| Citation: | Jing-jie Li, Sheng Lian, Ming-guo Wang, Huai-sheng Zhang, Tao Yang, 2024. Hydrochemical characteristics of surface water in Hengduan mountain region of Eastern Xizang and its response to human activities: A case study of Duoqu Basin, Jinsha River, China Geology, 7, 630-641. doi: 10.31035/cg2023053 |
Hydrochemical characteristics of surface water in Hengduan mountain region of Eastern Xizang and its response to human activities: A case study of Duoqu Basin, Jinsha River
-
Abstract
The analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and influencing factors of surface river on plateau is helpful to study water hydrological cycle and environmental evolution, which can scientifically guide rational development and utilization of water resources and planning of ecological environment protection. With the expansion and diversification of human activities, the quality of surface rivers will be more directly affected. Therefore, it is of great significance to pay attention to the hydrochemical characteristics of plateau surface rivers and the influence of human activities on their circulation and evolution. In this study, surface water in the Duoqu basin of Jinsha River located in Hengduan mountain region of Eastern Xizang was selected as the representative case.Twenty-three groups of surface water samples were collected to analyze the hydrochemical characteristics and ion sources based on correlation analysis, piper trigram, gibbs model, hydrogen and oxygen isotopic techniques.The results suggest the following: (1) The pH showed slight alkalinity with the value ranged from 7.25 to 8.62. Ca2+, Mg2+ and HCO3– were the main cations and anions. HCO3-Ca and HCO3-Ca·Mg were the primary hydrochemical types for the surface water of Duoqu River. The correlation analysis showed that TDS had the most significant correlation with Ca2+, Mg2+ and HCO3–. Analysis on hydrogen and oxygen isotopes indicated that the surface rivers were mainly recharged by atmospheric precipitation and glacial melt water in this study area. (2) The surface water had a certain reverse cation alternating adsorption, and surface water ions were mainly derived from rock weathering, mainly controlled by weathering and dissolution of carbonates, and secondly by silicates and sodium rocks. (3) The influence of human activities was weak, while the development of cinnabar minerals had a certain impact on the hydrochemistry characteristics, which was the main factor for causing the increase of SO42–. The densely populated county towns and temples with frequent incense burning activities may cause some anomalies of surface water quality. At present, the Duoqu River watershed had gone through a certain influence of mineral exploitation, so the hydrological cycle and river eco-environment at watershed scale will still bound to be change.The results could provide basic support for better understanding water balance evolution as well as the ecological protection of Duoqu River watershed.
-

-
References
Craig H. 1961. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science, 133, 1702–1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702. Cui BL, Li XY. 2015. Runoff processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeast Qinghai-Xizang Plateau China: insights from stable isotope and hydrochemistry. Quaternary International, 380‒381(0), 123‒132. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2015.02.030. Dong WH, Meng Y, Wang YS, Wu XC, Lv Y, Zhao H. 2017. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation of the shallow groundwater in Fujin, Sanjiang Plain. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 47(2), 542–553 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.201702203. Fan BL, Zhao ZQ, Tao FX, Liu BJ, Tao ZH, Gao S, Zhang LH. 2014. Characteristics of carbonate, evaporite and silicate weathering in Huanghe River basin: A comparison among the upstream, midstream and downstream. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 96, 17–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.005. Fu CC, Li XQ, Cheng X. 2023. Unraveling the mechanisms underlying lake expansion from 2001 to 2020 and its impact on the ecological environment in a typical alpine basin on the Xizang Plateau. China Geology, 6(2), 216–227. doi: 10.31035/cg2023015. Gao JQ, Yu Y, Wang DH, Wang W, Dai HZ, Yu F, Qin Y. 2021. Composition and spatial distribution characteristics of hydrogen and oxyge isotopes of surface water in Altay, Xinjiang Province. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 40(3), 397–407 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101140007. He XJ, Xu WN, Weng BS, Qin TL, Yan DM. 2019. Research progress and prospect on mechanism of climate change affecting water quality in Plateau Cold Region. Yangtze River, 50(2), 70–74 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang X, Sillanpaeae M, GjessIing ET, Peraniemi S, Vogt RD. 2011. Water quality in the Southern Xizang Plateau: chemical evaluation of the Yarlung Tsangpo(Brahmaputra). River Research and Applications, 27(1), 113–21. doi: 10.1002/rra.1332. Jia LR. 2017. Study on the Stability of Complex Ancient Deposits in the Zangqu River Basin, East Xizang. Mianyang, China Southwest University of Science and Technology, Master thesis, 14‒23 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jasrotia AS, Taloor AK, Andotra U, Kumar R. 2019. Monitoring and assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and agricultural use in the Cenozoic rocks of Jammu Himalaya, India: A geospatial technology based approach. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 8, 554–566. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.02.003. Jiang LG, Yao ZJ, Liu ZF, Wang R, Wu SS. 2015a. Hydrochemistry and its controlling factors of rivers in the source region of the Yangtze River on the Xizang Plateau. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 155, 76–83. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.04.009. Jiang LG, Yao ZJ, Wang R, Liu ZF, Wang L Wu, SS. 2015b. Hydrochemistry of the middle and upper reaches of the Yarlung Tsangpo River System: Weathering processes and CO2 consumption. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(3), 2369–2379. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4237-6. Li CZ, Li BH, Bi EP. 2019. Characteristics of hydrochemistry and nitrogen behavior under long-term managed aquifer recharge with reclaimed water: A case study in north China. Science of the Total Environment, 668, 1030–1037. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.375. Li ZJ, Yang QC, Yang YS, Ma HY, Wang H, Luo JN, Bian JM, Martin JD. 2019. Isotopic and geochemical interpretation of groundwater under the influences of anthropogenic activities. Journal of Hydrology, 576, 685–697. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.037. Li CC, Gao XB, Liu YS, Wang YX. 2019. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the enrichment of fluoride and salinity in groundwater in the Yuncheng Basin constrained by Cl/Br ratio, δ18O, δ2H, δ13C and δ7 Li isotopes. Journal of Hydrology, 579, 124211. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124211. Li CC, Gao XB, Wang WZ, Zhang X, Zhang XB, Jiang CF, Wang YX. 2021. Hydrobiogeochemical processes of surface water leakage into groundwater in large scale karst water system: A case study at Jinci, northern China. Journal of Hydrology, 596(0), 125691. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125691. Li ZJ, Song LL, Gui J, Li ZX. 2022. Hydrochemical patterns indicating hydrological processes with the background of changing climatic and environmental conditions in China: A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 29(11), 15364–15379. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-18307-3. Li J, Wu HW, Zhou YQ, Zhao ZH, Wang XL, Cai YJ, He B, Chen W, Sun W. 2020. Variations of stable oxygen and deuterium isotopes in river and lake waters during flooding season along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river regions. Environmental Science, 41(3), 1176–1183. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201908160. Li XY, Ding YJ, Han TD, Mika S, Jing ZF, You XN, Liu S, Yang CY, Yu CR, Li GY. 2020. Seasonal and interannual changes of river chemistry in the source region of Yellow River, Xizang Plateau. Applied Geochemistry, 119, 104638. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104638. Li WP, Wang LF, Zhang YL, Wu LJ, Zeng LM, Tuo ZS. 2021. Determining the groundwater basin and surface watershed boundary of Dalinuoer Lake in the middle of Inner Mongolian Plateau, China and its impacts on the ecological environment. China Geology, 4(3), 498–508. doi: 10.31035/cg2021066. Liu CY, Huang GX, Jing JH, Liu JT, Zhang Y, Guo WX. 2023. Characteristics and driving mechanisms of evolution of groundwater chemistry in Huang- Huai- Hai Plain and its exploitation and utilization suggestions. Geology in China, 50(6), 1705–1719 (in Chinese with English abstract). Peng C, Liu YM, Chen HY, Yuan QW, Chen QZ, Mei SL, Wu ZH. 2021. Analysis of hydrogeo- chemical characteristics of tunnel groundwater based on multivariate satistical technology. Geofluids, 2021, 4867942. doi: 10.1155/2021/4867942. Qi HH, Ma CM, He ZK, Hu XJ, Gao L. 2019. Lithium and its isotopes as tracers of groundwater salinization: A study in the southern coastal plain of Laizhou Bay, China. Science of the Total Environment, 650(1), 878–890. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.122. Shi DP, Tan HB, Chen X, Rao WB, Basang R. 2021. Uncovering the mechanisms of seasonal river–groundwater circulation using isotopes and water chemistry in the middle reaches of the Yarlung zangbo River, Xizang. Journal of Hydrology, 603, 127010. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127010. Song HW, Meng YC, Jiang FT, Li LX, Li YQ, Du CH. 2021. Isotope characteristics of surface water and groundwater in the middle reaches of YarlungZangbo river and their indicators. Journal of Arid Land Resourcesand Environment. 35(7), 122‒128 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13448 /j.cnki.jalre.2021.195. Song MY, Li ZQ, Wang FT, Zhang MJ, Zhang X. 2020. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and hydrochemical parameters of water samples from the Jimunai River Basin, Xinjiang. Environmental Chemistry, 39(7), 1809–1820 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2019050402. Sun HY, Wang CS, Wei XF, Zhu XY, Huang XK. 2020. Hydrochemical characteristics and driving factors in the water of the Bayingaole Basin, Southern Great Xing'an Range. Environmental Chemistry, 39(9), 2507–2519 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032102. Tan HB, Chen X, Shi DP, Rao WB, Liu J, Liu JT, Christopher JE, Wang JR. 2021. Base flow in the Yarlung zangbo River, Xizang, maintained by the isotopically-depleted precipitation and groundwater discharge. The Science of the total environment, 759, 143510. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143510. Tang XW, Wu JK. 2014. Major ion chemistry of surface water in the Xilin River basin and the possible controls. Environmental Science, 35(1), 131. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.09.011. Thomas J, Joseph S, Thrivikramji KP. 2015. Hydrochemical variations of a tropical mountain river system in a rain shadow region of the southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India. Applied Geochemistry, 63(0), 456–471. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.03.018. Wu Y, Gibson CE. 1996. Mechanisms controlling the water chemistry of small lakes in Northern Ireland. Water Research, 30(1), 178–182. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(95)00140-G. Wang XX, Wang WK, Wang ZF, Zhao JL, Xie HL, Wang XD. 2014. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of river water and groundwater along the downstream Luanhe River, northeastern China. Hydrogeology and Engineering geology, 41(1), 25–33 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang WH, Wu TH, Zhao L, Li R, Xie CW, Qiao YP, Zhang HW, Zhu XF, Yang SH, Qin, YH. 2018. Wang MG, Yang L, Li JJ, Liang Q. 2022. Hydrochemical characteristics and controlling factors of surface water in upper Nujiang River, Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Minerals, 12(4), 490. doi: 10.3390/min12040490. Wang MG, Li JJ, Liang Q. 2023. Hydrochemical characteristics and material source of Requ River in eastern Xizang. Yangtze River, 54(2), 120–126. doi: 10.16232/j.cnki.1001-4179.2023.02.018. Wang SY, He XB, Ding YJ, Chang FX, Wu JK, Hu ZF, Wang LH, Yang GS, Deng MS. 2020. Characteristics and influencing factors of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in groundwater in the permafrost region of the source region of the Yangtze River. Environmental Science, 41(1), 166–172. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201907240. Xiao J, Jin ZD, Zhang F, Wang J. 2012. Major ion geochemistry of shallow groundwater in the Qinghai Lake catchment, NE Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Environmental Earth Sciences, 67(5), 1331–1344. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1576-4. Xiao J, Jin ZD, Zhang F. 2015. Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 159(0), 252–261. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.018. Yan YP, Niu FX, Liu J, Liu XT, Li Y, Peng H, Yan DH, Xiao SB. 2022. Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of the upper Yarlung Zangbo River in summer. China Environmental Science, 42(2), 815–825. doi: 10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2022.0037. Yi P, Wan CW, Jin HJ, Luo DL, Yang YZ, Wang QF, Yu ZB, Aldahan A. 2018. Hydrological insights from hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in source area of the Yellow River, east-northern part of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), 131–144. doi: 10.1007/s10967-018-5864-7. Yu TT, Gan YQ, Zhou AG, Liu CF, LiuYD, Li XQ, Cai HS. 2010. Characteristics of oxygen and hydrogen isotope distribution of surface runoff in the Lhasa River basin. Earth Science- Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(5), 873–878. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.101. Yu JS, Zhang HB, Yu FJ, Liu DP. 1980. Oxygen isotopic composition of meteoric water in the eastern part of Xizang. Geochimica, (2), 113–121. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.1980.02.001. Zhang LL, Zhao ZQ, Zhang W, Tao ZH, Huang L, Yang JX, Wu QX, Liu CQ. 2016. Characteristics of water chemistry and its indication of chemical weathering in Jinshajiang, Lancangjiang and Nujiang drainage basins. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(6), 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5115-y. Zhang Y, WuY, Yang J, Sun HY. 2015. Hydrochemical characteristic and reasoning analysis in Siyi Town, Langzhong City. Environmental Science, 36(9), 3230–3237 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2015.09.014. Zhang T, He J, Li JJ, Cao YT, Gong L, Liu JW, Bian C, Cai YM. 2018. Major ionic features and possible controls in the groundwater in the Hamatong River Basin. Environmental Science, 39(11), 4981–4990 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201804070. Zhang T, Wang MG, Zhang ZY, Liu T, He J. 2020. Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls of the surface water in Ranwu Lake Basin. Environmental Science, 41(9), 4003–4010 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202002080. Zhu BQ, Yang XP, Rioual P, Qin XG, Liu ZT, Xiong HG, Yu, JJ. 2011. Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China. Applied Geochemistry, 26(8), 1535–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.018. -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Distribution diagram of strata and sampling points in Duoqu River Basin.
-
Figure 2.
Proportion of equivalent concentration of main anions.
-
Figure 3.
Correlation between chemical parameters in the Duoqu River Basin
-
Figure 4.
Piper three-line diagram of main ions in the Duoqu River Basin.
-
Figure 5.
Relations of δD and δ18O isotopes.
-
Figure 6.
Ion exchange (a) for the plot of (HCO3– + SO42–) − (Ca2++ Mg2+) vs. Na+− Cl–, and (b)for the Chlor-alkali index plot.
-
Figure 7.
Gibbs model of surface water in the Duoqu River Basin.
-
Figure 8.
Ratios of Ca2+/Na+ to Mg2+/Na+ and HCO3–/Na+.
-
Figure 9.
Ca-Na-TDS relationship in the Duoqu River basin.
-
Figure 10.
Variation of γ(NO3–)/γ(Na+) with γ(Cl–)/γ(Na+).
-
Figure 11.
Variation of γ(SO42–)/ γ(Na+) with γ(NO3–)/ γ(Ca2+).
-
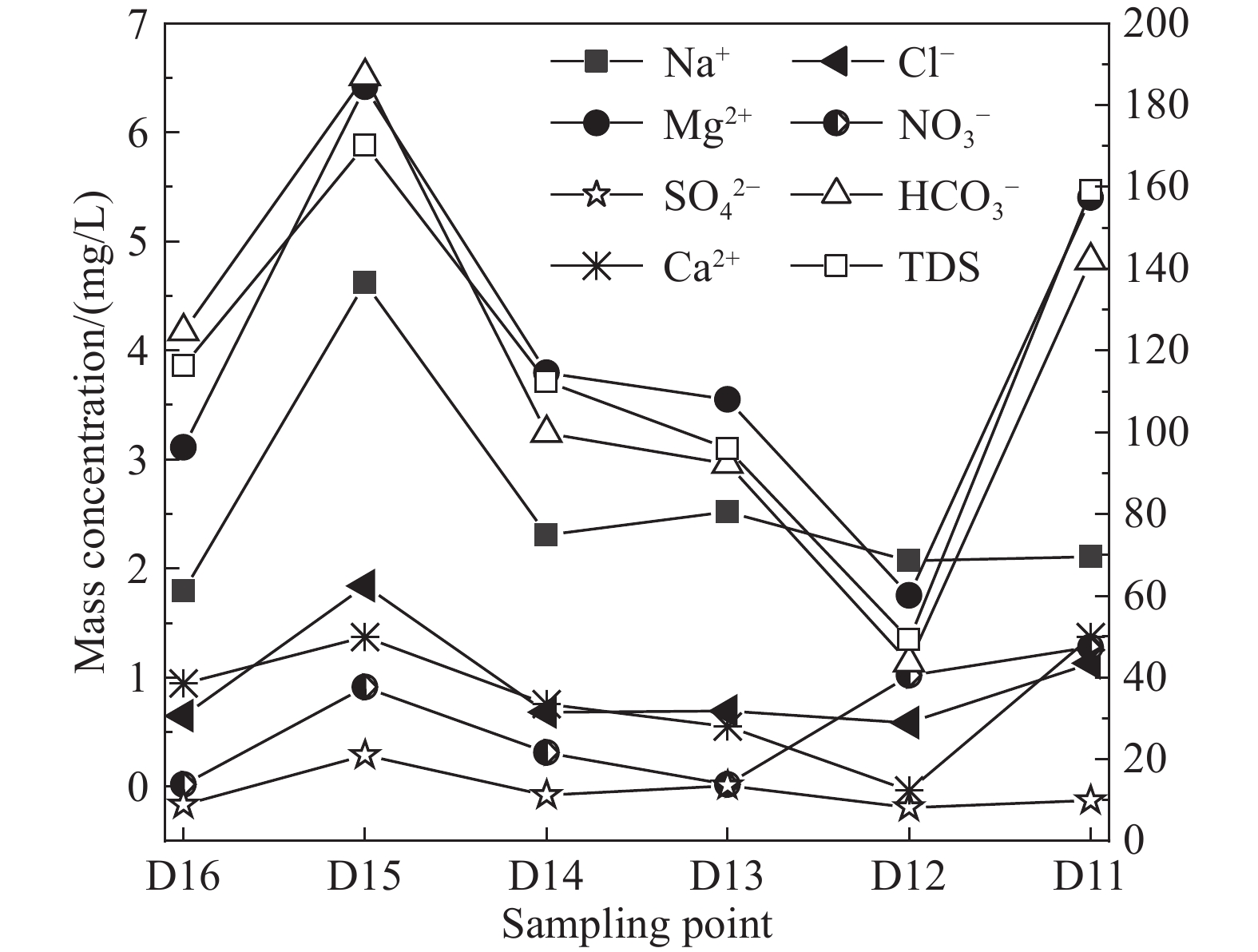
Figure 12.
Spatial variation of major ion concentrations along the Ziqu River.





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: