Changzheng LIU, Zhicheng CAO, Cheng PENG, Huijun CUI. Study on Direct Reduction of Sea Sand Ore Containing Vanadium and Titanium by Rotary Hearth Furnace[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(4): 52-57. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.07.008
| Citation: |
Changzheng LIU, Zhicheng CAO, Cheng PENG, Huijun CUI. Study on Direct Reduction of Sea Sand Ore Containing Vanadium and Titanium by Rotary Hearth Furnace[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(4): 52-57. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2020.07.008
|
Study on Direct Reduction of Sea Sand Ore Containing Vanadium and Titanium by Rotary Hearth Furnace
-
RHF Business Division, Baowu Group Environmental Resources Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201900, China
More Information
-
Corresponding author:
Zhicheng CAO, caozhicheng_560034@baosteel.com
-
Abstract
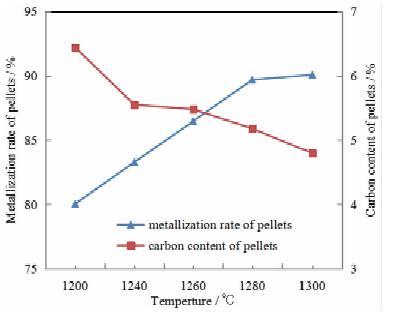
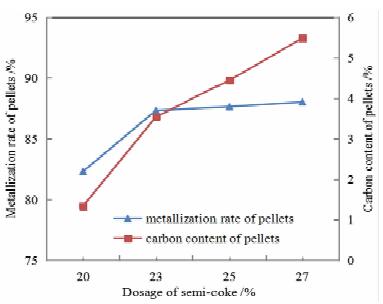
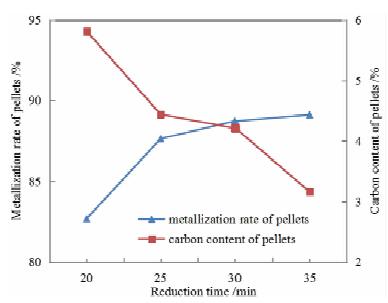
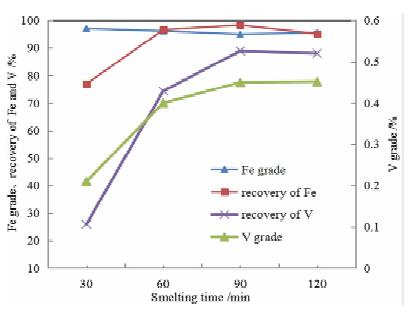
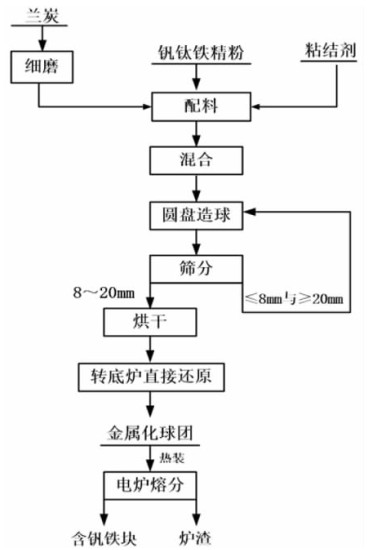
For the concentrate of Indonesian sand mine containing vanadium and titanium, the process of direct reduction by rotary hearth furnace and melting separation by electric furnace was adopted to complete the small-scale basic test and the pilot test successively. The metallized pellets could be obtained with the average metallization rate of 88.63% and carbon content of 4.81% by pilot test under the conditions of the mixed material ratio of the sea sand concentration, semi-coke, bentonite and organic binder at the ratio of 100:25:3:1, the thickness of containing coal pellets of 3 layers (54 mm), rotary hearth furnace roasting temperature of 1 260 ℃, reduction time of 30 minutes. Then the hot metallized pellets were fed into a 300 kVA electric furnace for smelting. The iron containing V could be obtained with TFe grade of 96.25%, iron recovery of 99.64%, V grade of 0.443% and V recovery of 88.96%. The grade of TiO2 in slag is 38.86%, and the recovery of titanium is 98.95%. The results showed that the technology of direct reduction by RHF and melting by electric furnace was feasible.
-

-
References
| [1] |
徐礼兵, 周明顺, 刘杰, 等.新西兰海砂矿烧结性能研究[J].矿冶工程, 2015, 38(4):91-94.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
张亚鹏, 张建良, 王振阳, 等.细磨海砂矿烧结特性及其对烧结矿质量影响机理[J].工程科学学报, 2016, 38(4):468-475.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
王振阳.海砂矿钛铁资源分级利用研究[D].北京: 北京科技大学, 2018.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
孟聪, 李丽匣, 申帅平, 等.某钛铁矿分级磁选分级浮选试验研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2017(1):59-63.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
李林.攀枝花低品位钒钛磁铁矿综合回收铁、钛试验研究[J].矿产保护与利用, 2015(2):27-32.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
朱建秋.钒钛矿大高炉开炉顺利达产实践[J].河北冶金, 2017, 261(9):52-56.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
高强健, 魏国, 刘常升, 等.二元碱度对印尼钒钛矿烧结过程及烧结矿质量的影响[J].东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(12):1726-1730.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
彭英健, 吕超.钒钛磁铁矿综合利用现状及进展[J].矿业研究与开发, 2019, 39(5):130-135.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
李志强, 张洋.新西兰钒钛海砂磁铁矿冶炼工艺分析[J].现代冶金, 2017, 45(4):31-33.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
NIGEL T·EVANS, 陈夏尔.新西兰钢铁公司的SL/RN法的发展[J].钢铁钒钛, 1983(1):97-103.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
刘依然, 张建良, 王振阳, 等.海砂矿的深度还原研究[J].金属矿山, 2015, 44(5):72-76.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
刘依然, 张建良, 王振阳, 等.海砂矿深度还原--磁选分离实验研究[J].2016, 38(2):工程科学学报, 181-186.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
曹志成.铜渣转底炉直接还原回收铁锌工艺及机理研究[D].北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
秦洁.含碳球团转底炉直接还原的关键技术[J].钢铁研究, 2012, 40(5):55-59.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
刘功国, 秦洁, 何绍刚.钒钛磁铁矿金属化球团生产工艺参数试验研究[J].矿冶, 2015, 24(5):41-44.
Google Scholar
|
-
-
Access History







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: