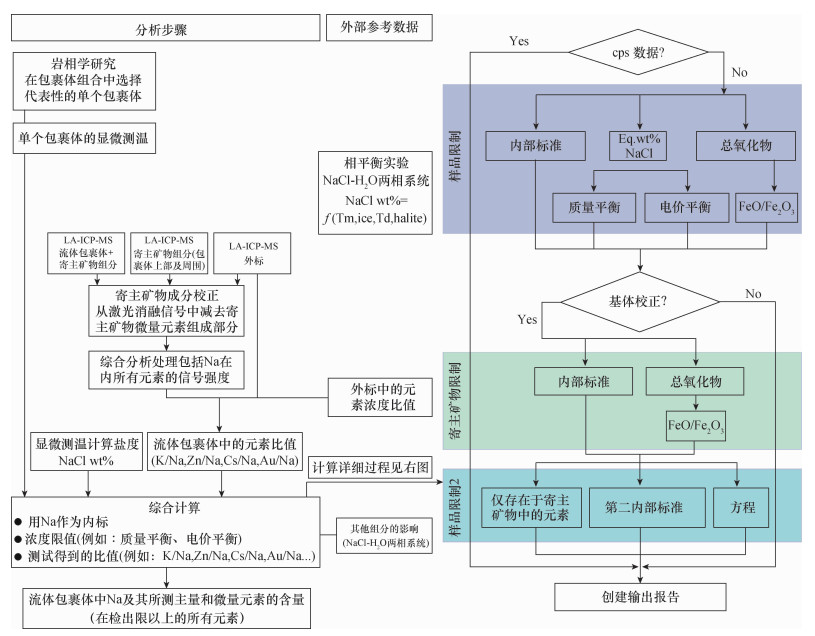
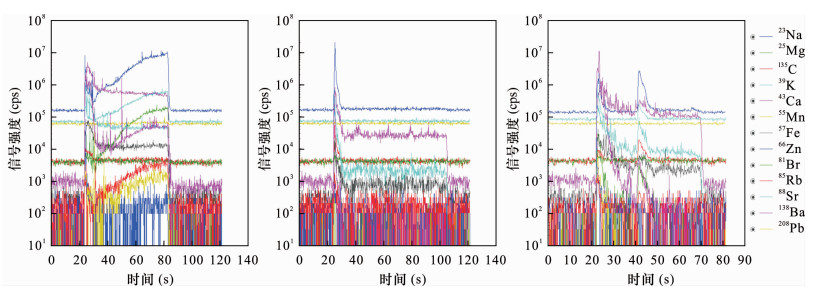
| [1] |
Audétat A, Günther D, Heinrich C A.Formation of a magmatic-hydrothermal ore deposit:Insights with LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions[J].Science, 1998, 279:2091-2094. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5359.2091
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Audétat A, Günther D, Heinrich C A.Causes for large-scale metal zonation around mineralized plutins:Fluid inclusion LA-ICP-MS evidence from the Mole Granite[J].Australia Economic Geology, 2000, 95(8):1563-1581. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.95.8.1563
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Audétat A, Günther D, Heinrich C A.Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution in a fractionating granite:A microchemical study of the Sn-W-F-mineralized Mole Granite (Austrilia)[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(19):3373-3393. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00428-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Zou H, Fang Y, Zhang S T, et al.The source of Fengjia and Langxi barite-fluorite deposits in Southeastern Sichuan, China:Evidence from rare earth elements and S, Sr, and Sm-Nd isotopic data[J].Geological Journal, 2017, 52:470-488. doi: 10.1002/gj.2779
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Zou H, Zhang S T, Chen A Q, et al.Hydrothermal fluid sources of the Fengjia barite-fluorite deposit in Southeast Sichuan, China:Evidence from fluid inclusions and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes[J].Resource Geology, 2016, 66:24-36. doi: 10.1111/rge.12084
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Chicharro E, Boiron M C, López-García J Á, et al.Origin, ore forming fluid evolution and timing of the Logrosán Sn-(W) ore deposits (Central Iberian Zone, Spain)[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72(1):896-913.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Seo J H, Guillong M, Aerts M, et al.Microanalysis of S, Cl, and Br in fluid inclusions by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology, 2011, 284(1-2):35-44.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Zhe M, Hu J Z, Song Y, et al.Fluid inclusions and hydrogen, oxygen, and lead isotopes of the antuoling molybdenum deposit, Northern Taihang Mountains, China[J].Resource Geology, 2017, 67(4):399-413. doi: 10.1111/rge.12135
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Kang M, Yuan Y, Yue C C, et al.Fluid inclusion and isotope characteristics of the Xishanwanyangchang silver polymetallic deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J].Geological Journal, 2018, 53:303-318. doi: 10.1002/gj.3189
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
倪培, 范宏瑞, 丁俊英.流体包裹体研究进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.01.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ni P, Fan H R, Ding J Y.Progress in fluid inclusions[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(1):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.01.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
孙小虹, 胡明月, 刘成林, 等.激光剥蚀ICP-MS法测定盐类矿物单个流体包裹体的成分[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(2):235-241.
Google Scholar
Sun X H, Hu M Y, Liu C L, et al.Composition determination of single fluid inclusions in salt minerals by laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(2):235-241.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Mavrogenes J A, Bodnar R J, Anderson A J.Assessment of the uncertainties and limitations of quantitative elemental analysis of individual fluid inclusions using synchrotron X-ray fluorescence (SXRF)[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(19):3987-3995. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00261-W
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Kurosawa M, Shimano S, Ishii S, et al.Quantitative trace element analysis of single fluid inclusions by proton-induced X-ray emission (PIXE):Application to fluid inclusions in hydrothermal quartz[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(22):4337-4352. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00378-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
王莉娟, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等.内蒙古大井锡多金属矿床流体成矿作用研究:单个流体包裹体组分LA-ICP-MS分析证据[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(10):1203-1210. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.10.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang L J, Wang Y W, Wang J B, et al.Study on fluid mineralization of Dajing tin polymetallic deposit in Iinner Mongolia:Evidence from LA-ICP-MS analysis of single fluid inclusion component[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(10):1203-1210. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.10.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
卢焕章, 郭迪江.流体包裹体研究的进展和方向[J].地质论评, 2000, 46(4):385-392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.04.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Lu H Z, Guo D J.Progress and trends of research on fluid inclusions[J].Geological Review, 2000, 46(4):385-392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.04.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Pettke T, Oberli F, Audétat A, et al.Recent develop-ments in element concentration and isotope ratio analysis of individual fluid inclusions by laser ablation single and multiple collector ICP-MS[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 44:10-38. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.11.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
孙贺, 肖益林.流体包裹体研究:进展、地质应用及展望[J].地球科学进展, 2009, 24(10):1105-1121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.10.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Sun H, Xiao Y L.Fluid inclusions:Latest development, geological applications and prospect[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2009, 24(10):1105-1121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2009.10.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Longerich A P, Jackson S E, Canther D.Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11(9):899-904. doi: 10.1039/JA9961100899
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Pettke T, Oberli F, Audétat A, et al.Recent developments in element concentration and isotope ratio analysis of individual fluid inclusions by laser ablation single and multiple collector ICP-MS[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 44:10-38. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.11.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 张道涵, 等.单个流体包裹体成分LA-ICPMS分析与矿床学应用进展[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(10):3832-3840. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.10.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
Fu L B, Wei J H, Zhang D H, et al.A review of LA-ICPMS analysis for individual fluid inclusions and its applications in ore deposits[J].Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(10):3832-3840. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2015.10.037
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Tsui T F.Laser Microprobe Analysis of Fluid Inclusions in Quartz[D].Massachusetts: Harvard University, 1976: 1-156.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Tsui T F, Holland H D.Analysis of fluid inclusions by laser microprobe[J].Economic Geology, 1979, 74(7):1647-1653. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.74.7.1647
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Ulrich T, Günther D, Heinrich C A.Gold concentrations of magmatic brines and the metal budget of porphyry copper deposits[J].Nature, 1999, 399(6737):676-679. doi: 10.1038/21406
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Heinrich C A, Günther D, Audétat A, et al.Metal fractionation between magmatic brine and vapor, determined by microanalysis of fluid inclusions[J].Geology, 1999, 27(8):755-758. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0755:MFBMBA>2.3.CO;2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Shepherd T J, Chenery S R.Laser ablation ICP-MS elemental analysis of individual fluid inclusions:An evaluation study[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(19):3997-4007. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00294-A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Ghazi A M, McCandless T E, Vanko D A, et al.New quantitative approach in trace elemental analysis of single fluid inclusions:Applications of laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11(9):667-674. doi: 10.1039/ja9961100667
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Moissette A, Shepherd T J, Chenery S R.Calibration strategies for the elemental analysis of individual aqueous fluid inclusions by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11(3):177-185. doi: 10.1039/ja9961100177
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Günther D, Audétat A, Frischknecht R.Quantitative analysis of major, minor and trace elements in fluid inclusions using laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1998, 13(4):263-270. doi: 10.1039/A707372K
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
McCandless T E, Lajack D J, Ruiz J, et al.Trace element determination of single fluid inclusions in quartz by laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Geostandards Newsletter, 1997, 21(2):279-287. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.1997.tb00676.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Shepherd T J, Ayora C, Cendón D I, et al.Quantitative solute analysis of single fluid inclusions in halite by LA-ICP-MS and cryo-SEM-EDS:Complementary microbeam techniques[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 1998, 10(6):1097-1108. doi: 10.1127/ejm/10/6/1097
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Loucks R R, Mavrogenes J A.Gold solubility in supercritical hydrothermal brines measured in synthetic fluid inclusions[J].Science, 1999, 284(5423):2159-2163. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5423.2159
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Schafer B, Frischknecht R, Günther D, et al.Determination of trace-element partitioning between fluid and melt using LA-ICP-MS analysis of synthetic fluid inclusions in glass[J].European Journal of Mineralogy, 1999, 11(3):415-426. doi: 10.1127/ejm/11/3/0415
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
吴石头, 许春雪, Klaus Simon, 等.193nm ArF准分子激光系统对LA-ICP-MS分析中不同基体的剥蚀行为和剥蚀速率探究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):451-459.
Google Scholar
Wu S T, Xu C X, Klaus S, et al.Study on ablation behaviors and ablation rates of a 193nm ArF excimer laser system for selected substrates in LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):451-459.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
周亮亮, 魏均启, 王芳, 等.LA-ICP-MS工作参数优化及在锆石U-Pb定年分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4):350-359.
Google Scholar
Zhou L L, Wei J Q, Wang F, et al.Optimization of the working parameters of LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(4):350-359.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
周文喜, 王华建, 付勇, 等.基于LA-ICP-MS多元素成像技术的早寒武世磷结核成因研究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(2):97-106.
Google Scholar
Zhou W X, Wang H J, Fu Y, et al.Study on the formation mechanism of phosphate nodules in the Early Cambrian period using LA-ICP-MS multi-element imaging technology[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(2):97-106.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
王家松, 许雅雯, 彭丽娜, 等.应用激光拉曼光谱研究锆石LA-ICP-MSU-Pb定年中的α通量基体效应[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):458-467.
Google Scholar
Wang J S, Xu Y W, Peng L N, et al.Laser-Raman spectroscopic study and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of zircons from the Badaling granitic complex[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5):458-467.
Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
蓝廷广, 胡瑞忠, 范宏瑞, 等.流体包裹体及石英LA-ICP-MS分析方法的建立及其在矿床学中的应用[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(10):3239-3262.
Google Scholar
Lan T G, Hu R Z, Fan H R, et al.In-situ analysis of major and trace elements in fluid inclusion and quartz:LA-ICP-MS method and applications to ore deposits[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(10):3239-3262.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Huang B, Yan Y, Piper J D A, et al.Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleogeography of the East Asian blocks during Late Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic times[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186:8-36. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Pettke T, Oberli F, Audétat A, et al.Recent developments in element concentration and isotope ratio analysis of individual fluid inclusions by laser ablation single and multiple collector ICP-MS[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 44:10-38. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.11.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Iain M S, Anthony E W, Katherine M A, et al.Source of fluids forming distal Zn-Pb-Ag skarns:Evidence from laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry analysis of fluid inclusions from El Mochito, Honduras[J].Geology, 2008, 36(12):947-950. doi: 10.1130/G25214A.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
Anthony E W, Iain M S, Katherine M A, et al.The genesis of distal zinc skarns:Evidence from the mochito deposit, Honduras[J].Economic Geology, 2010, 105(8):1411-1440. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.105.8.1411
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
Shu Q H, Lai Y, Sun Y, et al.Ore genesis and hydrothermal evolution of the baiyinnuo'er zinc-lead skarn deposit, Northeast China:Evidence from isotopes (S, Pb) and fluid inclusions[J].Economic Geology, 2013, 108(4):835-860. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.4.835
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
Tobias F, Thomas W, Markus W, et al.Fluid mixing forms basement-hosted Pb-Zn deposits:Insight from metal and halogen geochemistry of individual fluid inclusions[J].Geology, 2013, 41(6):679-682. doi: 10.1130/G34092.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
Li W, Audetat A, Zhang J.The role of evaporites in the formation of magnetite-apatite deposits along the Middle and Lower Yangtze River, China:Evidence from LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 67:264-278. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.12.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
Zhang Y, Shao Y, Wu C, et al.LA-ICP-MS trace element geochemistry of garnets:Constraints on hydrothermal fluid evolution and genesis of the Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au deposit, Eastern China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 86:426-439. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
Levresse G, Bouabdellah M, Gasquet D, et al.Basinal brines at the origin of the imiter Ag-Hg deposit (Anti-Atlas, Morocco):Evidence from LA-ICP-MS data on fluid inclusions, Halogen signatures, and stable isotopes (H, C, O)[J].Economic Geology, 2016, 112(5):1753-1781.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
Huang B, Yan Y, Piper J D A, et al.Paleomagnetic constraints on the paleogeography of the East Asian blocks during Late Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic times[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186:8-36. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
Guillong M, Meier D L, Allan M M, et al.SILLS: A MATLAB-based Program for the Reduction of Laser Ablation ICP-MS Data of Homogeneous Materials and Inclusions[M]//Sylvester P.Laser Ablation ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current Practices and Outstanding Issues.Quebec: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2008: 328-333.
Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
Longerich A P, Jackson S E, Canther D.Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11(9):899-904. doi: 10.1039/JA9961100899
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
Halter W E, Pettke T, Heinrich C A, et al.Major to trace element analysis of melt inclusions by laser-ablation ICP-MS:Methods of quantification[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 183:63-86. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00372-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
Allan M M, Yardley B, Forbes L J, et al.Validation of LA-ICP-MS fluid inclusion analysis with synthetic fluid inclusions[J].American Mineralogist, 2005, 90(11/12):1767-1775.
Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Luo Y, Gao S, Longerich H P, et al.The uncertainty budget of the multi-element analysis of glasses using LA-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22:122-130. doi: 10.1039/B608010C
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
于倩.石盐中单个流体包裹体LA-ICP-MS测试方法研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1015387230.htm
Google Scholar
Yu Q.Study on the Analysis Method of LA-ICP-MS for the Individual Fluid Inclusions Hosted in Halite[D].Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
李晓春, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等.单个流体包裹体LA-ICP-MS成分分析及在矿床学中的应用[J].矿床地质, 2010, 29(6):1017-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.06.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li X C, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al.An analysis of the individual fluid inclusion by LA-ICP-MS and its application to ore deposits[J].Mineral Deposits, 2010, 29(6):1017-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.06.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
Pettke T.Analytical Protocols for Element Concentration and Isotope Ratio Measurements in Fluid Inclusions by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS[M]//Sylvester P.Laser Ablation-ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current Practices and Outstanding Issues.Vancouver: Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2008: 189-218.
Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
Guillong M, Hametner K, Reusser E, et al.Preliminary characterisation of new glass reference materials (GSA-1G, GSC-1G, GSD-1G and GSE-1G) by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry using 193nm, 213nm and 266nm wavelengths[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2005, 29(3):315-331. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00903.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
Bodnar R J.Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57:683-684. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(93)90378-A
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
Kendrick M A, Phillips D.New constraints on the release of noble gases during in vacuo crushing and application to scapolite Br-Cl-I and 40Ar/39Ar age determinations[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(19), 5673-5692. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.06.032
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
Kendrick M A.High precision Cl, Br and I determina-tions in mineral standards using the noble gas method[J].Chemical Geology, 2012, 292-293:116-126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.11.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
Hammerli J, Rusk B, Spandler C, et al.In situ quantification of Br and Cl in minerals and fluid inclusions by LA-ICP-MS:A powerful tool to identify fluid sources[J].Chemical Geology, 2013, 337/338:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.12.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
Stoffell B, Wilkinson J J, Jeffries T E M, et al.Transport and deposition in hydrothermal veins revealed by 213nm UV laser ablation microanalysis of single fluid inclusions[J].American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(6):533-557. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.6.533
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [62] |
Leisen M, Dubessy J, Boiron M.Improvement of the determination of element concentrations in quartz-hosted fluid inclusions by LA-ICP-MS and Pitzer thermodynamic modeling of ice melting temperature[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 90:110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.04.040
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [63] |
Pettke T, Oberli F, Heinrich C A.The magma and metal source of giant porphyry-type ore deposits, based on lead isotope microanalysis of individual fluid inclusions[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 296(3/4):267-277.
Google Scholar
|
| [64] |
Grubbs F E.Procedures for detecting outlying observations in samples[J].Techno-Metrics, 1969, 11:1-21. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1969.10490657
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [65] |
Frezzotti M L, Tecce F, Casagli A.Raman spectroscopy for fluid inclusion analysis[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 112:1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.09.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [66] |
Guillong M, Latkoczy C, Seo J H, et al.Determination of sulfur in fluid inclusions by laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23(12):1581-1589. doi: 10.1039/b807383j
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [67] |
Schlegel T U, Wälle M, Steele M M, et al.Accurate and precise quantification of major and trace element compositions of calcic-sodic fluid inclusions by combined microthermometry and LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Chemical Geology, 2012, 334:144-153. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.10.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [68] |
胡圣虹, 胡兆初, 刘勇胜, 等.单个流体包裹体元素化学组成分析新技术——激光烧蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)[J].地学前缘, 2001, 8(4):434-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.04.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
Hu S H, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, et al.New techniques of major and minor elemental analysis in individual fluid inclusion-Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS)[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(4):434-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.04.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





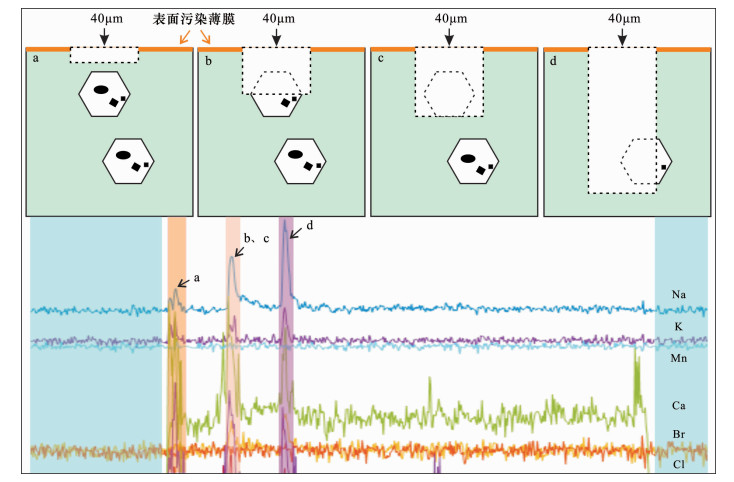

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: