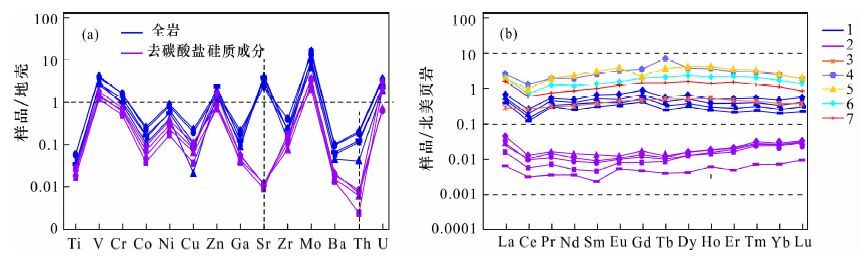
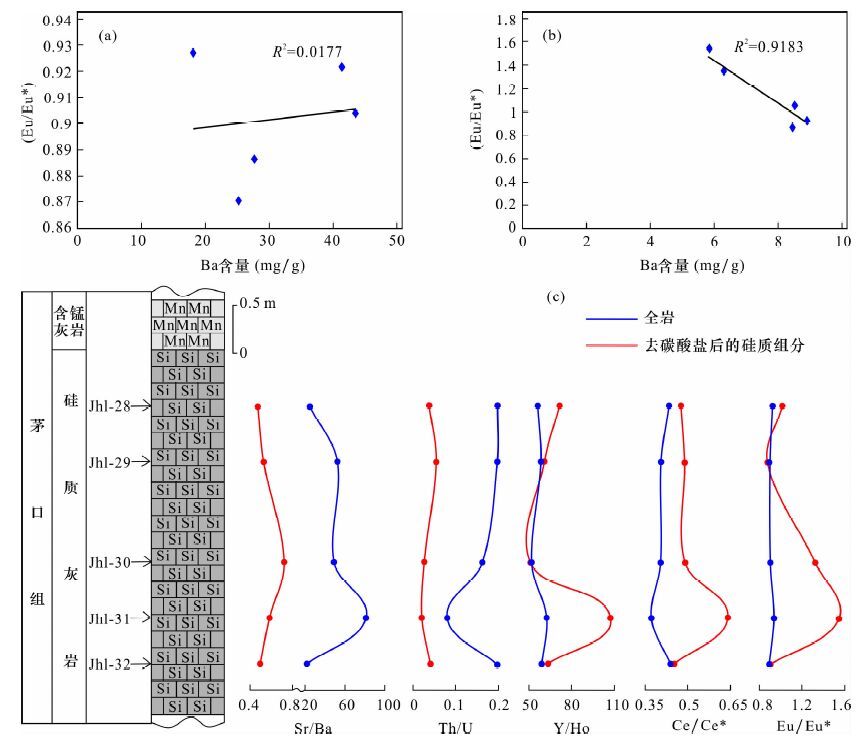
| [1] |
贵州省地质矿产局编著.贵州省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社,1987:558-560.
Google Scholar
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Guizhou Province.Regional Geology of Guizhou Province[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1987:558-560.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
刘巽锋,王庆生,高兴基等编著.贵州锰矿地质[M].贵阳:贵州人民出版社,1989:7-56.
Google Scholar
Liu X F,Wang Q S,Gao X J,et al.Manganese Deposits of Guizhou[M].Guiyang:Guizhou People's Publishing House,1989:7-56.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
陶平,杜昌乾,马荣,等.贵州及邻区二叠系锰矿地质特征及成矿作用探讨[J].贵州地质, 2005,22(2):102-108.
Google Scholar
Tao P,Du C Q,Ma R,et al.The Research on Geologic Feature and Metallogenesis of the Permian Manganese Ore Deposits in Guizhou and the Vicinages[J].Guizhou Geology,2005,22(2):102-108.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
林贵生,李赟.遵义锰矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J].中国锰业,2006,24(3):26-30.
Google Scholar
Lin G S,Li Y.Geological Characteristics and Prospectives of Zunyi Manganese Ores[J].China's Manganese Industry,2006,24(3):26-30.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
刘平,廖友常,殷科华,等.与火山活动有关的热水沉积锰矿——以贵州二叠纪锰矿为例[J].中国地质,2008,35(5):992-1006.
Google Scholar
Liu P,Liao Y C,Yin K H,et al.Hydrothermal Sedimentary Deposits Associated to Volcanic Activities-Permian Manganese Deposit in Guizhou[J].Geology in China,2008,35(5):992-1006.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
铁永洪,刘志臣,张远国,等.遵义锰矿地质特征及富集规律[J].矿业工程研究,2013,28(3):63-67.
Google Scholar
Tie Y H,Liu Z C,Zhang Y G,et al.Geological Characteristics and Enrichment Regularity of Zunyi Manganese Ore[J].Mineral Engineering Research,2013,28(3):63-67.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
刘志臣,张远国,陈登,等.贵州遵义锰矿区"白泥塘层"硅质岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].矿物学报,2013,33(4):665-670.
Google Scholar
Liu Z C,Zhang Y G,Chen D,et al.Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of ‘Bainitangceng’ Siliceous Rocks in Zunyi Manganese Ore Fields,Guizhou Province,China[J].Acta Mieralogica Sinica,2013,33(4):665-670.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
杜小全.黔北二叠纪锰矿成矿条件与找矿方向[J].矿产勘查,2011,2(3):249-253.
Google Scholar
Du X Q.Metallogenic Conditions and Prospecting Direction for Permian Manganess Deposit in Northern Guizhou[J].Mineral Exploration,2011,2(3):249-253.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
皮道会,刘丛强,邓海琳,等.贵州遵义牛蹄塘组黑色岩系有机质的稀土元素地球化学研究[J].矿物学报,2008,28(3):303-310.
Google Scholar
Pi D H,Liu C Q,Deng H L,et al.REE Geochemistry of Organic Matter from Black Shales of the Niutitang Formation,Zunyi,Guizhou Province[J].Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2008,28(3):303-310.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
裴浩翔,付勇,徐志刚,等.贵州道坨锰矿菱锰矿的稀土元素特征[J].沉积与特提斯地质,2015,35(1):76-85.
Google Scholar
Pei H X,Fu Y,Xu Z G,et al.REE Characteristics of Rhodochrosite from the Daotuo Manganese Deposit in Guizhou[J].Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2015,35(1):76-85.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
姚旭,周瑶琪,李素,等.硅质岩与二叠纪硅质沉积事件研究现状及进展[J].地球科学进展,2013,28(11):1189-1200.
Google Scholar
Yao X,Zhou Y Q,Li S,et al.Research Status and Advances in Chert and Permian Chert Event[J].Advances in Earth Science,2013,28(11):1189-1200.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Tribovillard N,Algeo T J,Lyons T,et al.Trace Metals as Paleoredox and Paleoproductivity Proxies:An Update[J].Chemical Geology,2006,232(1):12-32.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Dypvik H.Geochemical Compositions and Depositional Conditions of Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous Yorkshire Clays[J].England Geology,1984,121(5):489-504.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Dill H.Metallogenesis of Early Palaeozoic Graptolite Shales from the Graefenthal Horst (Northern Bavaria-Federal Republic of Germany)[J].Economic Geology,1986,81:889-903.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Liu K,Yang R D,Chen W Y,et al.Trace Element and REE Geochemistry of the Zhewang Gold Deposit,Southeastern Guizhou Province,China[J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry,2014,33:109-118.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Morford J L.Diagenesis of Oxyanions (V,U,Re,and Mo) in Pore Waters and Sediments from a Continental Margin[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2005,69(21):5021-5032.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Kimura H,Watanabe Y.Oceanic Anoxia at the Precam-brian-Cambrian Boundary[J].Geology,2001,29(11):995-998.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Wignall P B,Twitchett R J.Oceanic Anoxia and the End Permian Mass Extinction[J].Science,1996,272(5265):1155-1158.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Rona P A.Criteria for Recognition of Hydrothermal Mineral Deposits in Ocean Crust[J].Economic Geology,1987,73:135-160.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Owen A,Armstrong A H,Floyd D J.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Upper Ordovician Cherts from the Southern Uplands of Scotland[J].Journal of the Geological Society,1999,156(1):191-204.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Chen D Z,Qing H R,Yan X,et al.Hydrothermal Venting and Basin Evolution (Devonian,South China):Constraints from Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Chert[J].Sedimentary Geology,2006,183(3-4):203-216.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Wang J G,Chen D Z,Wang D,et al.Petrology and Geochemistry of Chert on the Marginal Zone of Yangtze Platform,Western Hunan,South China,during the Ediacaran-Cambrian Transition[J].Sedimentary Geology,2012,59(3):809-829.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Nozaki Y,Zhang J, Amakawa H,et al.The Fractionation between Y and Ho in the Marine Environment[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1997,148(1-2):329-340.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Dieudonne C I I, Cheo E H, Ghogomu R T.Textures and Rare Earth Elements Composition of Banded Iron Formations at Njweng Prospect,Mbalam Iron Ore District,Southern Cameroon[J].International Journal of Geosciences,2013,4:146-165.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Lawrence M G,Kamber B S.The Behaviour of the Rare Earth Elements during Estuarine Mixing-revisited[J].Marine Chemistry,2006,100(1):147-161.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Chen L,Lin A T S,Da X J,et al.Sea-level Changes Recorded by Cerium Anomalies in the Late Jurassic (Tithonian) Black Rock Series of Qiangtang Basin,North-Central Tibe[J].Oil Shale,2012,29(1):18-35.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
German C R,Elderfield H.Application of the Ce Anomaly as a Paleoredox Indicator:The Ground Rules[J].Paleoceanography,1990,5(5):823-833.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Kamber B S,Webb G E.The Geochemistry of Late Archaean Microbial Carbonate:Implications for Ocean Chemistry and Continental Erosion History[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2001,65(15):2509-2525.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Bolhar R,Van Kranendonk M J.A Non-marine Deposi-tional Setting for the Northern Fortescue Group,Pilbara Craton,Inferred from Trace Element Geochemistry of Stromatolitic Carbonates[J]. Precambrian Research,2007,155(3-4):229-250.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Jeans C V,Wray D S,Williams C T,et al.Redox Conditions in the Late Cretaceous Chalk Sea:The Possible Use of Cerium Anomalies as Palaeoredox Indicators in the Cenomanian and Turonian Chalk of England[J].Acta Geologica Polonica,2015,65(3):345-366.
Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Murray R W,Brink M R B,Jones D L,et al.Rare Earth Elements as Indicators of Different Marine Depositional Environment in Chert and Shale[J].Geology,1990,18(3):268-271.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Dulski P.Interferences of Oxide,Hydroxide and Chloride Analyte Species in the Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Geological Samples by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry[J].Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry,1994,350(4):194-203.
Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Anja G,Dirk M,Georg B.Origin of Middle Rare Earth Element Enrichment in Acid Mine Drainage-impacted Areas[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2014,21:6812-6823.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Dubinin A.Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements in the Ocean[J].Lithology and Mineral Resources,2004,39(4):289-307.
Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
German R C,Higgs C N,Thomson J.A Geochemical Study of Metalliferous Sediment from the TAG Hydrothermal Mound,2608'N,Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1993,98(B6):9683-9692.
Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Laurila T E,Hannington M D,Petersen S,et al.Early Depositional History of Metalliferous Sediments in the Atlantis Ⅱ Deep of the Red Sea:Evidence from Rare Earth Element Geochemistry[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2014,126:146-168.
Google Scholar
|





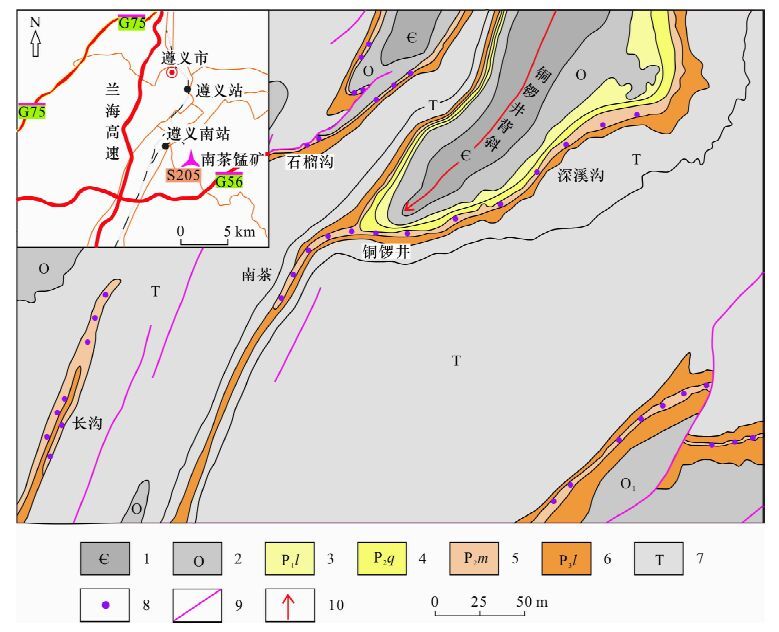

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: