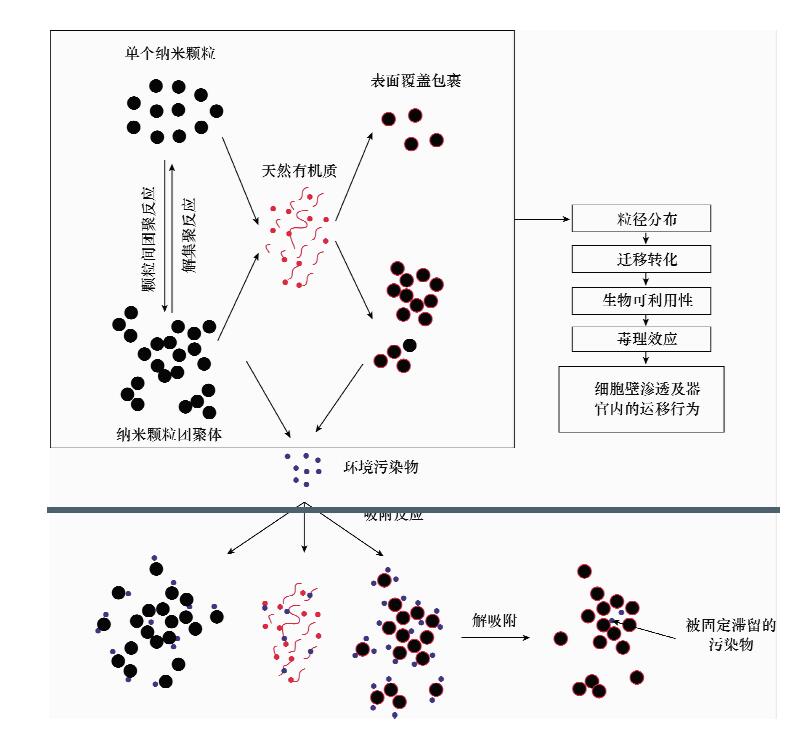
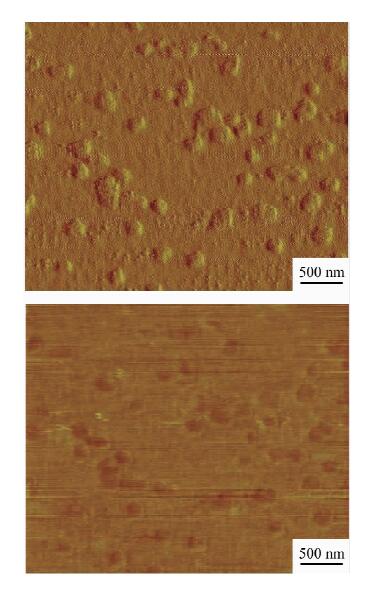
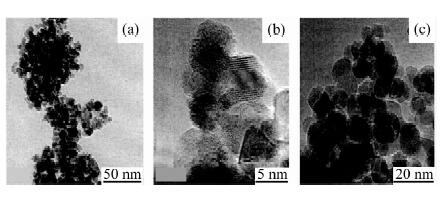
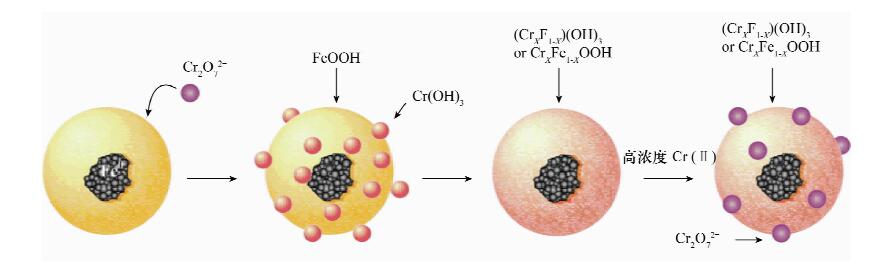
| [1] |
Farre M, Sanchis J, Barcelo D. Analysis and assessment of the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of nanomaterials in the environment [J].Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 30(3): 517-527. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2010.11.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Subcommitte on Nanoscale Science Engineering and Technology, National Scicence and Technology Council Committee on Technology. National Nanotechnology Initiative Strategic Plan [R].USA,2011.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Majewski P, Thierry B.Functionalized magnetite nanoparticles-Synthesis, properties, and bio-applications [J].Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 2007, 32(3-4):203-215.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Wei X C, Viadero R C.Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles with ferric iron recovered from acid mine drainage: Implications for environmental engineering [J].Colloids and Surfaces A—Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 294(1-3):280-286.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Zhang Q A, Thompson M S, Carmichael-Baranauskas A Y, Caba B L, Zalich M A, Lin Y N, Mefford O T, Davis R M, Riffle J S. Aqueous dispersions of magnetite nanoparticles complexed with copolyether dispersants: Experiments and theory [J].Langmuir, 2007, 23(13): 6927-6936. doi: 10.1021/la070116+
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
Hu J H, Johnston K P, Williams R O. Nanoparticle engineering processes for enhancing the dissolution rates of poorly water soluble drugs [J].Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2004, 30(3): 233-245. doi: 10.1081/DDC-120030422
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Mak S Y, Chen D H. Fast adsorption of methylene blue on polyacrylic acid-bound iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles [J].Dyes and Pigments, 2004, 61(1): 93-98. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2003.10.008
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Li X Q, Cao J S, Zhang W X. Stoichiometry of Cr(Ⅵ) immobilization using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI): A study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS) [J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(7): 2131-2139.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Hu J D, Zevi Y, Kou X M, Xiao J, Wang X J, Jin Y. Effect of dissolved organic matter on the stability of magnetite nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strength conditions [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(16): 3477-3489. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.033
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
De D, Mandal S, Bhattacharya J, Ram S, Roy S. Iron oxide nanoparticle-assisted arsenic removal from aqueous system [J].Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A—Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 2009, 44(2): 155-162.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Liu R Q, Zhao D Y. Reducing leachability and bioacce-ssibilty of lead in soils using a new class of stabilized iron phosphate nanoparticles [J].Water Research, 2007, 41(12): 2491-2502. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2007.03.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Liang P, Qin Y C, Hu B, Li C X, Peng T Y, Jiang Z C. Study of the adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions on nanometer-size titanium dioxide with ICP-AES [J].Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2000, 368(6): 638-640. doi: 10.1007/s002160000546
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Christian P, Von der Kammer F, Baalousha M, Hofmann T. Nanoparticles: Structure, properties, preparation and behaviour in environmental media [J].Ecotoxicology, 2008, 17(5): 326-343. doi: 10.1007/s10646-008-0213-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Hiemstra T, Antelo J, Rahnemaie R, van Riemsdijk W H. Nanoparticles in natural systems Ⅰ: The effective reactive surface area of the natural oxide fraction in field samples [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(1): 41-58. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.10.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Gilbert B, Ono R K, Ching K A, Kim C S. The effects of nanoparticle aggregation processes on aggregate structure and metal uptake [J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 339(2): 285-295. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2009.07.058
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Hiemstra T, Antelo J, van Rotterdam A M D, van Riemsdijk W H. Nanoparticles in natural systems Ⅱ: The natural oxide fraction at interaction with natural organic matter and phosphate [J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(1): 59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.10.019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Tombacz E. Colloidal properties of humic acids and spontaneous changes of their colloidal state under variable solution conditions [J].Soil Science,1999, 164(11): 814-824. doi: 10.1097/00010694-199911000-00005
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
胡俊栋.四氧化三铁纳米颗粒的稳定性及其在饱和多孔介质中的迁移持留行为[D].北京:北京大学,2010.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
王萌,陈世宝,李娜,马义兵.纳米材料在污染土壤修复及污水净化中应用前景探讨[J].中国生态农业学报, 2010, 18(4): 434-439.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Qiu H, Zhang S J, Pan B C, Zhang W M, Lü L. Effect of sulfate on Cu(Ⅱ) sorption to polymer-supported nano-iron oxides: Behavior and XPS study [J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2012, 366(1): 37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2011.09.070
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Sharma Y C, Srivastava V, Weng C H, Upadhyay S N. Removal of Cr(Ⅵ) from wasterwater by adsorption on iron nanoparticles [J].Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering,2009, 87(6): 921-929. doi: 10.1002/cjce.v87:6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Hu J, Chen G H, Lo I M C. Removal and recovery of Cr(Ⅵ) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles [J].Water Research,2005, 39(18): 4528-4536. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.05.051
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Klimkova S, Cernik M, Lacinova L, Filip J, Jancik D, Zboril R. Zero-valent iron nanoparticles in treatment of acid mine water from in situ uranium leaching [J].Chemosphere,2011, 82(8): 1178-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.11.075
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Carabante I, Grahn M, Holmgren A, Kumpiene J, Hedlund J.Adsorption of As(Ⅴ) on iron oxide nanoparticle films studied by in situ ATR-FTIR spectroscopy [J].Colloids and Surfaces A—Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2009,346(1-3): 106-113.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Hu J, Chen G H, Lo I M C.Selective removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater using maghemite nanoparticle: Performance and mechanisms [J].Journal of Environmental Engineering,2006, 132(7): 709-715. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2006)132:7(709)
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Nishio K, Gokon N, Tsubouchi S, Ikeda M, Narimatsu H, Sakamoto S, Izumi Y, Abe M, Handa H. Direct detection of redox reactions of sulfur-containing compounds on ferrite nanoparticle (FP) surface [J].Chemistry Letters,2006, 35(8): 974-975. doi: 10.1246/cl.2006.974
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Lin K S, Chang N B, Chuang T D. Fine structure characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles for decontamination of nitrites and nitrates in wastewater and groundwater [J].Science and Technology of Advanced Materials,2008,9(2):doi:10. 1088/1468-6996/9/2/025015.
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
Zhou J G, Fang H T, Hu Y F, Sham T K, Wu C X, Liu M, Li F. Immobilization of RuO2 on carbon nanotube: An X-ray absorption near-edge structure study [J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2009, 113(24): 10747-10750. doi: 10.1021/jp902871b
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Olegario J T, Yee N, Miller M, Sczepaniak J, Manning B. Reduction of Se(Ⅵ) to Se(-Ⅱ) by zerovalent iron nanoparticle suspensions [J].Journal of Nanoparticle Research,2010, 12(6): 2057-2068. doi: 10.1007/s11051-009-9764-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Pelley A J, Tufenkji N. Effect of particle size and natural organic matter on the migration of nano- and microscale latex particles in saturated porous media [J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2008, 321(1): 74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2008.01.046
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Zhang M Y, Wang Y, Zhao D Y, Pan G. Immobi-lization of arsenic in soils by stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron, iron sulfide (FeS), magnetite (Fe3O4) particles [J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2010, 55(4-5): 365-372. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0703-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Manzoori J L, Amjadi M, Hallaj T. Preconcentration of trace cadmium and manganese using 1-(2-pyridylazo)-2-naphthol-modified TiO2 nanoparticles and their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry [J].International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry,2009, 89(8-12): 749-758. doi: 10.1080/03067310902736955
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
Chidambaram D, Hennebel T, Taghavi S, Mast J, Boon N, Verstraete W, van der Lelie D, Fitts J P. Concomitant microbial generation of palladium nanoparticles and hydrogen to immobilize chromate [J].Environmental Science & Technology,2010, 44(19): 7635-7640.
Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Xiong Z, He F, Zhao D Y, Barnett M O.Immobi-lization of mercury in sediment using stabilized iron sulfide nanoparticles [J].Water Research,2009, 43(20): 5171-5179. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2009.08.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Jin Y, Chu Y J, Li Y S.Virus removal and transport in saturated and unsaturated sand columns [J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology,2000, 43(2): 111-128. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(00)00084-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
方婧,周艳萍,温蓓.二氧化钛纳米颗粒对铜在土壤中运移的影响[J].土壤学报, 2011, 48(3): 549-556. doi: 10.11766/trxb200912220584
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Ghosh S, Jiang W, McClements J D, Xing B S.Colloidal stability of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Influence of natural organic matter and synthetic polyelectrolytes [J].Langmuir,2011, 27(13): 8036-8043. doi: 10.1021/la200772e
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Pan B, Xing B S.Applications and implications of manufactured nanoparticles in soils: A review [J].European Journal of Soil Science,2012, 63(4): 437-456. doi: 10.1111/ejss.2012.63.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Franchi A, O′Melia C R.Effects of natural organic matter and solution chemistry on the deposition and reentrainment of colloids in porous media [J].Environmental Science & Technology,2003, 37(6): 1122-1129.
Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Uchimiya M, Lima I M, Klasson K T, Wartelle L H. Contaminant immobilization and nutrient release by biochar soil amendment: Roles of natural organic matter [J].Chemosphere,2010, 80(8): 935-940. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.05.020
CrossRef Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: