| Citation: | Chang-dong Li, Peng-fei Feng, Xi-hui Jiang, Shuang Zhang, Jie Meng, Bing-chen Li, 2024. Extensive identification of landslide boundaries using remote sensing images and deep learning method, China Geology, 7, 276-289. doi: 10.31035/cg2023148 |
Extensive identification of landslide boundaries using remote sensing images and deep learning method
-
Abstract
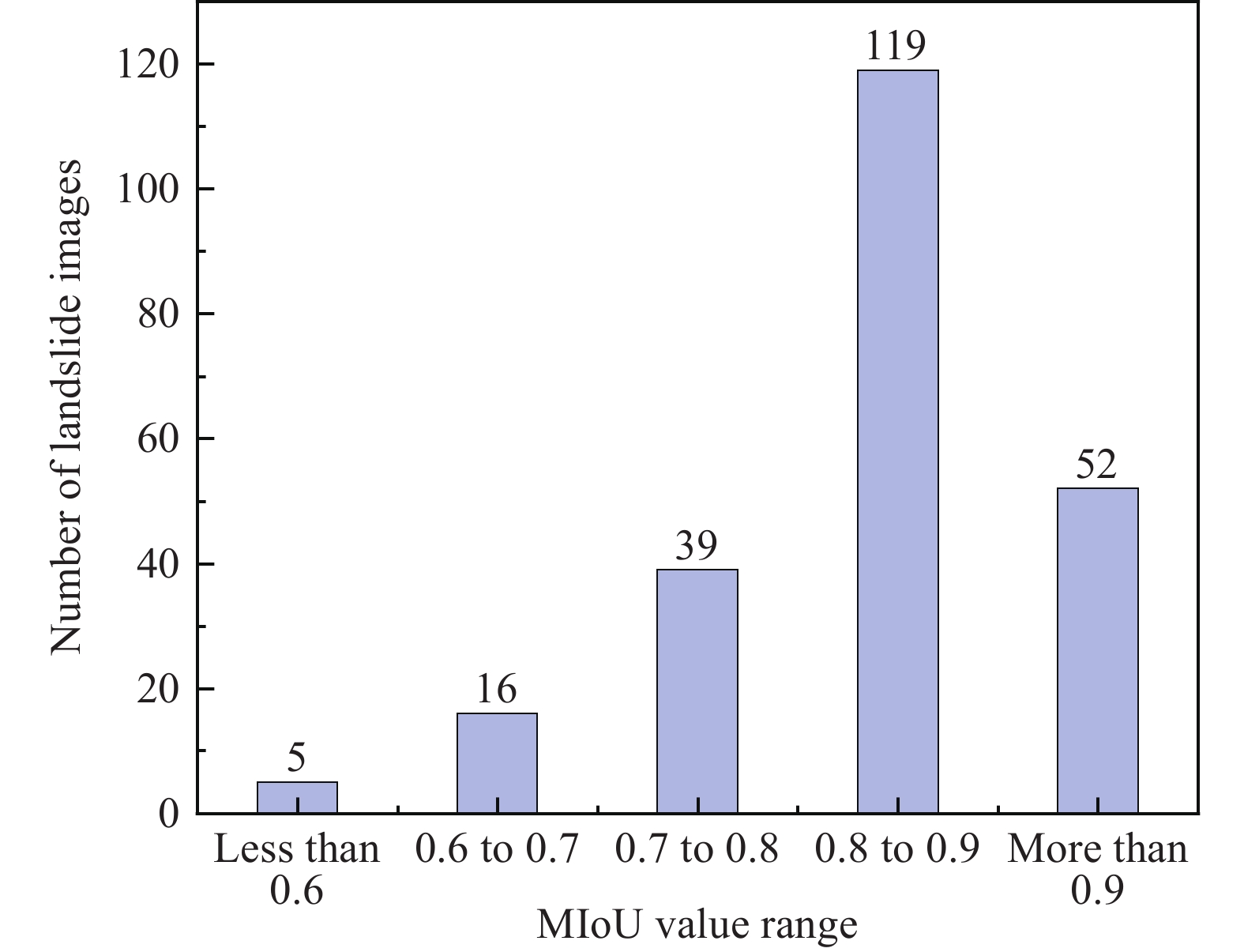
The frequent occurrence of extreme weather events has rendered numerous landslides to a global natural disaster issue. It is crucial to rapidly and accurately determine the boundaries of landslides for geohazards evaluation and emergency response. Therefore, the Skip Connection DeepLab neural network (SCDnn), a deep learning model based on 770 optical remote sensing images of landslide, is proposed to improve the accuracy of landslide boundary detection. The SCDnn model is optimized for the over-segmentation issue which occurs in conventional deep learning models when there is a significant degree of similarity between topographical geomorphic features. SCDnn exhibits notable improvements in landslide feature extraction and semantic segmentation by combining an enhanced Atrous Spatial Pyramid Convolutional Block (ASPC) with a coding structure that reduces model complexity. The experimental results demonstrate that SCDnn can identify landslide boundaries in 119 images with MIoU values between 0.8 and 0.9; while 52 images with MIoU values exceeding 0.9, which exceeds the identification accuracy of existing techniques. This work can offer a novel technique for the automatic extensive identification of landslide boundaries in remote sensing images in addition to establishing the groundwork for future investigations and applications in related domains.
-

-
References
Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. 2015. Segnet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. arXiv. Preprint arXiv: 1511.0051, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1511.00561. Bragagnolo L, Rezende LR, Silva RV, Grzybowski JMV. 2021. Convolutional neural networks applied to semantic segmentation of landslide scars. CATENA, 201, 105189. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105189. Cao WG, Fu Y, Dong QY, Wang HG, Ren Y, Li ZY, Du YY. 2023. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Western Henan Province based on a comparison of conventional and ensemble machine learning. China Geology, 6(3), 409–419. doi: 10.31035/cg2023013. Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL. 2017. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 40(4), 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184. Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H. 2018. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 833‒851. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1802.02611. Czikhardt R, Papco J, Bakon M, Liscak P, Ondrejka P, Zlocha M. 2017. Ground stability monitoring of undermined and landslide prone areas by means of sentinel-1 multi-temporal InSAR, case study from Slovakia. Geosciences, 7(3), 87. doi: 10.3390/geosciences7030087. Dahal RK , Hasegawa S , Nonomura A. 2008. Predictive modelling of rainfall-induced landslide hazard in the Lesser Himalaya of Nepal based on weights-of-evidence. Geomorphology, 102 (3‒4), 496‒510. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.041. Dai C, Li WL, Wang D, Lu HY, Xu Q, Jian J. 2021. Active landslide detection based on Sentinel-1 Data and InSAR Technology in Zhouqu County, Gansu Province, Northwest China. Journal of Earth Science, 32(5), 1092–1103. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1380-0. Ding A, Zhang Q, Zhou X, Dai B. 2016. Automatic recognition of landslide based on CNN and texture change detection. 2016 31st Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Wuhan, China, 444–448. doi: 10.1109/YAC.2016.7804935. Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y. 2011. Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12(7), 2121–2159. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2146788. Feng PF, Li CD, Zhang S, Meng J, Long JJ. 2024. Integrating shipborne images with multichannel deep learning for landslide detection. Journal of Earth Science, 35(1), 296–300. doi: 10.1007/s12583-023-1957-5. Ghorbanzadeh O, Blaschke T, Gholamnia K, Meena SR, Tiede D, Aryal J. 2019. Evaluation of different machine learning methods and deep-learning convolutional neural networks for landslide detection. Remote Sensing, 11(2), 196. doi: 10.3390/rs11020196. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 770‒778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. Ji S, Yu D, Shen C, Li W, Xu Q. 2020. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks. Landslides, 17(6), 1337–1352. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01353-2. Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE. 2017. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6), 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386. Kingma DP, Ba J. 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. 2015. Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539. Li C, Criss RE, Fu Z, Long J, Tan Q. 2021. Evolution characteristics and displacement forecasting model of landslides with stair-step sliding surface along the Xiangxi River, three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Engineering Geology, 283, 105961–105975. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105961. Li Y, Ma J, Zhang Y. 2021. Image retrieval from remote sensing big data: A survey. Information Fusion, 67, 94–115. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.10.008. Li Y, Wang P, Feng Q, Ji X, Jin D, Gong J. 2023. Landslide detection based on shipborne images and deep learning models: A case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area in China. Landslides, 20(3), 547–558. doi: 10.1007/s10346-022-01997-2. Liu P, Wei Y, Wang Q, Xie J, Chen Y, Li Z, Zhou H. 2021. A Research on Landslides Automatic Extraction Model Based on the Improved Mask R-CNN. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(3), 168. doi: 10.3390/ijgi1003016. Liu Y, Wu L. 2016. Geological Disaster Recognition on Optical Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning. Procedia Computer Science, 91, 566–575. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.07.144. Long Y, Xia GS, Li S, Yang W, Yang MY, Zhu XX, Li D. 2021. On creating benchmark dataset for aerial image interpretation: Reviews, guidances, and million-aid. IEEE Journal of selected topics in applied earth observations and remote sensing, 14, 4205–4230. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3070368. Lü ZY, Shi W, Zhang X, Benediktsson JA. 2018. Landslide Inventory Mapping From Bitemporal High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Using Change Detection and Multiscale Segmentation. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(5), 1520–1532. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2803784. Meng J, Li CD, Zhou JQ, Zhang ZH, Yan SY, Zhang YH, Huang DW, Wang GH. 2023. Multiscale evolution mechanism of sandstone under wet-dry cycles of deionized water: from molecular scale to macroscopic scale. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 15(5), 1171–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.10.008. Mohan A, Singh AK, Kumar B, Dwivedi R. 2021. Review on remote sensing methods for landslide detection using machine and deep learning. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32(7), e3998. doi: 10.1002/ett.3998. Mondini AC, Guzzetti F, Reichenbach P, Rossi M, Cardinali M, Ardizzone F. 2011. Semi-automatic recognition and mapping of rainfall induced shallow landslides using optical satellite images. Remote sensing of environment, 115(7), 1743–1757. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.03.006. Qi T, Zhao Y, Meng X, Chen G, Dijkstra T. 2021. AI-Based susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides induced by heavy rainfall in Tianshui, China. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1819. doi: 10.3390/rs13091819. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. 2015. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), 9351, 234–241. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1505.04597. Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen LC. 2018. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 4510‒4520. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1801.04381. Simonyan K, Zisserman A. 2014. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556. Solari L, Del SM, Raspini F, Barra A, Bianchini S, Confuorto P, Casagli N, Crosetto M. 2020. Review of Satellite Interferometry for Landslide Detection in Italy. Remote Sensing, 12(8), 1351. doi: 10.3390/rs12081351. Sun Q, Zhang L, Ding XL, Hu J, Li ZW, Zhu JJ. 2015. Slope deformation prior to Zhouqu, China landslide from InSAR time series analysis. Remote Sensing of Environment, 156, 45–57. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.09.029. Tieleman T, Hinton G. 2012. Lecture 6.5-RMSProp: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA: Neural Networks for Machine Learning, 4, 26‒31. Wang H, Zhang L, Yin K, Luo H, Li J. 2021. Landslide identification using machine learning. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(1), 351–364. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.02.012. Wei FQ, Sergey C, Konstantin A, Dmitry P, Olga T, Su PC, Jiang YH, Xu A, Alexey P. 2010. A seismically triggered landslide in the Niujuan Valley near the epicenter of the 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake. Journal of Earth Science, 21(6), 901–909. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0143-8. Xu C, Li C, Cui Z, Zhang T, Yang J. 2020. Hierarchical semantic propagation for object detection in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 58(6), 4353–4364. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2963243. Zhang TL, Zhou AG, Sun Q, Wang HS, Wu JB, Liu ZH. 2020. Hydrological response characteristics of landslides under typhoon-triggered rainstorm conditions. China Geology, 3(3), 455–461. doi: 10.31035/cg2020028. Zhang X, Yu W, Pun MO, Shi W. 2023. Cross-domain landslide mapping from large-scale remote sensing images using prototype-guided domain-aware progressive representation learning. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 197, 1–17. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.01.018. Zhao C, Lu Z. 2018. Remote Sensing of Landslides—A Review. Remote Sensing, 10(2), 279. doi: 10.3390/rs10020279. Zhong C, Li H, Xiang W, Su AJ, Huang XF. 2012. Comprehensive study of landslides through the integration of multi remote sensing techniques: Framework and latest advances. Journal of Earth Science, 23(2), 243–252. doi: 10.1007/s12583-012-0245-6. Zhou PC, Cheng G, Yao XW, Han JW. 2021. Machine learning paradigms in high-resolution remote sensing image interpretation. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 25(1), 182–197. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210164. Zhu XX, Tuia D, Mou L, Xia GS, Zhang L, Xu F, Fraundorfer F. 2017. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 5(4), 8–36. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307. -
Access History

-
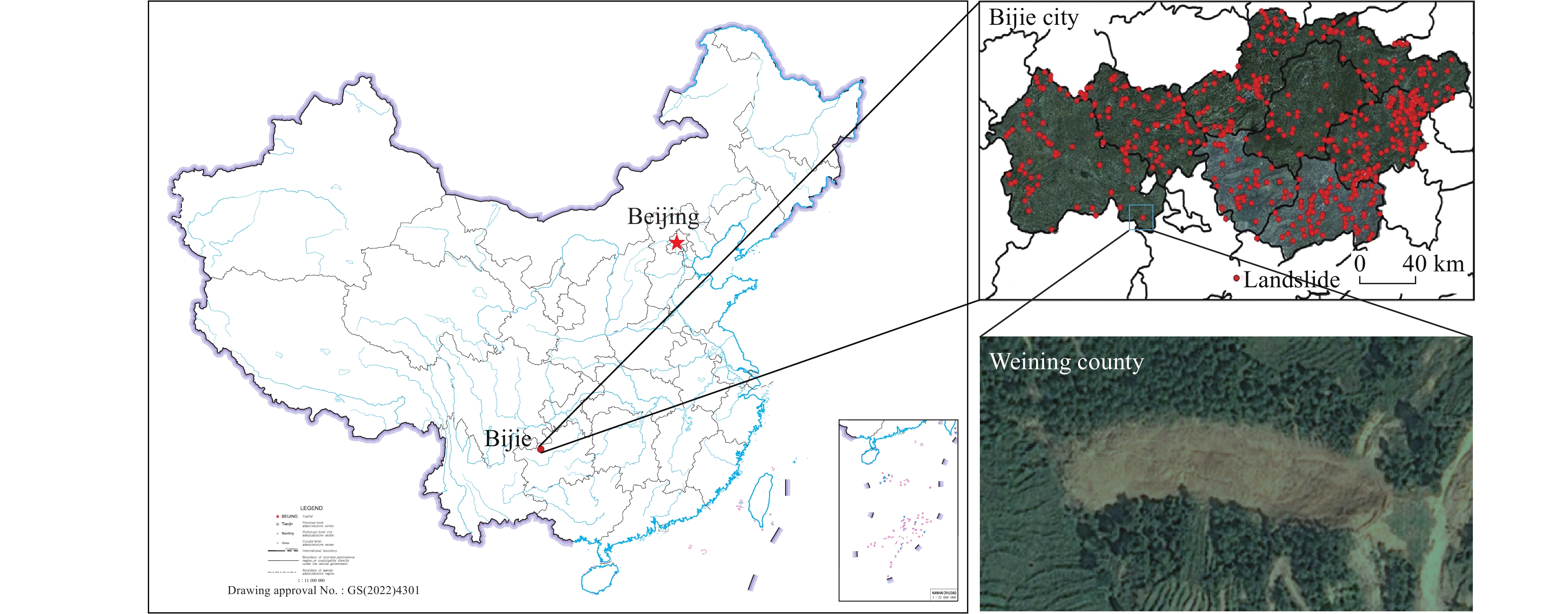
Figure 1.
Study area map for the Three Gorges Reservoir, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020).
-
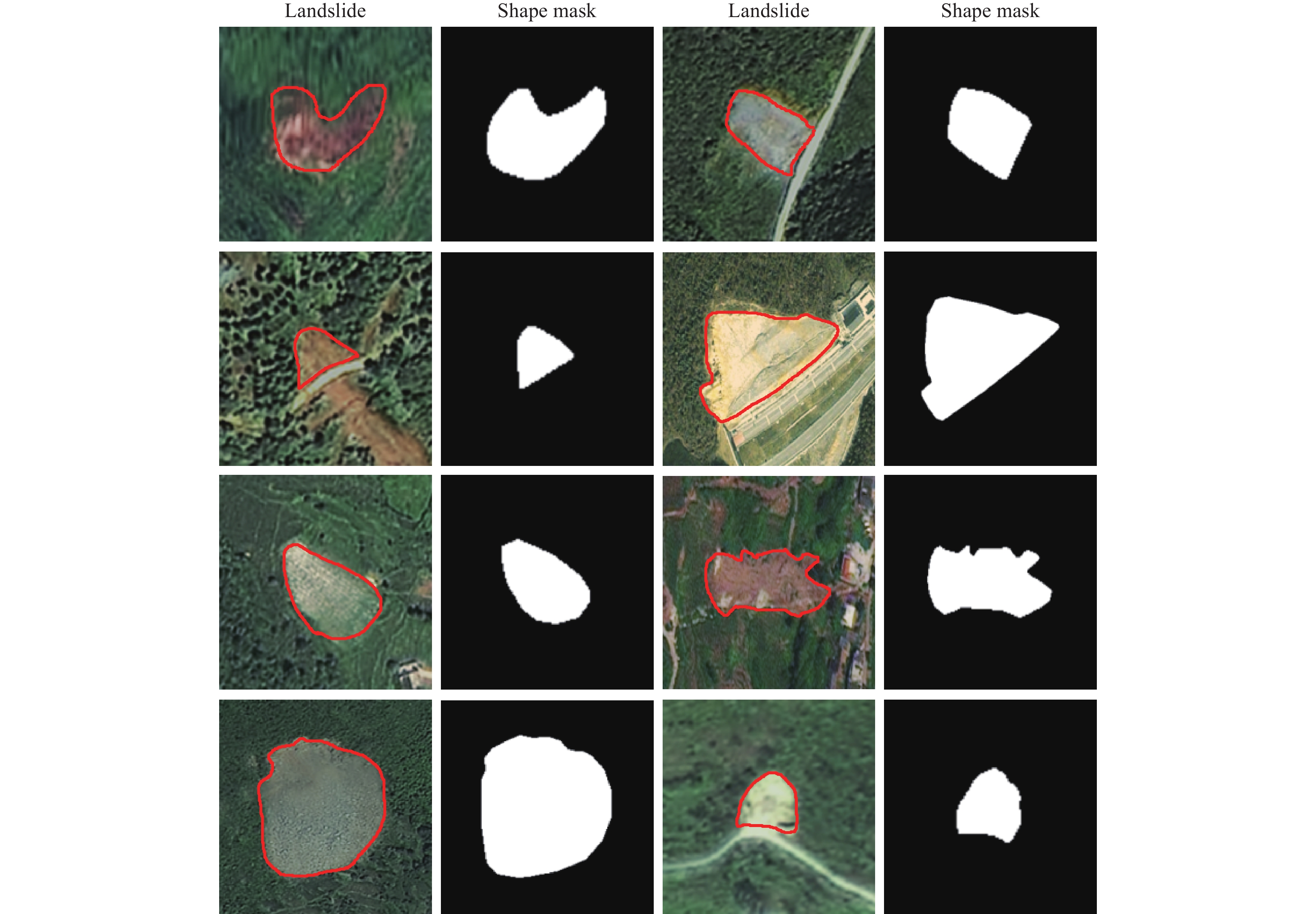
Figure 2.
Bijie landslide image and landslide shape mask dataset, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020).
-
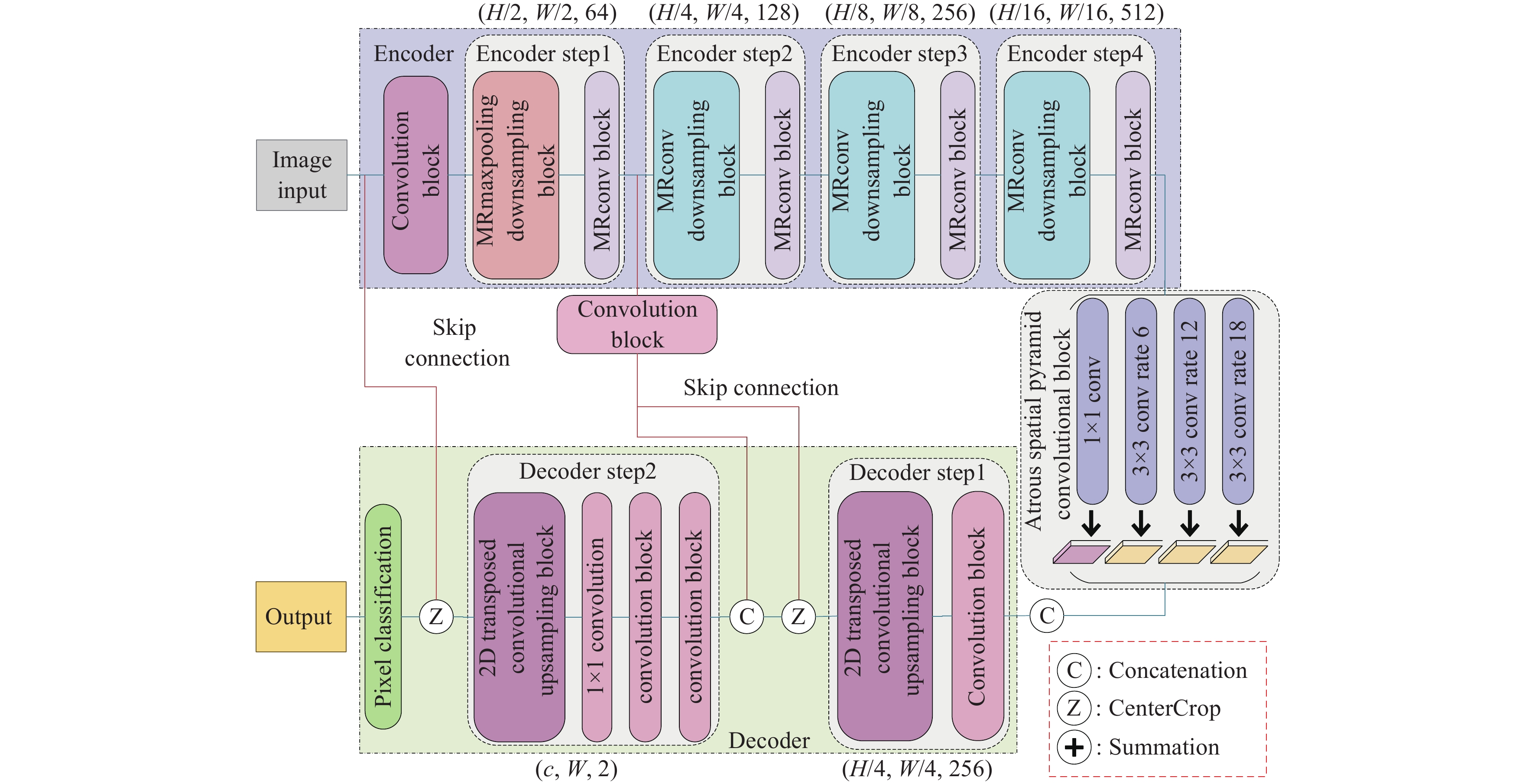
Figure 3.
Architecture of Skip Connection DeepLab neural network.
-
Figure 4.
Mixed Residual and Maximum Pooling Downsampling Block (Legends are same as Fig. 3).
-
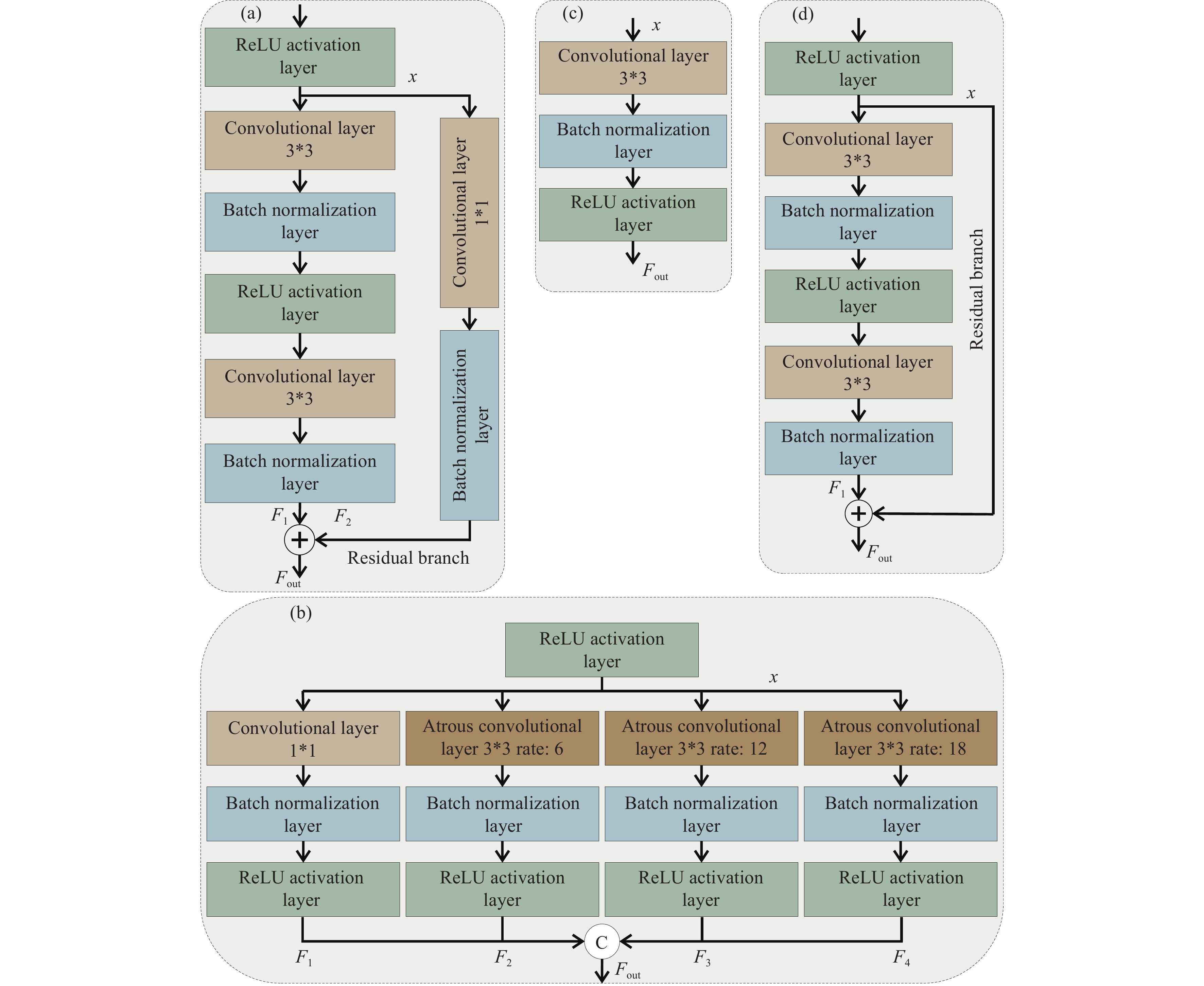
Figure 5.
Other Component Blocks of SCDnn: a‒Mixed Residual and Convolutional Downsampling Block; b‒Atrous Spatial Pyramid Convolutional Block; c‒Convolution Block; d‒Mixed Residual and Convolutional Block (Legends are same as Fig. 3).
-
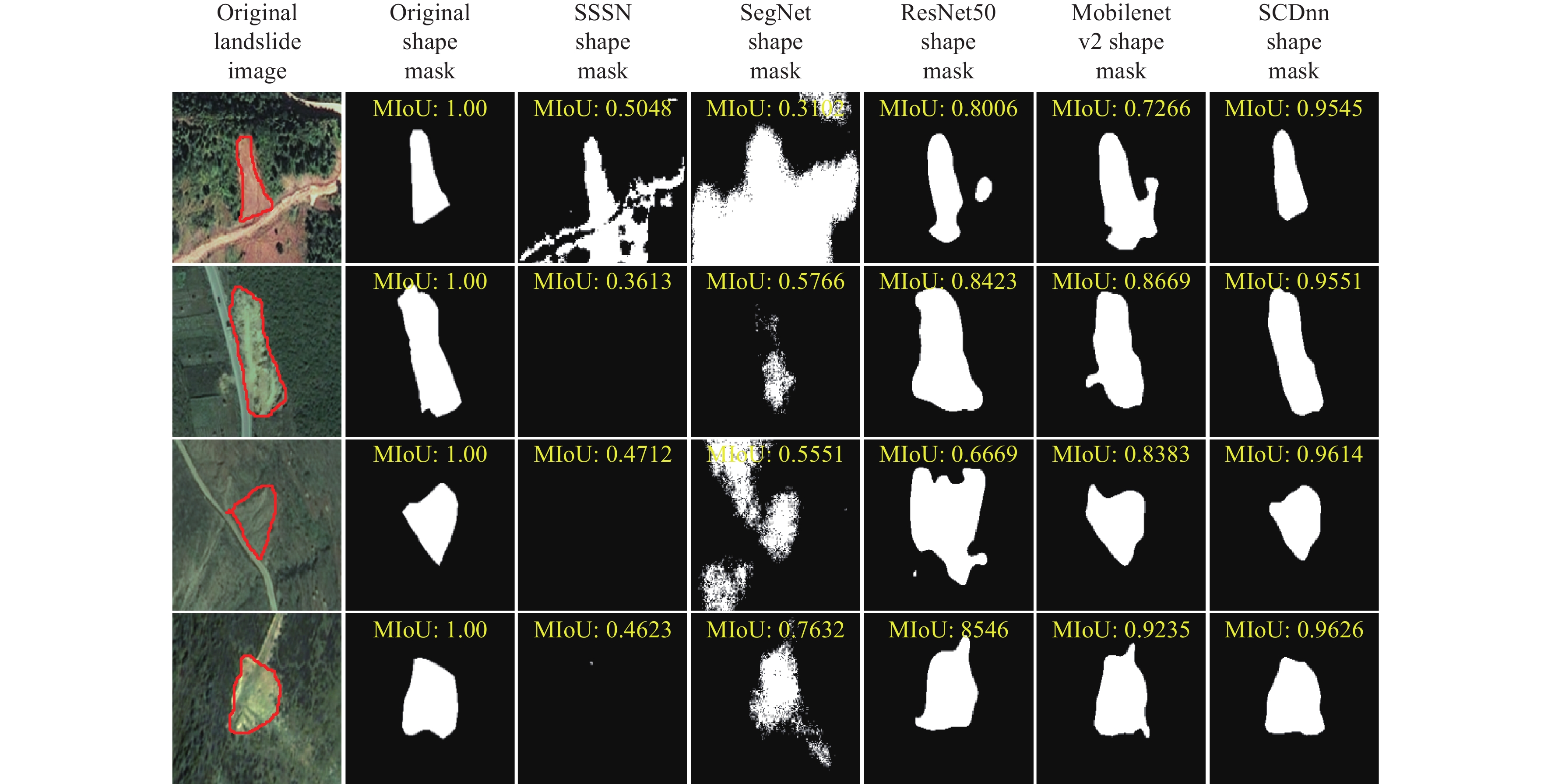
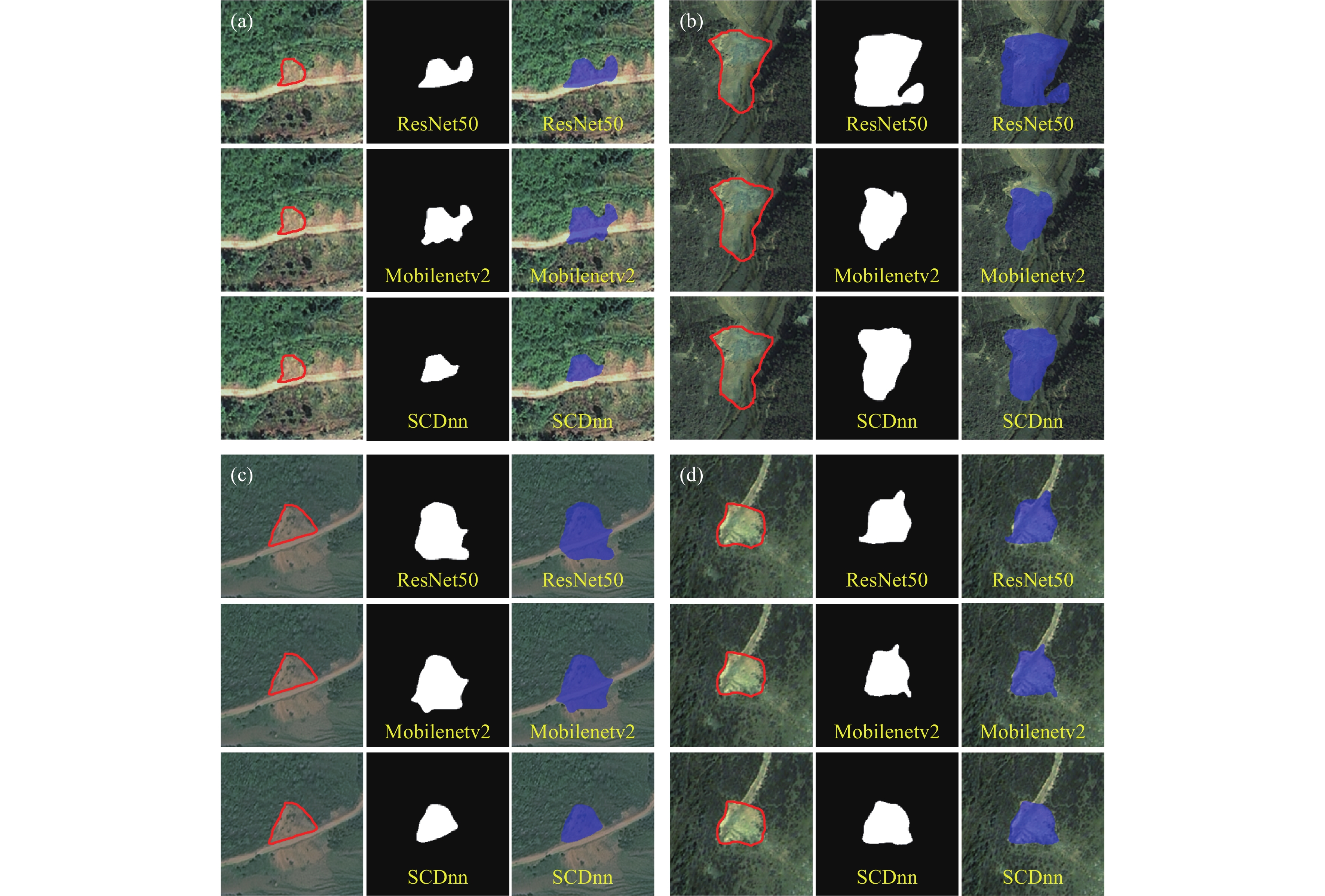
Figure 6.
Segmented images generated by different network architecture models for precise location identification of landslides, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020).
-
Figure 7.
Segmentation results of different models for individual classes of landslide dataset, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020). a‒SSSN and SCDnn models for individual classes of landslide dataset; b‒ResNet50 and SCDnn models for individual classes of landslide dataset.
-
Figure 8.
Statistics on the range of individual image’s MIoU values for the segmentation results of the SCDnn model for the landslide dataset.
-
Figure 9.
Some of the remote sensing images and shape masks from SCDnn model with segmentation results’ MIoU values between 0.8 and 0.9 and MIoU values larger than 0.9, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020).
-
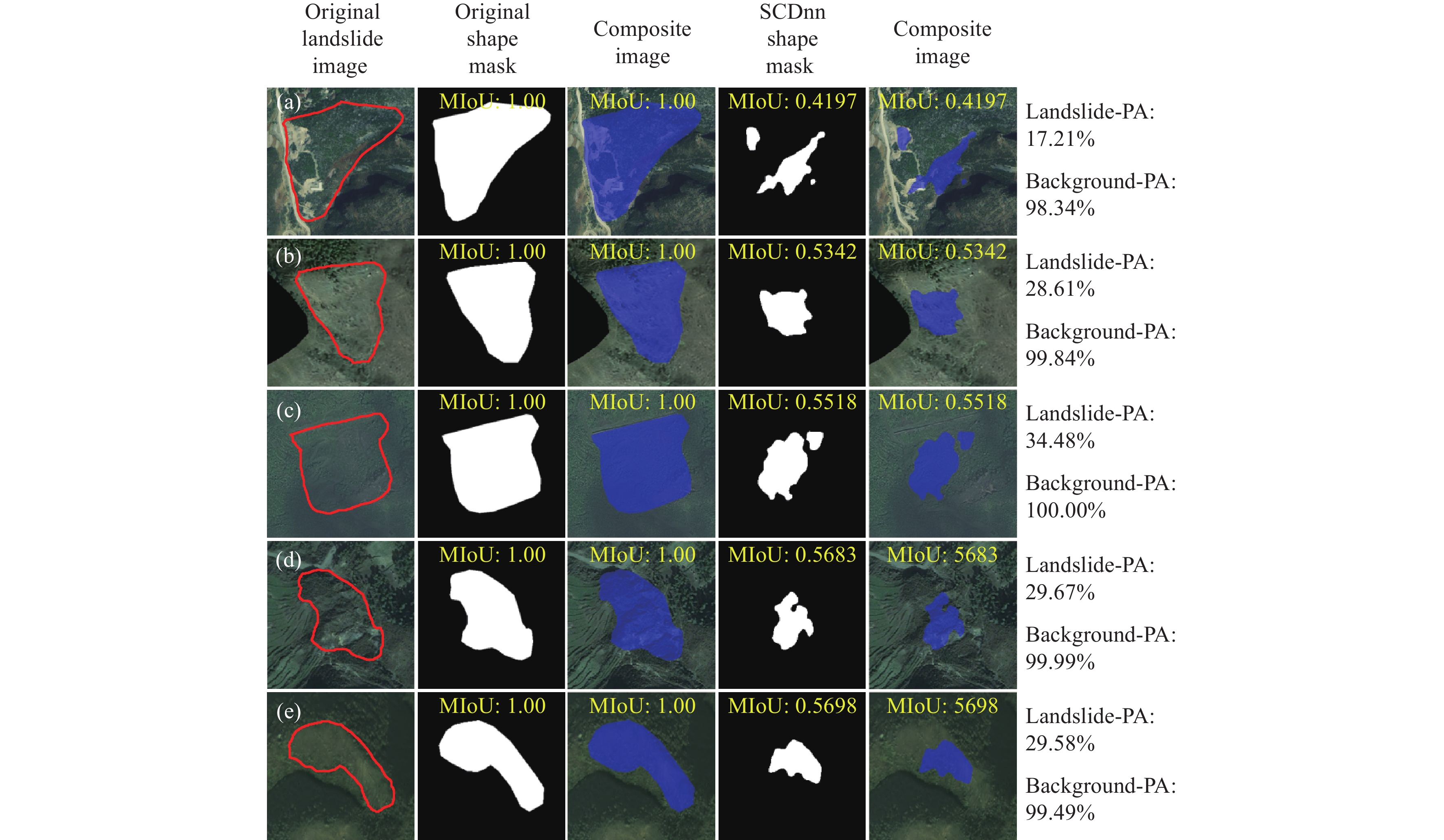
Figure 10.
Some of the remote sensing images and shape masks from SCDnn model with segmentation results’ MIoU values less than 0.6, with the landslide images sourced from the research of Ji S et al. (2020).




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: