| Citation: | Zhi-wen Shang, Jian-fen Li, Holger Freund, Pei-xin Shi, Hong Wang, 2023. Quantitative relationship between surface sedimentary diatoms and water depth in North-Central Bohai Bay, China, China Geology, 6, 61-69. doi: 10.31035/cg2022040 |
Quantitative relationship between surface sedimentary diatoms and water depth in North-Central Bohai Bay, China
-
Abstract
To study the quantitative relationship between surface sedimentary diatoms and water depth, 67 surface samples were collected for diatom analysis on eight profiles with water depth variation from the muddy intertidal zone to the shallow sea area in North-Central Bohai Bay, China. The results showed that the distribution of diatoms changed significantly in response to the change in water depth. Furthermore, the quantitative relationship between the distribution of dominant diatom species, their assemblages, and the water depth was established. The water depth optima for seven dominant species such as Cyclotella striata/stylorum, Paralia sulcata, and Coscinodiscus perforatus and the water depth indication range of seven diatom assemblages were obtained in the study area above the water depth (elevation) of −10 m. The quantitative relationship between surface sedimentary diatoms and water depth provides a proxy index for diatom-paleo-water depth reconstruction in the strata in Bohai Bay, China.
-

-
References
Brugam RB, McKeever K, Kolesa L. 1998. A diatom-inferred water depth reconstruction for an upper peninsula, Michigan, lake. Journal of Paleolimnology, 20, 267–276. doi: 10.1023/A:1007948616511. Dalu T, Cuthbert RN, Weyl OLF, Wasserman RJ. 2022. Community structure and environmental factors affecting diatom abundance and diversity in a Mediterranean climate river system. Science of the Total Environment, 810, 152366. dio: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152366. National Marine Data and Information Service. 2008. Vol. 1 from the Yalu river mouth to the Changjiang river mouth, Tide tables. Jinan, Shandong Cartographic Publishing House, 1–509 (in Chinses). Guo YJ, Qian SB. 2003. Chinese Seaweed. Beijing, Science Press, 1–493 (in Chinses). Hasle GR, Syvertsen E E. 1997. Marine Diatoms. In: Tomas CR (ed.), Identifying Marine Phytoplankton. California, Academic Press, 5–385. He JS, Liang X, Li J, Yang JL. 2015. Environmentally sensitive grain-size extraction of deep hole sediment from Tianjin coastal plain and its significance. Earth Science, 40(7), 1215–1225 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.101. Hendey NI. 1964. An Introductory Account of the Smaller Algae of British Coastal Waters: Part V. Bacillariophyceae (Diatoms). Fishery Investigations Series IV., London, Otto Koeltz, 1–317. Hofmann AM, Geist J, Nowotny L, Raeder U. 2020. Depth-distribution of lake benthic diatom assemblages in relation to light availability and substrate: Implications for paleolimnological studies. Journal of Paleolimnology, 64, 315–334. doi: 10.1007/s10933-020-00139-9. Hong I, Horton BP, Hawkes AD, O′Donnell III RJ, Padgett JS, Dura T, Engelhart SE. 2021. Diatoms of the intertidal environments of Willapa Bay, Washington, USA as a sea-level indicator. Marine Micropaleontology, 167, 102033. doi: 10.1016/j.marmicro.2021.102033. Hu SX, Qi J. 2000. Shrink of estuaries in Haihe Basin and its effects on the flood disaster. Haihe Water Resources, (1), 11–13 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jin DX, Cheng ZD, Lin JM, Liu SC. 1982. Diatom of China Sea (I). Beijing, Marine Press, 1–323 (in Chinese). Jin DX, Cheng ZD, Liu SC, Ma JX. 1991. Diatom of China Sea (II). Beijing, Marine Press, 1–437 (in Chinese). Jiang H. 1987. Diatoms of the surface sediments in the neritic seas of China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 9(6), 735–743 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang H, Seidenkrantz MS, Knudsen KL, Eiŕiksson J. 2001. Diatom surface sediments assemblages around iceland and their relationship to oceanic environmental variables. Marine Micropaleontology, 41(1–2), 73–96. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8398(00)00053-0. Laird KR, Kingsbury MV, Cumming BF. 2010. Diatom habitats, species diversity and water-depth inference models across surface-sediment transects in Worth Lake, northwest Ontario, Canada. Journal of Paleolimnology, 44, 1009–1024. doi: 10.1007/s10933-010-9470-0. Li JF, Shang ZW, Wang F, Chen YS, Tian LZ, Jiang XY, Yu Q, Wang H. 2021. Holocene sea level trend on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China: Reanalysis and standardization. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 40(7), 198–246. doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1730-5. Liu SC, Jin DX, Lan DZ. 1984. Diatoms of the surficial sediments in the coastal and neritic sea of the south Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 5(suppl.), 927–945 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu J. 2001. Diatom distribution in surface sediments in the deep-sea area of the South China Sea. Marine Gology & Quaternary Geology, 21(2), 27–30 (in Chinese with English abstract). Moos MT, Laird KR, Cumming BF. 2005. Diatom assemblages and water depth in lake 239 (Experimental lake area, Ontario): Implications for paleoclimatic studies. Journal of Paleolimonlogy, 34, 217–227. doi: 10.1007/s10933-005-2382-8. Ng SL, Sin FS. 2003. A diatom model for inferring sea level change in the coastal waters of Hong Kong. Journal of Paleolimnology, 30, 427–440. doi: 10.1023/B:JOPL.0000007233.09972.85. Pei YD, Wang YS, Fan CF, Wang F, Tian LZ, Shang ZW, Che JY, Wang H. 2009. The surface sediment types and distribution of Tianjin intertidal zone, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(5), 682–687 (in Chinese with English abstract). Richard WB. 1986. Diatom Analysis, Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology. John Wiley& Sons Ltd, 527–570. Ran LH, Jiang H. 2005. Distributions of the surface sediment diatoms from the South China Sea and their palaeoceanographic significance. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 22(1), 97–106 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2005.01.010. Rivera-Rondón CA, Catalan J. 2020. Diatoms as indicators of the multivariate environment of mountain lakes. Science of Total Environment, 703, 135517. dio: 10.1016/j. scitotenv. 2019.135517. Shang ZW, Tian LZ, Wang H, Li JF. 2012. Diatom assemblages from surficial sediments in north-central Bohai Bay and their implications for environments. Geology in China, 39(4), 1099–1107 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.04.027. Shang ZW, Wang H, Che JY, Tian LZ, Pei YD, Fan CF, Wang F, Liu ZG. 2006. Diatom assemblages in the surface sediments of Bohai Bay. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 26(5), 21–26 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang FC, Shi PX, Shang ZW, Xiao GQ, Wang F. 2019. Research on the coastline of Tianjin. Geological Survey and Research, 42(4), 278–281 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang F, Pei YD Li JF, Shang ZW, Fan CF, Tian LZ, Song MY, Geng Y, Wang H. 2010. Current elevation of Tianjin tidal zone and the urban safety of Bohai New Area, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(5), 682–687 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.05.007. Wang KF, Jiang H, Feng WK. 1988. Diatom assemblages from surface sediments in the northern south China sea and their relation with the environments. Tropic Oceanology, 7(3), 19–25 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang KF, Jiang H, Zhang YL, Wang YJ, Xu JS. 1985. Environmental discussion on distribution of the diatom in the surface sediments on the Huanghai Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 16(5), 400–407 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang KF, Jiang H, Zhi CY, Tao MH, Wang HG. 2001. Study on the relationship between diatom assemblage in surface sediments and the environment in the East China Sea. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 18(4), 379–384 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2001.04.007. Wu KY, Zhao WQ, Li MJ, Picazo F, Soininen J, Shen J, Zhu LF, Cheng XY, Wang JJ. 2020. Taxonomic dependency of beta diverstiy components in benthic communities of bacteria, diatoms and chironomids along a water-depth gradient. Science of the Total Environment, 741, 140462. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140462. Yang JR, Duthie HC. 1995. Regression and weighted averaging models relatin surficial sedimentary diatom assemblages to water depth in lake Ontario. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 21(1), 84–94. doi: 10.1016/S0380-1330(95)71023-1. Yang P, Tian LZ, Wen MZ, Wang F, Liu B, Lin GQ. 2020. Application of shipborne sea-land integrated three-dimensional terrain surveying technology in monitoring of coastal zone erosion and deposition. Geological Survey and Research, 43(4), 348–352 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang SR, Ji L. 1994. Fossil diatom studies in paleolimnolog: Developments since the 1980s. Journal of Lakes sciences, 6(2), 177–185 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/1994.0212. Yu SW, Wang JB, Li YM, Peng P, Kai JL, Kou QQ, Laug A. 2019. Spatial distribution of diatom assemblages in the surface sediments of Selin Co, central Xizang Plateau, China, and the controlling factors. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 45(6), 1069–1079. doi: 10.1016/j.jglr.2019.09.006. Yang XD, Kamenik C, Schmidt R, Wang SM. 2003. Diatom-based conductivity and water-level inference models from eastern Xizang (Qinghai-Xizang) Plateau lakes. Journal of Paleolimnology, 30, 1–19. doi: 10.1023/A:1024703012475. Zhang JP, Tomczak M, Witkowski A, Zhen X, Li C. 2022. A fossil diatom-based reconstruction of sea-level changes for the Late Pleistocene and Holocene period in the NW South China Sea. Oceanologia. doi: 10.1016/j.oceano.2022.05.004. Zhang KX, Pan GT, He WH, Xiao QH, Xu YD, Zhang ZY, Lu SN, Deng JF, Feng YM, Li JY, Zhao XM, Xing GF, Wang YH, Yin FG, Hao GJ, Zhang CJ, Zhang J, Gong YM. 2015. New division of tectonic-strata super region in China. Earth Science, 40(2), 206–233 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.016. Zhi CY, Wang KF, Lan DZ, Li C. 2005. Diatom ecotype of habitation and their distribution in the surface sediments around Xiamen island and in Taiwan straits. Journal of Tongji University, 33(7), 971–975 (in Chinese with English abstract). -
Access History

-
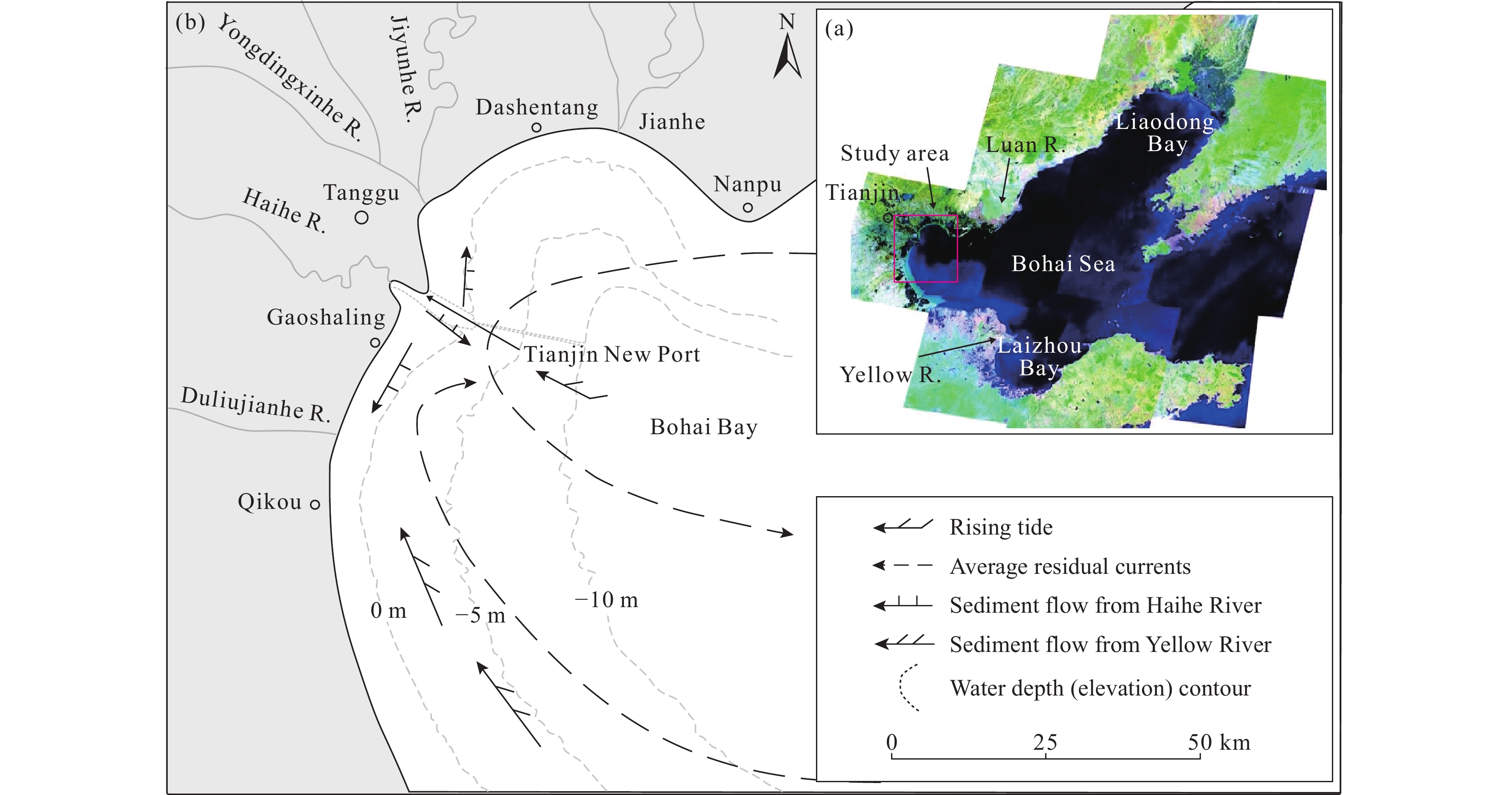
Figure 1.
Map showing the Bohai Sea, China. a-Regional background and the location of the study area (marked with a red square); b-map showing the study area, Bohai Bay. R.−River.
-
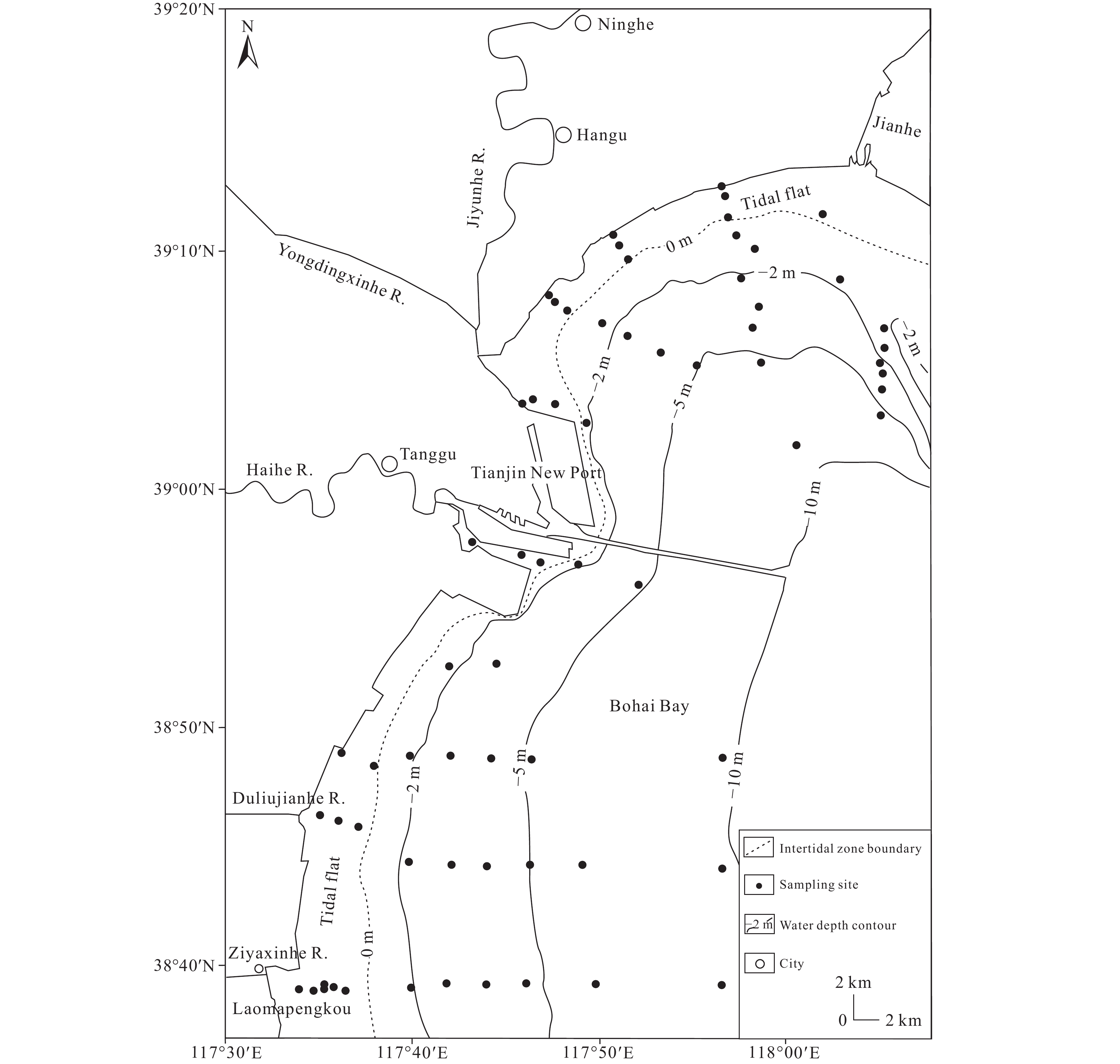
Figure 2.
Location map of the surficial sampling stations for diatom analysis in the North-Central Bohai Bay. The bottom water depth contours were drawn based on the measured data from 2006 to 2008. R.−River.
-
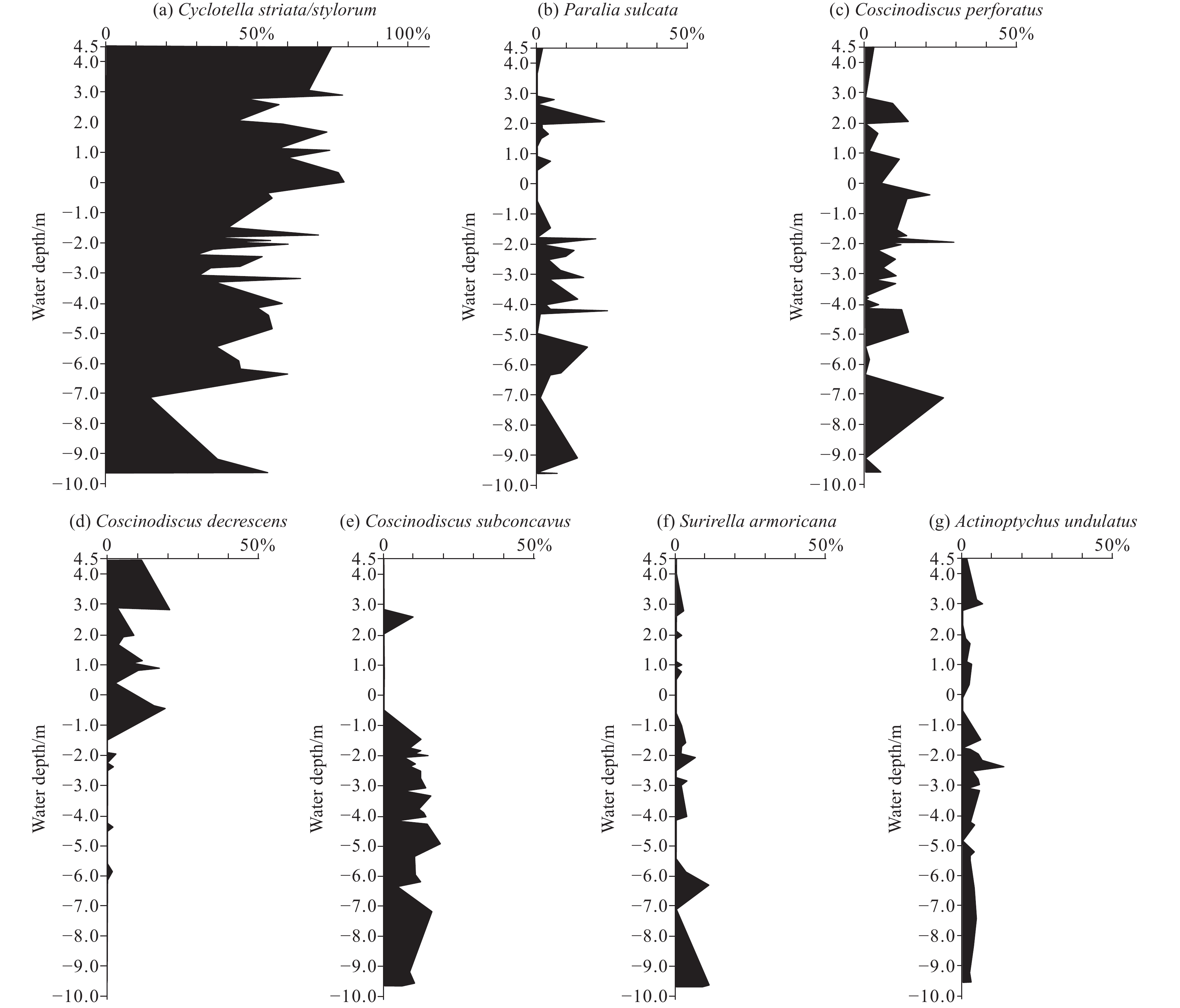
Figure 3.
Vertical distribution characteristics of the dominant non-planktonic diatom species response to the change of water depth of the surficial sediments in the muddy intertidal zone and the contiguous shallow sea area in the North-Central Bohai Bay, China.
-
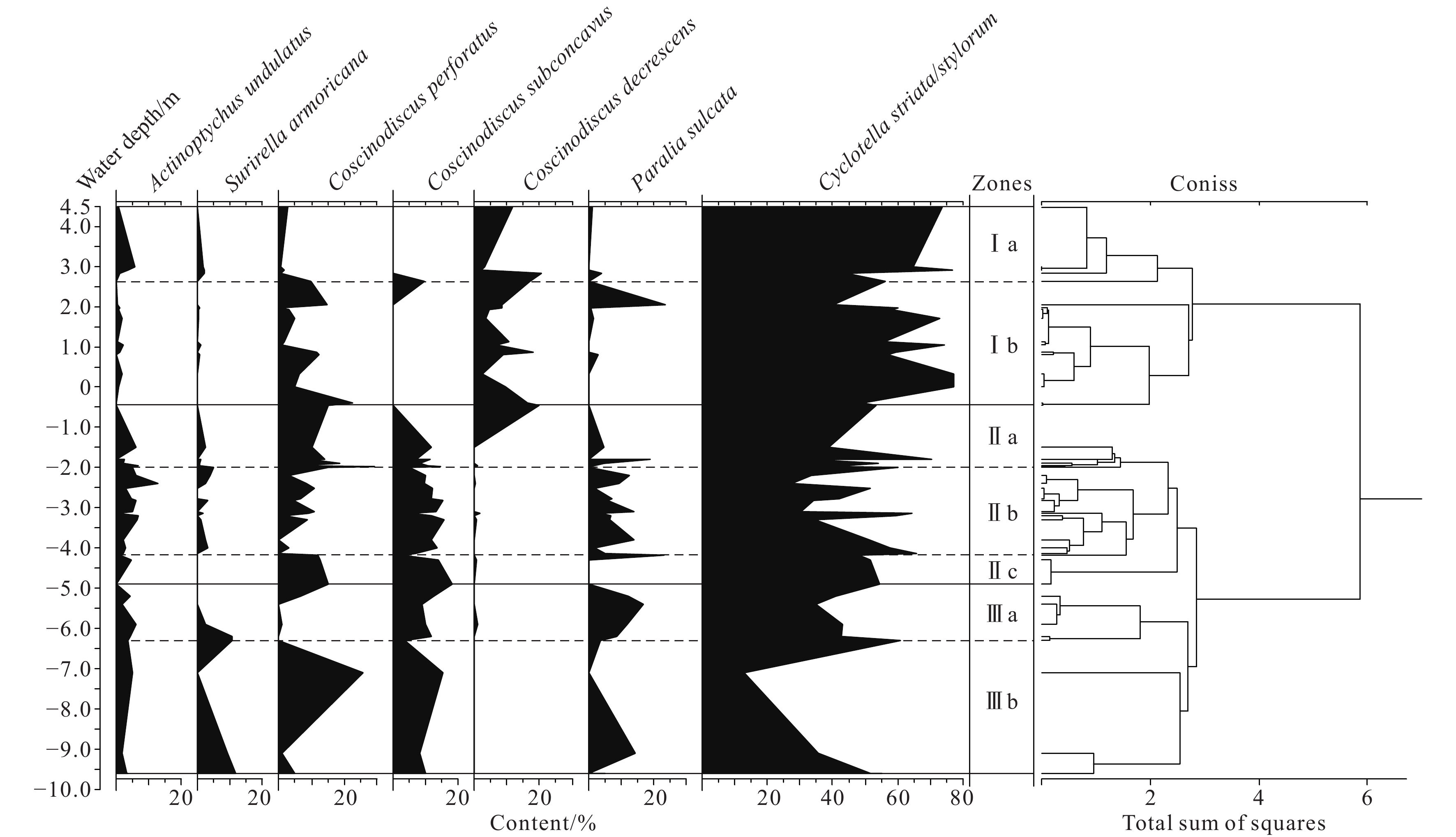
Figure 4.
Vertical cluster characteristics of the surface sedimentary diatom assemblages’ response to the water depth change in the muddy intertidal zone and the contiguous shallow sea in North-Central Bohai Bay, China.
-
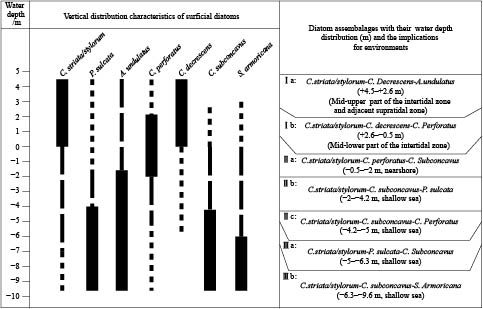
Figure 5.
Vertical zonations of the surface sedimentary diatom species, assemblages, and their relationships with water depth in the muddy intertidal zone and the contiguous shallow sea in the North-Central Bohai Bay, China.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: