| [1] |
Sarkar D, Khan G G, Singh A K, et al.High-performance pseudocapacitor electrodes based on α-Fe2O3/MnO2 core-shell nanowire heterostructure arrays[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(30):15523-15531. doi: 10.1021/jp4039573
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Yun Y S, Kim J M, Park H H, et al.Free-standing heterogeneous hybrid papers based on mesoporous γ-MnO2 particles and carbon nanotubes for lithium-ion battery anodes[J].Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 244:747-751. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.11.056
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Biswal A, Tripathy B C, Sanjay K, et al.Electrolytic manganese dioxide (EMD):A perspective on worldwide production, reserves and its role in electrochemistry[J].RSC Advances, 2015, 5(72):58255-58283. doi: 10.1039/C5RA05892A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
牛莎莎.从锰阳极渣制备微粒电解二氧化锰及锰酸锂的研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
Google Scholar
Niu S S.The study on preparing particle manganese dioxide and LiMn2O4 from manganese anode slag[D].Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
杨爱江, 吴维, 袁旭, 等.电解锰废渣重金属对周边农田土壤的污染及模拟酸雨作用下的溶出特性[J].贵州农业科学, 2012, 40(3):190-193.
Google Scholar
Yang A J, Wu W, Yuan X, et al.Pollution of metals in the soils around electrolytic manganese residue and dissolving-out characteristics of heavy metals in waste residues in simulated acid rain[J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(3):190-193.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
蔡敬怡, 谭科艳, 路国慧, 等.贵州万山废弃矿区小流域系统沉积物及悬浮物重金属的空间分布特征[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(3):305-315.
Google Scholar
Cai J Y, Tan K Y, Lu G H, et al.The spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in river sediments and suspended matter in small tributaries of the abandoned Wanshan mercury mines, Guizhou Province[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(3):305-315.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Li X, Zhong H, Wang S, et al.Leaching behavior and risk assessment of heavy metals in a landfill of electrolytic manganese residue in western Hunan, China[J].Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2014, 20(5):1249-1263. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2013.849482
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
陈海棠, 周丹丹, 薛南冬, 等.电子固体废弃物拆解作坊附近土壤重金属污染特征及风险[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(5):956-964.
Google Scholar
Chen H T, Zhou D D, Xue N D, et al.Contamination and health risk of heavy metals in soils near e-waste recycling workshops[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(5):956-964.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Li Z, Ma Z, van der Kuijp T J, et al.A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China:Pollution and health risk assessment[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 468-469:843-853. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.090
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang W, et al.Multivariate statistical techniques for evaluating and identifying the environmental significance of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Yangtze River, China[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71:1183-1193. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2522-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Huang Z, Pan X D, Wu P G, et al.Heavy metals in vegetables and the health risk to population in Zhejiang, China[J].Food Control, 2014, 36:248-252. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.08.036
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Ernst E.Risks of herbal medicinal products[J]. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety, 2004, 13:767-771. doi: 10.1002/pds.1014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Khan S, Soylak M, Alosmanov R M, et al.Development of phosphate-containing polymer-based solid phase extraction procedure for the separation, enrichment, and determination of cadmium in water and food samples by FAAS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(4):158-163.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
王增焕, 王许诺, 谷阳光, 等.疏水性螯合物固相萃取-原子吸收光谱法测定海水中5种重金属[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4):360-366.
Google Scholar
Wang Z H, Wang X N, Gu Y G, et al.Determination of 5 heavy metals in seawater by atomic absorption spectrometry with solid-phase extraction of hydrophobic chelate[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(4):360-366.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Chen S, Zhu S, Lu D.Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction coupled with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for speciation of antimony in environmental water samples by electrothermal vaporization ICP-MS[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(2):55-61. doi: 10.46770/AS.2018.02.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
田志仁, 封雪, 姜晓旭, 等.生态环境监测工作中应用AAS/AFS和XRF法测定土壤重金属数据质量评价[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(5):479-488.
Google Scholar
Tian Z R, Feng X, Jiang X X, et al.Evaluation of data quality on the detection of heavy metals in soils by atomic absorption spectrometry or atomic fluorescence spectrometry and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry in ecological environment monitoring[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(5):479-488.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
胡南, 周军媚, 刘运莲, 等.硫酸锰废渣的浸出毒性及无害化处理的研究[J].中国环境监测, 2007, 23(2):49-52.
Google Scholar
Hu N, Zhou J M, Liu Y L, et al.A study of the extraction procedure toxicity and harmless disposal of manganese sulphate waste residue[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2007, 23(2):49-52.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
周亚武, 陆谢娟, 高明刚, 等.电解锰渣固结体中重金属浸出毒性及其在模拟酸雨下的淋溶特性分析[J].武汉科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(2):127-132.
Google Scholar
Zhou Y W, Lu X J, Gao M G, et al.Leaching toxicity and leaching properties in simulated acid rain of heavy metals in solidified electrolytic manganese residue[J].Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 41(2):127-132.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
罗乐, 王金霞, 周皓.锰渣中重金属在模拟酸雨环境下的浸出规律[J].湿法冶金, 2019, 38(5):352-357.
Google Scholar
Luo L, Wang J X, Zhou H.Leaching regularities of heavy metals in electrolytic manganese residue using simulation acid rain[J].Hydrometallurgy of China, 2019, 38(5):352-357.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Zack T, Hogmalm K J.Laser ablation Rb/Sr dating by online chemical separation of Rb and Sr in an oxygen-filled reaction cell[J].Chemistry Geology, 2016, 437:120-133. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.05.027
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Muramatsu Y, Matsuzaki H, Toyama C, et al.Analysis of 129I in the soils of Fukushima Prefecture:Preliminary reconstruction of 131I deposition related to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP)[J].Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2015, 139:344-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2014.05.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Vetere A, Prcfrock D, Schrader W, et al.Quantitative and qualitative analysis of three classes of sulfur compounds in crude oil[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2017, 56(36):10933-10937. doi: 10.1002/anie.201703205
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Balcaen L, Bolea-Fernandez E, Resano M, et al.Inductively coupled plasma-tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS):A powerful and universal tool for the interference-free determination of (ultra)trace elements-A tutorial review[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2015, 894:7-19. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.08.053
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Virgilio A, Amais R S, Amaral C D B, et al.Reactivity and analytical performance of oxygen as cell gas in inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 2016, 126:31-36. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2016.10.013
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Fu L, Xie H, Shi S.Multielement analysis of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. essential oil using ICP-MS/MS[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2018, 410(16):3769-3778. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1040-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Boting K, Treu S, Leonhard P, et al.First experimental proof of asymmetric charge transfer in ICP-MS/MS (ICP-QQQ-MS) through isotopically enriched oxygen as cell gas[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(3):578-582. doi: 10.1039/c3ja50234a
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Walkner C, Gratzer R, Meisel T, et al.Multi-element analysis of crude oils using ICP-QQQ-MS[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 103:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.10.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Galusha A L, Haig A C, Bloom M S, et al.Ultra-trace element analysis of human follicular fluid by ICP-MS/MS:Pre-analytical challenges, contamination control, and matrix effects[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2019, 34(4):741-752. doi: 10.1039/C8JA00423D
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Fu L, Xie H, Huang J, et al.Rapid determination of trace elements in serum of hepatocellular carcinoma patients by inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2020, 1112:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2020.03.054
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Zhang Y, Pan Z, Jiao P, et al.Solvent extraction ICP-MS/MS method for the determination of REE impurities in ultra-high purity Ce chelates[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2019, 40(5):167-172. doi: 10.46770/AS.2019.05.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Amaral C D B, Amais R S, Fialho L L, et al.A novel strategy to determine As, Cr, Hg and V in drinking water by ICP-MS/MS[J].Analytical Methods, 2015, 7(3):1215-1220. doi: 10.1039/C4AY02811B
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Witt B, Bornhorst J, Mitze H, et al.Arsenolipids exert less toxicity in a human neuron astrocyte co-culture as compared to the respective monocultures[J].Metallomics, 2017, 9(5):442-446. doi: 10.1039/C7MT00036G
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Jackson B P.Fast ion chromatography-ICP-QQQ for arsenic speciation[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(6):1405-1407. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00049A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Meyer S, Raber G, Ebert F, et al.In vitro toxicological characterisation of arsenic-containing fatty acids and three of their metabolites[J].Toxicology Research, 2015, 4(5):1289-1296. doi: 10.1039/C5TX00122F
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Barros J A V A, Virgilio A, Schiavo D, et al.Determination of ultra-trace levels of Mo in plants by inductively coupled plasma tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS)[J].Microchemical Journal, 2017, 133:567-571. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2017.04.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Amais R S, Virgilio A, Schiavo D, et al.Tandem mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) for overcoming moly-bdenum oxide interferences on Cd determination in milk[J].Microchemical Journal, 2015, 120:64-68. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2015.01.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
张洁, 阳国运.树脂交换分离-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定铅锌矿中钨钼锡锗硒碲[J].岩矿测试, 2018, 37(6):657-663.
Google Scholar
Zhang J, Yang G Y.Determination of tungsten, molybdenum, tin, germanium, selenium and tellurium in lead-zinc ore by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry with resin exchange separation[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(6):657-663.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
刘宏伟, 谢华林, 聂西度.松香中杂质元素的质谱分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(2):603-606.
Google Scholar
Liu H W, Xie H L, Nie X D.Determination of impurity elements in rosin with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(2):603-606.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Moraleja I, Esteban-Fernandez D, Lazaro A, et al. Printing metal-spiked inks for LA-ICP-MS bioimaging internal standardization:Comparison of the different nephrotoxic behavior of cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408(9):2309-2318. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9327-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





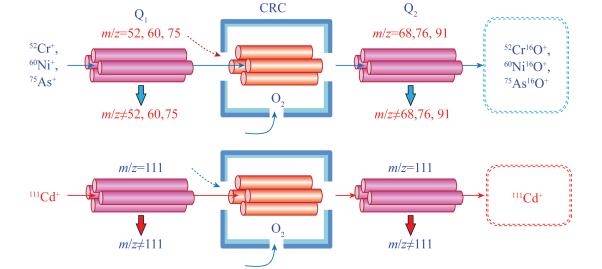

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: