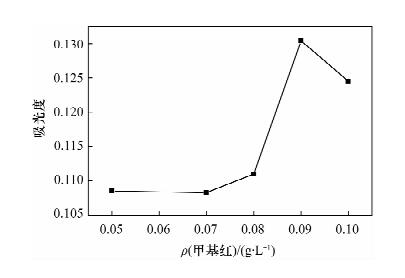
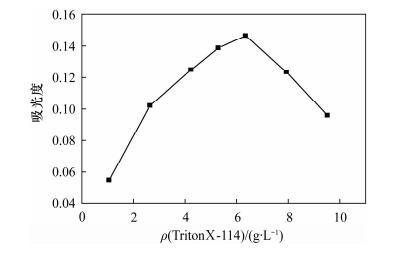
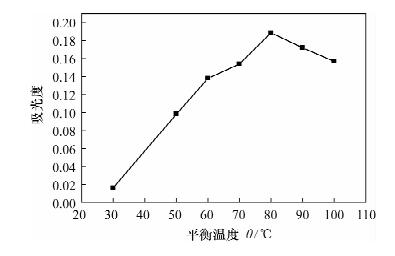
| [1] |
Han H Y, Zhou J, Xu Y Y, Jia C L, Xia H. Determination of water-soluble and acid-soluble zinc in soils by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction [J].Soil Science and Plant Analysis,2012,43(18):2389-2399. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2012.708072
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
查立新,马玲,刘文长,刘洪青,陈波,冯玲玲.振荡提取和超声提取用于土壤样品中元素形态分析[J].岩矿测试,2011,30(4):393-399.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Han H Y, Xu Y Y, Zhang C.Determination of available cadmium and lead in soil by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction [J].Soil Science and Plant Analysis,2011,42(14):1739-1751. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2011.584595
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
尹君,刘文菊,谢建治,肖崇彬.土壤中有效态镉、汞浸提剂和浸提条件研究[J].河北农业大学学报,2000,23(20):25-28.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
靳霞.土壤中重金属有效态的联合测定及其植物修复研究[D].临汾:山西师范大学,2012.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
王畅,郭鹏然,陈杭亭,舒永红.土壤和沉积物中重金属生物可利用性的评估[J].岩矿测试,2009,28(2):108-112.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
HJ/T 166—2004,土壤环境监测技术规范[S].
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
李亮亮,张大庚,李天来,依艳丽,臧健,胡睿.土壤有效态重金属提取剂选择的研究[J].土壤,2008,40(5):819-823.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
熊礼明,鲁如坤. 土壤有效Cd浸提剂对Cd的浸提机制[J].环境化学,1992,11(3):41-47.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
梁沛,李春香,秦永超,胡斌,江祖成.纳米二氧化钛分离富集和ICP-AES测定水样中Cr(Ⅵ)/Cr(Ⅲ) [J].分析科学学报,2000,16(4):300-303.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Hosseini M S, Sarab A R R.Cr(Ⅵ)/Cr(Ⅲ) speciation in water samples by extractive separation using Amberlite CG 50 and final determination by FAAS [J].Inter-national Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry,2007,87(5):375-385. doi: 10.1080/03067310601068866
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Marques M J, Salvador A, Morales-Rubio A, de la Guardia M. Chromium speciation in liquid matrices:A survey of the literature [J].Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2000,367(7):601-613. doi: 10.1007/s002160000422
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Balcerzak M, Swiecicka E.Determination of ruthenium and osmium in each other′s presence in chloride solutions by direct and third order derivative spectrophotometry [J].Talanta,1996,43:471-478. doi: 10.1016/0039-9140(95)01776-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Keith L H,Gron L U,Young J L. Green analytical methodologies [J].Chemical Reviews,2007,107(6):2695-2708. doi: 10.1021/cr068359e
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
LY/T 1260—1999,森林土壤有效铜的测定[S].
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
GB/T 17138—1997,土壤质量;铜、锌的测定;火焰原子吸收分光光度法[S].
Google Scholar
|





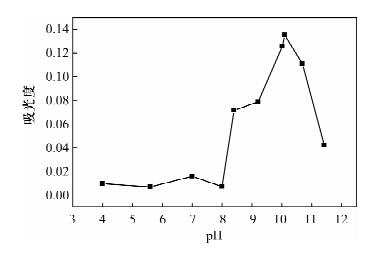

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: