| [1] |
(英)科林·伦福儒, 保罗·巴恩著.陈淳, 译.考古学理论、方法与实践[M].上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2015.
Google Scholar
Renfrew C, Bahn P G(Editor).Chen C (Translator).Archaeology: Theories, methods and practice[M].Shanghai: Shanghai Classics Publishing House, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Rehren T, Freestone I C.Ancient glass:From kaleidoscope to crystal ball[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 56:233-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2015.02.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Dussubieux L, Golitko M, Gratuze B.Recent advances in laser ablation ICP-MS for archaeology[M].Heidelberg:Springer, 2016:137-211.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Humphry D.Some experiments and observations on the colours used in painting by the ancients[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 1815, 105(1):97-124.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Seligman C G, Beck H C.Far eastern glass:Some western origins[J].The Bulletin of the Museum of Far Eastern Antiquities, 1938(10):1-64.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Gratuze B, Giovagnoli A, Barrandon J N, et al.Apport de la méthode ICP-MS couplée à l'ablation laser pour la caractérisation des archéomatériaux[J].Revue d'Archéométrie, 1993(17):89-104.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Lin J, Liu Y, Yang Y, et al.Calibration and correction of LA-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS analyses for element contents and isotopic ratios[J].Solid Earth Sciences, 2016, 1(1):5-27.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
刘勇胜, 胡兆初, 李明, 等.LA-ICP-MS在地质样品元素分析中的应用[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(36):3753-3769.
Google Scholar
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Li M, et al.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(32):3863-3878.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Li Z, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, et al.Accurate determination of elements in silicate glass by nanosecond and femtosecond laser ablation ICP-MS at high spatial resolution[J].Chemical Geology, 2015, 400:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Guillong M, Horn I, Günther D.A comparison of 266nm, 213nm and 193nm produced from a single solid state Nd:YAG laser for laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2003, 18:1224-1230. doi: 10.1039/B305434A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Wagner B, Nowak A, Bulska E, et al.Critical assessment of the elemental composition of Corning archeological reference glasses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 402:1667-1677. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5597-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
王辉, 汪方跃, 关炳庭, 等.激光能量密度对LA-ICP-MS分析数据质量的影响研究[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6):609-619.
Google Scholar
Wang H, Wang F Y, Guan B T, et al.Effect of laser energy density on data quality during LA-ICP-MS measurement[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6):609-619.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
吴石头, 许春雪, Klaus S, 等.193nm ArF准分子激光系统对LA-ICP-MS分析中不同基体的剥蚀行为和剥蚀速率探究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):451-459.
Google Scholar
Wu S T, Xu C X, Klaus S, et al.Study on ablation behaviors and ablation rates of a 193nm ArF excimer laser system for selected substrates in LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):451-459.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
吴石头, 王亚平, 许春雪.激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱:双外标结合基体归一定量校准策略[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 45(7):965-972.
Google Scholar
Wu S T, Wang Y P, Xu C X.Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer:A quantification strategy based on two reference materials and bulk normalization as 100%(wt)[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 45(7):965-972.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICPMS without applying an internal standard[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Luo Y, Gao S, Longerich H P, et al.The uncertainty budget of the multi-element analysis of glasses using LA-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22:122-130. doi: 10.1039/B608010C
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Rehren T, Connolly P, Schibille N, et al. Changes in glass consumption in Pergamon (Turkey) from Hellenistic to Late Byzantine and Islamic times[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 55:266-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2014.12.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Bertini M, Izmer A, Vanhaecke F, et al.Critical evaluation of quantitative methods for the multi-elemental analysis of ancient glasses using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2013, 28:77-91. doi: 10.1039/C2JA30036B
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Miliszkiewicz N, Walas S, Tobiasz A.Current approaches to calibration of LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(2):327-338. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00325J
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
袁继海, 詹秀春, 孙冬阳, 等.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱分析硅酸盐矿物基体效应的研究[J].分析化学, 2011, 39(10):1582-1588.
Google Scholar
Yuan J H, Zhan X C, Sun D Y, et al.Investigation on matrix effects in silicate minerals by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(10):1582-1588.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Jochum K P, Nohl U, Herwig K, et al.GeoReM:A new geochemical database for reference materials and isotopic standards[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2005, 29(3):333-338. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00904.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
斯琴毕力格, 李青会, 干福熹.激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱/质谱法分析中国古代钾玻璃组分[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(9):1328-1333.
Google Scholar
Siqin B L G, Li Q H, Gan F X.Analysis of ancient Chinese potash glass by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(9):1328-1333.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Vicenzi E P, Eggins S, Logan A, et al. Microbeam characterization of Corning archeological reference glasses:New additions to the Smithsonian microbeam standard collection[J]. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2002, 107:719-727. doi: 10.6028/jres.107.058
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Shortland A, Rogers N, Eremin K.Trace element discri-minants between Egyptian and Mesopotamian Late Bronze Age glasses[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2007, 34:781-789. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2006.08.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Longerich H P, Jackson S E, Günther D.Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11:899-904. doi: 10.1039/JA9961100899
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Horn I, Guillong M, Günther D.Wavelength dependant ablation rates for metals and silicate glasses using homogenized laser beam profiles-Implications for LA-ICP-MS[J].Applied Surface Science, 2001, 182(1-2):91-102. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(01)00465-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Fryer B J, Jackson S E, Longerich H P.The design, operation and role of the laser-ablation microprobe coupled with an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LAM-ICP-MS) in the Earth sciences[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 1995, 33:303-312.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
赵令浩, 孙冬阳, 胡明月, 等.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱小激光斑束线扫描定量分析技术[J].分析化学, 2018, 46(6):931-937.
Google Scholar
Zhao L H, Sun D Y, Hu M Y, et al.Line scanning quantitative analysis by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with small laser beam[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(6):931-937.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Pollard A M, Heron C.Archaeological chemistry[M].Cambridge:The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1996:172.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Evans D, Müller W.Automated extraction of a five-year LA-ICP-MS trace element data set of ten common glass and carbonate reference materials:Long-term data quality, optimisation and laser cell homogeneity[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2018, 42(2):159-188. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12204
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
林怡娴, Rehren T.凉山州博物馆藏盐源征集费昂斯串珠的考察[J].四川文物, 2017(6):60-71.
Google Scholar
Lin Y X, Rehren T.A string of faience beads in the museum of Liangshan Yi autonomous prefecture[J].Sichuan Cultural Relics, 2017(6):60-71.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Tite M, Shortland A J.Production technology of faience and related early vitreous materials[M].Oxford School of Archaeology, 2008:38-42.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Turner W S.Studies in ancient glass and glassmaking processes.Part Ⅴ.Raw materials and melting processes[J].Journal of Society of Glass Technology, 1956(40):277-300.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
宁夏考古所, 彭阳县文物管理所.王大户与九龙山——北方青铜文化墓地[M].北京:文物出版社, 2016:703-736.
Google Scholar
Ningxia Institute of Archaeology, Pengyang County Heritage Management Institute.Excavation report on Wangdahu and Jiulongshan[M].Beijing:Cultural Relics Press, 2016:703-736.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Mullins P R.The archaeology of consumption[J]. Annual Review of Anthropology, 2011(40):133-144.
Google Scholar
|





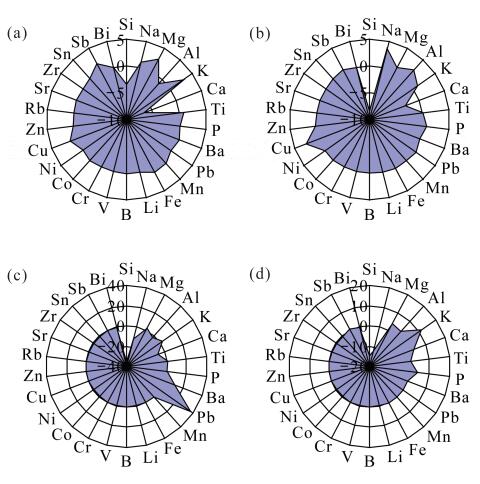

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: