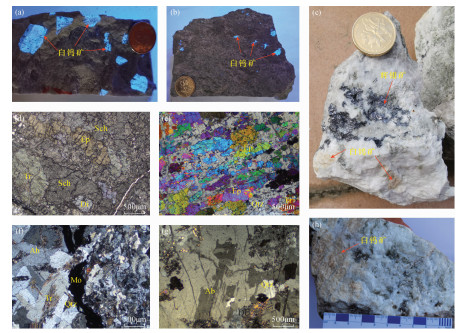
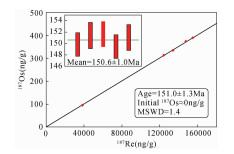
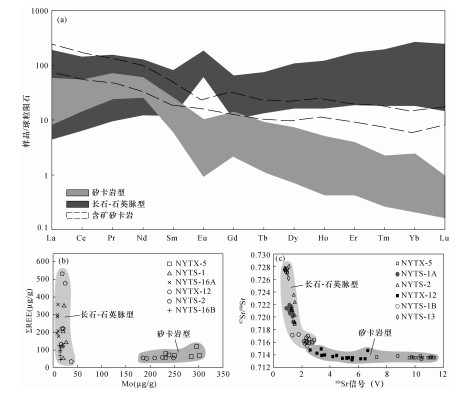
| [1] |
Lecumberri-Sanchez P, Vieira R, Heinrich C A, et al.Fluid-rock interaction is decisive for the formation of tungsten deposits[J].Geology, 2017, 45(7):579-582. doi: 10.1130/G38974.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Wu D, Liu Y, Chen C, et al.In-situ trace element and Sr isotopic compositions of mantle xenoliths constrain two-stage metasomatism beneath the Northern North China Craton[J].Lithos, 2017, 288-289:338-351. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.07.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Christensen J N, Halliday A N, Lee D C, et al.In situ Sr isotopic analysis by laser ablation[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 136:79-85.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Ramos F C, Wolff J A, Tollstrup D L.Measuring 87Sr/86Sr variations in minerals and groundmass from basalts using LA-MC-ICPMS[J].Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1-2):0-158.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Schmidberger S S, Simonetti A, Heaman L M, et al.Lu-Hf, in-situ Sr and Pb isotope and trace element systematics for mantle eclogites from the Diavik diamond mine:Evidence for Paleoproterozoic subduction beneath the Slave craton, Canada[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 254(1-2):0-68.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
杨岳衡, 吴福元, 谢烈文, 等.地质样品Sr同位素激光原位等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICP-MS)测定[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(12):331-341.
Google Scholar
Yang Y H, Wu F Y, Xie L W, et al.In-situ Sr isotopic measurement of natural geological samples by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(12):331-341.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Zhao X F, Zhou M F, Gao J F, et al.In situ Sr isotope analysis of apatite by LA-MC-ICPMS:Constraints on the evolution of ore fluids of the Yinachang Fe-Cu-REE deposit, Southwest China[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50(7):871-884. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0578-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
谭洪旗, 刘玉平.滇东南猛洞岩群构造环境:变质碎屑岩地球化学约束[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(7):1416-1432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.07.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Tan H Q, Liu Y P.Tectonic setting of the Mengdong Group Complex, Southeast Yunnan Province:Geochemical constraints from metasedimentary rocks[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(7):1416-1432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.07.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
张世涛, 冯明刚, 吕伟.滇东南南温河变质核杂岩解析[J].中国区域地质, 1998, 17(4):390-397.
Google Scholar
Zhang S T, Feng M G, Lü W.Analysis of the Nanwenhe metamorphic core complex in Southeastern Yunnan[J].Regional Geology of China, 1998, 17(4):390-397.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
谭洪旗, 刘玉平.滇东南猛洞岩群变质-变形研究及构造意义[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(1):15-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.01.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Tan H Q, Liu Y P.Metamorphism and deformation of the Mengdong group-complex in Southeastern Yunnan Province and their tectonic implications[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(1):15-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.01.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Xu B, Jiang S Y, Wang R, et al.Late Cretaceous granites from the giant Dulong Sn-polymetallic ore district in Yunnan Province, South China:Geochronology, geochemistry, mineral chemistry and Nd-Hf isotopic compositions[J].Lithos, 2015, 218-219:54-72. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.01.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Zhou X, Yu J H, O'Reilly S Y, et al.Sources of the Nanwenhe-Song Chay granitic complex (SW China-NE Vietnam) and its tectonic significance[J].Lithos, 2017, 290-291:76-93. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.07.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
刘玉平, 李正祥, 李惠民, 等.都龙锡锌矿床锡石和锆石U-Pb年代学:滇东南白垩纪大规模花岗岩成岩-成矿事件[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(5):967-976.
Google Scholar
Liu Y P, Li Z X, Li H M, et al.U-Pb geochronology of cassiterite and zircon from the Dulong Sn-Zn deposit:Evidence for Cretaceous large-scale granitic magmatism and mineralization events in Southeastern Yunnan Province, China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(5):967-976.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
冯佳睿, 毛景文, 裴荣富, 等.云南瓦渣钨矿区老君山花岗岩体的SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及成因探讨[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(3):845-857.
Google Scholar
Feng J R, Mao J W, Pei R F, et al.HRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and geochemical characteristics of Laojunshan granite intrusion from the Wazha tungsten deposit, Yunnan Province and their implications for petrogenesis[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(3):845-857.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
刘艳宾, 莫宣学, 张达, 等.滇东南老君山地区白垩世花岗岩的成因[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3271-3286.
Google Scholar
Liu Y B, Mo X X, Zhang D, et al.Petrogenesis of the Late Cretaceous granite discovered in the Laojunshan Region, Southeastern Yunnan Province[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(11):3271-3286.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
冯佳睿, 毛景文, 裴荣富, 等.滇东南老君山地区印支期成矿事件初探——以新寨锡矿床和南秧田钨矿床为例[J].矿床地质, 2011, 30(1):57-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Feng J R, Mao J W, Pei R F, et al.A tentative discussion on Indosinian ore-forming events in Laojunshan area of Southeastern Yunnan:A case study of Xinzhai tin deposit and Nanyangtian tungsten deposit[J].Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(1):57-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
李建康, 王登红, 李华芹, 等.云南老君山矿集区的晚侏罗世-早白垩世成矿事件[J].地球科学, 2013, 38(5):1023-1036.
Google Scholar
Li J K, Wang D H, Li H Q, et al.Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous mineralization in the Laojunshan ore concentration area, Yunnan Province[J].Earth Science, 2013, 38(5):1023-1036.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al.Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Li C, Zhou L, Zhao Z, et al.In-situ Sr isotopic measure-ment of scheelite using fs-LA-MC-ICPMS[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.03.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
李超, 杨雪, 赵鸿, 等.pg-ng级Os同位素热表面电离质谱高精度分析测试技术[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
Li C, Yang X, Zhao H, et al.High precise isotopic measurements of pg-ng Os by negative ion thermal ionization mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
冯佳睿, 毛景文, 裴荣富, 等.滇东南老君山南秧田钨矿床的成矿流体和成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 2011, 30(3):403-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.03.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Feng J R, Mao J W, Pei R F, et al.Ore-forming fluids and metallogenesis of Nanyangtian tungsten deposit in Laojunshan, Southeastern Yunnan Province[J].Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(3):403-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.03.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
曾志刚, 李朝阳, 刘玉平, 等.老君山成矿区变质成因夕卡岩的地质地球化学特征[J].矿物学报, 1999, 19(1):48-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1999.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zeng Z G, Li C Y, Liu Y P, et al.Geology and geochemistry of metamorphogenic skarn from Laojunshan metallogenic province[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1999, 19(1):48-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1999.01.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
刘玉平, 李正祥, 叶霖, 等.滇东南老君山矿集区钨成矿作用Ar-Ar年代学[J].矿物学报, 2011(增刊1):617-618.
Google Scholar
Liu Y P, Li Z X, Ye L, et al.Ar-Ar chronology of tungsten mineralization in Laojunshan ore concentration area in Southeast Yunnan[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011(Supplement 1):617-618.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
谭洪旗, 刘玉平, 叶霖, 等.滇东南南秧田钨锡矿床金云母40Ar-39Ar定年及意义[J].矿物学报, 2011(增刊1):639-640.
Google Scholar
Tan H Q, Liu Y P, Ye L, et al.40Ar-39Ar dating of metallomica and its significance from the South Yangtian tungsten-tin deposit in Southeast Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2011(Supplement 1):639-640.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
曾志刚, 李朝阳, 刘玉平, 等.滇东南南秧田两种不同成因类型白钨矿的稀土元素地球化学特征[J].地质地球化学, 1998, 26(2):34-38.
Google Scholar
Zeng Z G, Li C Y, Liu Y P, et al.REE geochemistry of scheelite of two genetic types from Nanyangtian, Southeastern Yunnan[J].Geological Geochemistry, 1998, 26(2):34-38.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
谭筱虹, 李志均, 杜再飞.滇东南南温河地区深变质岩中似层状白钨矿[J].云南地质, 2010, 29(4):382-387. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2010.04.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
Tan Y H, Li Z J, Du Z F.On the stratoid scheelite of Kata-Metamorphite in Nanwenhe area of SE Yunnan[J].Yunnan Geology, 2010, 29(4):382-387. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2010.04.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Sun K K, Chen B.Trace elements and Sr-Nd isotopes of scheelite:Implications for the W-Cu-Mo polymetallic mineralization of the Shimensi Deposit, South China[J].American Mineralogist, 2017, 102:1114-1128.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Zhao W, Zhou M, Williams-Jones A, et al.Constraints on the uptake of REE by scheelite in the Baoshan tungsten skarn deposit, South China[J].Chemical Geology, 2018, 477:123-136. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.12.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
任云生, 赵华雷, 雷恩, 等.延边杨金沟大型钨矿床白钨矿的微量和稀土元素地球化学特征与矿床成因[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(12):3720-3726.
Google Scholar
Ren Y S, Zhao H L, Lei E, et al.Trace element and rare earth element geochemistry of the scheelite and ore genesis of the Yangjingou large scheelite deposit in Yanbian area, Northeastern China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(12):3720-3726.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
刘善宝, 刘战庆, 王成辉, 等.赣东北朱溪超大型钨矿床中白钨矿的稀土、微量元素地球化学特征及其Sm-Nd定年[J].地学前缘, 2017, 24(5):17-30.
Google Scholar
Liu S B, Liu Z Q, Wang C H, et al.Geochemical characteristics of REEs and trace elements and Sm-Nd dating of scheelite from the Zhuxi giant tungsten deposit in Northeast Jiangxi[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(5):17-30.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
聂利青, 周涛发, 张千明, 等.安徽东顾山钨矿床白钨矿主微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素特征及其对成矿作用的指示[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(11):3518-3530.
Google Scholar
Nie L Q, Zhou T F, Zhang Q M, et al.Trace elements and Sr-Nd isotopes of scheelites:Implications for the skarn tungsten mineralization of the Donggushan deposit, Anhui Province, China[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(11):3518-3530.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
丁腾, 马东升, 陆建军, 等.湘南黄沙坪多金属矿床花岗斑岩的矿物化学及其对矽卡岩白钨矿成矿的指示意义[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(3):716-728.
Google Scholar
Ding T, Ma D S, Lu J J, et al.Mineral geochemistry of granite porphyry in Huangshaping pollymetallic deposit, Southern Hunan Province, and its implications for metallogensis of skarn scheelite mineralization[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(3):716-728.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Ding T, Ma D, Lu J, et al.Garnet and scheelite as indica-tors of multi-stage tungsten mineralization in the Huangshaping deposit, Southern Hunan Province, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 94:193-211. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.01.029
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
闫国强, 丁俊, 黄勇, 等.西藏努日白钨矿床微量和稀土元素地球化学特征——对成矿流体与矿床成因的指示[J].矿物学报, 2015, 35(1):87-94.
Google Scholar
Yan G Q, Ding J, Huang Y, et al.Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements and trace elements in the Nuri scheelite deposit, Tibet, China——Indications for ore-forming fluid and deposit genesis[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(1):87-94.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Song G, Qin K, Li G, et al.Scheelite elemental and isotopic signatures:Implications for the genesis of skarn-type W-Mo deposits in the Chizhou area, Anhui Province, Eastern China[J].American Mineralogist, 2014, 99(2-3):303-317. doi: 10.2138/am.2014.4431
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
洪为, 张作衡, 蒋宗胜, 等.新疆西天山查岗诺尔铁矿床磁铁矿和石榴石微量元素特征及其对矿床成因的制约[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(7):2089-2102.
Google Scholar
Hong W, Zhang Z H, Jiang Z S, et al.Magnetite and garnet trace element characteristics from the Chagangnuoer iron deposit in the Western Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, NW China:Constrain for ore genesis[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 28(7):2089-2102.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Brugger J, Lahaye Y, Costa S, et al.Inhomogeneous dis-tribution of REE in scheelite and dynamics of archaean hydrothermal systems (Mt.Charlotte and Drysdale gold deposits, Western Australia)[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 139(3):251-264. doi: 10.1007/s004100000135
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Brugger J, Maas R, Lahaye Y, et al.Origins of Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic variations in single scheelite grains from Archaean gold deposits, Western Australia[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 182(2):203-225.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
王冠, 杜谷, 刘书生, 等.电感耦合等离子体质谱法对白钨矿中稀土元素的准确测定——以云南麻栗坡南秧田白钨矿床的成因探讨为例[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):1050-1057. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang G, Du G, Liu S S, et al.Accurate determination of rare earth elements in scheelite using high resolution-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry-An instance of Nanyangtian scheelite mining, Malipo, Yunnan[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):1050-1057. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.06.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Ghaderi M, Palin J M, Campbell I H, et al.Rare earth element systematics in scheelite from hydrothermal gold deposits in the Kalgoorlie-Norseman Region, Western Australia[J]. Economy Geology, 1999, 94:423-438. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.94.3.423
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
蔡倩茹, 燕永锋, 杨光树, 等.滇东南南秧田矽卡岩型钨矿床成矿演化[J].矿床地质, 2018, 37(1):116-136.
Google Scholar
Cai Q R, Yan Y F, Yang G S, et al.Evolution of scheelite skarn mineralization at Nanyangtian deposit, Southeast Yunnan Province[J].Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(1):116-136.
Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
Yan D P, Zhou M F, Wang C Y, et al.Structural and geochronological constraints on the tectonic evolution of the Dulong-Song Chay tectonic dome in Yunnan Province, SW China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 28(4-6):332-353. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.10.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
张斌辉, 丁俊, 任光明, 等.云南马关老君山花岗岩的年代学、地球化学特征及地质意义[J].地质学报, 2012, 86(4):587-601. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang B H, Ding J, Ren G M, et al.Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Laojunshan granites in Maguan County, Yunnan Province, and its geological implications[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(4):587-601. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





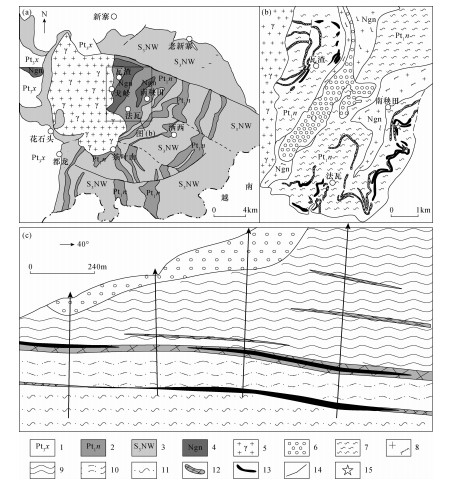

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: