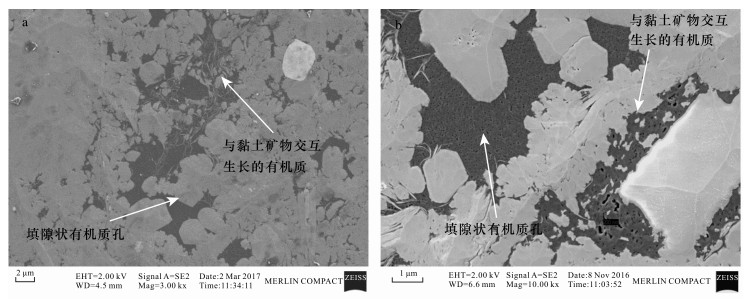
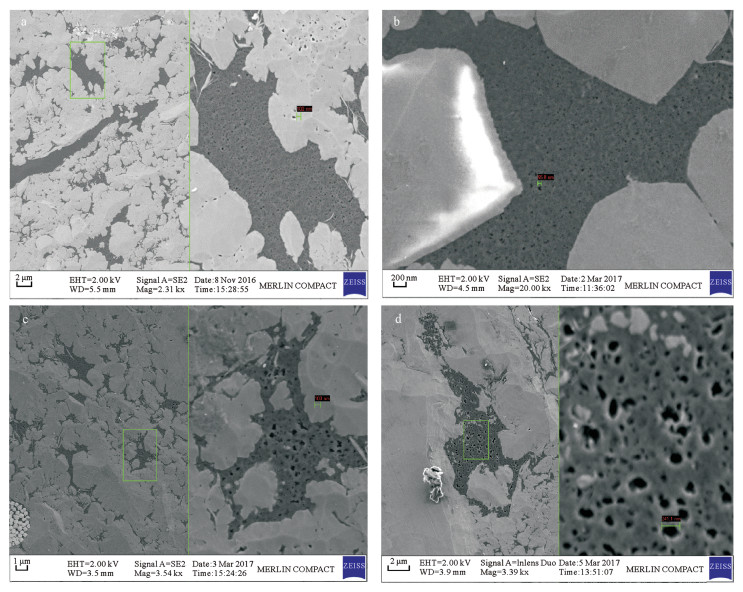
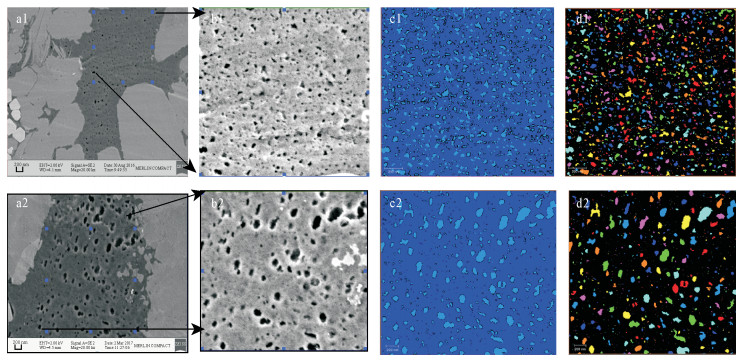
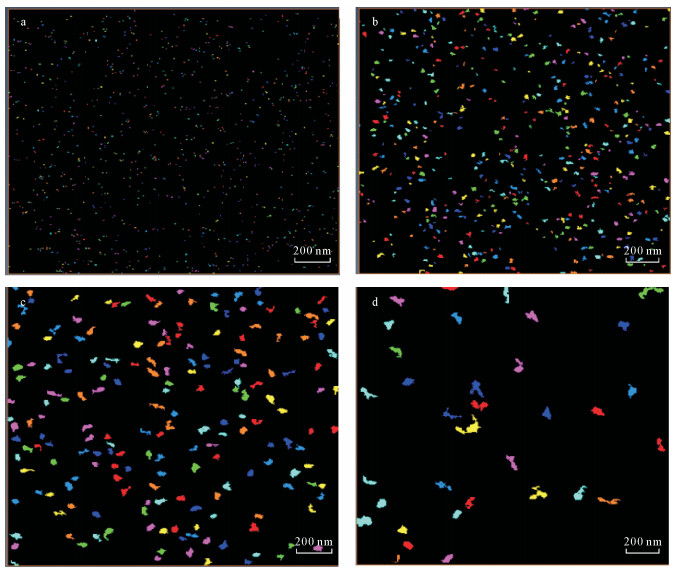
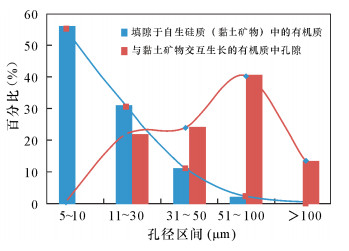
| [1] |
Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(9):848-861.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Schieber J. Common themes in the formation and preserv-ation of intrinsic porosity in shales and mudstones-illuminated with examples across the phanerozoic[R]. 2010, SPE132370: 2-10.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C.Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Chalmers G R, Bustin R M, Power I M.Characterization of gas shale pore systems by porosimetry, pycnometry, surface area, and field emission scanning electron microscopy/transmission electron microscopy image analyses:Examples from the Barnett, Woodford, Haynesville, Marcellus, and Doigunits[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1099-1119. doi: 10.1306/10171111052
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Löhr S C, Baruch E T, Hall P A.Is organic pore development in gas shales influenced by the primary porosity and structure of thermally immature organic matter?[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2015, 87:119-132. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.07.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Loucks R G, Reed R M.Scanning electron microscope petrographic evidence for distinguishing organic matter pores associated with depositional organic matter versus migrated organic matter in mudrock[J].GCAGS Journal, 2014, 3:51-60.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等.中国油气储层中纳米孔首次发现及其科学价值[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864.
Google Scholar
Zou C N, Zhu R K, Bai B, et al.First discovery of nanopore throat in oil and gas reservoir in China and its scientific value[J].Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(6):1857-1864.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
帅琴, 黄瑞成, 高强, 等.页岩气实验测试技术现状与研究进展[J].岩矿测试, 2012, 31(6):931-938.
Google Scholar
Shuai Q, Huang R C, Gao Q, et al.Research development of analytical techniques for shale gas[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(6):931-938.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
于炳松.页岩气储层孔隙分类与表征[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):211-220.
Google Scholar
Yu B S.Classification and characterization of gas shale pore system[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):211-220.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
张盼盼, 刘小平, 王雅杰, 等.页岩纳米孔隙研究新进展[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(11):1242-1249. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1242
CrossRef Google Scholar
Zhang P P, Liu X P, Wang Y J, et al.Research progress in shale nanopores[J].Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(11):1242-1249. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1242
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
焦淑静, 张慧, 薛东川, 等.泥页岩孔隙类型、形态特征及成因研究[J].电子显微学报, 2015, 34(5):422-427.
Google Scholar
Jiao S J, Zhang H, Xue D C, et al.Study on morphological characteristics of micropores and microcracks in shale[J].Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2015, 34(5):422-427.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
伍岳, 樊太亮, 蒋恕, 等.海相页岩储层微观孔隙体系表征技术及分类方案[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(4):92-97.
Google Scholar
Wu Y, Fan T L, Jiang S, et al.Characterizing techniques and classification methods for microscope pore system in marine shale reservoir[J].Geological Science and Technology Information, 2014, 33(4):92-97.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Clarkson C R, Solano N, Bustin R M, et al.Pore structure characterization of North American shale gas reservoirs using USANS/SANS, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J].Fuel, 2013, 103:606-616. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2012.06.119
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
郭旭升, 李宇平, 刘若冰, 等.四川盆地焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(6):9-16.
Google Scholar
Guo X S, Li Y P, Liu R B, et al.Characteristics and controlling factors of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi shale play in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J].Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6):9-16.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
武景淑, 于炳松, 张金川, 等.渝东南渝页1井下志留统龙马溪组页岩孔隙特征及其主控因素[J].地学前缘, 2013, 20(3):260-269.
Google Scholar
Wu J S, Yu B S, Zhang J C, et al.Pore characteristics and controlling factors in the organic-rich shale of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation revealed by samples from a well in Southeastern Chongqing[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3):260-269.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
姜振学, 唐相路, 李卓, 等.川东南地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构全孔径表征及其对含气性的控制[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(2):126-134.
Google Scholar
Jiang Z X, Tang X L, Li Z, et al.The whole-aperture pore structure characteristics and its effect on gas content of the Longmaxi Formation shale in the Southeast Sichuan Basin[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2):126-134.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
杨文新, 李继庆, 赵江艳, 等.四川盆地涪陵地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构定性定量研究[J].石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1):98-102.
Google Scholar
Yang W X, Li J Q, Zhao J Y, et al.Qualitative and quantitative study of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi Formation shale in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(1):98-102.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
王玉满, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等.川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层特征[J].石油学报, 2012, 33(4):551-561. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204003
CrossRef Google Scholar
Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Li J Z, et al.Reservoir characteristics of shale gas in Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, Southern Sichuan[J].Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4):551-561. doi: 10.7623/syxb201204003
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
蔡潇, 王亮, 靳雅夕, 等.渝东南地区页岩有机孔隙类型及特征[J].天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3):513-519. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0513
CrossRef Google Scholar
Cai X, Wang L, Jin Y X, et al.Types and characteristics of organic pore in shale gas reservoir of Southeastern Chongqing area[J].Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3):513-519. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0513
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
耿一凯, 金振奎, 赵建华, 等.页岩储层孔隙类型控制因素研究——以川东焦石坝地区龙马溪组为例[J].石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1):72-78.
Google Scholar
Geng Y K, Jin Z K, Zhao J H, et al.Controlling factors of pore types in shale reservoirs:A case study from the Longmaxi Formation in Jiaoshiba area, Eastern Sichuan Basin[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(1):72-78.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
刘尧文, 王进, 张梦吟, 等.四川盆地涪陵地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩气层孔隙特征及对开发的启示[J]石油实验地质, 2018, 40(1):45-50.
Google Scholar
Liu Y W, Wang J, Zhang M Y, et al.Pore features of shale gas layer in Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Fuling area of Sichuan Basin and the application to development[J].Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(1):45-50.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
陈生蓉, 帅琴, 高强, 等.基于扫描电镜-氮气吸脱附和压汞法的页岩孔隙结构研究[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(6):636-642.
Google Scholar
Chen S R, Shuai Q, Gao Q, et al.Analysis of the pore structure of shale in Ordos Basin by SEM with nitrogen gas adsorption-desorption[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(6):636-642.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
王羽, 金婵, 汪丽华, 等.应用氩离子抛光-扫描电镜方法研究四川九老洞组页岩微观孔隙特征[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(3):278-285.
Google Scholar
Wang Y, Jin C, Wang L H, et al.Characterization of pore structures of Jiulaodong Formation Shale in the Sichuan Basin by SEM with Ar-ion milling[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(3):278-285.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
庞河清, 曾焱, 刘成川, 等.基于氮气吸附-核磁共振-氩离子抛光场发射扫描电镜研究川西须五段泥质岩储层孔隙结构[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1):66-74.
Google Scholar
Pang H Q, Zeng Y, Liu C C, et al.Investigation of pore structure of an argillaceous rocks reservoir in the 5th member of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan, using NAM, NMR and AIP-FESEM[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1):66-74.
Google Scholar
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: