| [1] |
杨常青, 张双双, 吴楠, 等.微波消解-氢化物发生原子荧光光谱法和质谱法测定高有机质无烟煤中汞砷的可行性研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):481-487.
Google Scholar
Yang C Q, Zhang S S, Wu N, et al. Feasibility study on content determination of mercury and arsenic in high organic anthracite by microwave digestion-hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry and mass spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5):481-487.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
李刚, 胡斯宪, 陈琳玲.原子荧光光谱分析技术的创新与发展[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(3):359-376.
Google Scholar
Li G, Hu S X, Chen L L.Innovation and development for atomic fluorescence spectrometry analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(3):359-376.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
张锦茂, 梁敬, 董芳.中国30多年来原子荧光光谱仪器的发展与应用[J].中国无机分析化学, 2013, 3(4):1-10.
Google Scholar
Zhang J M, Liang J, Dong F. Development of vapor generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometer and its applications in China in last more than thirty years[J].Inorganic Analytical Abstracts of China, 2013, 3(4):1-10.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Li Z X, Yang X M, Guo Y A, et al.Simultaneous deter-mination of arsenic, antimony, bismuth and mercury in geological materials by vapor generation-four-channel non-dispersive atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2008, 74:915-921. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.07.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
刘曙, 华若男, 朱志秀, 等.原子荧光光谱法测定萤石中砷含量:实验室内验证[J].分析试验室, 2015, 34(8):939-943.
Google Scholar
Liu S, Hua R N, Zhu Z X, et al.Determination of arsenic content in fluorite by atomic fluorescence spectrometry:In-house validation[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2015, 34(8):939-943.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
何军, 冯伟.氢化物发生-原子荧光法同时测定水中的砷和铅的研究[J].中国环境监测, 2011, 27(5):30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2011.05.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
He J, Feng W.Simultaeous determination of trace amount of As and Pb in water by HG-AFS[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2011, 27(5):30-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2011.05.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Yang X A, Lu X P, Zhang W B, et al.Selective deter-mination of four arsenic species in rice and water samples by modified graphite electrode-based electrolytic hydride generation coupled with atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2016, 159:127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.06.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Carolina L T, Rodrigo A G, Marlo S A, et al.Deter-mination of total arsenic in seawater by hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Microchemical Journal, 2010, 96:157-160. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2010.03.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
张庆建, 丁仕兵, 郭兵, 等.原子荧光光谱法测定固体废弃物——氧化皮中的砷[J].中国无机分析化学, 2013, 3(2):25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2013.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang Q J, Ding S B, Guo B, et al.Determination of arsenic in mill scale solid waste by atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Inorganic Analytical Abstracts of China, 2013, 3(2):25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2013.02.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
张洪文, 张永辉, 韩康琴, 等.多道全自动原子荧光光谱法测定土壤中的砷和汞[J].中国无机分析化学, 2014, 4(1):18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2014.01.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang H W, Zhang Y H, Han K Q, et al.Determination of arsenic and mercury in soils by multi-channel automatic atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 4(1):18-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1035.2014.01.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Duan X C, Zhang J Y, Bu F L.Direct determination of arsenic in soil samples by fast pyrolysis-chemical vapor generation using sodium formate as a reductant followed by nondispersive atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 2015, 111:87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2015.07.005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
齐素芬.AFS-2202双道原子荧光计测定砷锡铋汞中应注意的几个问题[J].岩矿测试, 2006, 25(2):197-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.02.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
Qi S F.Discussion on some problems in determination of As, Sn, Bi and Hg by AFS-2202 double-channel atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2006, 25(2):197-198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2006.02.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
李学文, 金兰淑, 李会杰, 等.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定痕量砷时仪器工作条件的选择[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2009, 45(1):73-74.
Google Scholar
Li X W, Jin L S, Li H J, et al.Choice of working condition of instrument in HG-AFS determination of trace amounts of arsenic[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2009, 45(1):73-74.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
岳宇超, 常恺, 唐志华.原子荧光仪测定砷实验条件的优化[J].分析仪器, 2018(1):167-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232x.2018.01.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yue Y C, Chang K, Tang Z H.Optimization of experimental conditions for determination of arsenic by atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Analytical Instrumentation, 2018(1):167-173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-232x.2018.01.031
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Cabon J Y, Giamarchi P, Bihan A L.Determination of iron in seawater by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry and atomic fluorescence spectrometry:A comparative study[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2010, 664:114-120. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.02.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
赵如琳, 王骏峰, 孙梅, 等.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法测定处理废水中砷[J].冶金分析, 2013, 33(1):59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.01.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhao R L, Wang J F, Sun M, et al.Determination of arsenic in treated sewage by hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(1):59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7571.2013.01.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
程新良, 郭金鑫, 高远.双通道原子荧光法同时测定水中砷和硒[J].化学分析计量, 2015, 24(4):75-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2015.04.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
Cheng X L, Guo J X, Gao Y.Simultaneous determination of arsenic and selenium in water samples by double channel atomic fluorescence spectrometry[J].Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2015, 24(4):75-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-6145.2015.04.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
马旻, 柴昌信, 祝建国.氢化物发生-原子荧光光谱法的干扰及其消除[J].分析测试技术与仪器, 2011, 17(3):179-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3757.2011.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
Ma M, Chai C X, Zhu J G.Brief discussion on interference in hydride generation-atomic fluorescence spectrometry and its elimination[J].Analysis and Testing Technology and Instuments, 2011, 17(3):179-182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3757.2011.03.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





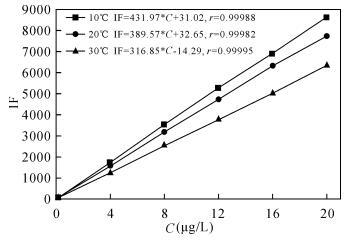

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: