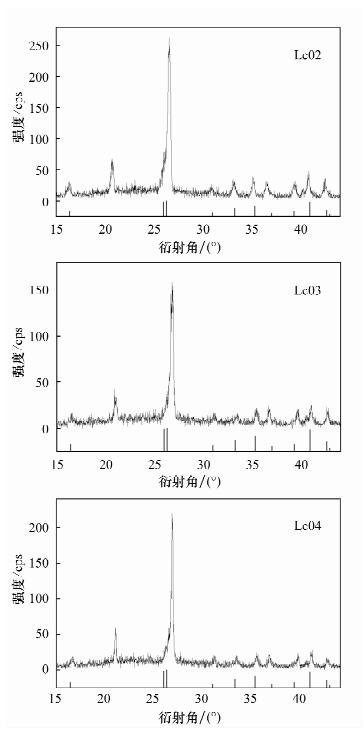
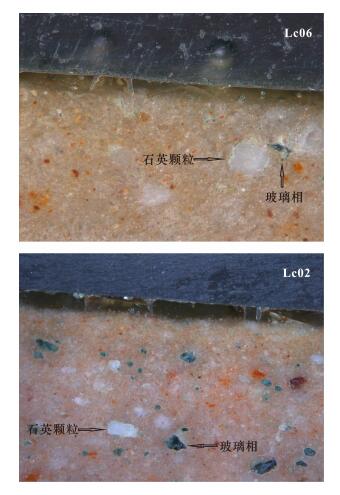
| [1] |
李江.河北省临漳曹村窑址初探与试掘简报[M]//中国古陶瓷学会.中国古陶瓷研究(第十六辑).北京: 紫禁城出版社, 2010: 43-52.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
刘毅, 袁胜文.北方早期青瓷初论[J].中原文物, 1992(2): 82-87.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
李迎华, 杨益民, 周卫荣, 董亚巍, 王昌燧, 金普军, 张尚欣.古代陶范原料配方含有草木灰的化学判断方法[J].岩矿测试, 2009, 28(2): 134-138.
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
朱铁权, 王昌燧, 李艳, 毛振伟, 陈江峰, 后德俊, 蔡路武, 陈丽琼.不同窑口青白瓷瓷胎化学元素特征研究[J].岩矿测试, 2006, 25(2): 114-118.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
凌雪, 毛振伟, 冯敏, 胡耀武, 王昌燧, 刘洪淼.巩窑唐代早期白瓷的EDXRF线扫描分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2005, 25(7): 1145-1150.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
张茂林, 贾兴和, 毛振伟, 朱铁权, 王昌燧, 黄宇营, 何伟.斯里兰卡曼泰遗址出土青花瓷的化学成分分析及产地初探[J].岩矿测试, 2008, 27(1): 37-40.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
朱铁权, 王昌燧, 毛振伟, 袁传勋, 徐靖, 姚政权.不同窑口古瓷断面能量色散X射线荧光光谱线扫描分析[J].岩矿测试, 2007, 26(5): 381-384.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Villa R V, Giménez R G, Domínguez M D, Rucandio M I. Physicochemical and chemometric characterisation of late Roman amphorae from straits of Gibraltar [J]. Microchimica Acta, 2003, 142(1-2): 115-122. doi: 10.1007/s00604-002-0955-z
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Colomban P, Liem N Q, Sagon G, Tinh H X, Hoành T B. Microstructure, composition and processing of 15th Century vietnamese porcelains and celadons [J]. Journal of Cultural Heritage, 2003, 4(3): 187-197. doi: 10.1016/S1296-2074(03)00045-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Schleicher L S, Miller J W, Watkins-Kenney S C, Carnes-McNaughton L F, Wilde-Ramsing M U. Non-destructive chemical characterization of ceramic sherds from Shipwreck 31CR314 and Brunswick Town, North Carolina[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2008, 35(10): 2824-2838. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2008.05.012
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
李迎华, 王昌燧.瓷器测温的模拟实验研究[J].陶瓷学报, 2011, 32(3): 443-447.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
施继龙, 董亚巍, 周卫荣, 戴志强, 王昌燧.萧梁钱范烧成温度的测试分析[J].文物保护与考古科学, 2005(3): 7-11.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
周理坤, 王涛, 李珺, 任雪岩, 王昌燧.南庄头遗址早期陶器烧成温度研究[J].岩矿测试, 2010, 29(2): 148-152.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
李敏生, 黄素英. 山西襄汾陶寺遗址陶片的测试和分析[J].考古, 1993(2): 176-188.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
李乃胜, 张敬国, 毛振伟, 冯敏, 胡耀武, 王昌燧.五千年前陶质建材的测试研究[J].文物保护与考古科学, 2004(4): 13-20.
Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
郑乃章, 刘阳, 朱小平, 张勇, 王群.景德镇瓷坯料组成与性能的关系[J].陶瓷学报, 1999, 20(2): 92-98.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
徐安武, 杨晓勇, 林辉, 王昌燧, 王吉怀, 梁中合, 陈星灿.安徽蒙城尉迟寺遗址大口尊古陶器的稀土元素地球化学研究[J].稀土, 1999, 20(3): 3-6.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
杨益民, 汪丽华, 朱剑, 王昌燧, 阎焰, 陈栋梁, 何伟, 黄宇营, 华巍, 徐伟.红绿彩瓷化妆土的线扫描分析[J].核技术, 2008, 31(9): 653-657.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
罗武干, 秦颍, 田建花, 王昌燧.淮阴高庄战国墓出土青铜器产地初步研究[J].土壤, 2009, 41(4): 670-675. doi: 10.11766/trxb200711120415
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
李家治.古代中国陶瓷的科学技术——中国文化中的火凤凰[M]//王昌燧, 主编.科技考古论丛(第二辑).合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2000: 5-12.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
俞康泰.现代陶瓷色釉料与装饰技术手册[M].武汉: 武汉理工大学出版社, 1999: 135-141.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
李家治.中国科学技术史陶瓷卷[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 116-119, 167,467.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
李家驹.日用陶瓷工艺学[M].武汉: 武汉工业大学出版社, 1992: 293-297.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
陈彦堂.关于汉代低温铅釉陶器研究的几个问题[M]//古代文明(第4卷).北京: 文物出版社, 2008: 303-315.
Google Scholar
|
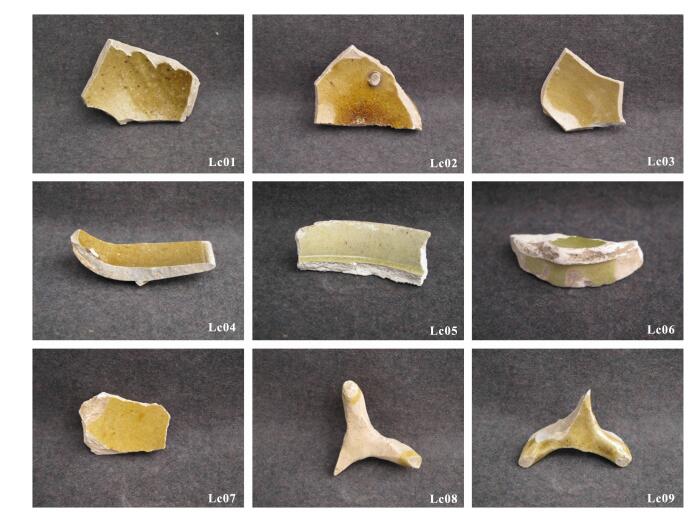







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: