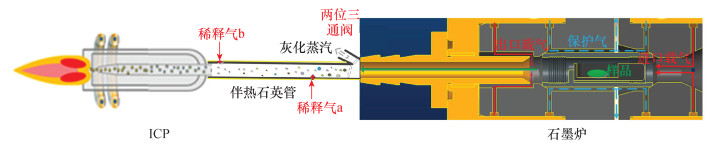
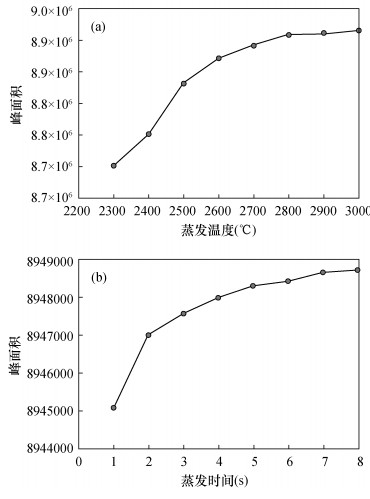
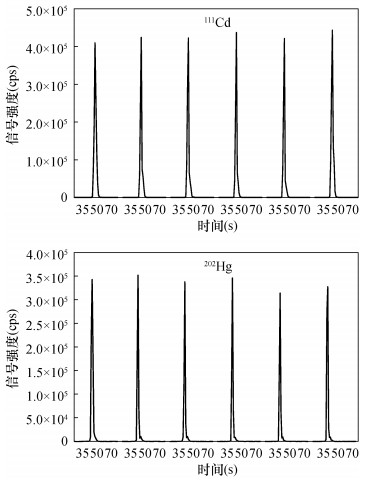
| [1] |
Legret M, Pagotto C.Heavy metal deposition and soil pollution along two major rural highways[J]. Environmental Technology, 2006, 27(3):247-254. doi: 10.1080/09593332708618641
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
蔡美芳, 李开明, 谢丹平, 等.我国耕地土壤重金属污染现状与防治对策研究[J].环境科学与技术, 2014, 37(2):223-230.
Google Scholar
Cai M F, Li K M, Xie D P, et al.The status and protection strategy of farmland soils polluted by heavy metals[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 37(2):223-230.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
骆永明.中国土壤环境污染态势及预防、控制和修复策略[J].环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(12):27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
Luo Y M.Trends in soil environmental pollution and the prevention-controlling-remediation strategies in China[J].Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2009, 31(12):27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.12.021
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
王玉军, 欧名豪.徐州农田土壤养分和重金属含量与分布研究[J].土壤学报, 2017, 54(6):128-140.
Google Scholar
Wang Y J, Ou M H.Contents and distribution of soil nutrients and heavy metal elements in farmlands of Xuzhou[J].Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2017, 54(6):128-140.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Rahman M U, Kazi T G, Shaikh H, et al.Fractionation of manganese in soil samples collected from the Lakhra Coal Field in Pakistan using two modes of atomic absorption spectrometry[J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 39(6):258-263.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
李小莉, 张勤.粉末压片-X射线荧光光谱法测定土壤、水系沉积物和岩石样品中15种稀土元素[J].冶金分析, 2013, 33(7):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.07.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li X L, Zhang Q.Determination of fifteen rare earth elements in soil, stream sediment and rock samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with pressed powder pellet[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(7):35-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.07.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
殷惠民, 杜祯宇, 李玉武, 等.能量色散X射线荧光光谱仪和简化的基体效应校正模型测定土壤、沉积物中重金属元素[J].冶金分析, 2018, 38(4):1-10.
Google Scholar
Yin H M, Du Z Y, Li Y W, et al.Determination of heavy metal elements in soil and sediment by energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer with simplified matrix effect correction model[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2018, 38(4):1-10.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
凤海元, 时晓露, 黄勤.微波消解-氢化物发生原子荧光光谱法测定茶园土壤中的铅[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(1):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.01.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
Feng H Y, Shi X L, Huang Q.Determination of lead in tea garden soil by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry with microwave digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(1):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2013.01.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
李晋荣, 党晋华, 宋姗娟, 等.双道原子荧光光谱法测定土壤中汞[J].中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(3):1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.03.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li J R, Dang J H, Song S J, et al.Determination of mercury in soil by double-channel atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(3):1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.03.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
何锦强.原子吸收光谱法测定土壤重金属含量实验[J].能源与环境, 2018, 147(2):87-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2018.02.042
CrossRef Google Scholar
He J Q.Determination of heavy metal contents in soil by atomic absorption spectrometry[J].Energy and Environment, 2018, 147(2):87-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2018.02.042
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
邓琴, 吴迪, 秦樊鑫, 等.岩溶铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征[J].中国岩溶, 2017, 36(2):248-254.
Google Scholar
Deng Q, Wu D, Qin F X, et al.Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in soil of lead-zinc mining in karst areas[J].Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(2):248-254.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
吴峥, 熊英, 王龙山.自制氢化物发生系统与电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法联用测定土壤和水系沉积物中的砷锑铋[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5):533-538.
Google Scholar
Wu Z, Xiong Y, Wang L S.Determination of As, Sb and Bi in soil and stream sediment by a self developed hydride generation system coupled with inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5):533-538.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
何恬叶, 张颖红, 胡子文.微波消解ICP-OES法测定土壤样品中22种元素[J].分析试验室, 2018, 37(1):84-87.
Google Scholar
He T Y, Zhang Y H, Hu Z W.Determination of 22 elements in soil by ICP-OES with microwave digestion[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2018, 37(1):84-87.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
乐淑葵, 段永梅.电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)测定土壤中的重金属元素[J].中国无机分析化学, 2015, 5(3):16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Le S K, Duan Y M.Determination of heavy metal elements in soil by ICP-MS[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 5(3):16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2015.03.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Ohno T, Muramatsu Y, Shikamori Y, et al.Determination of ultratrace 129I in soil samples by triple quadrupole ICP-MS and its application to Fukushima soil samples[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2018, 28(8):1283-1287.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
吴永盛, 徐金龙, 庄姜云, 等.微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法同时测定土壤中8种重金属元素[J].中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(4):16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.04.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wu Y S, Xu J L, Zhuang J Y, et al.Simultaneous determination of eight heavy metals in soil by microwave digestion-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(4):16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2017.04.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Wu C H, Jiang S J, Sahayam A C.Using electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to determine S, As, Cd, Hg, and Pb in fuels[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2018, 147(10):115-120.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Scheffler G L, Makonnen Y, Pozebon D, et al.Solid sampling analysis of Mg alloy using electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(10):2041-2045. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00203C
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Borno F, Richter S, Deiting D, et al.Direct multi-element analysis of plastic materials via solid sampling electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(5):1064-1071. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00442F
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Albena D, Peter B, Juergen H.Calibration possibilities and modifier use in ETV-ICP-OES determination of trace and minor elements in plant materials[J].Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 394(5):1485-1495.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Yilmaz H C, Hattendorf B.A comparison of signal sup-pression and particle size distributions for ns- and fs-LA for metallic samples by LA-ETV-ICPMS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(10):1980-1987. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00176B
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
毛雪飞.固体进样电热蒸发原子阱捕获光谱技术快速测定农产品中镉和汞的研究[D].北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015.http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y2787807
Google Scholar
Mao X F.Study on Determination of Cadmium and Mercury in Agri-foods by Solid Sampling Electrothermal Vaporization Spectrometry Using Atomic Traps[D].Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Silva J S, Henn A S, Dressler V L, et al.Feasibility of rare earth element determination in low concentration in crude oil:Direct sampling electrothermal vaporization-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(11):7064-7071. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01460
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Hsu W H, Jiang S J, Sahayam A C.Determination of Pd, Rh, Pt, Au in road dust by electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with slurry sampling[J].Analytical Chimica Acta, 2013, 794(17):15-19.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Sadiq N, Huang L, Kaveh F, et al.Solid sampling ETV-ICPOES coupled to a nebulization/pre-evaporation system for direct elemental analysis of glutinous rice by external calibration with standard solutions[J].Food Chemestry, 2017, 237(15):1-6.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
de Gois J S D, Pereira É R, Welz B, et al.Simultaneous deter-mination of bromine and chlorine in coal using electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and direct solid sample analysis[J].Analytical Chimica Acta, 2014, 852(10):82-87.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
王樊, 何蔓, 陈贝贝, 等.二氧化钛涂覆中空纤维膜微萃取-电热蒸发-电感耦合等离子体质谱分析环境样品中痕量重金属[J].分析化学, 2015, 43(9):1313-1321.
Google Scholar
Wang F, He M, Chen B B, et al.TiO2-coated hollow fiber micro-extraction combined with electrothermal vaporization-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for trace elements analysis in environmental water samples[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(9):1313-1321.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Henn A S, Flores E M M, Dressler V L, et al.Feasibility of As, Sb, Se and Te determination in coal by solid sampling electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2018, 33(8):1384-1393. doi: 10.1039/C8JA00129D
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
陈江, 姚玉鑫, 费勇, 等.微波消解等离子体发射光谱和石墨炉原子吸收光谱法联合测定土壤中多元素[J].岩矿测试, 2009, 28(1):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Chen J, Yao Y X, Fei Y, et al.Determination of multi-elements in soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry with microwave digestion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(1):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.01.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Lum T S, Leung K.Strategies to overcome spectral interference in ICP-MS detection[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(5):1078-1088. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00497G
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Frank V, Martín R, Luc M.Electrothermal vaporisation ICP-mass spectrometry (ETV-ICP-MS) for the determination and speciation of trace elements in solid samples-A review of real-life applications from the author's lab[J].Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2002, 374(2):188-195.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Hanć A, Piechalak A, Tomaszewska B, et al.Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry in quantitative analysis and imaging of plant's thin sections[J].International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 2014, 363(1):16-22.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Kaveh F, Beauchemin D.Improvement of the capabilities of solid sampling ETV-ICP-OES by coupling ETV to a nebulisation/pre-evaporation system[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(8):1371-1377. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00041B
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Zhang Y F, Hu B.Determination of some refractory elements and Pb by fluorination assisted electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with platform and wall vaporization[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 1(6):163-169.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Zhang S, He M, Yin Z, et al.Elemental fractionation and matrix effect in laser sampling based spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(2):358-382. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00273G
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
李世珍, 朱祥坤, 吴龙华, 等.干法灰化和湿法消解植物样品的铜锌铁同位素测定对比研究[J].地球学报, 2011, 32(6):754-760. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.06.14
CrossRef Google Scholar
Li S Z, Zhu X K, Wu L H, et al.A comparative study of plant sample preparation by dry ashing and wet digestion for isotopic determination of Cu, Zn and Fe[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(6):754-760. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2011.06.14
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
刘珂珂, 霍现宽, 褚艳红, 等.超声辅助-王水提取法在测定土壤中重金属元素的应用[J].冶金分析, 2019, 39(1):48-53.
Google Scholar
Liu K K, Huo X K, Chu Y H, et al.Application of ultrasonic-assisted aqua regia extraction in the determination of heavy metal elements in soil[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2019, 39(1):48-53.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
黄楚楚, 李青, 张国霞, 等.上海市区大气颗粒物(PM2.5)中铅、镉的分析测定和污染特征研究[J].分析化学, 2016, 44(7):1047-1052.
Google Scholar
Huang C C, Li Q, Zhang G X, et al.Analysis of pollution characteristics of cadmium and lead in atmospheric particulates(PM2.5) of Shanghai downtown[J].Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 44(7):1047-1052.
Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Diegor W, Longerich H, Abrajano T, et al.Applicability of a high pressure digestion technique to the analysis of sediment and soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Analytical Chimica Acta, 2001, 431(2):195-207. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01339-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
周雪明, 郑乃嘉, 李英红, 等.2011~2012北京大气PM2.5中重金属的污染特征与来源分析[J].环境科学, 2017, 38(10):4054-4060.
Google Scholar
Zhou X M, Zheng N J, Li Y H, et al.Chemical characteristics and sources of heavy metals in fine particles in Beijing in 2011-2012[J].Environmental Science, 2017, 38(10):4054-4060.
Google Scholar
|





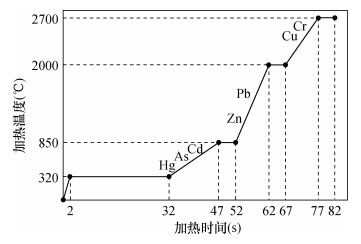

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: