| Citation: | Ming-jian Wang, Guo-lin Xiao, Chang-qing Yang, Yan-qiu Yang, Xi Chen, Long Huang, 2019. Characteristics and evaluation of Mesozoic source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf, China Geology, 2, 133-141. doi: 10.31035/cg2018079 |
Characteristics and evaluation of Mesozoic source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf
-
Abstract
Source rocks are the material basis of oil and gas generation and determine the potential resources of exploration blocks and have important research value. This paper studies the lithology, thickness, and geochemistry of Mesozoic source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf. The results show that the Mesozoic source rocks are mainly dark mudstone and coal-bearing strata. The total thickness of Lower–Middle Jurassic source rocks ranges from 100 m to 700 m, and that of Lower Cretaceous source rocks ranges from 50 m to 350 m. The overall thickness of Mesozoic source rocks is distributed in the NE direction and their thickness center is located in the Jilong Depression. The Lower–Middle Jurassic source rocks are mainly developed shallow marine dark mudstone and transitional coal measure strata. Those of the Lower Cretaceous are mainly mudstone of a fan delta front. Lower–Middle Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous hydrocarbon source rocks are dominated by type III kerogen, with Lower–Middle Jurassic hydrocarbon source rocks having high organic matter abundance and being medium–good hydrocarbon source rocks, while Lower Cretaceous hydrocarbon source rocks have relatively poor quality. From northwest to southeast, the vitrinite reflectance Ro of Mesozoic source rocks increases gradually. Source rocks in the study area are divided into three types. The first hydrocarbon-generating area is mainly located in the southeastern region of the study area, and the Jilong Depression is the hydrocarbon-generating center. The results of this study can provide a basis for exploration of Mesozoic oil and gas resources in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf.
-
Keywords:
- East China Sea continental shelf /
- Southeastern part /
- Mesozoic /
- Source rocks /
- Evaluation
-

-
References
[1] Cong Y, Liu Z, Lu K, Meng XJ, Zhang XF. 2016. Residual thickness of the Mesozoic in the Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(5), 39–44. [2] Duan XY, Li YX, Li XG, Yin P. 2018. Historical records and the sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the East China Sea. China Geology, 1(4), 505–511. doi: 10.31035/cg2018058 [3] Feng XJ, Cai DS, Wang CX. 2003. The Meso-Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution in East China Sea Shelf Basin. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 17(1), 33–37. [4] Geng YS, Shen QH, Song HX. 2018. Metamorphic petrology and geology in China: A review. China Geology, 1(1), 137–157. doi: 10.31035/cg2018012 [5] Gong JM, Li G, Yang CS, Xu XH, Zhang JW, Wang HR, Xu LM. 2013. Hydrocarbon Prospecting of Mesozoic Strata in Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 43(1), 20–27. [6] Guo Z, Liu CY, Tian JF. 2015. Longjing Movement structural effect and background in East China Sea developmental basin. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 45(5), 801–810. [7] Jiang DH, Tang J, Wang DP, Xu LM, Li G, Yang CQ. 2017. Mesozoic stratigraphic framework of the Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin and its correlation with adjacent areas. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(4), 16–21. [8] Jiang XY, Fu ZF. 2010. Tectonic evolution features and exploration prospect of Jilong sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Petroleum geology and engineering, 2010, 24(2), 21–25. [9] Jin CS, Qiao DW, Xu XH, Li G, Liang JS, Jiang ZX, Xu LM. 2015. Oil and gas potential and target selection in southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Geology in China, 42(5), 1601–1609. [10] Li DY, Guo TY, Jiang XD, Zhao HQ, Wang HP. 2015. Erosion thickness recovery and tectonic evolution characterization of southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(6), 913–923. [11] Li G, Gong JM, Yang CQ, Yang CS, Wang WJ, Wang HR, Li SZ. 2012. Stratigraphic features of the Mesozoic “great East China Sea”- new exploration field. Marine Geology & Quarternary Geology, 32(3), 97–104. [12] Liang J, Chen JW, Zhang YG, Yang YQ, Li G, Li Q, Dong G, Yang CS. 2016. Type and origin of Mesozoic reservoirs in western depression zone of east China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology & Quarternary Geology, 36(5), 131–138. [13] Liang RB. 2017. Analysis of hydrocarbon exploration potential in the Mesozoic of the Southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Offshore Oil, 37(3), 16–22. [14] Liu JH, Wu JS, Fang YX. 2007. Pre-Cenozoic groups in the Shelf Basin of the East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 29(1), 66–75. [15] Su Ao, Chen HH, Zhan HY. 2015. Development prospects and geological characteristics of nearly tight and tight sandstone gas reservoirs in western secondary sag and western slope zone of Xihu depression, East China Sea. Geology in China, 42(4), 1115–1125. [16] Wang GL, Zhang W, Ma F, Lin WJ, Liang JY, Zhu X. 2018. Overview on hydrothermal and hot dry rock researches in China. China Geology, 1(2), 273–285. doi: 10.31035/cg2018021 [17] Wang MJ, Chen X, Lei BH, Zhu XQ. 2018. Current status and problems of oil and gas exploration in South Yellow Sea Basin. Marine Geology Frontiers, 34(11), 20–25. [18] Wang MJ, He Df, Bao HP, Lu RQ, Gui BL. 2011. Upper Palaeozoic gas accumulations of the Yimeng uplift, Ordos Basin. Petroleum exploration and development, 38(1), 30–39. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60013-X [19] Wang MJ, Meng XJ, Chen X, Zhu XQ. 2016. Geochemistry characteristics and evaluation of Upper Paleozoic source rock in Yimeng uplift, Ordos Basin. Marine Geology Frontiers, 32(9), 26–31. [20] Yang CQ, Han BF, Yang YQ, Yang CS, Sun J, Yan ZH, Jiang DH, Li G, Liu X, Wang JQ. 2017. Oil and gas exploration in the Mesozoic of East China Sea Shelf Basin: progress and challenges. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(4), 1–8. [21] Yang CQ, Yang CS, Li G, Liao J, Gong JM. 2012. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and prototype basin characteristics in the southern East China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology & Quarternary Geology, 32(3), 105–111. [22] Yang CS, Yang CQ, Li G, Yang YQ, Sun J, Yan ZH, Wang JQ. 2018. Prospecting of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology & Quarternary Geology, 38(2), 136–147. [23] Yang YQ, Yang CQ, Yang CS, Li G. 2016. Mesozoic traps in the west of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology Frontiers, 33(4), 49–52. [24] Yao G, Dong XX, Li LL, Ma GQ, Meng LS. 2018. High-precision gravity and magnetic interpretation technique in tectonic division of East China Sea Shelf Basin. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(2), 517–524. [25] Zhai GY, Wang YF, Zhou Z, Liu GH, Yang YR, Li J. 2018. “Source-Diagenesis-accumulation” enrichment and accumulation regularity of marine shale gas in southern China. China Geology, 1, 319–330. doi: 10.31035/cg2018059 [26] Zhai GY, Wang YF, Zhou Z, Yu SF, Chen XL, Zhang YX. 2018. Exploration and research progress of shale gas in China. China Geology, 1(2), 257–272. doi: 10.31035/cg2018024 [27] Zhang GH, Zhang JP. 2015. A discussion on the tectonic inversion and its genetic mechanism in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1), 260–270. [28] Zhang JP, Zhang T, Tang XJ. 2014. Basin type and dynamic environment in the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(11), 2033–2043. [29] Zhang T, Zhang JP, Zhang SL, Yu YF, Tang XJ. 2015. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of the west depression belt of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Marine Geology Frontiers, 31(5), 1–7. [30] Zhao HQ, Li DY, Wang HP, Li CL, Ji ZY. 2014. Cenezoic prototype, analogy and the significance of oil and gas exploration in the Shelf Basin of Southern East China Sea. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 36(6), 21–25. [31] Zhong K, Zhu WL, Gao SL. 2018. Key Geological Questions of the Formation and evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of the East China Sea Shelf Basin. Earth Science, 43(10), 3485–3497. -
Access History

-
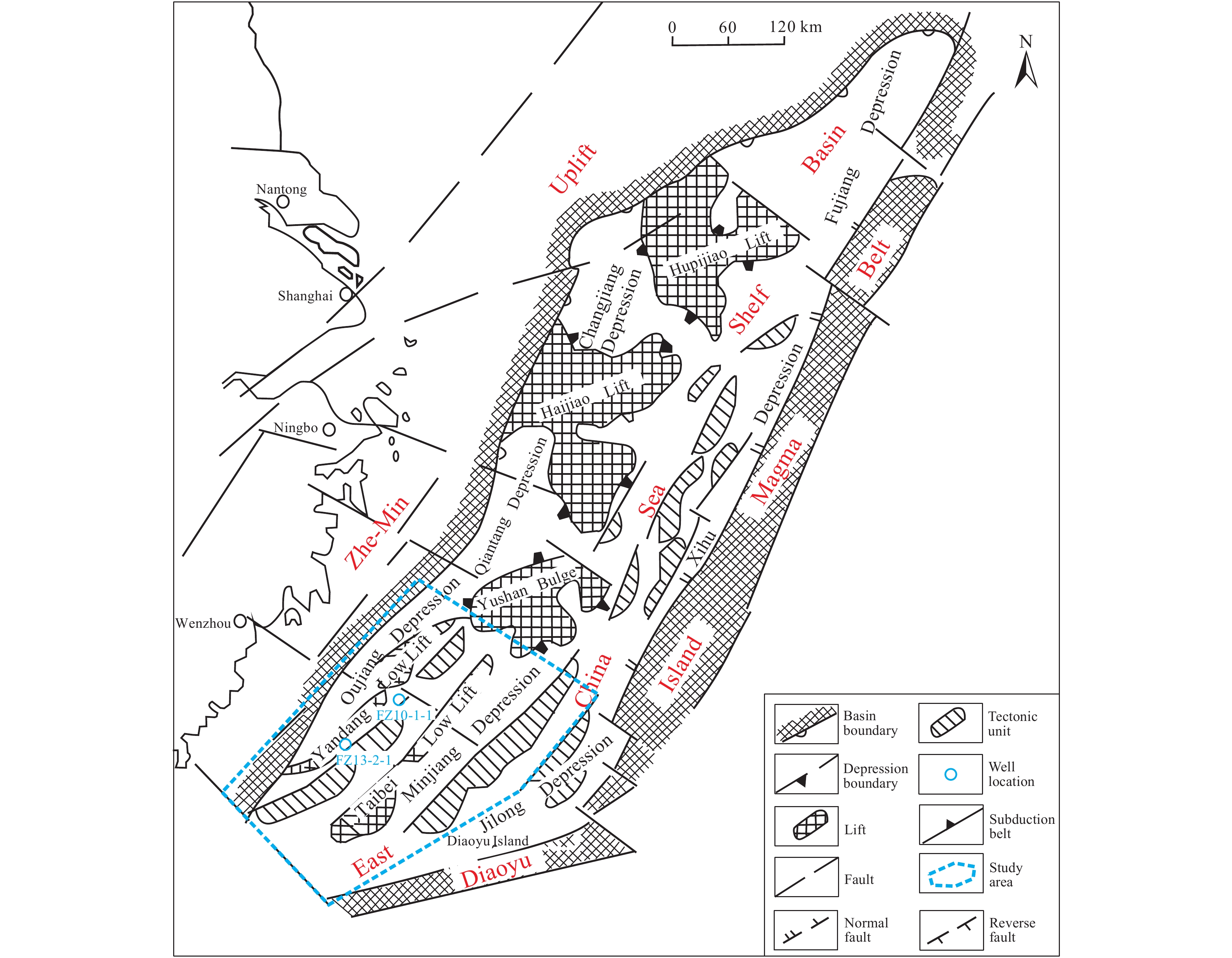
Figure 1.
Tectonic map of the East China Sea Shelf Basin.
-
Figure 2.
Cores from the Fuzhou Formation in the Lower–Middle Jurassic (well FZ10-1-1; 3378–3382 m).
-
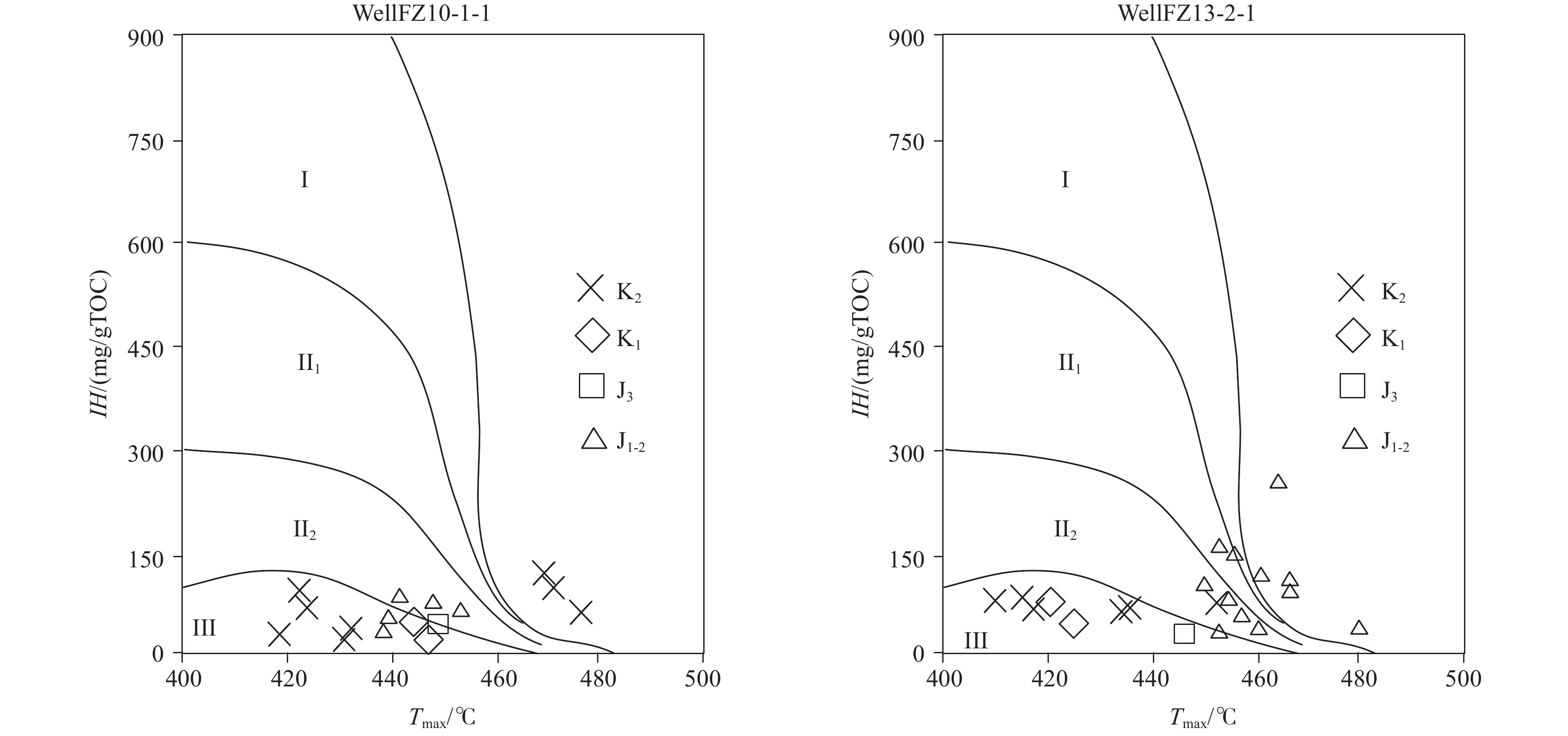
Figure 3.
TOC content and pyrolysis S1+S2 numerical scatter plot of mudstones in the Fuzhou Formation of the Lower–Middle Jurassic drilled in the southern East China Sea.
-
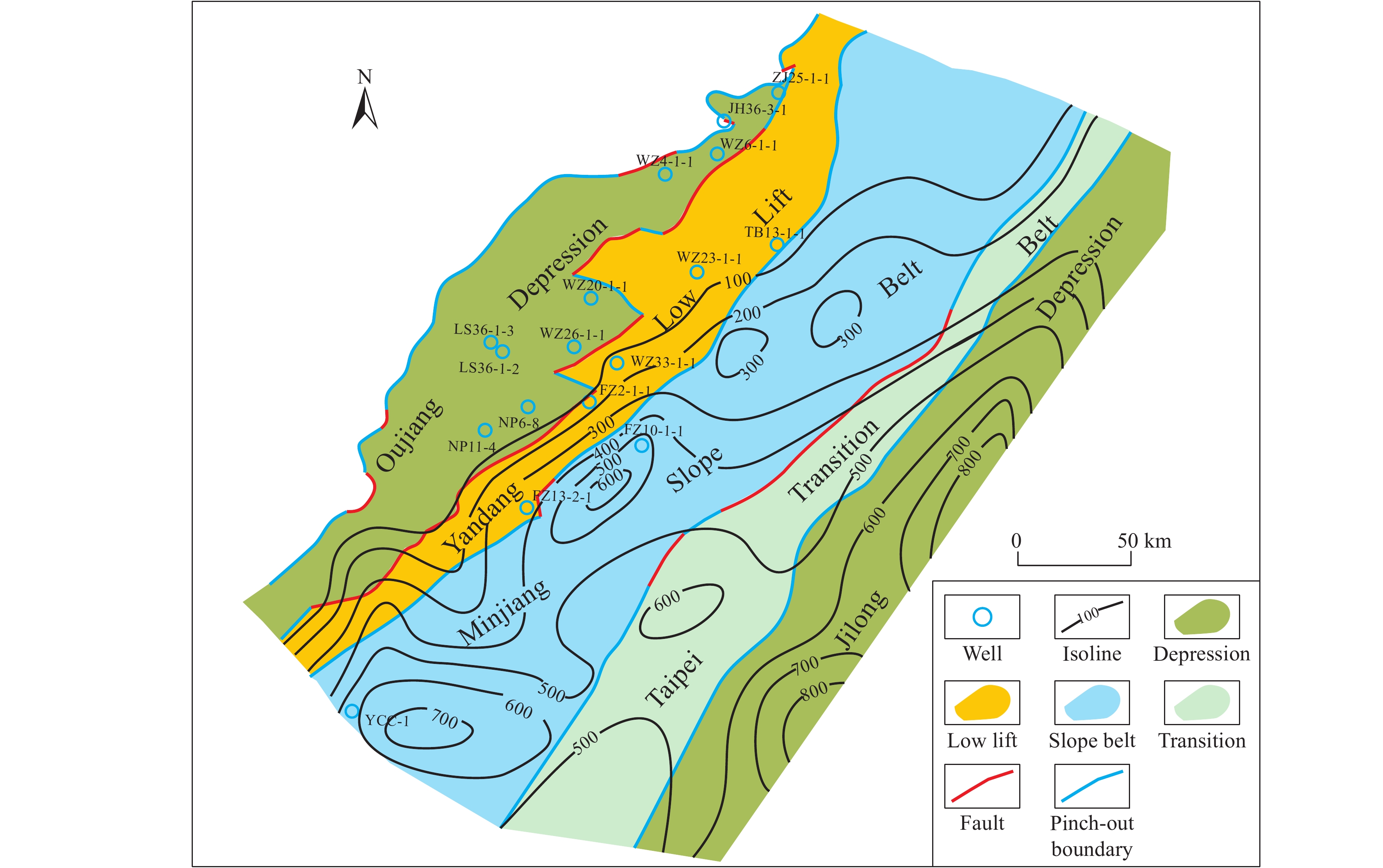
Figure 4.
Thickness map for Lower–Middle Jurassic source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf (with the base map being the Mesozoic tectonic regionalization map).
-
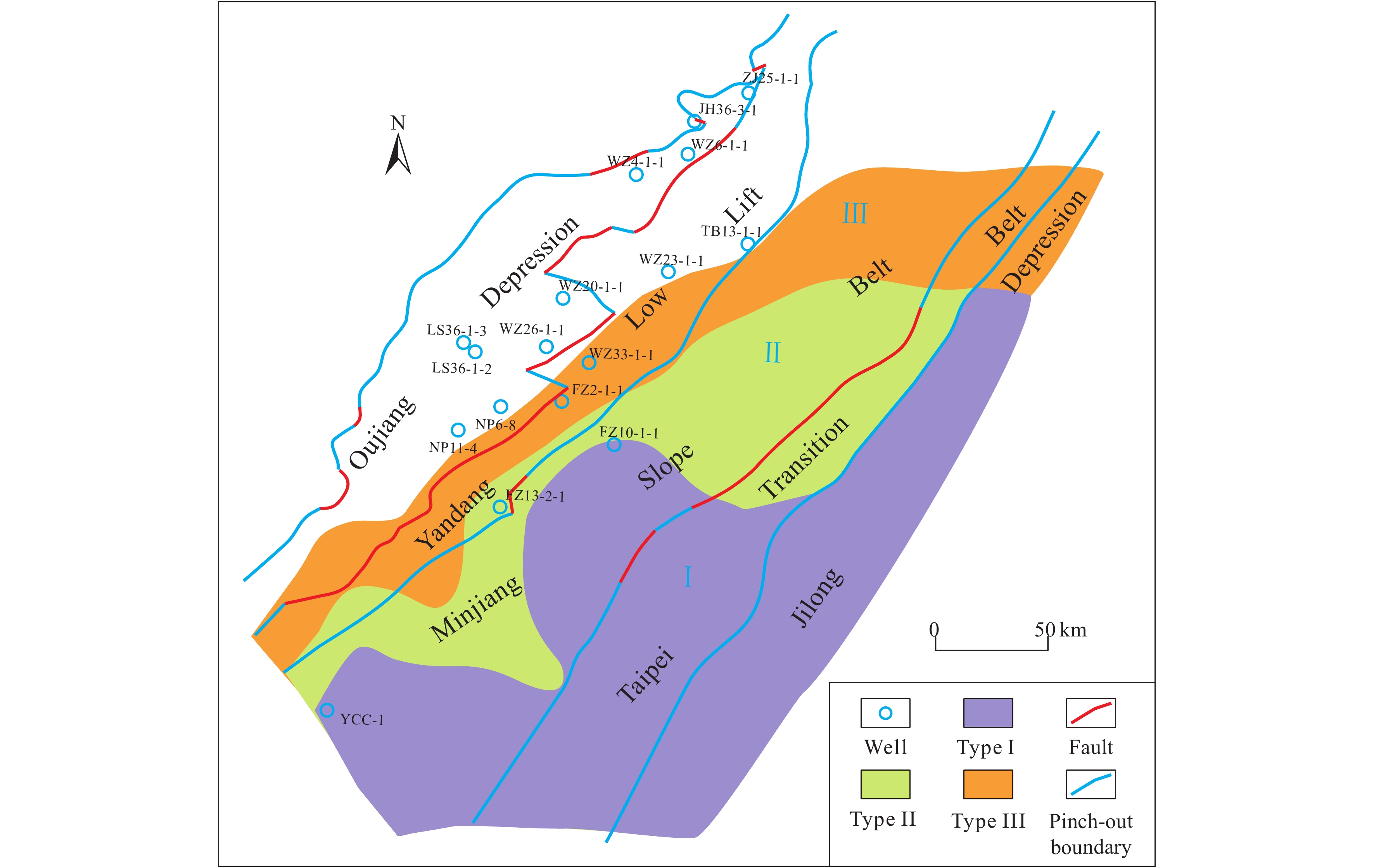
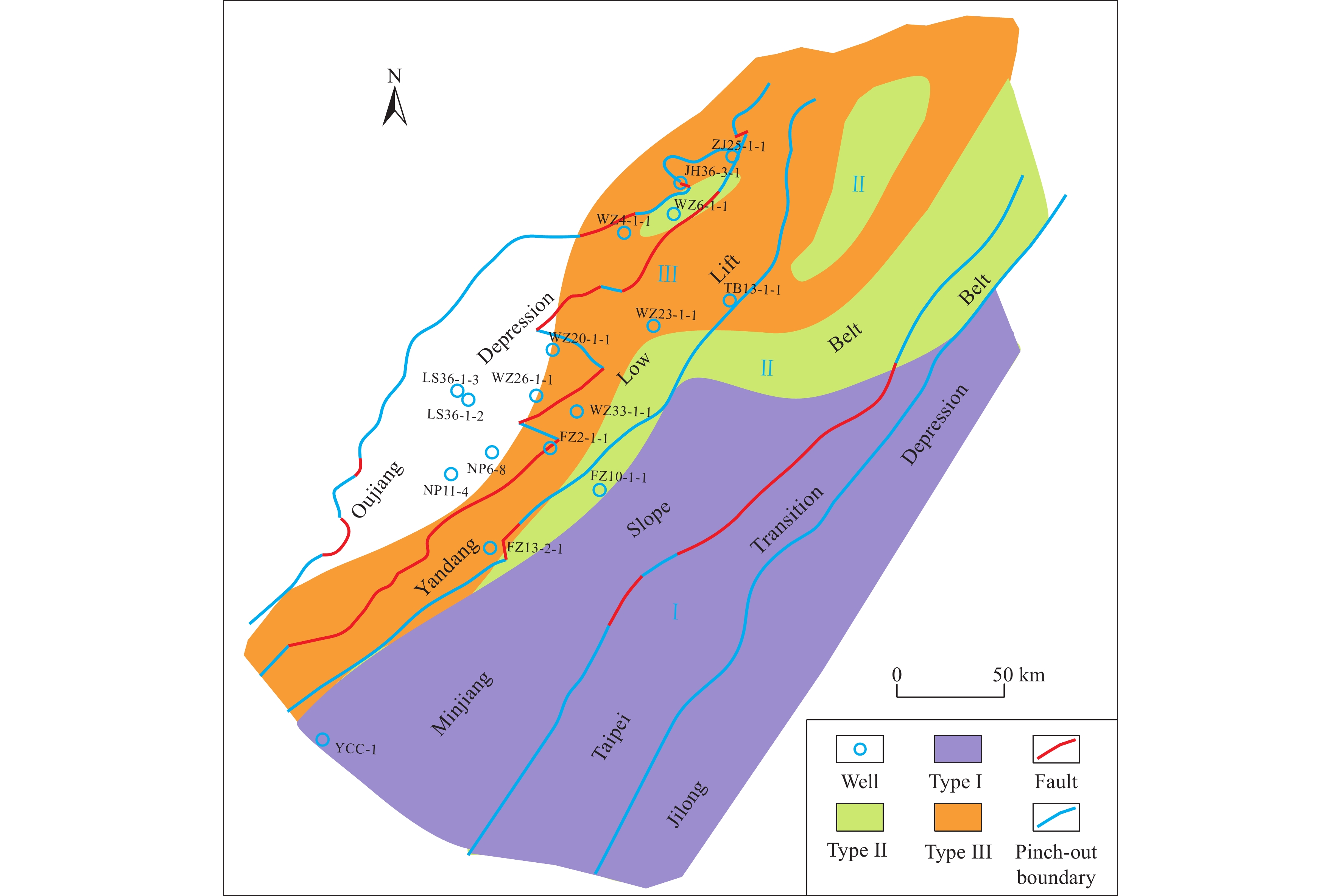
Figure 5.
Classification and evaluation map for Jurassic source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf (with the base map being the Mesozoic tectonic regionalization map).
-
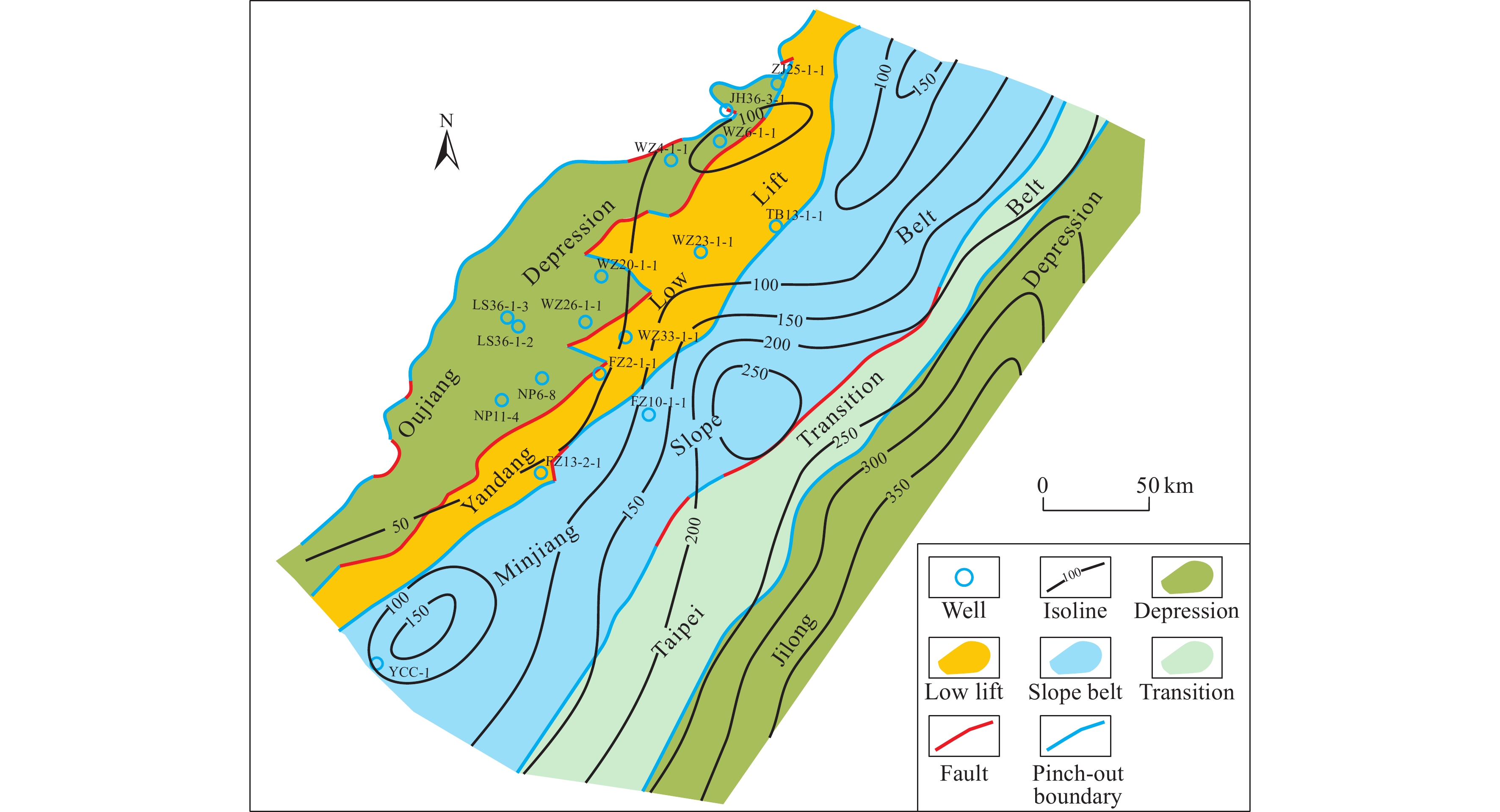
Figure 6.
Thickness map for Lower Cretaceous source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf (with the base map being the Mesozoic tectonic regionalization map).
-
Figure 7.
Classification and evaluation map for Lower Cretaceous source rocks in the southeastern East China Sea continental shelf (with the base map being the Mesozoic tectonic regionalization map).




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: