| [1] |
毛景文, 李红艳.江南古陆某些金矿床成因讨论[J].地球化学, 1997, 26(5):71-81.
Google Scholar
Mao J W, Li H Y.Research on Genesis of the Gold Deposits in the Jiangnan Terrain[J]. Geochimica, 1997, 26(5):71-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
王加昇, 温汉捷, 李超, 等.黔东南石英脉型金矿毒砂Re-Os同位素定年及其地质意义[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(6):955-964.
Google Scholar
Wang J S, Wen H J, Li C, et al.Re-Os Isotope Dating of Arsenopyrite from the Quartz Vein-type Gold Deposit, Southeastern Guizhou Province, and Its Geological Implications[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(6):955-964.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
李超, 裴浩翔, 王登红, 等.山东孔辛头铜钼矿成矿时代及物质来源:来自黄铜矿、辉钼矿Re-Os同位素证据[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(2):240-249.
Google Scholar
Li C, Pei H X, Wang D H, et al.Age and Source Constraints for Kongxintou Copper Molybdenum Deposit Shandong from Re-Os Isotope in Molybdenite and Chalcopyrite[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(2):240-249.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
李超, 屈文俊, 杜安道, 等.含有普通锇的辉钼矿Re-Os同位素定年研究[J].岩石学报, 2012, 28(2):702-708.
Google Scholar
Li C, Qu W J, Du A D, et al.Study on Re-Os Isotope in Molybdenite Containing Common Os[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2):702-708.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
和文言, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等.滇西北衙金多金属矿床锆石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(4):1301-1310.
Google Scholar
He W Y, Mo X X, Yu X H, et al.Zircon U-Pb and Molybdenite Re-Os Dating for the Beiya Gold Polymetallic Deposit in the Western Yunnan Province and Its Geological Significance[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(4):1301-1310.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
抄尉尉, 叶会寿, 田野, 等.豫西熊耳山矿集区栾灵金矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2016, 35(1):103-116.
Google Scholar
Chao W W, Ye H S, Tian Y, et al.Re-Os Isotopic Dating of Molybdenite from Luanling Gold Deposit in Xiong'er Mountain Ore Concentration Area of Western Henan Province and Its Geological Significance[J].Mineral Deposits, 2016, 35(1):103-116.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
杜安道, 屈文俊, 李超, 等.铼-锇同位素定年方法及分析测试技术的进展[J].岩矿测试, 2009, 28(3):288-304.
Google Scholar
Du A D, Qu W J, Li C, et al.A Review on the Development of Re-Os Isotopic Dating Methods and Techniques[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(3):288-304.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
杨雪, 李超, 李欣尉, 等.半封闭硝酸溶解体系ICP-MS快速测定辉钼矿的Re-Os年龄及Re含量[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1):24-31.
Google Scholar
Yang X, Li C, Li X W, et al.A Rapid Method to Determine the Re-Os Age and Re Content of Molybdenite by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1):24-31.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
李超, 杨雪, 赵鸿, 等.pg-ng级Os同位素热表面电离质谱高精度分析测试技术[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
Li C, Yang X, Zhao H, et al.High Precise Isotopic Measurements of pg-ng Os by Negative Ion Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(4):392-398.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
漆亮, 黄小文.地质样品铂族元素及Re-Os同位素分析进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(2):171-189.
Google Scholar
Qi L, Huang X W.A Review on Platinum-group Elements and Re-Os Isotopic Analyses of Geological Samples[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology, and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(2):171-189.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
王洋洋, 肖益林, 杨晓勇.长江中下游成矿带铜陵新桥矿床Re-Os同位素及流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(4):1031-1039.
Google Scholar
Wang Y Y, Xiao Y L, Yang X Y.Re-Os Isotopes Systematics and Fluid Inclusions of Xinqiao Deposit in Tongling, the Middle Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(4):1031-1039.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
孙升升, 薛春纪, 陶剑锋, 等.西天山博故图金矿床H-O-S-Pb同位素示踪和Re-Os法测年[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(5):1346-1360.
Google Scholar
Sun S S, Xue C J, Tao J F, et al.H-O-S-Pb Isotopic Tracing and Re-Os Dating of Bogutu Gold Deposit, Western Tienshan, Xinjiang[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(5):1346-1360.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Kerr A, Selby D.The Timing of Epigenetic Gold Mineralization on the Baie Verte Peninsula, Newfoundland, Canada:New Evidence from Re-Os Pyrite Geochronology[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(3):325-337. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0375-2
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Morelli R M, Bell C C, Creaser R A, et al.Constraints on the Genesis of Gold Mineralization at the Homestake Gold Deposit, Black Hills, South Dakota from Rhenium-Osmium Sulfide Geochronology[J].Minerallium Deposita, 2010, 45(5):461-480. doi: 10.1007/s00126-010-0284-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Shi G Y, Sun X M, Pan W J, et al.Re-Os Dating of Auriferous Pyrite from the Zhenyuan Super-large Gold Deposit in Ailaoshan Gold Belt, Yunnan Province, Southwestern China[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(35):4578-4586. doi: 10.1007/s11434-012-5275-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Stein H J, Morgan J W, Schersten A.Re-Os Dating of Low-level Highly Radiogenic (LLHR) Sulfides:The Harnäs Gold Deposit, South-West Sweden, Records Continental-scale Tectonic Events[J].Economic Geology, 2000, 95(8):1657-1671.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Ying L J, Wang C H, Tang J X, et al.Re-Os Systematics of Sulfides (Chalcopyrite, Bornite, Pyrite and Pyrrhotite) from the Jiama Cu-Mo Deposit of Tibet, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79:497-506. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.10.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Wang J S, Fan B, Zhu Y.Age and Metal Source Constraints for Gold Deposits in Southeast Guizhou Province, China, from Re-Os and He-Ar Isotopes in Arsenopyrites[J].Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2014, 88(Supplement 2):1015-1016.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Yu G, Yang G, Chen J F, et al.Re-Os Dating of Gold-bearing Arsenopyrite of the Maoling Gold Deposit, Liaoning Province, Northeast China and Its Geological Significance[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(14):1509-1514. doi: 10.1360/04wd0229
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Chinnasamy S S, Uken R, Reinhardt J R, et al.Pressure, Temperature, and Timing of Mineralization of the Sedimentary Rock-hosted Orogenic Gold Deposit at Klipwal, Southeastern Kaapvaal Craton, South Africa[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50:739-766. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0573-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Gao L Z, Ding X Z, Zhang C H, et al.Revised Chronostratigraphic Framework of the Metamorphic Strata in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt, South China and Its Tectonic Implications[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(2):339-349. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00664.x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
王尚彦, 陶平, 代传固编著.贵州东部金矿[M].北京:地质出版社, 2006:1-177.
Google Scholar
Wang S Y, Tao P, Dai C G.Gold Deposits in Eastern Guizhou Province[M].Beijing:Geological Press, 2006:1-177.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
朱笑青, 王甘露, 卢焕章, 等.黔东南金矿形成时代的确定兼论湘黔加里东金矿带[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(5):1092-1099.
Google Scholar
Zhu X Q, Wang G L, Lu H Z, et al.Determination of the Age of Gold Deposits in Southeastern Guizhou:With a Discussion of the Caledonian Hunan-Guizhou Gold Ore Belt[J].Geology in China, 2006, 33(5):1092-1099.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
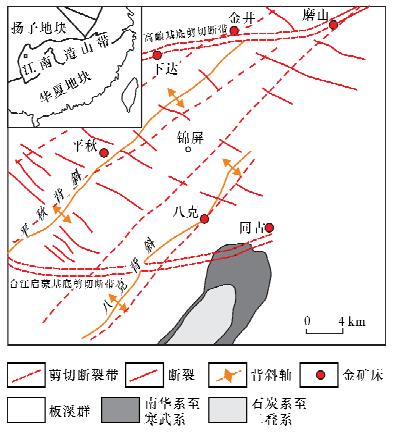
张洪信, 张华, 彭慈刚, 等.黔东南锦屏平秋金矿找矿前景初步分析[J].贵州地质, 2005, 22(4):242-245.
Google Scholar
Zhang H X, Zhang H, Peng C G, et al.Initiative Investigation on Foreground of Prospecting at Pingqiu Gold Deposit, Jingping County, Southeastern Guizhou[J].Guizhou Geology, 2005, 22(4):242-245.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
余大龙.黔东八克金矿地质地球化学特征研究[J].地质地球化学, 1997(1):12-17.
Google Scholar
Yu D L.A Study on the Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of Bake Gold Deposit, East Guizhou[J].Geology and Geochemistry, 1997(1):12-17.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
赵鸿, 李超, 江小均, 等.浙江长兴"金钉子"灰岩Re-Os富集机制研究[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(10):1783-1791.
Google Scholar
Zhao H, Li C, Jiang X J, et al.Enrichment Mechanism of Re-Os in Limestone from Changxing Permian-Triassic Boundary in Zhejiang[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(10):1783-1791.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
屈文俊, 杜安道.电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定辉钼矿含量质量分馏效应的校正[J].质谱学报, 2004, 25(增刊):181-182.
Google Scholar
Qu W J, Du A D.Correction of Mass Discrimination in the Determination of the Isotope Abundance for Rhenium and Osmium in Molybdenite by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry[J].Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2004, 25(Supplement):181-182.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Ludwig K R.Isoplot 3.00, a Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M].Berkeley:Berkeley Geochronology Center, 2003.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
张国伟, 郭安林, 王岳军, 等.中国华南大陆构造与问题[J].中国科学(地球科学), 2013, 43(10):1553-1582. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4679-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang G W, Guo A L, Wang Y J, et al.Tectonics of South China Continent and Its Implications[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2013, 56(11):1804-1828. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4679-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
李三忠, 王涛, 金宠, 等.雪峰山基底隆升带及其邻区印支期陆内构造特征与成因[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(1):93-105.
Google Scholar
Li S Z, Wang T, Jin C, et al.Features and Causes of Indosinian Intra-contiental Structures in the Xuefengshan Precambrian Basement and Its Neighboring Regions[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(1):93-105.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
李华芹, 王登红, 陈富文, 等.湖南雪峰山地区铲子坪和大坪金矿成矿作用年代学研究[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):900-905.
Google Scholar
Li H Q, Wang D H, Chen F W, et al.Study on Chronology of the Chanziping and Daping Gold Deposit in Xuefeng Mountains, Hunan Province[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(7):900-905.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad:

