| Citation: | Guang-xue Zhang, Zhen Yang, Li Zhang, Wei Yan, Kun-sheng Qiang, 2018. Study of overthrust nappe structure and its geodynamic mechanism along the southeastern margin of Nansha Trough, China Geology, 1, 459-465. doi: 10.31035/cg2018060 |
Study of overthrust nappe structure and its geodynamic mechanism along the southeastern margin of Nansha Trough
-
Abstract
On the basis of interpretation of comprehensive geophysical data and foreign data analysis, there existed a lot of overburden detachment shear thrust faults along the southeastern margin of Nansha Trough, which composed imbricated overthrust nappe structure. Thrust-faulted nappe structure pattern is determined in this area, which consists of frontal fault zone, thrust fault-folded zone and root zone structures, and presents regularly zonation on plane. The detail description of the structural geometrical characteristics is given in shallow thrust fault zone, and the kinematical mechanism of thrust fault nappe structure is furtherly discussed. Overthrust nappe structure in this area is resulted from island arc-continent collision and orogenic activities.
-
Keywords:
- Overthrust /
- Structure /
- Geodynamic /
- Mechanism /
- Nansha Trough
-

-
References
[1] Back S, Strozyk F, Kukla PA, Lambiase JJ. 2008. Three-dimensional restoration of original sedimentary geometries in deformed basin fill, onshore Brunei Darussalam, NW Borneo. Basin Research, 20, 99–117. doi: 10.1111/bre.2008.20.issue-1 [2] Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P. 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the tertiary tectonics of southeast Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(B4), 6299–6328. doi: 10.1029/92JB02280 [3] Cullen A, Patriat P, Trapponier P. 2010. Transverse segmentation of the Baram-Balabac basin, NW Borneo: refining the model of Borneo’s tectonic evolution. Petroleum Geoscience, Geological Society of London, 16, 3–29. [4] Chen Z, Yan W, Huang CY. 2007. Geological settings and indicators of potential gas hydrates in the Nansha Trough area, South China Sea. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(6):299-308 [5] Franke D, Barckhausen U, Heyde I, Mark T, Nordin R. 2008. Seismic images of a collision zone offshore NW Sabah/Borneo. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 25(7), 606–624. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.11.004 [6] Hall R. 2002. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: Computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4), 353–431. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(01)00069-4 [7] Hall R. 2013. Contraction and extension in northern Borneo driven by subduction rollback. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 76, 399-411. [8] Han B, Zhu BD, Wan L. 2015. Deep-water fold and thrust tectonic in the southeastern Nansha Trough. Geological Review, 61(5), 1061–1066. [9] Hesse S, Back S, Franke D. 2009. The deep-water fold-and-thrust belt offshore NW Borneo: Gravity-driven versus basement-driven shortening. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121, 939–953. doi: 10.1130/B26411.1 [10] Hesse S, Back S, Franke D. 2010. The structural evolution of folds in a deep-water fold and thrust belt: a case study from the Sabah continental margin offshore NW Borneo, SE Asia. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 27(2), 442–254. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.09.004 [11] Hinz K, Fritsch J, Kempter EH, Hannover, Manaf MA, Lumpur MK, Meyer J, Mohamed D, Vosberg H, Weber J, Benavidez J, Makati. 1989. Thrust tectonics along the north-western continental margin of Sabah/Borneo. Geologische Rundschau, 78(3), 705–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01829317 [12] Hinz K, Schluter HU. 1985. Geology of the dangerous grounds, South China Sea, and the continental margin off southwest Palawan: Results of Sonne Cruises So-23 and So-27. Energy, 10(3/4), 297–315. [13] Hutchison CS. 2010. The North-West Borneo trough. Marine Geology, 271, 32–43. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.01.007 [14] King R., Back G, Morley C, Richard R, Hillisa MR P Tingayd. 2010. Balancing deformation in NW Borneo: Quantifying plate-scale vs. gravitational tectonics in a delta and deep-water fold-thrust belt system. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 27(1), 238–246. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.07.008 [15] Li CF, Li JB, Ding WW, Franke D, Yao YJ, Shi HS, Pang X, Cao Y, Lin J, Kulhanek DK, Williams T, Bao R, Briais A, Brown EA, Chen YF, Clift PD. Colwell FS, Dadd KA, Hernández AI, Huang XL, Hyun S, Jiang T, Koppers AAP, Li QY, Liu CL, Liu QS, Liu ZF, Nagai RH, Peleo AA, Su X, Sun Z, Tejada MLG, Trinh HS, Yeh YC, Zhang CL, Zhang F, Zhang GL, Zhao XX. 2015. Seismic stratigraphy of the central South China Sea basin and implications for neotectonics. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120, 1377–399. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011686 [16] Li CF, Xu X, Lin J, Sun Z, Zhu J, Yao YQ, Zhao XX, Liu QS, Kulhanek DK, Wang J, Song TR, Zhao JF, Qiu N, Guan YX, Zhou ZY, Williams T, Bao R, Anne B, Elizabeth AB, Chen YF, Peter DC, Frederick SC, Kelsie AD, Ding WW, Almeida IA, Huang XL, Hyun S, Jiang T, Koppers AAP, Li QY, Liu, CL, Liu ZF, Renata HN, Alampay AP, Xin Su, Maria LGT, Trinh HS, Yeh YC, Zhang CL, Zhang F, Zhang GL. 2014. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 15, 4958–4983. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005567 [17] Milkov A V, Sassen R. 2002. Economic geology of offshore gas hydrate accumulations and provinces. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 19:1-11. [18] Morley CK, Back S, Van RP, Crevello P, Lambiase JJ. 2003. Characteristics of repeated, detached, Miocene-Pliocene tectonic inversion events, in Large delta province on an active margin, Brunei Darussalam, Borneo. Journal of Structural Geology, 25, 1147–1169. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(02)00130-X [19] Morley CK. 2009. Growth of folds in a deep-water setting. Geosphere, 5(2), 59–89. doi: 10.1130/GES00186.1 [20] Rangin G, Bellon H, Benard F, Letouzeyc J, Mullerd C, Sanudine T. 1990. Neogene arc-continent collision in Sabah, northern Borneo (Malaysia). Tectonophysics, 183, 305–319. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90423-6 [21] Schluter HU. 1985. Geology of the dangerous grounds, South China Sea, and the continental margin off southwest Palawan: Results of SONNE CRUISES SO-23 and SO-27. Energy, 10(3/4), 297–315. [22] Shi X, Qiu X, Xia K, Zhou D. 2003. Characteristics of surface heat flow in the South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 22(3), 265–277. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00059-2 [23] Song TR, Li CF. 2015. Rifting to drifting transition of the Southwest Subbasin of the South China Sea. Marine Geophys Research, 36, 167–185. doi: 10.1007/s11001-015-9253-0 [24] Taylor B, Hayes DE. 1980. The Tectonic Evolution of the South China Basin. Tectonic & Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas & Islands, 23, 89–104. [25] Vijayana VR, Clive F, Howard S. 2013. Crustal character and thickness over the dangerous grounds and beneath the northwest Borneo Trough. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 76, 389–398. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.06.004 [26] Yan P, Liu H. 2004. Tectonic-stratigraphic divisions and blind fold structures in Nansha waters, South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(3), 337–348. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.12.005 [27] Zhang C, Wu SM, Qiu X L. 2007. Formation of foreland Basins in the south of the South China Sea. Marine geology and Quaternary, 27(1), 61–70. -
Access History

-
Figure 1.
Structural map of the fold and thrust belt southeastern Nansha Trough and location of seismic line (modified from Hall R, 2002,2013).
-
Figure 2.
Geoseismic section of line BGR86-10 (modified from Hinz K et al., 1989).
-
Figure 3.
Geoseismic section of line BGR86-22 (modified from Hinz K et al., 1985).
-
Figure 4.
Geoseismic section of line SO27-007 (modified from Hinz K et al., 1989).
-
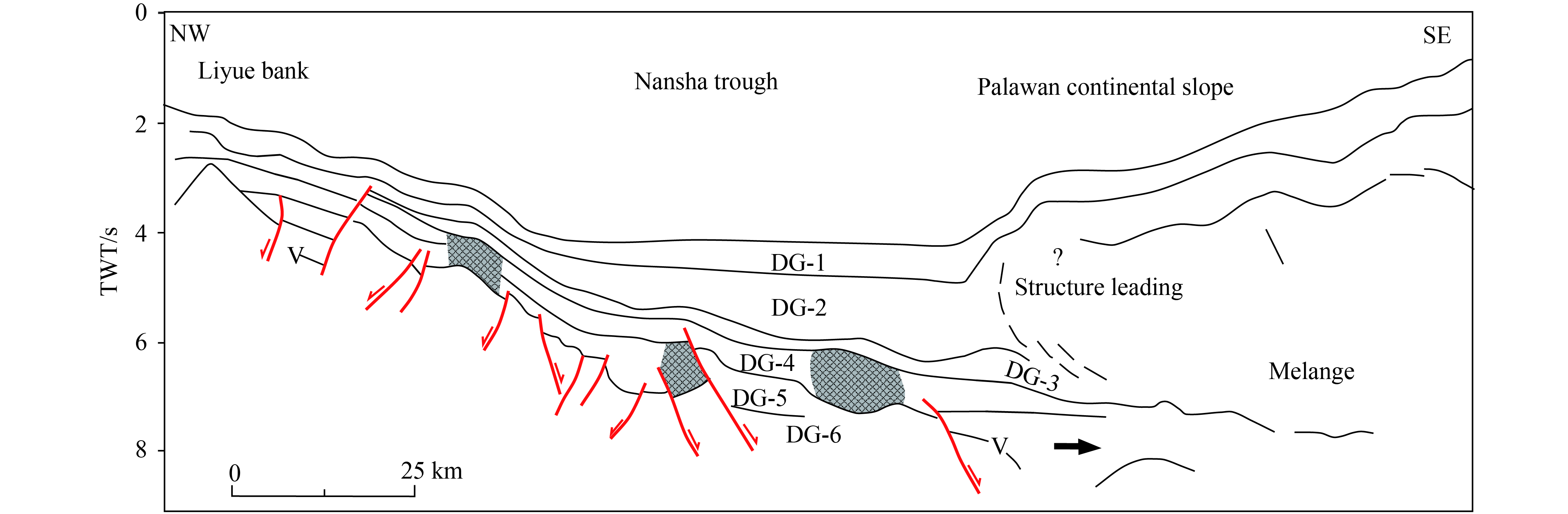
Figure 5.
Interpretation of 2D seismic line running across the fold and thrust belt.
-
Figure 6.
A diagram showing the Cenozoic structural evolution of Nansha trough and its southeast margin.





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: