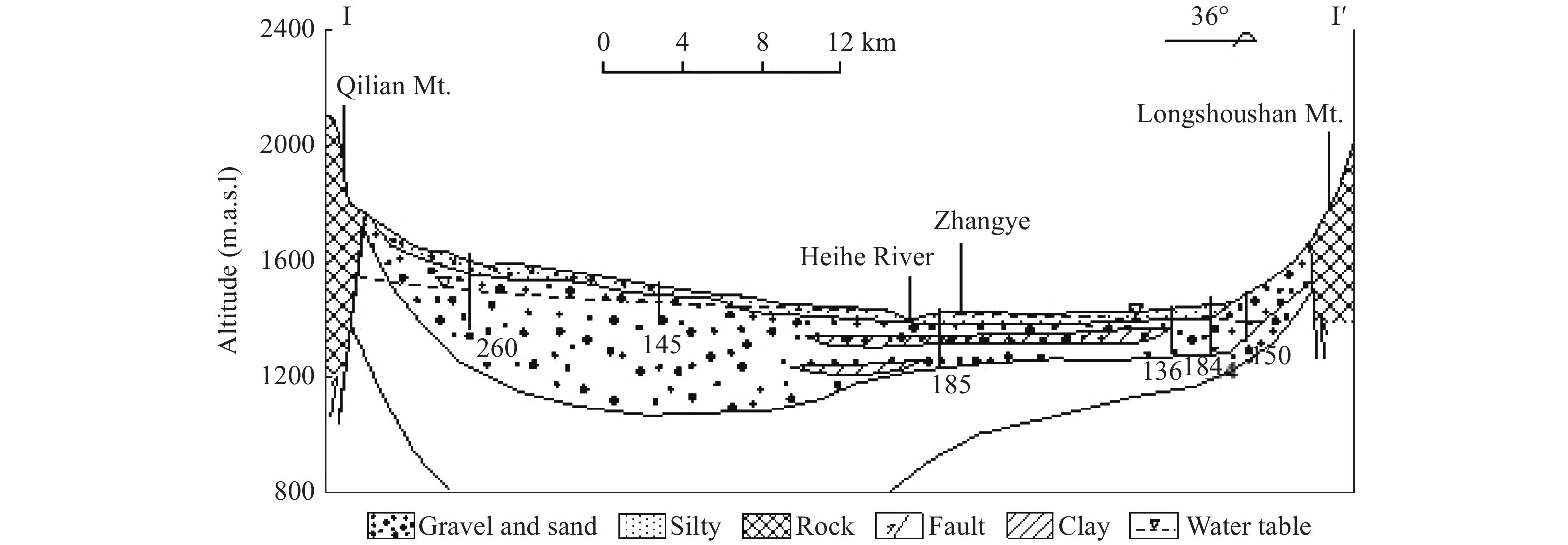
Figure 3.
Hydrogeological cross section along transect I-I' in Fig. 1
-
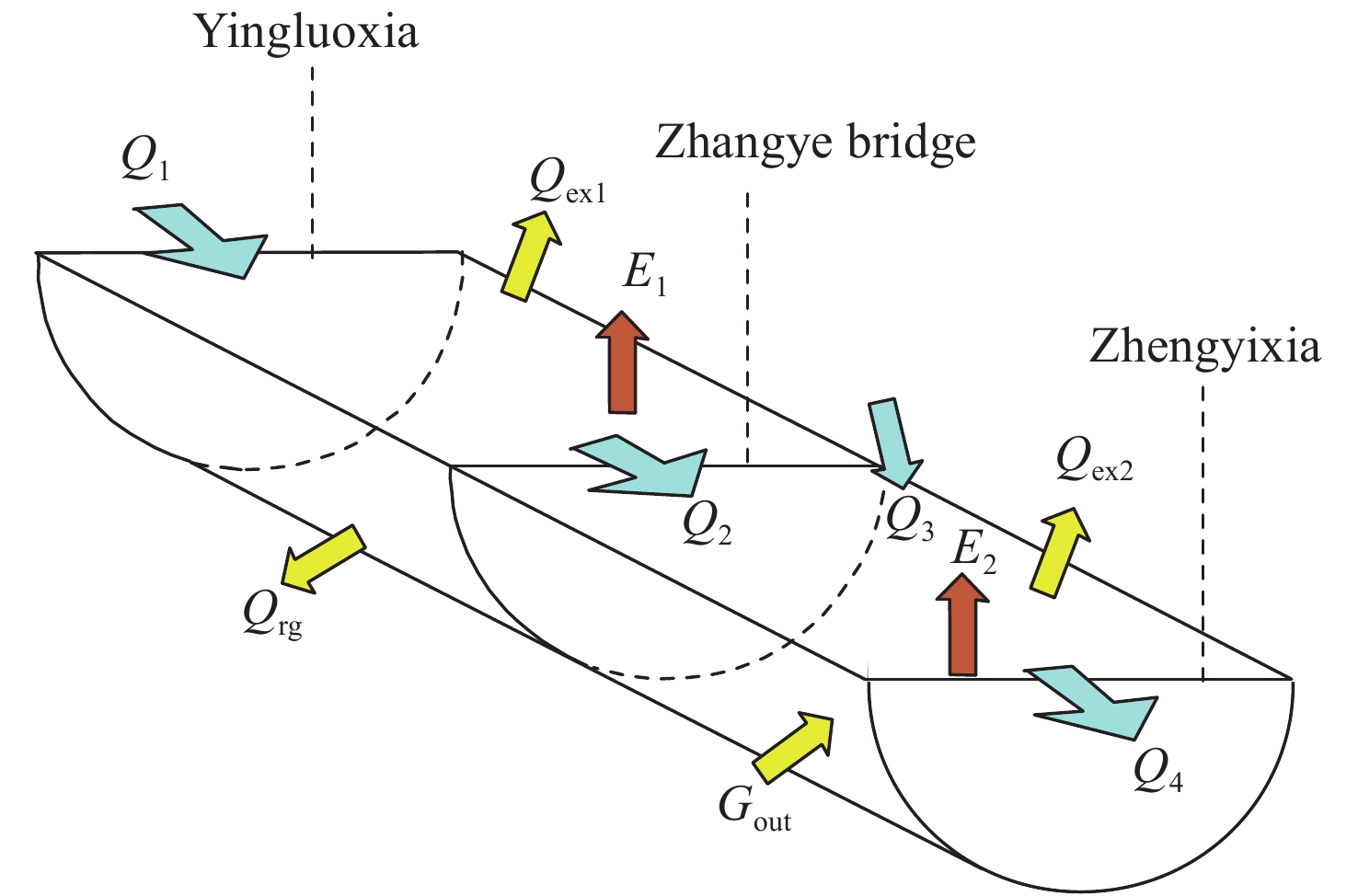
Figure 4.
Elements of water budget in Heihe River




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: