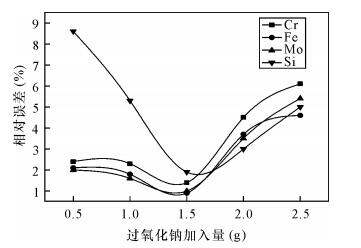
| [1] |
Chen R R, Ding H S, Yang J R, et al.Temperature field calculation on cold crucible continuous melting and directional solidifying Ti50Al alloys[J].Rare Metal Materials & Engineering, 2012, 22(3):647-653.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Chen X, Xie F Q, Ma T J, et al.Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of linear friction welded Ti2AlNb alloy[J].Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015, 646:490-496.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
陈学源.溴化碲分光光度法测定钛铝合金中微量碲[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 1997, 26(4):56-59.
Google Scholar
Chen X Y.TeBr4 spectrophotometric determination of trace Te in TiAl alloy[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1997, 26(4):56-59.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
牛金龙, 陈学源.铀试剂光度法测定钛铝合金中微量锑[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 1997, 26(6):56-59.
Google Scholar
Niu J L, Chen X Y.5-Br-PADAP extraction spectro-photometric determination of trace antimony in TiAl alloy[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1997, 26(6):56-59.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
陈学源, 牛金龙.钛铝合金中微量磷的测定[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 1998, 27(2):119-121.
Google Scholar
Chen X Y, Niu J L.Determination of trace phosphorus in titanium-aluminium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 1998, 27(2):119-121.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
高颂, 庞晓辉, 王桂军.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定高铌钛铝合金中硼硅钨锰[J].冶金分析, 2013, 33(11):59-62.
Google Scholar
Gao S, Pang X H, Wang G J.Determination of boron, silicon, tungsten and manganese in high niobium titanium aluminum alloy by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2013, 33(11):59-62.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
杜米芳.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定钛合金中钼锆铌[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(10):77-81.
Google Scholar
Du M F.Determination of molybdenum, zirconium and niobium in titanium alloy by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(10):77-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
高颂, 庞晓辉, 梁红玲.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定TG6钛合金中镁钒铬铁钴铜锰钼钨[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(3):51-55.
Google Scholar
Gao S, Pang X H, Liang H L.Determination of magnesium, vanadium, chromium, iron, cobalt, copper, manganese, molybdenum and tungsten in TG6 titanium alloy by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(3):51-55.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
王卿, 赵伟, 张会堂, 等.过氧化钠碱熔-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定钛铁矿中铬磷钒[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):971-974.
Google Scholar
Wang Q, Zhao W, Zhang H T, et al.Determination of Cr, V and P in ilmenite by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry with sodium peroxide fusion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):971-974.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
王小强, 夏辉, 秦九红, 等.过氧化钠碱熔-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定多金属矿中的锡钨钛等主次量成分[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):52-58.
Google Scholar
Wang X Q, Xia H, Qin J H, et al.Determination of Sn, W, Ti and other elements in polymetallic ore by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry with sodium peroxide fusion[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):52-58.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
马兰, 余琼, 覃广河, 等.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定硼铁合金中的硼[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2015, 51(4):478-479.
Google Scholar
Ma L, Yu Q, Qin G H, et al.Determination of boron in ferroboron alloy by ICP-AES[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2015, 51(4):478-479.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
聂富强, 杜丽丽, 李景滨, 等.碱熔-电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)测定高碳高硅钢中的硅含量[J].中国无机分析化学, 2015, 5(4):74-78.
Google Scholar
Nie F Q, Du L L, Li J B, et al.Determination of silicon content in high carbon and high silicon steel by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry with sodium peroxide fusion[J].Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 5(4):74-78.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
仝晓红, 刘攀, 聂富强.碱熔-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定高碳铬铁中铬[J].冶金分析, 2015, 35(9):36-41.
Google Scholar
Tong X H, Liu P, Nie F Q.Determination of chromium in high-carbon ferrochrome by alkali fusion-inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2015, 35(9):36-41.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
赵庆令, 李清彩.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定锆钛砂矿中铪钛锆[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):883-886.
Google Scholar
Zhao Q L, Li Q C.Determination of Hf, Ti and Zr in zirconium-titanium placer by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6):883-886.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
李红光, 王雪, 王哲, 等.电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法测定锆钛砂矿中锆钛铁钍铪[J].冶金分析, 2014, 34(2):62-65.
Google Scholar
Li H G, Wang X, Wang Z, et al.Determination of zirconium, titanium, iron, thorium and hafnium in zirconium-titanium placer by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J].Metallurgical Analysis, 2014, 34(2):62-65.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
成勇.ICP-AES测定钛合金中硅钒铁铝镍钼铬[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(10):183-186.
Google Scholar
Cheng Y.Determination of the silicon, vanadium, iron, aluminum, nickel, molybdenum and chromium in titanium alloy by ICP-AES[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(10):183-186.
Google Scholar
|





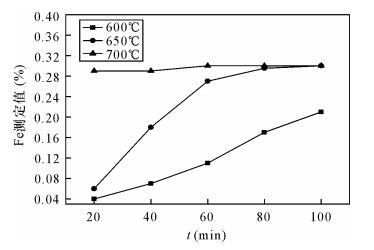

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: