| Citation: | Hong-xian Chu, Sai Mei, Xiao-hui Gao, Zhong-hua Fang, Jing Feng, 2019. Analysis of formation and slope stability in Caofeidian Channel in Bohai Bay, China Geology, 2, 189-197. doi: 10.31035/cg2018057 |
Analysis of formation and slope stability in Caofeidian Channel in Bohai Bay
-
Abstract
In this paper, by studying bathymetric survey and shallow seismic detection data over multiple periods of history, the authors outline the geomorphic features of the Caofeidian Channel. The results of our studies indicate that the channel at the front end is dominated by erosion. The maximum water depth reaches 42.2 m, which sets the highest record for the water depth in Bohai Bay; the authors preliminarily conclude that the formation of the early channel occurred because the subsidence rate of the deep structure is slightly smaller than the deposition rate of the upper strata, and the Caofeidian Channel has existed for a long time, over 20 ka. The trending of the channel experienced a transition from the NS to the NE and then NW direction; the authors conclude that endogenic and exogenic processes, such as geological structures, the evolution of the ancient Luanhe River Delta, marine hydrodynamics, and human activity, jointly control the development and evolution of the geographic system in the Caofeidian sea area. The slope stabilities under the extreme conditions of a heavy storm and an earthquake are analyzed by performing simulations.
-
Keywords:
- Caofeidian /
- channel /
- tidal current /
- deposition /
- erosion /
- stability
-

-
References
[1] Bai DP. 2011. The geological disasters and tidal dynamic geomorphology of Nanpu area in the east of Bohai Bay. Ocean University of China, 40−50. [2] Chu HX, Li C. 2008. Special geological topic on marine engineering evaluation for geological environment protection in the Caofeidian area. Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology. [3] Chu HX, Li Q, Wang WH. 2013. Scout and deposit analysis around artificial island at Caofeidian shallow sea. Marine Geology Frontiers, 29(6), 41–43. [4] Chu HX, Shi HJ, Yang Y. 2010. The application of surge wave filters to improve the accuracy of seabed topography. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 30(4), 51–62. [5] Ji RY, Lu YJ, Zuo LQ. 2011. Formation mechanism and stability of Caofeidian channel in the Bohai Bay. Acta Geographica Sinica, 3(66), 348–355. [6] Jia YL, Ke XK, Xu YH. 1999. Sedimentary transport trends of within a sand bar/lagoon system in the Bohai sea. Marine Sciences, 3, 56–59. [7] Kong L, Zhang ZH, Yuan QM, Liang QY, Shi YH, Lin JL. 2018. Multi-factor sensitivity analysis on the stability of submarine hydrate-bearing slope. China Geology, 1(3), 367–373. doi: 10.31035/cg2018051 [8] Liu JG, Li AC, Xu ZK. 2006. Grain size characteristics of sediments in Bohai Bay during Holocene. Marine Sciences, 30(3), 60–64. [9] Lu YJ, Ji RR, Zuo LQ. 2009. Morphodynamic responses to the deep water harbor development in the Caofeidian sea area, China’s Bohai Bay. Coastal Engineering, 56(8), 83l–843. [10] Lu YJ, Ji RR, Zuo LQ. 2009. Stability and engineering effect of shoals and channels in Caofeidian deep-water harbor area. Advance in Water Science, 12(4), 33–34. [11] Lu YJ, Ji RR, Zuo LQ. 2011. Formation mechanism and stability of Caofeidian channel in the Bohai Bay. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 3(66), 33–36. [12] Lu YJ, Zuo LQ, Ji RY. 2007. Effect of development of Caofeidian harbor area in Bohai bay on hydrodynamic sediment environment. Journal of Waterway and harbor, 18(6), 94–95. [13] Lu YJ, Zuo LQ, Ji RY. 2008. Effect of development of Caofeidian harbor area in Bohai Bay on hydrodynamic sediment environment. China Ocean Engineering, 22(1), 97–112. [14] Sun YF, Dong LF, Pu GJ. 2006. Stability analysis of slopes in the subaqueous delta of the yellow river under storm wave loading. Journal of engineering geology, 14(5), 582–586. [15] Tao CF. 2008. Research on the characteristics of marine engineering geology and the depth of pile penetration in Caofeidian shoal. Ocean University of China, 10−16. [16] Wang Y. 2000. Restorations of paleoenvironments in Caofeidian area since the last stage of the late Pleistocene epoch. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai and Bohai Sea, 18(3), 50–52. [17] Wu P, Jiang JJ. 2011. Site selection of Caofeidian port area. Port and Waterway Engineering, 9(9), 457–458. [18] Xu J, Ran YK, San XJ. 2004. Development of the quaternary system in the Bohai sea area. Seismology and geology, 1(26), 24–28. [19] Yin YH. 2009. The significance of protection of the Caofeidian shoal tidal channel and comparison of the new Caofeidian plan of sea reclamation land to the old one. Geoscience, 23(2), 200–209. [20] Zhu L. 2010. Study on high-precision method of shallow profile seismic data processing and interpretation. Ocean University of China, 30−70. -
Access History

-
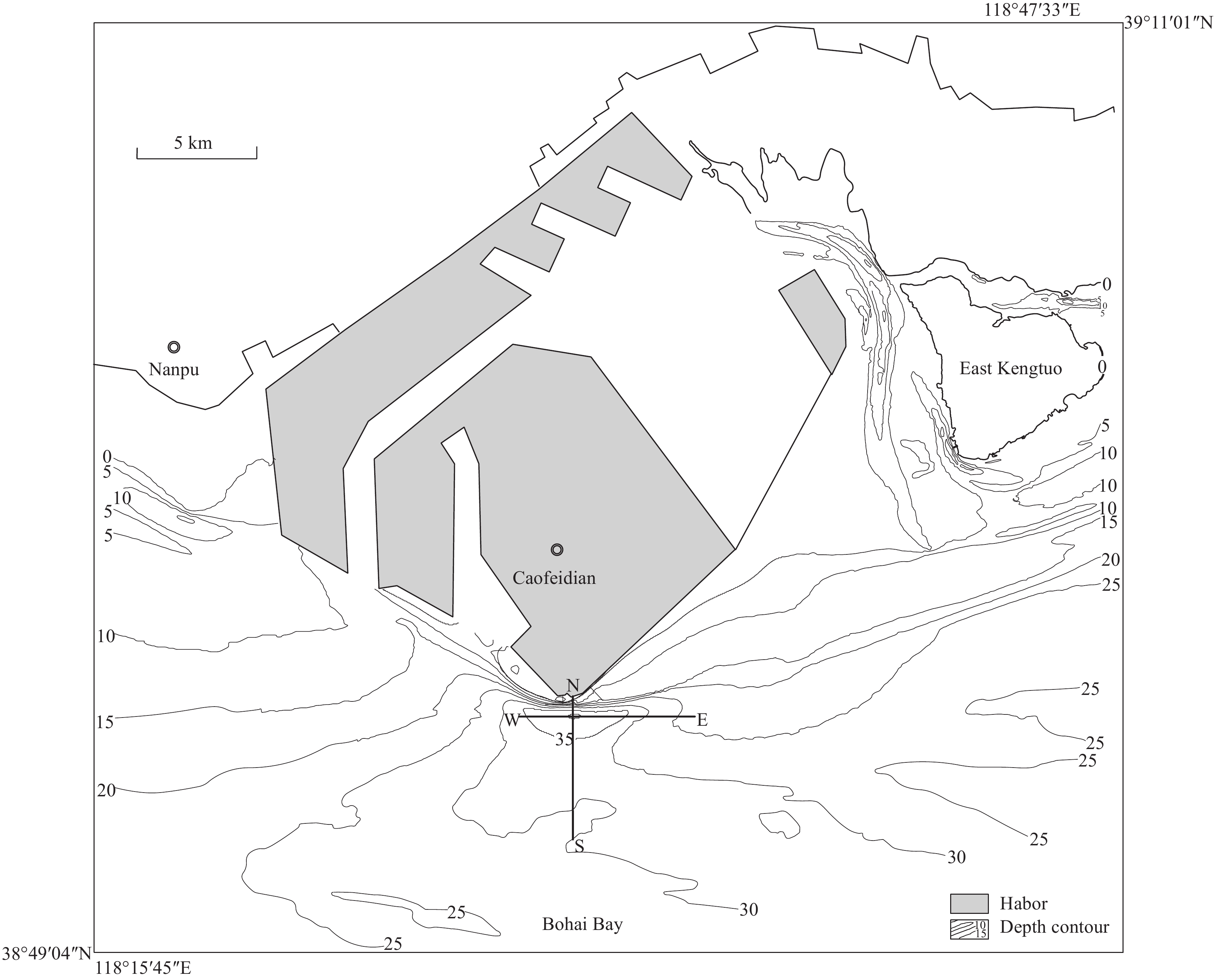
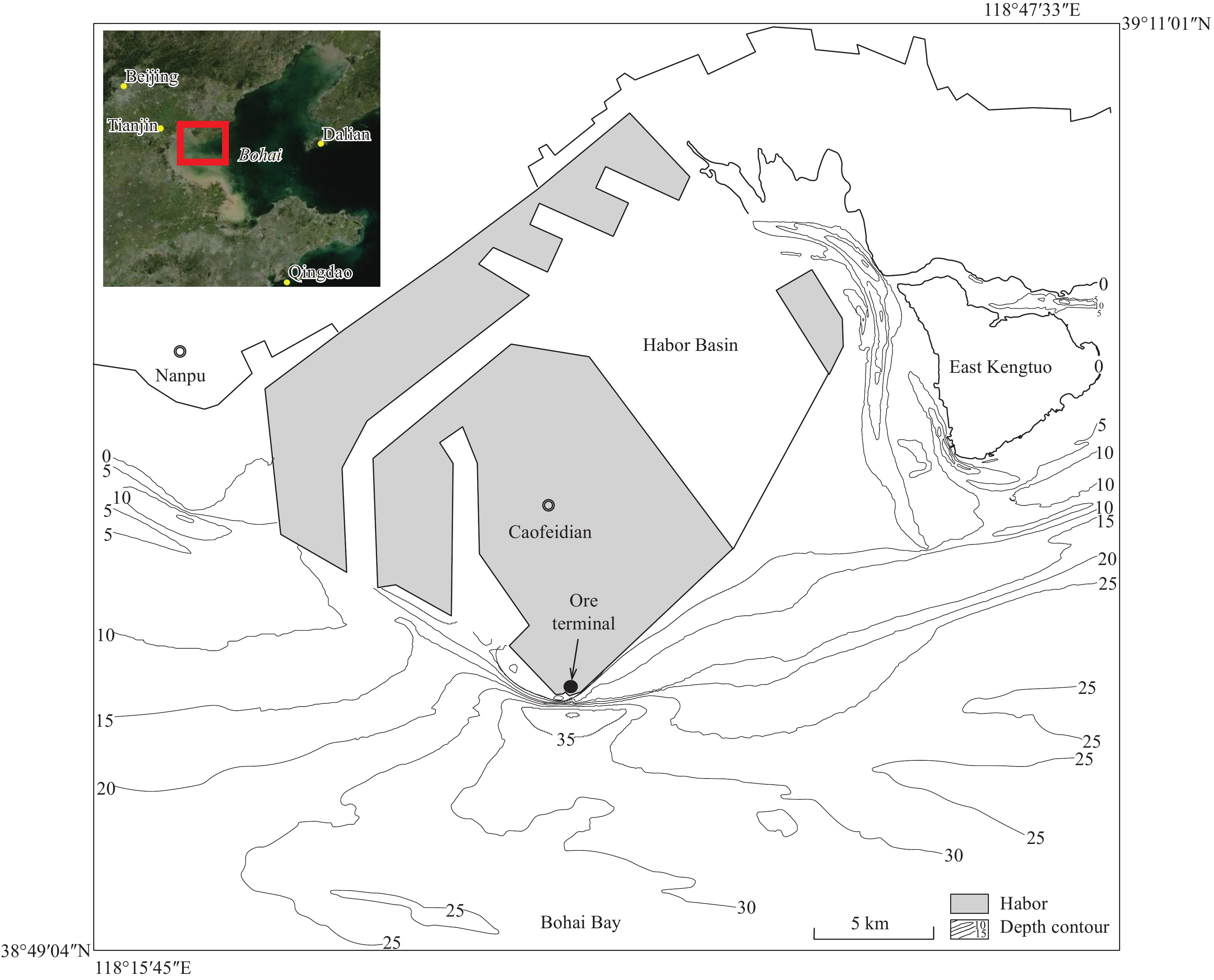
Figure 1.
Location of Caofeidian Channel study area.
-
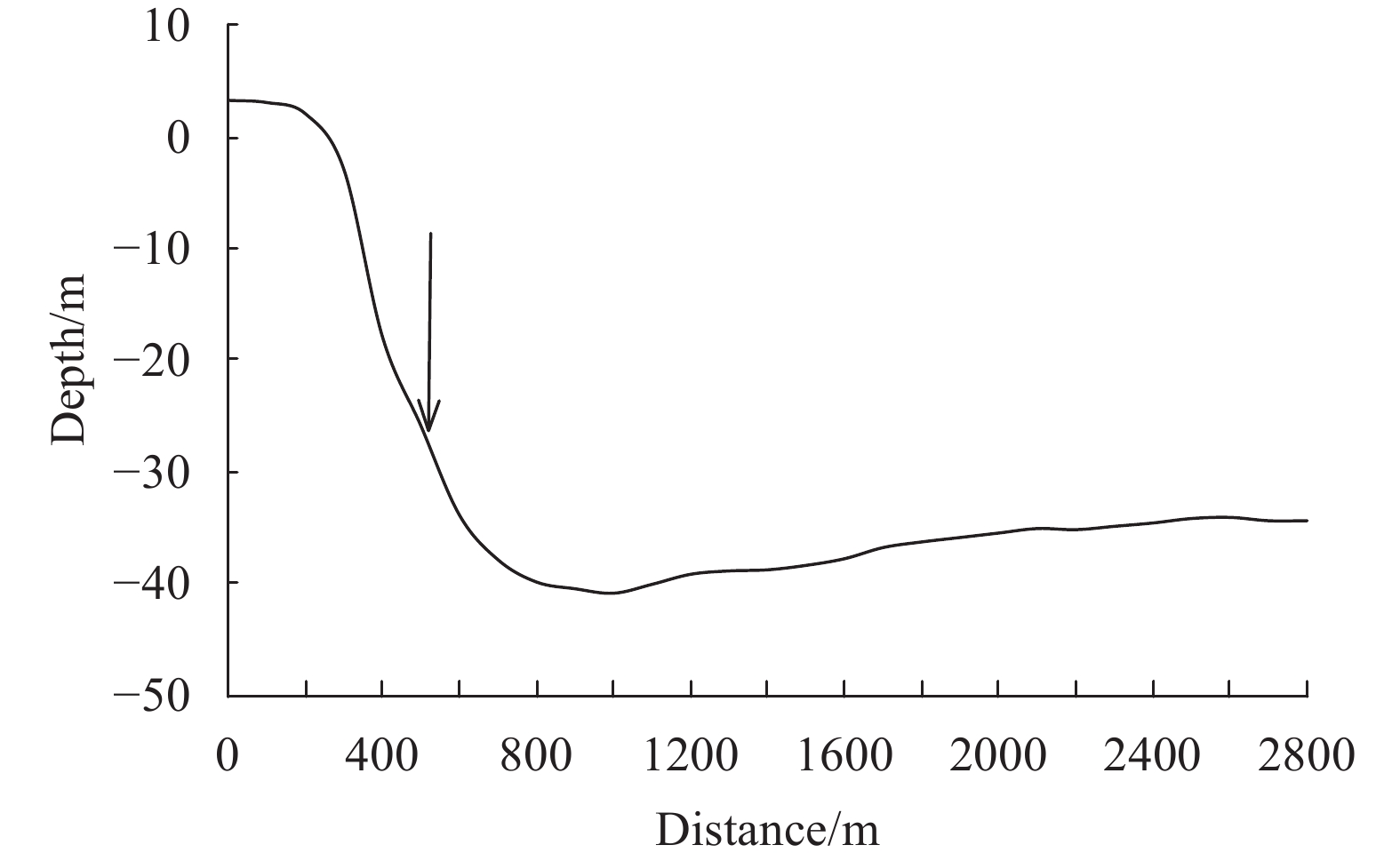
Figure 2.
Caofeidian south seabed profile.
-
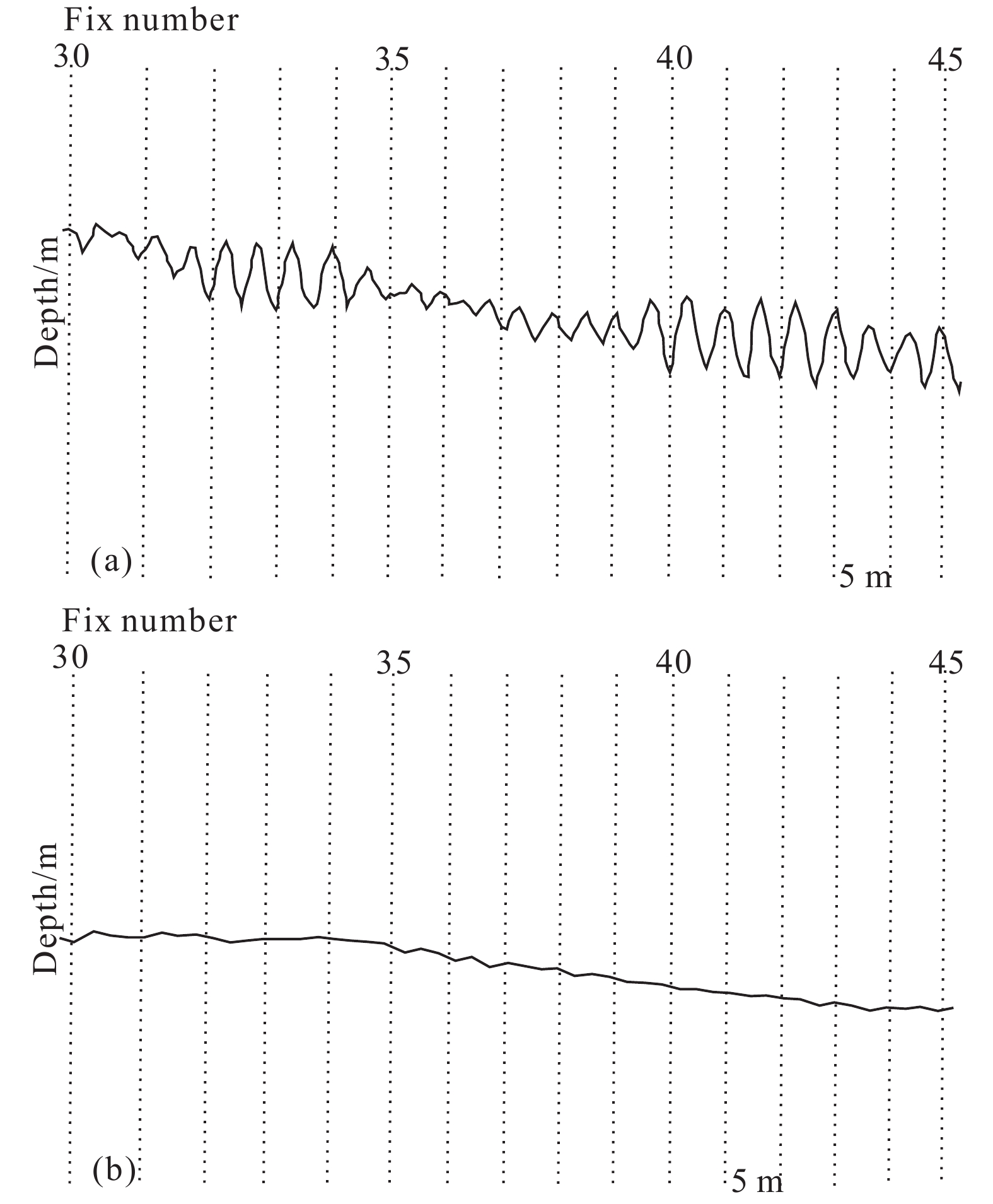
Figure 3.
The application effect of surge filter. a−Before correction; b−after correction.
-
Figure 4.
The topographic map of the Caofeidian sea area with the location of the profile.
-
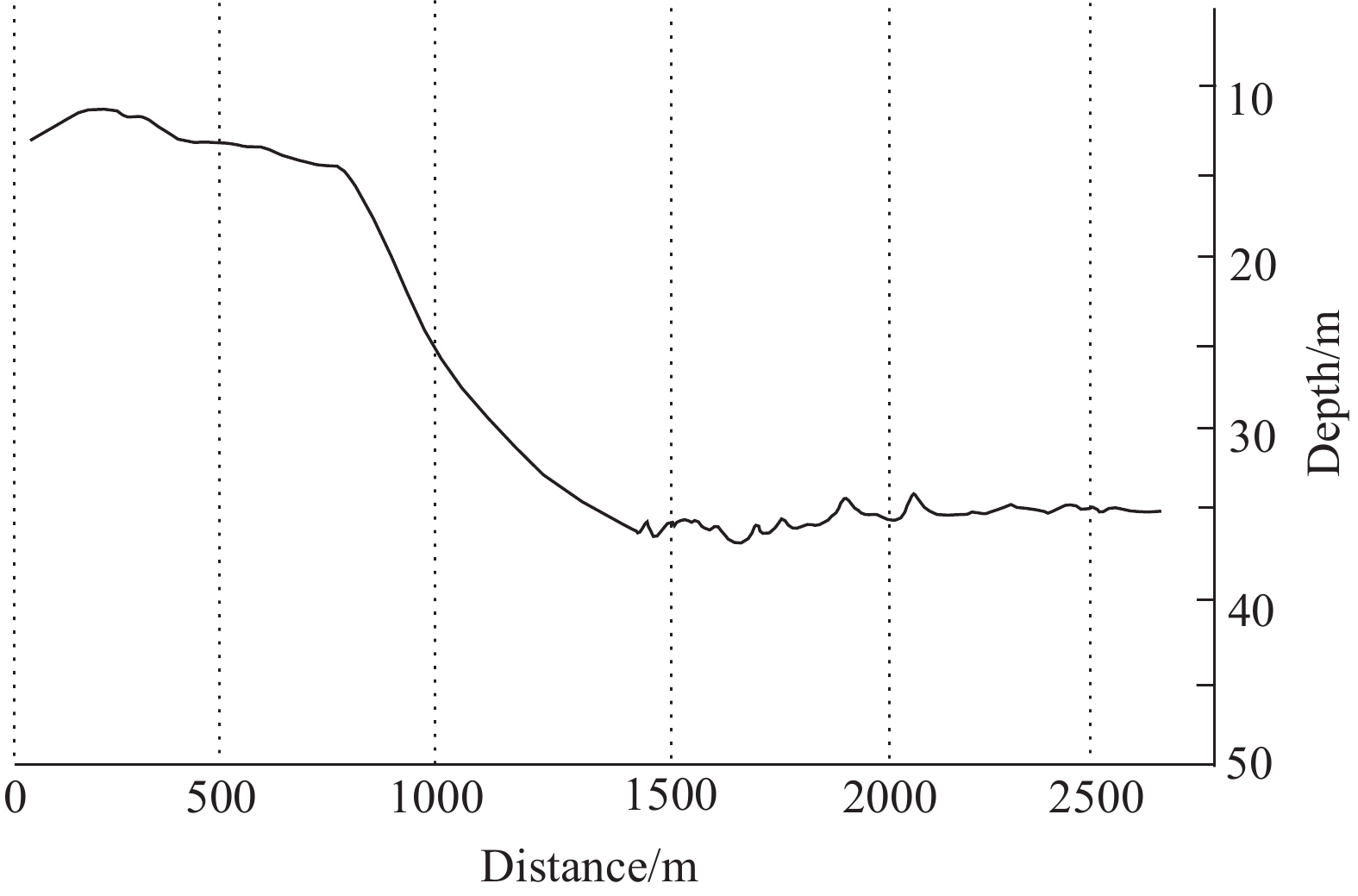
Figure 5.
Instantaneous water depth profile of the Caofeidian south area.
-
Figure 6.
Sand waves on the sub-bottom profile and side-scan sonar image.
-
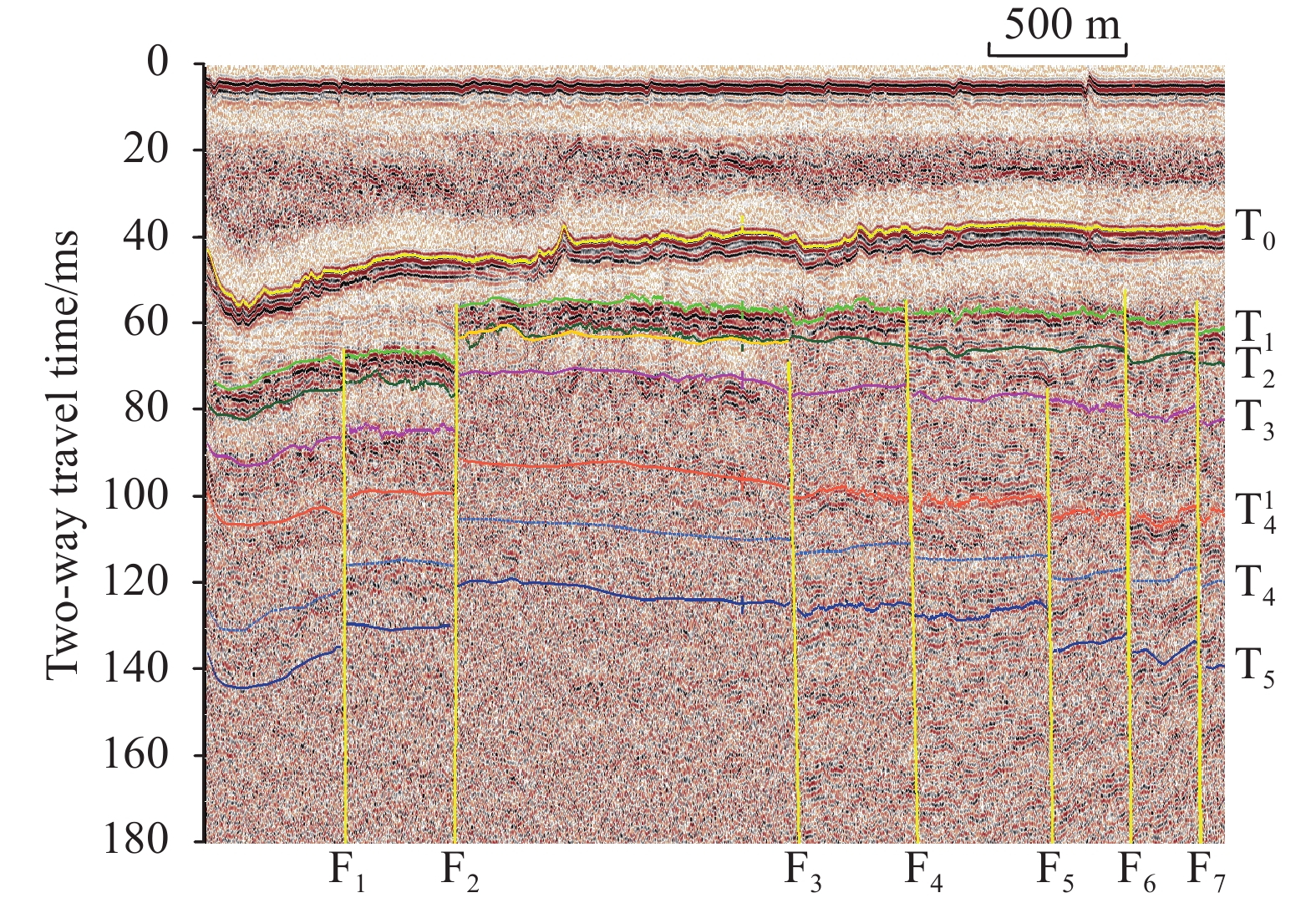
Figure 7.
Sub-bottom profile of the Caofeidian channel. F1−F7 represent faults; T0−T6 represent stratigraphic boundaries.
-
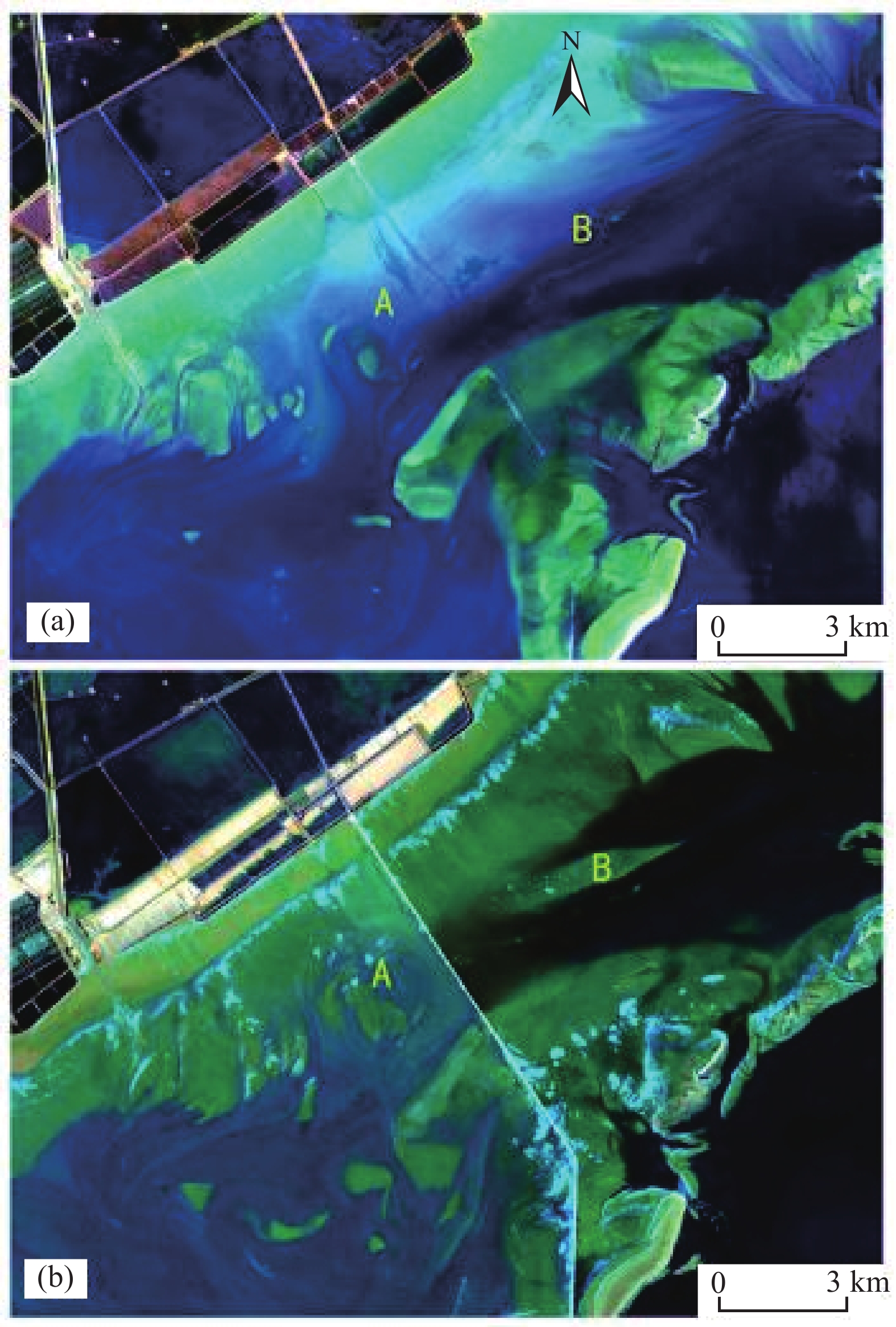
Figure 8.
Geomorphic evolution impacted by the construction of the Caofeidian channel highway. a−Before construction; b−after construction.
-
Figure 9.
Sketch map of the underwater slope stability calculation model.




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: