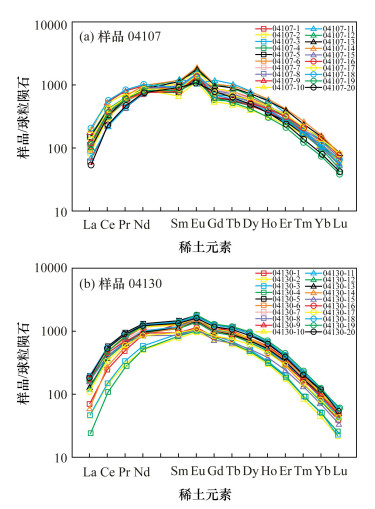
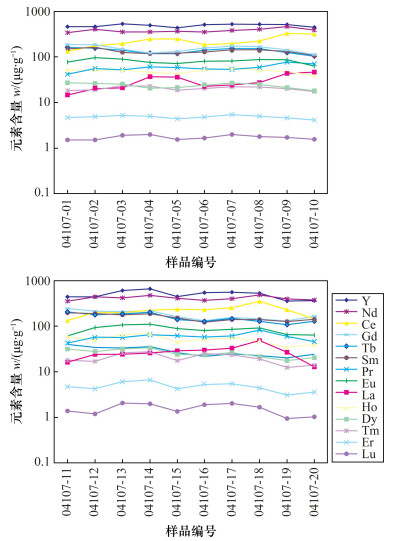
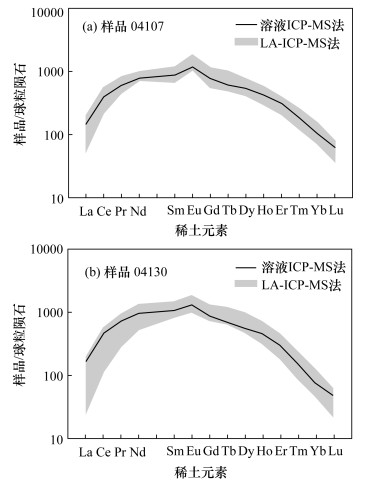
| [1] |
Ghaderi M, Palim J M, Campbell I H, Sylvester P J.Rare earth element systematics in scheelite from hydrothermal gold deposits in the Kalgoorlie-Norseman region, Western Australia[J].Economic Geology, 1999, 94: 423-438. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.94.3.423
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Brugger J, Lahaye Y, Costa S, Lambert D, Bateman R. Inhomogeneous distribution of REE in scheelites and dynamics of Archaean hydrothermal systems(Mt. Charlotte and Drysdale gold deposits, Western Australia)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 139(3): 251-264. doi: 10.1007/s004100000135
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Brugger J, Giere R, Grobety B, Uspensky E. Scheelite-powellite and paraniite-(Y) from the Fe-Mn deposit at Fianel, Eastern Swiss Alps[J].American Mineralogist, 1998, 83: 1100-1110. doi: 10.2138/am-1998-9-1019
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
曾志刚,李朝阳,刘玉平,涂光炽.滇东南南秧田两种不同成因类型白钨矿的稀土元素地球化学特征[J].地质地球化学,1998, 26(2): 34-38.
Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Brugger J, Maas R, Lahaye Y, McRae C, Ghaderi M, Costa S, Lambert D, Bateman R, Prince K. Origins of Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic variations in single scheelite grains from Archaean gold deposits, Western Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 182: 203-225. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00290-X
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
彭建堂,胡瑞忠,赵军红,符亚洲,林源贤.湘西沃溪Au-Sb-W矿床中白钨矿Sm-Nd和石英Ar-Ar定年[J].科学通报,2003,48(18): 1976-1981. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.18.015
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
彭建堂,胡瑞忠,赵军红,符亚洲,袁顺达.湘西沃溪金锑钨矿床中白钨矿的稀土元素地球化学[J].地球化学,2005, 34(2): 115-122.
Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
柳小明,高山,第五春荣,袁洪林,胡兆初.单颗粒锆石的20μm小斑束原位微区LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄和微量元素的同时测定[J].科学通报,2007,52(2): 228-235.
Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
汤倩,孙晓明,梁金龙,徐莉,翟伟,梁业恒.CCSD HP-UHP变质岩中磷灰石稀土元素(REE)地球化学及其示踪意义[J].岩石学报,2007, 23(12): 3255-3266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.12.018
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Prince C I, Kosler J, Vance D, Günther D.Comparison of laser ablation ICP-MS and isotope dilution REE analyses-Implications for Sm-Nd garnet geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2000, 168: 255-274. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00203-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
宗克清,刘勇胜,柳小明,张斌辉.CCSD主孔100~1100m榴辉岩中单矿物的原位微区微量元素地球化学研究[J].岩石学报,2006, 22(7): 1891-1904.
Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Gagono J E, Samson I M, Fryer B J, Williams-Jones A E.Compositional heterogeneity in fluorite and the genesis of fluorite deposits: Insights from LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 2003, 41: 365-382. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.41.2.365
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
漆亮,胡静,许东禹.激光熔蚀-等离子体质谱法测定锰结壳中的稀土及微量元素[J].分析试验室,2000,19(4): 56-59.
Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
薛婷,孙晓明,张美,刘珊珊,何高文,王生伟,陆红锋.西太平洋海山富钴结壳稀土元素(REE)组成原位LA-ICPMS测定[J].岩石学报,2008, 24(10): 2423-2432.
Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Sylvester P J, Ghaderi M.Trace element analysis of scheelite by excimer laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ELA-ICP-MS) using a synthetic silicate glass standard[J].Chemical Geology, 1997, 141: 49-65. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00057-0
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
彭建堂,张东亮,胡瑞忠,吴梦君,柳小明,漆亮,虞有光.湘西渣滓溪钨锑矿床白钨矿中稀土元素的不均匀分布及其地质意义[J].地质论评,2010,56(6): 810-819.
Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
金世昌,韩润生.改造型矿床的成矿热液系统地球化学特征--以元阳金矿床为例[J].云南地质,1994,13(1): 17-22.
Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
毕献武,胡瑞忠,何明友.哀牢山金矿带的成矿时代及其成矿机制探讨[J].地质地球化学,1996(1): 16-19.
Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
韩润生,金世昌,雷丽.云南元阳大坪改造型金矿床的成矿热液系统地球化学[J].矿物学报,1997,17(3): 337-344.
Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
应汉龙.云南大坪金矿床围岩蚀变和同位素地球化学特征[J].黄金科学技术,1998,6(4): 14-23.
Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
毕献武,胡瑞忠,何明友.哀牢山金矿带成矿流体稀土元素地球化学[J].地质论评,1998,44(3): 264-269.
Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
毕献武,胡瑞忠.云南大坪金矿床矿化剂来源及其对金成矿的制约[J].矿物学报,1999,19(1): 28-33.
Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
熊德信,孙晓明,石贵勇,王生伟,高剑锋,薛婷.云南大坪金矿白钨矿微量元素、稀土元素和Sr-Nd同位素组成特征及其意义[J].岩石学报,2006, 22(3): 733-741.
Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
熊德信,孙晓明,石贵勇.云南哀牢山喜马拉雅期造山型金矿带矿床地球化学及成矿模式[M].北京:地质出版社,2007: 44-58.
Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Sun X M, Zhang Y, Xiong D X, Sun W D, Shi G Y, Zhai W, Wang S W.Crust and mantle contributions to gold-forming process at the Daping deposit, Ailaoshan gold belt, Yunnan, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 36(1-3): 235-249. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.05.002
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and Isotope Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[M]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. London: Geological Society, 1989: 313-345.
Google Scholar
|





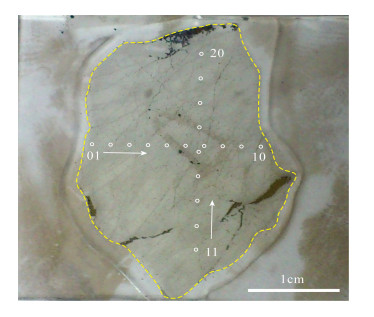

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: