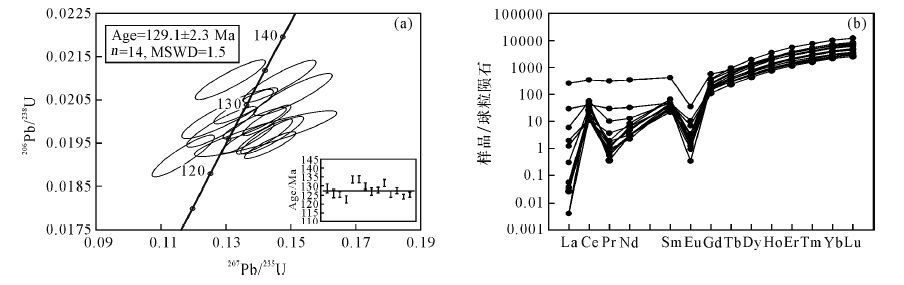
| [1] |
Ding L,Lai Q Z.New Geological Evidence of Crustal Thickening in the Gangdese Block Prior to the Indo-Asian Collision[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2003,48(15):1604-1610. doi: 10.1007/BF03183969
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
翟庆国,李才,王天武,等.西藏折无地区晚白垩世二云母花岗岩地球化学特征及构造环境[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2004,34(1):27-31.
Google Scholar
Zhai Q G,Li C,Wang T W,et al.The Geochemistry and Tectonic Settings of Two-Micagranite in Zhewu Area,Tibet[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2004,34(1):27-31.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
翟庆国,李才,李惠民,等.西藏冈底斯中部淡色花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报,2005,24(4):349-353.
Google Scholar
Zhai Q G,Li C,Li H M,et al.U-Pb Zircon Age of Leucogranite in the Central Ggangdise,Tibet,and Its Geological Significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China,2005,24(4):349-353.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
杨德明,黄映聪,戴琳娜,等.西藏嘉黎县措麦地区含石榴子石二云母花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其意义[J].地质通报,2005,24(3):235-238.
Google Scholar
Yang D M,Huang Y C,Dai L N.SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Age of Garnet-bearing Two-Mica Granite at Comai Township,Lhari County,Tibet,and Its Significance[J].Geological Bulletin of China,2005,24(3):235-238.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
和钟铧,杨德明,王天武.冈底斯带桑巴区早白垩世后碰撞花岗岩类的确定及构造意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2006,25(3):185-193.
Google Scholar
He Z H,Yang D M,Wang T W.The Determination of Carly Cretaceous Post-collision Granitoids in Sangba Area of Gangdese Tectonic Belt and Its Tectonic Significance[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2006,25(3):185-193.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
高一鸣,陈毓川,唐菊兴,等.西藏工布江达县亚贵拉铅锌钼多金属矿床石英斑岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义[J].地质学报,2009,83(10):1436-1444.
Google Scholar
Gao Y M,Chen Y C,Tang J X,et al.SHRIMP U-Pb Dating of Zircon from Quartz Porphyry in the Yaguila Pb-Zn-Mo Deposit,Gongbujiangda County,Tibet and Its Geological Implication[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2009,83(10):1436-1444.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
费光春,温春齐,王成松,等.西藏墨竹工卡县洞中拉铅锌矿床花岗斑岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年[J].中国地质,2010,37(2):470-476.
Google Scholar
Fei G C,Wen C Q,Wang C S,et al.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Age of Porphyry Granite in the Dongzhongla Lead-Zinc Deposit,Maizhokunggar County,Tibet[J].Geology in China,2010,37(2):470-476.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
崔晓亮,唐菊兴,多吉,等.西藏洞中拉铅锌矿床石英斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究[J].成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,38(5):557-562.
Google Scholar
Cui X L,Tang J X,Dorji,et al.Zircon U-Pb Age of the Quartz Porphyry from Dongzhongla Pb-Zn Deposit in Tibet,China[J].Journal of Chengdu University of Technology,2011,38(5):557-562.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
杜欣,刘俊涛,王亚平.西藏拉屋铅锌多金属矿床地质特征及成因分析[J].矿产与地质,2004,18(5):410-414.
Google Scholar
D Xin,Liu J T,Wang Y P.Geological Character and Ore Genesis of the Lawu Copper-Lead-Zinc Polymetallic Ore Deposit[J].Mineral Resources & Geology,2004,18(5):410-414.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏工布江达县亚贵拉铅锌矿床地质特征及成因分析[J].地质与勘探,2009,45(5):570-576.
Google Scholar
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Yaguila Lead-Zinc Deposit in the Gongbujiangda County of Tibet Province[J].Geology & Exploration,2009,45(5):570-576.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏当雄县拉屋铜铅锌多金属矿床喷流沉积成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2010,40(5):1041-1046.
Google Scholar
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Exhalative Sedimentary Genesis of Lawu Copper-Lead-Zinc Deposit in Dangxiong County of Tibet[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2010,40(5):1041-1046.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
连永牢,曹新志,燕长海,等.西藏念青唐古拉地区铅锌银矿床成矿系列及找矿前景[J].贵州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,28(2):31-36.
Google Scholar
Lian Y L,Cao X Z,Yan C H,et al.Metallogenic Series and Prospecting Potential of Lead-Zinc-Silver Ore District in Nyainqentanglha,Tibet[J].Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science Edition),2011,28(2):31-36.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
唐菊兴,王立强,郑文宝,等.冈底斯成矿带东段矿床成矿规律及找矿预测[J].地质学报,2014,88(12):2545-2555.
Google Scholar
Tang J X,Wang L Q,Zheng W B,et al.Ore Deposits Metallogenic Regularity and Prospecting in the Eastern Section of the Gangdese Metallogenic Belt[J].Acta Geologica Sinica,2014,88(12):2545-2555.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
顾枫华,章永梅,刘瑞萍,等.内蒙古沙德盖花岗岩岩浆混合作用:岩相学、矿物化学和年代学证据[J].岩石学报,2015,31(5):1374-1390.
Google Scholar
Gu F H,Zhang Y M,Liu R P,et al.Magma Mixing and Mingling of the Shadegai Granite in Inner Mongolia:Evidence from Petrography,Mineral Chemistry and Geochronology[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2015,31(5):1374-1390.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Zong K Q,et al.Reappraisement and Refinement of Zircon U-Pb Isotope and Trace Element Analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
吴元保,郑永飞.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J].科学通报,2004,49(16):1589-1604.
Google Scholar
Wu Y B,Zheng Y F.Genesis of Zircon and Its Constraints on Interpretation of U-Pb Age[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(16):1589-1604.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Sun S S,McDonough W F.Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts:Implications for Mantle Composition and Process//Saundern A D,Norry M J(eds.).Magmatism in the Ocean Basins[J].Geological Society London Special Publication,1989,42(1):313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Belousova E A,Griffin W L,O'Reilly S Y,et al.Igneous Zircon:Trace Element Composition as an Indicator of Source Rock Type[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2002,143:602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
钟玉芳,马昌前,佘振兵.锆石地球化学特征及地质应用研究综述[J].地质科技情报,2006,25(1):27-34.
Google Scholar
Zhong Y F,Ma C Q,She Z B.Geochemical Characteristics of Zircon and Its Applications in Geosciences[J].Geological Science & Technology Information,2006,25(1):27-34.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
赵振华.副矿物微量元素地球化学特征在成岩成矿作用研究中的应用[J].地学前缘,2010,17(1):267-286.
Google Scholar
Zhao Z H.Trace Element Geochemistry of Accessory Minerals and Its Applications in Petrogenesis and Metallogenesis[J].Earth Science Frontiers,2010,17(1):267-286.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Watson E B,Wark D A,Thomas J B.Crystallization Thermometers for Zircon and Rutile[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2006,151:413-433. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
高晓英,郑永飞.金红石Zr和锆石Ti含量地质温度计[J].岩石学报,2011,27(2):417-432.
Google Scholar
Gao X Y,Zheng Y F.On the Zr-in-Rutile and Ti-in-Zircon Geothermometers[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011,27(2):417-432.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Ferry M,Watson E B.New Thermodynamic Models and Revised Calibrations for the Ti-in-Zircon and Zr-in-Rutile Thermometers[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,2007,154(4):429-437. doi: 10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Hayden L A,Watson E B.Rutile Saturation in Hydrous Siliceous Melts and Its Bearing on Ti-Thermometry of Quartz and Zircon[J].Earth Planetary Science Letters,2007,258(3-4):561-568. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Lee J,Williams I,Ellis D.Pb,U and Th Diffusion in Nature Zircon[J].Nature,1997,390:159-162. doi: 10.1038/36554
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





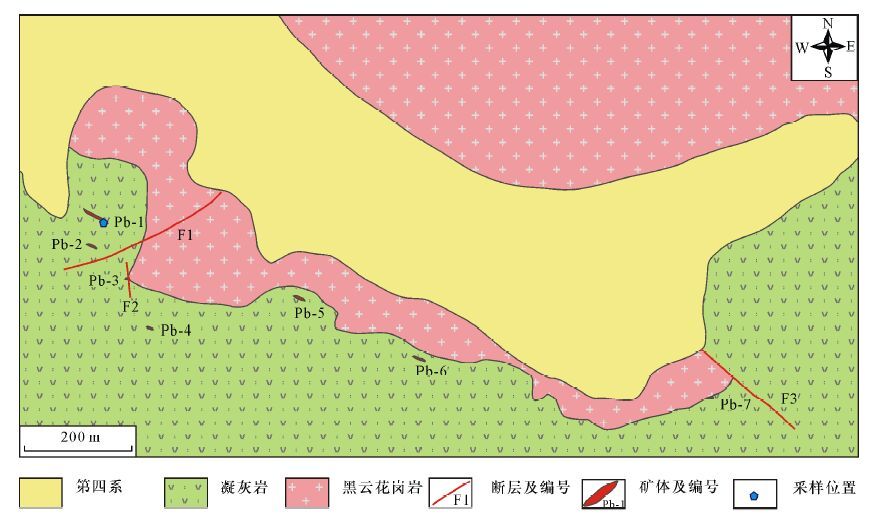

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: