| [1] |
Daughton C H, Ternes T A. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Agents of subtle change? [J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 1999, 107(6): 907-938.
Google Scholar
|
| [2] |
Luo Y, Xu L, Rysz M, Wang Y Q, Zhang H, Alvarez P J J.Occurrence and transport of tetracycline, sulfonamide, quinolone, and macrolide antibiotics in the Haihe River Basin, China [J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(5): 1827-1833.
Google Scholar
|
| [3] |
Li W H, Shi Y L, Gao L H, Liu J M, Cai Y Q.Occurrence of antibiotics in water, sediments, aquatic plants, and animals from Baiyangdian Lake in North China [J].Chemosphere, 2012, 89(11): 1307-1315. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.079
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [4] |
Kumar R R, Lee J T, Cho J Y.Fate, occurrence, and toxicity of veterinary antibiotics in environment [J].Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry, 2012, 55(6): 701-709. doi: 10.1007/s13765-012-2220-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [5] |
Silva B F D, Jelic A, Rebeca L S, Mozeto A A, Petrovic M, Barceló D.Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in surface water, suspended solids and sediments of the Ebro River Basin, Spain [J].Chemosphere, 2011, 85(8): 1331-1339. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.051
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [6] |
王路光,朱晓磊,王靖飞,田在锋.环境水体中的残留抗生素及其潜在风险[J].工业水处理, 2009, 29(5): 11-14.
Google Scholar
|
| [7] |
Hoa P T P, Managaki S, Nakada N, Takada H, Shimizu A, Anh D H, Viet P H, Suzuki S.Antibiotic contamination and occurrence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquatic environments of northern Vietnam [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(15): 2894-2901. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.030
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [8] |
Oluyege J O, Dada A C, Odeyemi A T.Incidence of multiple antibiotic resistant gram-negative bacteria isolated from surface and underground water sources in south western region of Nigeria [J].Water Science and Technology, 2009, 59(10): 1929-1934. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.219
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [9] |
Sanderson H, Brain R A, Johnson D J, Wilson C J, Solomon K R.Toxicity classification and evaluation of four pharmaceuticals classes: Antibiotics, antineoplastics, cardiovascular, and sex hormones [J].Toxicology, 2004, 203: 27-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3127.2004.01.011
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [10] |
Lascowski K M S, Guth B E C, Martins F H, Rocha S P D, Irino K, Pelayo J S.Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in drinking water supplies of north Parana State, Brazil [J].Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2013, 114(4): 1230-1239. doi: 10.1111/jam.2013.114.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [11] |
Ivone V M, Olga C N, Célia M M.Diversity and antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas spp. from drinking water [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 426: 366-374. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.046
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [12] |
Emmanuelle V, Cécile C O, Marie F G L.Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and hormones in drinking water treated from surface waters [J].Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2011, 9(1): 103-114. doi: 10.1007/s10311-009-0253-7
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [13] |
Jones O A, Lester J N, Voulvoulis N.Pharmaceuticals: A threat to drinking water? [J].Trends in Biotechnology, 2005, 23(4): 163-167. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.02.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [14] |
Sim W J, Lee J W, Lee E S, Shin S K, Hwang S R, Oh J E.Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures [J].Chemosphere, 2011, 82(2): 179-186. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [15] |
Fick J, Soederstrom H, Lindberg R H, Phan C, Tysklind M, Larsson D G J.Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production [J].Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2009, 28(12): 2522-2527. doi: 10.1897/09-073.1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [16] |
Verlicchi P, Aukidy M A, Galletti A, Petrovic M, Barceló D.Hospital effluent: Investigation of the concentrations and distribution of pharmaceuticals and environmental risk assessment [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 430: 109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.04.055
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [17] |
Brown K D, Kulis J, Thomson B, Chapman T H, Mawhinney D B.Occurrence of antibiotics in hospital, residential, and dairy effluent, municipal wastewater, and the Rio Grande in New Mexico [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 366(2-3): 772-783. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.10.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [18] |
Sarmahet A K, Meyer M T, Boxall A B A.A global perspective on the use, sales exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment [J].Chemosphere, 2006,65(5): 725-759. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.03.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [19] |
Zhao L, Dong Y H, Wang H.Residues of veterinary antibiotics in manures from feedlot livestock in eight provinces of China [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2010, 408(5): 1069-1075. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.11.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [20] |
Li Y X, Zhang X L, Li W, Lu X F, Liu B, Wang J.The residues and environmental risks of multiple veterinary antibiotics in animal faeces [J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(3): 2211-2220. doi: 10.1007/s10661-012-2702-1
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [21] |
Zheng Q, Zhang R J, Wang Y H, Pan X H, Tang J H, Zhang G.Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities [J].Marine Environmental Research, 2012, 78: 26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2012.03.007
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [22] |
Lalumera G M, Calamari D, Galli P, Castiglioni S, Crosa G, Fanelli R.Preliminary investigation on the environmental occurrence and effects of antibiotics used in aquaculture in Italy [J].Chemosphere,2004,54(5): 661-668. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.08.001
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [23] |
Gao P P, Mao D Q, Luo Y, Wang L M, Xu B J, Xu L.Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in aquaculture environment [J].Water Research, 2012, 46(7): 2355-2364. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [24] |
Kumar K, Thompson A, Singh A K, Chander Y, Gupta S C.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for ultratrace determination of antibiotics in aqueous samples [J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 2004, 33(1): 250-256. doi: 10.2134/jeq2004.2500
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [25] |
Shelver W L, Shappell N W, Franek M, Rubio F R.ELISA for sulfonamides and its application for screening in water contamination [J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2008, 56(15): 6609-6615. doi: 10.1021/jf800657u
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [26] |
Sacher F, Lange F T, Brauch H J, Blankenhorn I.Pharmaceuticals in groundwaters analytical methods and results of a monitoring program in Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany [J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2001, 938(1-2): 199-210. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)01266-3
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [27] |
Wen Y Y, Li J H, Zhang W W, Chen L X.Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with capillary electrophoresis for simultaneous determination of sulfonamides with the aid of experimental design [J].Electrophoresis, 2011, 32(16): 2131-2138. doi: 10.1002/elps.v32.16
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [28] |
García-Campaa A M, Gámiz-Gracia L, Lara F J, del Olmo Iruela M, Cruces-Blanco C.Applications of capillary electrophoresis to the determination of antibiotics in food and environmental samples [J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 395(4): 967-986. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2867-9
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [29] |
Suárez B, Santos B, Simonet B M, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M.Solid-phase extraction-capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry for the determination of tetracyclines residues in surface water by using carbon nanotubes as sorbent material [J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2007, 1175(1): 127-132. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.033
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [30] |
Blackwell P A, Lützhft H C H, Ma H P, Halling-Srensen B, Boxall A B A, Kay P.Fast and robust simultaneous determination of three veterinary antibiotics in groundwater and surface water using a tandem solid-phase extraction with high-performance liquid chromato-graphy-UV detection [J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1045(1-2): 111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.05.063
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [31] |
Xu X, Su R, Zhao X, Liu Z, Zhang Y P, Li D, Li X Y, Zhang H Q, Wang Z M.Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and derivatization of sulfonamides in river water, honey, milk, and animal plasma [J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2011, 707(1): 92-99.
Google Scholar
|
| [32] |
Herrera-Herrera A V, Hernández-Borges J, Borges-Miquel T M, Rodríguez-Delgado M A.Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of 25 sulfonamide and quinolone antibiotics in water samples [J].Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2013, 75: 130-137. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2012.11.026
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [33] |
López-Serna R, Petrovic M, Barceló D.Development of a fast instrumental method for the analysis of pharmaceuticals in environmental and wastewaters based on ultra high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC)-tandem mass spectrometry(MS/MS) [J].Chemosphere, 2011, 85(8): 1390-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.071
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [34] |
Le Fur C, Legeret B, de Sainte Claire P, Wong-Wah-Chung P, Sarakha M.Liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the analysis of sulfaquinoxaline byproducts formed in water upon solar light irradiation [J].Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2013, 27(6): 722-730. doi: 10.1002/rcm.v27.6
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [35] |
Gros M, Petrovic M, Barceló D.Tracing pharmaceutical residues of different therapeutic classes in environmental waters by using liquid chromatography/quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry and automated library searching [J].Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81: 898-912. doi: 10.1021/ac801358e
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [36] |
Barnes K K, Kolpin D W, Furlong E T, Zaugg S D, Meyer M T, Barber L B.A national reconnaissance of pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants in the United States— Ⅰ) Groundwater [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 402(2-3): 192-200. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.04.028
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [37] |
Fram M S, Belitz K.Occurrence and concentrations of pharmaceutical compounds in groundwater used for public drinking-water supply in California [J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011,409(18): 3409-3417. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.05.053
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [38] |
Bartelt-Hunt S, Snow D D, Damon-Powell T, Miesbach D.Occurrence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in shallow groundwater impacted by livestock waste control facilities [J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2011, 123(3-4): 94-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2010.12.010
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [39] |
Hu X G, Zhou Q X, Luo Y.Occurrence and source analysis of typical veterinary antibiotics in manure, soil, vegetables and groundwater from organic vegetable bases, northern China [J].Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(9): 2992-2998. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.05.023
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [40] |
Zhou L J, Ying G G, Liu S, Zhao J L, Chen F, Zhang R Q, Peng F Q, Zhang Q Q.Simultaneous determination of human and veterinary antibiotics in various environmental matrices by rapid resolution liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry [J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2012, 1244: 123-138. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.076
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [41] |
Vulliet E, Cren-Olivé C.Screening of pharmaceuticals and hormones at the regional scale, in surface and groundwaters intended to human consumption [J].Environmental Pollution,2011,159(10): 2929-2934. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.04.033
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [42] |
López-Serna R, Jurado A, Vázquez-Sué A, Carrera J, Petrovic M, Barceló D.Occurrence of 95 pharmaceuticals and transformation products in urban groundwaters underlying the metropolis of Barcelona, Spain [J].Environmental Pollution, 2013, 174: 305-315. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2012.11.022
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [43] |
Navrátilová P, Borkovc I O, Dracková M, Jantová B, Vorlová L.Occurrence of tetracycline, chlortetracyclin, and oxytetracycline residues in raw cow’s milk [J].Czech Journal of Food Sciences, 2009, 27(5): 379-385.
Google Scholar
|
| [44] |
Hurtado D M J, Maggi L, Bonetto L, Carmena B R, Lezana A, Mocholí F A, Carmona M.Validation of antibiotics in catfish by on-line solid phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry [J].Food Chemistry, 2012, 134(2): 1149-1155. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.02.108
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [45] |
Vragovic N, Baulic D, Njari B.Risk assessment of streptomycin and tetracycline residues in meat and milk on Croatian market [J].Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2011, 49(2): 352-355. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.11.006
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [46] |
Kim Y K, Lim S J, Han M H, Cho J Y.Sorption characteristics of oxytetracycline, amoxicillin, and sulfathiazole in two different soil types [J].Geoderma, 2012, 185-186: 97-101.
Google Scholar
|
| [47] |
Huang C H, Renew J E, Smeby K L, Pinkston K, Sedlak D L.Assessment of potential antibiotic contaminants in water and preliminary occurrence analysis [J].Journal of Contemporary Water Research and Education, 2001, 120(1): 30-40.
Google Scholar
|
| [48] |
Xuan R C, Arisi L, Wang Q Q, Yates S R, Biswas K C.Hydrolysis and photolysis of oxytetracycline in aqueous solution [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health: Part B, 2010, 45(1): 73-81.
Google Scholar
|
| [49] |
Kümmerer K.Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review Part Ⅰ [J].Chemosphere, 2009, 75(4): 417-434. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.086
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [50] |
Biak-Bielinska A, Stolte S, Matzke M, Fabianska A, Maszkowska J, Koodziejska M, Liberek B, Stepnowski P, Kumirsk J.Hydrolysis of sulphonamides in aqueous solutions [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 221-222 : 264-274.
Google Scholar
|
| [51] |
Werner J J, Arnold W A, McNeill K.Water hardness as a photochemical parameter: Tetracycline photolysis as a function of calcium concentration, magnesium concentration, and pH [J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(23): 7236-7241.
Google Scholar
|
| [52] |
Pouliquen H, Delépée R, Larhantec-Verdier M, Morvan M L, Bris H L.Comparative hydrolysis and photolysis of four antibacterial agents (oxytetracycline oxolinic acid, flumequine and florfenicol) in deionised water, freshwater and seawater under abiotic conditions [J].Aquaculture, 2007, 262(1): 23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.10.014
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [53] |
Wammer K H, Korte A R, Lundeen R A,Sundberg J E, McNeill K, Arnold W A.Direct photochemistry of three fluoroquinolone antibacterials: Norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and enrofloxacin [J].Water Research, 2013, 47(1): 439-448. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.10.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [54] |
Lai H T, Wang T S, Chou C C.Implication of light sources and microbial activities on degradation of sulfonamides in water and sediment from a marine shrimp pond [J].Bioresource Technology,2011,102(8): 5017-5023. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.01.070
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [55] |
Werner J J, McNeill K, Arnold W A.Photolysis of chlortetracycline on a clay surface [J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2009, 57(15): 6932-6937. doi: 10.1021/jf900797a
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [56] |
Di Paola A, Addamo M, Augugliaro V, García-López E, Loddo V, Marcì G, Palmisano L.Photodegradation of lincomycin in aqueous solution [J].International Journal of Photoenergy, 2006, 1: 1-6.
Google Scholar
|
| [57] |
Tong L, Eichhorn P, Pérez S, Wang Y X, Barceló D.Photodegradation of azithromycin in various aqueous systems under simulated and natural solar radiation: Kinetics and identification of photoproducts [J].Chemosphere, 2011, 83(3): 340-348. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.12.025
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [58] |
Tong L, Pérez S, Gonalves C, Alpendurada F, Wang Y X, Barceló D.Kinetic and mechanistic studies of the photolysis of metronidazole in simulated aqueous environmental matrices using a mass spectrometric approach [J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2011, 399(1): 421-428. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4320-5
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [59] |
Wammer K H, Slattery M T, Stemig A M, Ditty J L.Tetracycline photolysis in natural waters: Loss of antibacterial activity [J].Chemosphere, 2011, 85(9): 1505-1510. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.051
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [60] |
Maki T, Hasegawa H, Kitami H, Fumoto K, Munekage Y, Ueda K.Bacterial degradation of antibiotic residues in marine fish farm sediments of Uranouchi Bay and phylogenetic analysis of antibiotic-degrading bacteria using 16S rDNA sequences [J].Fisheries Science, 2006, 72(4): 811-820. doi: 10.1111/fis.2006.72.issue-4
CrossRef Google Scholar
|
| [61] |
Girardi C, Greve J, Lamshft M, Fetzer I, Miltner A, Schffer A, Kstner M.Biodegradation of ciprofloxacin in water and soil and its effects on the microbial communities [J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 198: 22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.004
CrossRef Google Scholar
|





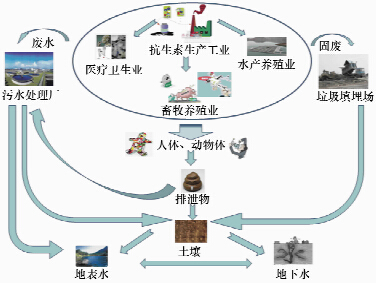

 DownLoad:
DownLoad: