| [1] |
Arukwe A, Celius T, Walther B T, Goksoyr A.Plasma level of vitellogenin anf eggsh ellzona radiata proteins in 4-nonylphenol and o,p'-DDT treated juvenil Atlantic salmon (Salmosalar)[J].Marine Environmental Research, 1998, 46(1-5):133-136. doi: 10.1016/S0141-1136(98)00002-6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Furuichi T, Kannan K, Giesy J P, Masunaga S.Contribution of known endocrine disrupting substances to the estrogenic activity in Tama River water samples from Japan using instrumental analysis and in vitro reporter gene assay[J].Water Research,2004,38:4491-4501. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.08.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
BS ISO 24293:2009, Water Quality-Determination of Individual Isomers of Nonylphenol-Method Using Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS)[S].
Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Lahnsteiner F, Berger B, Grubinger F, Weismann T.The effect of 4-nonylphenol on semen quality, viability of gametes, fertilization success, and embryo and larvae survival in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)[J].Aquatic Toxicology, 2005, 71: 297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.11.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Kawahata H, Ohta H, Inoue M, Suzuki A.Endocrine disrupter nonylphenol and bisphenol A contamination in Okinawa and Ishigaki Islands, Japan within coral reefs and adjacent river mouths[J].Chemosphere, 2004(55):1519-1527.
Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
沈慧云,徐培渝,余文三,刘玉清,吴德生.对-壬基酚对MCF-7人类乳腺癌细胞雌激素受体表达的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2003,34(4):641-645.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
薛光璞,姚朝英.4-烷基酚的GC/MS检测及长江南京段的污染状况[J].环境科学与管理,2010,35(6):1027-1031.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
傅明珠,李正炎,王波.夏季长江口及其临近海域不同环境介质中壬基酚的分布特征[J].海洋环境科学, 2008,27(6):561-565.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
金星龙,江桂斌,黄国兰,周群芳,刘景富.污水处理流程中几种典型酚类化合物的分布[J].环境科学学报, 2004,24(6):1027-1031.
Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
李正炎,Li D H.西瓦湖中壬基酚和双酚A的污染特征[J].青岛海洋大学学报,2003,33(6):847-853.
Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Xian F S, Xin N Z, Guo H X, Qing X Z.Fluorometric determination of nonylphenol in water samples enriched with zirconium doped titanium dioxide nanotubes solid phase extraction[J].Chinese Chemical Letters, 2012, 23(8):969-972. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2012.06.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Careri M, Elviri L, Mangia A.Development and valid-ation of a method using on-line solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection for the determination of bisphenol A, octylphenol, and nonylphenol in groundwater[J].Journal of AOAC International, 2011,84(5):1383-1392.
Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Komarek K, Safarikova M, Hubka T, Safarik I, Kandelova M, Kujalova H.Extraction of alkylphenols and nonylphenol mono-and diethoxylates from water using magnetically modified adsorbents [J].Chromatographia, 2009,69(1-2):133-137. doi: 10.1365/s10337-008-0833-x
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Manh H P, Shinji T, Michihiko I,Yayoi K, Kousuke K, Hung V P, Masanori F, Minoru T.Sim L taneous determination of degradation products of nonylphenol polyethoxylates and their halogenated derivatives by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry after trimethylsilylation[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 1020(2):161-172. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.08.064
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Ding W H, Wu C Y.Determination of estrogenic nonyl-phenol and bisphenolA in river water by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 2000, 47(5):1155-1160. doi: 10.1002/jccs.v47.5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
郝瑞霞,梁鹏,赵曼,曹可心,周玉文.城市污水再生处理过程中壬基酚的迁移转化行为研究[J].环境污染治理技术与设备,2006,7(2):66-70.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
郝瑞霞,梁鹏,赵曼,王俊安,周玉文.固相萃取-气相色谱-质谱-选择离子法检测污水中壬基酚[J].环境科学,2006,27(11):2222-2227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.11.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
郝瑞霞,梁鹏,赵曼,王俊安,周玉文.固相萃取法分离富集污水样品中痕量壬基酚[J].环境工程,2006,24(3):71-73.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
金士威,徐盈,惠阳,廖涛.污水中8种雌激素化合物的定量测定[J].中国给水排水,2005,21 (12):250-254.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
刘文萍,石晓勇,王晓波,张传松.北黄海辽宁近岸水环境中壬基酚污染状况调查及生态风险评估[J].海洋环境科学,2009,28(6):664-667.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
侯绍刚,徐建,汪磊,孙红文,戴树桂,刘昕宇.黄河(兰州段)水环境中壬基酚及壬基酚聚氧乙烯醚污染的初步研究[J].环境化学,2005,24(3):250-254.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
林福华,邱宁宁,黄晓佳,袁东星.搅拌棒固相萃取与液相色谱联用测定水样品中烷基酚类污染物[J].分析化学,2010,38(1):67-71.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
陈玲,周海云,刘岚,邓芹英.自动固相微萃取-气相色谱法检测水样中壬基酚[J].中山大学学报,2007,46(5):45-48.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Zhang C, Eganhouse R P, Pontolillo J, Cozzarelli I M, Wang Y.Determination of nonylphenol isomers in landfill leachate and municipal wastewater using steam distillation extraction coupled with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry [J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 12(30):110-116.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Fu X M, Wang L, Dai S G.Mechanism study on the extraction of nonylphenol by ionic liquids in water through IR spectroscopy and quantum chemical calculation[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2011,31(3):625-629.
Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
付新梅,戴树桂,张余.离子液体与传统有机溶剂萃取性能的比较研究[J].分析化学,2006(5):598.
Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
EPA 8270D, Semivolatile Organic Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) [S].2007.
Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
EPA 3520C,Continuous Liquid-Liquid Extraction[S].1996.
Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
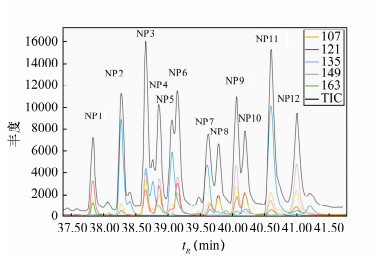
王世玉,刘菲,刘玉龙,陈亮.气相色谱-质谱法检测地下水中12种对壬基酚同分异构体[J].分析化学,2013,41(11):1699-1703.
Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
张全争,谢建荣.水中低残留有机物萃取过程的盐析作用及色谱分析[J].环境化学,2001,20(3):286-290.
Google Scholar
|






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: