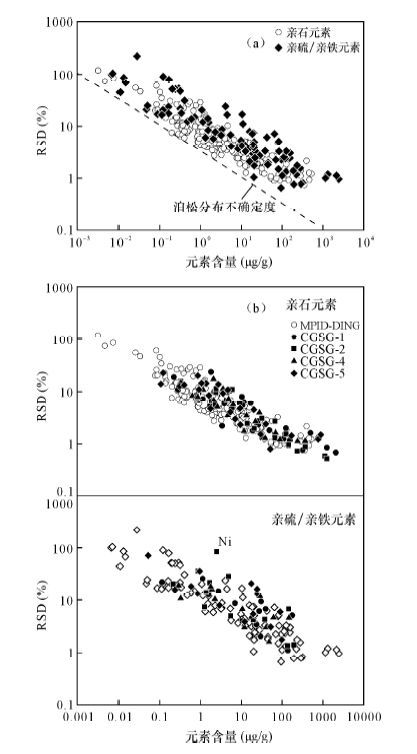
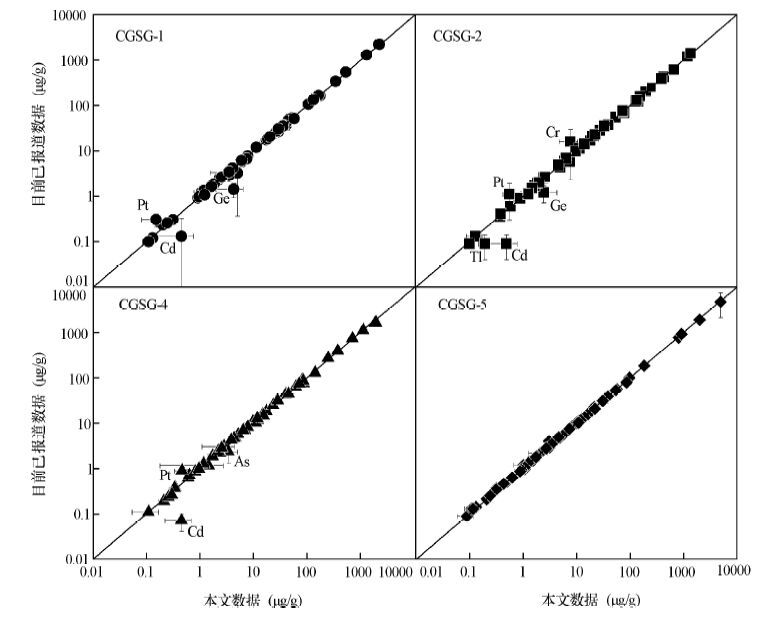
| [1] |
Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Li M,et al.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the Elemental Analyses of Geological Samples[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(32):3863-3878. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Russo R E,Mao X,Gonzalez J J,et al.Laser Ablation in Analytical Chemistry[J].Analytical Chemistry,2013,85(13):6162-6177. doi: 10.1021/ac4005327
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Gao S,et al.In situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard[J].Chemical Geology,2008,257(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Ubide T,McKenna C A,Chew D M,et al.High-resolution LA-ICP-MS Trace Element Mapping of Igneous Minerals:In Search of Magma Histories[J].Chemical Geology,2015,409:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.05.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
袁继海,詹秀春,范晨子,等.玻璃标样结合硫内标归一定量技术在激光剥蚀-等离子体质谱分析硫化物矿物中的应用[J].分析化学,2012,40(2):201-207. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(11)60528-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yuan J H,Zhan X C,Fan C Z,et al.Quantitative Analysis of Sulfide Minerals by Laser Ablation-Inductive Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry Using Glass Reference Materials with Matrix Normalization Plus Sulfur Internal Standardization Calibration[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2012,40(2):201-207. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(11)60528-8
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Jackson S E,Pearson N J,Griffin W L,et al.The Application of Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry to in situ U-Pb Zircon Geochronology[J].Chemical Geology,2004,211(1):47-69.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Yuan H L,Gao S,Dai M N,et al.Simultaneous Determinations of U-Pb Age,Hf Isotopes and Trace Element Compositions of Zircon by Excimer Laser-Ablation Quadrupole and Multiple-collector ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology,2008,247(1-2):100-118. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Liu Y S,Hu Z C,Zong K Q,et al.Reappraisement and Refinement of Zircon U-Pb Isotope and Trace Element Analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(15):1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Paton C,Woodhead J D,Hellstrom J C,et al.Improved Laser Ablation U-Pb Zircon Geochronology through Robust Downhole Fractionation Correction[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2010,11(3):1-36.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Günther D,Audétat A,Frischknecht R,et al.Quantitative Analysis of Major,Minor and Trace Elements in Fluid Inclusions Using Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1998,13(4):263-270. doi: 10.1039/A707372K
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Wálle M,Heinrich C A.Fluid Inclusions Measurements by Laser Ablation Sector-field ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,2014,29(6):1052-1057. doi: 10.1039/c4ja00010b
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Halter W E,Pettke T,Heinrich C A,et al.Major to Trace Element Analysis of Melt Inclusions by Laser-Ablation ICP-MS:Methods of Quantification[J].Chemical Geology,2002,183(1-4):63-86. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00372-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Garbe-Schonberg D,Müller S.Nano-Particulate Pressed Powder Tablets for LA-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,2014,29(6):990-1000. doi: 10.1039/c4ja00007b
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
吴石头,王亚平,许春雪.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱元素微区分析标准物质研究进展[J].岩矿测试,2015,34(5):503-511.
Google Scholar
Wu S T,Wang Y P,Xu C X.Research Progress on Reference Mterials for in situ Elemental Analysis by Laser Ablation-Inductive Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis,2015,34(5):503-511.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Jochum K P,Enzweiler J.Treatise on Geochemistry (Second Edition):Reference Materials in Geochemical and Environmental Research[M].Oxford:Elsevier Press,2014:43-70.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Jochum K P,Weis U,Stoll B,et al.Determination of Reference Values for NIST SRM 610-617 Glasses Following ISO Guidelines[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2011,35(4):397-429. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2011.35.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Jochum K P,Stoll B,Herwig K,et al.MPI-DING Reference Glasses for in Situ Microanalysis:New Reference Values for Element Concentrations and Isotope Ratios[J].Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems,2006,7(2):1-44.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Jochum K P,Willbold M,Raczek I,et al.Chemical Characterisation of the USGS Reference Glasses GSA-1G,GSC-1G,GSD-1G,GSE-1G,BCR-2G,BHVO-2G and BIR-1G Using EPMA,ID-TIMS,ID-ICP-MS and LA-ICP-MS[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2005,29(3):285-302. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2005.29.issue-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Hu M Y,Fan X T,Stoll B,et al.Preliminary Charact-erisation of New Reference Materials for Microanalysis:Chinese Geological Standard Glasses CGSG-1,CGSG-2,CGSG-4 and CGSG-5[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2011,35(2):235-251. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2011.35.issue-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Jochum K P,Stoll B,Weis U,et al.Non-Matrix-Matched Calibration for the Multi-element Analysis of Geological and Environmental Samples Using 200 nm Femtosecond LA-ICP-MS:A Comparison with Nanosecond Lasers[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2014,38(3):265-292. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2014.38.issue-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Denton J,Murrell M,Goldstein S,et al.Evaluation of New Geological Reference Materials for Uranium-Series Measurements:Chinese Geological Standard Glasses (CGSG) and Macusanite Obsidian[J].Analytical Chemistry,2013,85(20):9975-9981. doi: 10.1021/ac4017117
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Jochum K P,Dingwell D B,Rocholl A,et al.The Preparation and Preliminary Characterisation of Eight Geological MPI-DING Reference Glasses for in-situ Microanalysis[J].Geostandards Newsletter,2000,24(1):87-133. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2000.24.issue-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Klemme S,Prowatke S,Münker C,et al.Synthesis and Preliminary Characterisation of New Silicate,Phosphate and Titanite Reference Glasses[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2008,32(1):39-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2008.00873.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Yang Q C,Jochum K P,Stoll B,et al.BAM-S005 Type A and B:New Silicate Reference Glasses for Microanalysis[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2012,36(3):301-313. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2012.36.issue-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Wilson S A,Ridley W I,Koenig A E.Development of Sulfide Calibration Standards for the Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Technique[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,2002,17(4):406-409. doi: 10.1039/B108787H
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Harries D.Homogeneity Testing of Microanalytical Reference Materials by Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA)[J].Chemie der Erde-Geochemistry,2014,74(3):375-384. doi: 10.1016/j.chemer.2014.01.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Armstrong J T.Citzaf-A Package of Correction Programs for the Quantitative Electron Microbeam X-Ray-Analysis of Thick Polished Materials,Thin-films,and Particles[J].Microbeam Analysis,1995,4(3):177-200.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Hu Z C,Liu Y S,Chen L,et al.Contrasting Matrix Induced Elemental Fractionation in NIST SRM and Rock Glasses during Laser Ablation ICP-MS Analysis at High Spatial Resolution[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,2011,26(2):425-430. doi: 10.1039/C0JA00145G
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Li Z,Hu Z,Liu Y,et al.Accurate Determination of Elements in Silicate Glass by Nanosecond and Femtosecond Laser Ablation ICP-MS at High Spatial Resolution[J].Chemical Geology,2015,400:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Fryer B J,Jackson S E,Longerich H P.The Design,Operation and Role of the Laser-Ablation Microprobe Coupled with an Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer (LAM-ICP-MS) in the Earth Sciences[J].Canadian Mineralogist,1995,33:303-312.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Manka A J G,Masonb P R D.A Critical Assessment of Laser Ablation ICP-MS as an Analytical Tool for Depth Analysis in Silica-based Glass Samples[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry,1999,14(8):1143-1153. doi: 10.1039/a903304a
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
吴石头,王亚平,许春雪,等.193 nm ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统高空间分辨率下元素分馏研究[J].分析化学,2016,44(7):1035-1041. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(16)60943-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wu S T,Wang Y P,Xu C X,et al.Elemental Fractionation Studies of 193 nm ArF Excimer Laser Ablation System at High Spatial Resolution Mode[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2016,44(7):1035-1041. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(16)60943-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
van der Veen A M,Linsinger T P,Pauwels J.Uncertainty Calculations in the Certification of Reference Materials.2.Homogeneity Study[J].Accreditation and Quality Assurance,2001,6(1):26-30. doi: 10.1007/s007690000238
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Jochum K P,Scholz D,Stoll B,et al.Accurate Trace Element Analysis of Speleothems and Biogenic Calcium Carbonates by LA-ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology,2012,318:31-44.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Gao S,Liu X M,Yuan H L,et al.Determination of Forty-two Major and Trace Elements in USGS and NIST SRM Glasses by Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J].Geostandards Newsletter,2002,26(2):181-196. doi: 10.1111/ggr.2002.26.issue-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
袁继海,詹秀春,孙冬阳,等.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱分析硅酸盐矿物基体效应的研究[J].分析化学,2011,39(10):1582-1588. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(10)60477-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
Yuan J H,Zhan X C,Sun D Y,et al.Investigation on Matrix Effects in Silicate Minerals by Laser Ablation-Inductive Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2011,39(10):1582-1588. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(10)60477-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Tong X,Liu Y,Hu Z,et al.Accurate Determination of Sr Isotopic Compositions in Clinopyroxene and Silicate Glasses by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research,2015,40(1):85-99.
Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
刘勇胜,胡圣虹,柳小明,等.高级变质岩中Zr,Hf,Nb,Ta的ICP-MS准确分析[J].地球科学——中国地质大学学报,2003,28(2):151-156.
Google Scholar
Liu Y S,Hu S H,Liu X M, et al.Accurate Analysis of Zr,Hf,Nb and Ta in High-grand Metamorphic Rocks with ICP-MS[J].Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences,2003,28(2):151-156.
Google Scholar
|





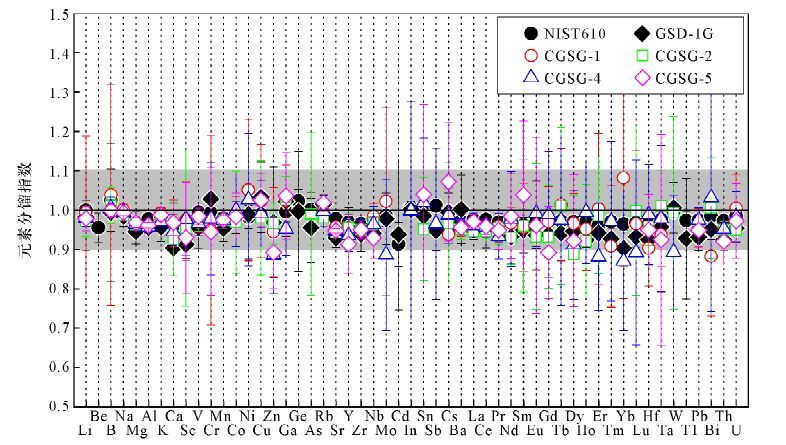

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: