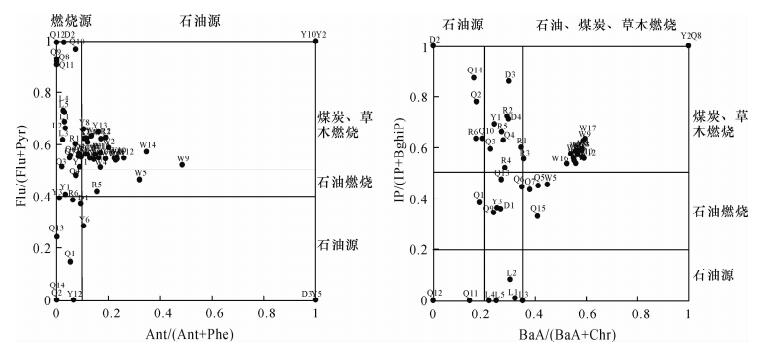
| [1] |
Callén M S, López J M, Iturmendi A, et al.Nature and Sources of Particle Associated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Atmospheric Environment of an Urban Area[J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 183:166-174. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.009
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Guo G H, Wu F C, He H P, et al.Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of PAHs in Surface Waters of China[J].Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2012, 55(6):914-925.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhu Z J.Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Sediments of the Yalujiang Estuary, North China[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2003, 46:619-625. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00035-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Chen C W, Chen C F.Distribution, Origin, and Potential Toxicological Significance of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2011, 63:417-423. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.04.047
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
陆志强, 郑文教, 马丽.九龙江口及邻近港湾红树林区沉积物中多环芳烃污染现状及评价[J].台湾海峡, 2007, 26(3):321-326.
Google Scholar
Lu Z Q, Zheng W J, Ma L.Status and Assessment of PAHs Pollution in Surface Sediment of Mangrove Areas in Jiulongjiang Estuary and Neighboring Harbors[J].Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2007, 26(3):321-326.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
王学军, 任丽然, 戴永宁, 等.天津市不同土地利用类型土壤中多环芳烃的含量特征地理研究[J].地理研究, 2003, 22(3):360-366.
Google Scholar
Wang X J, Ren L R, Dai Y N, et al.Contents of PAH Compounds in Different Types of Soils in Tianjin Area[J].Geographical Research, 2003, 22(3):360-366.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
邓伟.南黄海、东海表层沉积物中脂肪烃与多环芳烃的分布特征及来源初步研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学, 2013.
http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10423-1013348246.htm
Google Scholar
Deng W.A Preliminary Study on the Composition, Distribution and Source Apportionment of Aliphatic and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments from the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D].Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2013.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
李杨帆, 朱晓东, 邹欣庆.我国海岸带环境灾害的基本特征与减灾对策[J].灾害学, 2005, 20(1):65-66.
Google Scholar
Li Y F, Zhu X D, Zou X Q.Characteristics of Coastal Environmental Hazards in China and Strategies for Hazard Mitigation[J].Journal of Catastrophology, 2005, 20(1):65-66.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
钟兆站.中国海岸带自然灾害与环境评估[J].地理科学进展, 1997, 16(1):44-50.
Google Scholar
Zhong Z Z.Feature and Evaluation of Natural Disasters and Environment in the Coastal Zones of China[J].Progress in Geography, 1997, 16(1):44-50.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
冯砚青, 牛佳.中国海岸带环境问题的研究综述[J].海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(10):1-5.
Google Scholar
Feng Y Q, Niu J.Some Problems about the Coastal Environment of China[J].Marine Geology Letters, 2004, 20(10):1-5.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
洪华生, 丁原红, 洪丽玉, 等.我国海岸带生态环境问题及其调控对策[J].环境污染治理技术与设备, 2003, 4(1):89-94.
Google Scholar
Hong H S, Ding Y H, Hong L Y, et al.Costal Zone Eco-environmental Problems and Their Mitigation Counter Measures in China[J].Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2003, 4(1):89-94.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
沈瑞生, 冯砚青, 牛佳.中国海岸带环境问题及其可持续发展对策[J].地域研究与开发, 2005, 24(3):124-128.
Google Scholar
Shen R S, Feng Y Q, Niu J.Synthesis of the Chinese Coastal Zone Environment Problems[J].Area Research and Development, 2005, 24(3):124-128.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Wang M, Wang C Y, Hu X K, et al.Distributions and Sources of Petroleum, Aliphatic Hydrocarbons and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Surface Sediments from Bohai Bay and Its Adjacent River, China[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 90:88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.017
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
张明亮, 黎慧, 徐英江, 等.莱州湾表层沉积物中多环芳烃(PAHs)来源及生态风险评价[J].海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(1):6-11.
Google Scholar
Zhang M L, Li H, Xu Y J, et al.The Source and Ecological Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) of Surficial Sediment in Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(1):6-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
王江涛, 谭丽菊, 张文浩, 等.青岛近海沉积物中多环芳烃、多氯联苯和有机氯农药的含量和分布特征[J].环境科学, 2010, 31(11):2713-2722.
Google Scholar
Wang J T, Tan L J, Zhang W H, et al.Concentrations and Distribution Characteristic of PAHs, PCBs and OCPs in the Surface Sediments of Qingdao Coastal Area[J].Environmental Science, 2010, 31(11):2713-2722.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
郎印海, 薛荔栋, 刘爱霞, 等.日照近岸海域表层沉积物中多环芳烃(PAHs)来源的识别和解析[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 39(3):535-542.
Google Scholar
Lang Y H, Xue L D, Liu A X, et al.Identification and Source Spportionment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Coastal Surface Sediments from Rizhao Offshore Area[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2009, 39(3):535-542.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Baumard P, Budzinski H, Garrigues P.Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sediments and Mussels of the Western Mediterranean Sea[J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1998, 17(5):765-776. doi: 10.1002/etc.v17:5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
麦碧娴, 林峥, 张干, 等.珠江三角洲河流和珠江口表层沉积物中有机污染物研究——多环芳烃和有机氯农药的分布及特征[J].环境科学学报, 2000, 20(2):192-197.
Google Scholar
Mai B X, Lin Z, Zhang G, et al.Organic Contaminants in Surface Sediments from Rivers of the Pearl River Delta and Estuary-The Distributions and Characteristics of PAHs and Organo Chlorine Pesticides[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2000, 20(2):192-197.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
田蕴, 郑天凌, 王新红.厦门西港表层沉积物中多环芳烃(PAHs)的含量、分布及来源[J].海洋与湖沼, 2004, 35(1):15-20.
Google Scholar
Tian Y, Zheng T L, Wang X H.Concentration, Distribution and Source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments of Xiamen Western Harbor[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2004, 35(1):15-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
刘亮, 张俊海, 胡莹莹, 等.大连湾表层沉积物中多环芳烃的生态风险评估[J].海洋环境科学, 2011, 30(4):477-480.
Google Scholar
Liu L, Zhang J H, Hu Y Y, et al.Ecological Risk Assessment on Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments of Dalian Bay[J].Marine Environmental Science, 2011, 30(4):477-480.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
聂利红, 刘宪斌, 降升平, 等.天津高沙岭潮间带表层沉积物中多环芳烃的分布及风险评价[J].矿物岩石, 2008, 28(2):113-117.
Google Scholar
Nie L H, Liu X B, Jiang S P, et al.Distribution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Surface Sediments from the Intertidal Zone in Gaoshaling Area, Tianjin[J].Journal of Mineral Petrology, 2008, 28(2):113-117.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
林建清, 王新红, 洪华生, 等.湄洲湾表层沉积物中多环芳烃的含量分布及来源分析[J].厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 42(5):633-638.
Google Scholar
Lin J Q, Wang X H, Hong H S, et al.PAHs' Distribution and Source Analysis in Surface Sediments of the Meizhou Bay[J].Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2003, 42(5):633-638.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
陈卓敏, 高效江, 宋祖光, 等.杭州湾潮滩表层沉积物中多环芳烃的分布及来源[J].中国环境科学, 2006, 26(2):233-237.
Google Scholar
Chen Z M, Gao X J, Song Z G, et al.Distribution and Source Identification of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Tide-beach Surface Sediments of Hangzhou Bay[J].China Environmental Science, 2006, 26(2):233-237.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
国文, 薛文平, 姚文君, 等.渤海表层沉积物中多环芳烃赋存特征及来源分析[J].海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(3):330-336.
Google Scholar
Guo W, Xue W P, Yao W J, et al.Occurrence and Source of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAHs) in the Surficial Sediment of the Bohai Sea[J].Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(3):330-336.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Mostafa A R, Wade T L, Sweet S T, et al.Distribution and Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Sediments of Hadhramout Coastal Area, Gulf of Aden, Yemen[J].Journal of Marine Systems, 2009, 78:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2009.02.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Nilsen E B, Rosenbaue R J, Fuller C C, et al.Sedimen-tary Organic Biomarkers Suggest Detrimental Effects of PAHs on Estuarine Microbial Biomass during the 20th Century in San Francisco Bay, CA, USA[J].Chemosphere, 2015, 119:961-970. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.053
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Mielke H W, Wang G D, Gonzales C R, et al.PAHs and Metals in the Soils of Inner-city and Suburban New Orleans, Louisiana, USA[J].Environment Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2004, 18(3):243-247. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2003.11.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Dobbins R A, Fletcher R A, Benner J B A, et al.Poly-cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Flames, in Diesel Fuels, and in Diesel Emissions[J].Combustion and Flame, 2006, 144(4):773-781. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.09.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
朱艳景, 张彦, 高思, 等.生态风险评价方法学研究进展与评价模型选择[J].城市环境与城市生态, 2015, 28(1):17-21.
Google Scholar
Zhu Y J, Zhang Y, Gao S, et al.Progress of Ecological Risk Assessment Methodology and Choice of Assessment Models[J].Urban Environment & Urban Ecology, 2015, 28(1):17-21.
Google Scholar
|





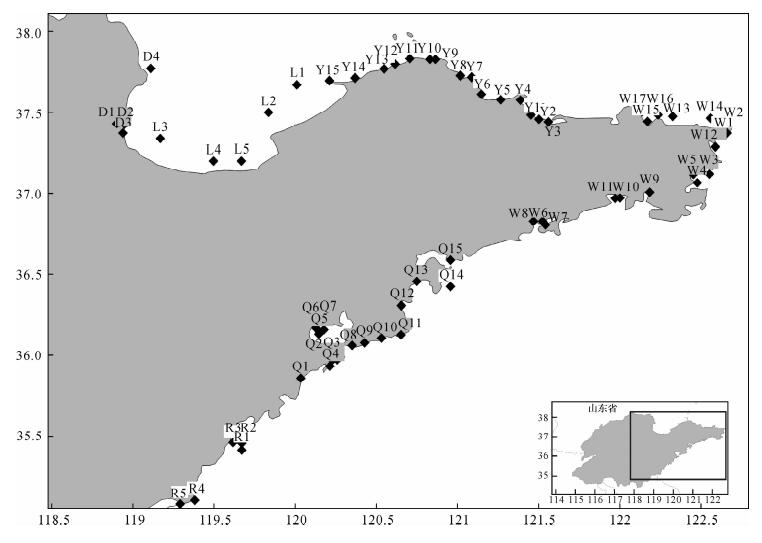

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: