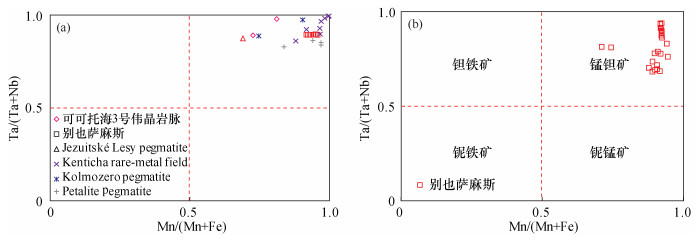
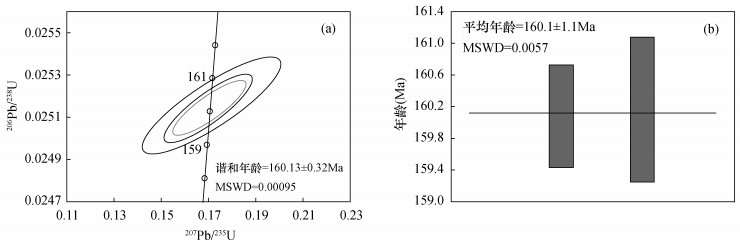
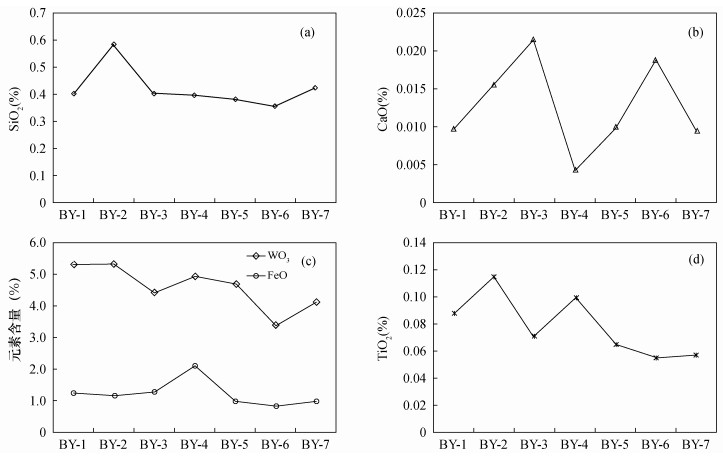
| [1] |
王贤觉, 邹天人, 徐建国, 等.阿尔泰伟晶岩矿物学研究[M].北京:科学出版社, 1981:1-140.
Google Scholar
Wang X J, Zou T R, Xu J G, et al.Mineralogy of pegmatite in Altay[M].Beijing:Science Press, 1981:1-140.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
王贤觉, 牛贺才, 郭国章.阿尔泰三号伟晶岩脉岩浆演化过程中铌、钽示踪的研究[J].地球化学, 1998, 27(1):1-11.
Google Scholar
Wang X J, Niu H C, Guo G Z.The tracking study of Nb and Ta in magmatic evolutionary process for pegmatite vein No.3, Altay, China[J].Geochimica, 1998, 27(1):1-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
陈毓川, 叶庆同, 王京彬, 等.中国新疆阿尔泰成矿带矿床地质、成矿规律与技术经济评价[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003:1-401.
Google Scholar
Chen Y C, Ye Q T, Wang J B, et al.The mineral deposits, metallogeny, technical and economic evaluation in Altay metallogenic belt, Xinjiang, China[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2003:1-401.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
张爱铖, 王汝成, 胡欢.新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉重钽铁矿研究[J].高校地质学报, 2003, 9(2):268-272.
Google Scholar
Zhang A C, Wang R C, Hu H.Tapiolite from the Koktokay No.3 rare metal granitic pegmatite dyke, Altai, Xinjiang Autonomous Region[J].Geological Journal of China Universities, 2003, 9(2):268-272.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
夏建明, 陈邦建.苏州富铌钽花岗岩的物质组成及钽的赋存状态研究[J].江苏地质, 1999, 23(4):236-240.
Google Scholar
Xia J M, Chen B J.Material composition of niobium and tantalum-rich granite and study of tantalum's occurrence state in Suzhou of Jiangsu Province[J].Geology of Jiangsu, 1999, 23(4):236-240.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
王汝成, Monchoux P, Fontan F.法国中央高原Beauvoir花岗岩中铌钽矿的带状构造:类型、化学成分和形成条件[J].矿物学报, 1991, 11(3):225-233.
Google Scholar
Wang R C, Monchoux P, Fontan F.Zoning in columbite crystals from the Beauvoir granite, massif central, France:Types, composition and constraints on their formation[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1991, 11(3):225-233.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Cerny P, Chapman R, Ferreira K, et al.Geochemistry of oxide minerals of Nb, Ta, Sn, and Sb in the Varutrask granitic pegmatite, Sweden:The case of an "anomalous" columbite-tantalite trend[J].American Mineralogist, 2004, 89:505-518. doi: 10.2138/am-2004-0405
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Llorens T, Moro M C.Microlite and tantalite in the LCT granitic pegmatites of LA Canalita, Navasfrías Sn-W district, Salamanca, Spain[J].The Canadian Mineralogist, 2010, 48:375-390. doi: 10.3749/canmin.48.2.375
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Chudík P, Uher P, Gadas P, et al.Niobium-tantalum oxide minerals in the Jezuitské Lesy granitic pegmatite, Bratislava Massif, Slovakia:Ta to Nb and Fe to Mn evolutionary trends in a narrow Be, Cs-rich and Li, B-poor dike[J].Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 102:15-27. doi: 10.1007/s00710-011-0163-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
刘源俊, 黎家祥, 胡蓉.铌钽地质及普查勘探[M].北京:地质出版社, 1979:1-191.
Google Scholar
Liu Y J, Li J X, Hu R.Geology and general exploration of niobium-tantalum[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 1979:1-191.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
王文瑛, 杨岳清, 陈成湖, 等.福建南平花岗伟晶岩中的铌钽矿物学研究[J].福建地质, 1999, 20(3):113-134.
Google Scholar
Wang W Y, Yang Y Q, Chen C H, et al.Study on the Nb and Ta-minerals from the granitic pegmatites in Nanping, Fujian Province[J].Geology of Fujian, 1999, 20(3):113-134.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Badanina E V, Sitnikova M A, Gordienko V V, et al.Mineral chemistry of columbite-tantalite from spodumene pegmatites of Kolmozero, Kola Peninsula (Russia)[J].Ore Geology Review, 2015, 64:720-735. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.05.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Shao T, Jiang K, Liu Y, et al.Geochemistry and a metal-logenic model for Nb-Ta-bearing granitic pegmatites from the Northern Qaidam Basin[J].Geological Journal, 2018, 53(Supplement 1):113-123.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Che X D, Wang R C, Wu F Y, et al.Episodic Nb-Ta mineralisation in South China:Constraints from in situ LA-ICP-MS columbite-tantalite U-Pb dating[J].Ore Geology Review, 2019, 105:71-85. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.11.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Zhou Q F, Qin K Z, Tang D M, et al.LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon, columbite-tantalite and 40Ar-39Ar muscovite age constraints for the rare-element pegmatite dykes in the Altai orogenic belt, NW China[J].Geological Magazine, 2018, 155(3):707-728. doi: 10.1017/S0016756816001096
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Yan Q H, Qiu Z W, Wang H, et al.Age of the Dahongliutan rare metal pegmatite deposit, West Kunlun, Xinjiang (NW China):Constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of columbite-(Fe) and cassiterite[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 100:561-573. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.11.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Singh Y, Sastry D V L N, Bagora S, et al.Dating of columbite-tantalite and monazite from pegmatites of the Kawadgaon-Challanpara area, Bastar Craton, Central India[J].Journal of the Geological Society of India, 2018, 92(1):7-10. doi: 10.1007/s12594-018-0946-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Zhang R Q, Lu J J, Lehmann B, et al.Combined zircon and cassiterite U-Pb dating of the Piaotang granite-related tungsten-tin deposit, southern Jiangxi tungsten district, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 82:268-284. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.039
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
王倩, 侯克军, 邹天人.适合于稀有金属矿床的同位素定年方法及其应用[J].地质学报, 2019, 93(6):1523-1532.
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Hou K J, Zou T R.Isotopic dating method suitable for rare-metal deposits and its application[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6):1523-1532.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
杨富全, 张忠利, 王蕊, 等.新疆阿尔泰稀有金属矿地质特征及成矿作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(6):1010-1026.
Google Scholar
Yang F Q, Zhang Z L, Wang R, et al.Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of rare metal deposits in Altay, Xinjiang[J].Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(6):1010-1026.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
王瑞江, 王登红, 李建康, 等.稀有稀土稀散矿产资源及其开发利用[M].北京:地质出版社, 2015:1-425.
Google Scholar
Wang R J, Wang D H, Li J K, et al.The development and utilization of rare metals, rare earth scattered mineral resources[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2015:1-425.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
王登红, 王瑞江, 李建康, 等.中国三稀矿产资源战略调查研究进展综述[J].中国地质, 2013, 40(2):361-371.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Wang R J, Li K J, et al.The progress in the strategic research and survey of rare earth, rare metal and rare-scattered elements mineral resources[J].Geology in China, 2013, 40(2):361-371.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
丁建刚, 杨成栋, 杨富全, 等.新疆阿尔泰别也萨麻斯稀有金属矿床含矿伟晶岩与花岗岩围岩成因关系[J].地球科学院与环境学报, 2020, 42(1):71-85.
Google Scholar
Ding J G, Yang C D, Yang F Q, et al.Genetic relationship between ore-forming pegmatite and the surrounding granite of Bieyesamasi rare metal deposit in Altay of Xinjiang, China[J].Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(1):71-85.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
沈曹军.新疆富蕴县别也萨麻斯一带稀有金属矿地质特征[J].新疆有色金属, 2018(6):15-16.
Google Scholar
Shen C J.Geological characteristics of rare metal deposits in Bieyesamasi area, Fuyun County, Xinjiang[J].Xinjiang Nonferrous Metal, 2018(6):15-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Ludwig K R.PBDAT for MS-DOS.A computer program for IBM PC compatibles for processing raw Pb-U-Th isotope data, version 1.24[R].US Geological Survey, 1995.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Ludwig K R.Isoplot-aplotting and regression program for radiogenic-isotope data, version 2.95[R].US Geological Survey, 1997.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Stacey J S, Kramers J D.Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 26:207-221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
周红英, 李惠民.金红石U-Pb同位素稀释法定年技术的改进[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2008, 27(1):77-80.
Google Scholar
Zhou H Y, Li H M.The improvement of the rutile isotope dilution U-Pb dating methodology[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2008, 27(1):77-80.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Tadesse S, Zerihun D.Composition, fractionation trend and zoning accretion of the columbite-tantalite group of minerals in the Kenticha rare-metal field (Adola, southern Ethiopia)[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences, 1996, 23(3):411-431.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Tindle A G, Breaks F W.Columbite-tantalite mineral chemistry from rare-element granitic pegmatites:Separation Lake area, N.W.Ontario, Canada[J].Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 70:165-198. doi: 10.1007/s007100070002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
杨富全, 毛景文, 闫升好, 等.新疆阿尔泰蒙库同造山斜长花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(4):485-499.
Google Scholar
Yang F Q, Mao J W, Yan S H, et al.Geochronology, geochemistry and geological implications of the Mengku synorogenic plagiogranite pluton in Altay, Xinjiang[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(4):485-499.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
王登红, 陈毓川.新疆阿尔泰阿祖拜稀有金属-宝石矿床的成矿时代:燕山期稀有金属[J].地质论评, 2000, 46(3):307-311.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Chen Y C.40Ar/39Ar dating for the Azubai rare metal-gem deposit in Altay, Xinjiang-New evidence for Yanshanian[J].Geological Review, 2000, 46(3):307-311.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
王登红, 陈毓川, 徐志刚.阿尔泰加里东期变质成因伟晶岩型白云母矿床的成矿年代证据及其意义[J].地质学报, 2001, 75(3):419-425.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Chen Y C, Xu Z G.Chronological study of Caledonian metamorphic pegmatite muscovite deposits in the Altay Mountains, northwestern China, and its significance[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(3):419-425.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
王登红, 陈毓川, 徐志刚.阿尔泰造山带岩石和矿石的氩同位素研究[J].长春科技大学学报, 2001, 31(2):110-115.
Google Scholar
Wang D H, Chen Y C, Xu Z G.Argon isotopic study of rock and ore from the Altay orogenic belt[J].Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2001, 31(2):110-115.
Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: