| Citation: | Changxiang CHEN, Lihua CAO, Zhenye ZHUANG, Jishang XU, Shunliang YANG, Dongbo ZHAO. YINGDONG SAND RIDGES IN EAST BEIBU GULF ANDTHEIR IMPACT ON PIPELINE ENGINEERING[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2018, 34(4): 49-55. doi: 10.16028/j.1009-2722.2018.04007 |
YINGDONG SAND RIDGES IN EAST BEIBU GULF ANDTHEIR IMPACT ON PIPELINE ENGINEERING
-
Abstract
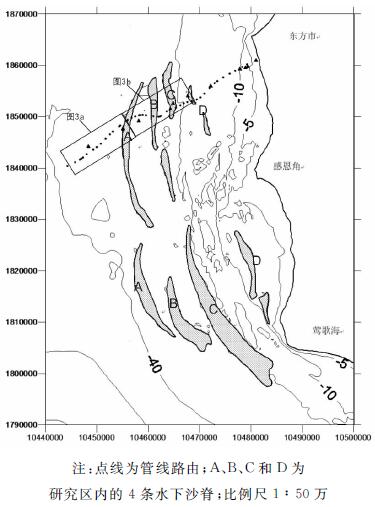
The Yingdong tidal sand ridge, which occurs in the east of Beibu gulf, is a part of the Qiongxinan sand ridge system. It is well developed outside the Ganen Cornor and smmothly extends to Dongfang. The sand ridge area can be divided into three sections, the deep water flat section, the current ridge and sand wave section and the nearshore section, from the offshore to the coast. In the current ridge and sand wave section, there are four sand ridges in NS or NW-SE direction roughly parallel to the main flow. The ridges are about 45km long with a large width. The valleys between ridges are usually 20-30m in depth, while the ridge top is 5-8m below sea level. Sand valleys are asymmetrical, steep on the land side and gentle on the sea side. The sand ridges were formed in the period of low sea level in Holocene and then eroded by modern wave. The foundation of sand ridge is strong and firm. Only in case of storm wave or strong current, can the surface sediment move in a small distance. In 2003, the Dongfang 1-1 seafloor pipeline was constructed, which passed through the Yingdong tidal sand ridge. Through the analysis of the Dongfang 1-1 offshore pipeline survey data acquired by OUC after construction, it is found that there are 130 points where the pipeline are suspended. The suspended part is 33m long on average and the distance between the pipe and the sea bottom is 1m in maximum. The suspension of pipeline is caused by the changes in bedforms and/or water dynamics. -

-
References
[1] 夏东兴, 吴桑云, 刘振夏, 等.海南东方岸外海底沙波活动性研究[J].海洋科学进展, 2001, 19(1):17-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2001.01.003 [2] 王伟伟, 范奉鑫, 李成钢, 等.海南岛西南海底沙波活动及底床冲淤变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(4):23-28. [3] 曹立华, 徐继尚, 李广雪, 等.海南岛西部岸外沙波的高分辨率形态特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(4):15-22. [4] 王琳, 吴建政, 石巍.海南乐东陆架海底沙波形态特征及活动性研究[J].海洋湖沼通报, 2007(s1):53-59. [5] 王文介.南海北部的潮波传播与海底沙脊和沙波发育[J].热带海洋学报, 2000, 19(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2000.01.001 [6] 刘昭蜀.南海地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002. [7] 刘乐军, 李培英, 杜军, 等.莺歌海油气资源开发区工程地质和灾害地质特征[C]//我国专属经济区和大陆架勘测研究专项学术交流会, 2004: 455-464. [8] Allen J R L. Sedimentary structures:their character and physical basis[M]. New York:Elsevier scientific Publishing Co, 1982. [9] Rubin D M, Hunter R E. Bedform climbing in theory and nature[J]. Sedimentology, 1982, 29(1): 121-138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1982.tb01714.x [10] 董志华, 曹立华, 薛荣俊.台风对北部湾南部海底地形地貌及海底管线的影响[J].海洋技术学报, 2004, 23(2):24-28. [11] Chiew Y M. Mechanics of local scour around submarine pipelines[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1990, 116(4):515-529. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1990)116:4(515) [12] Gao F P, Yang B, Wu Y X, et al. Steady current induced seabed scour around a vibrating pipeline[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2006, 28(5):291-298. [13] Sumer B M, Truelsen C, Sichmann T, et al. Onset of scour below pipelines and self-burial[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2001, 42(4):313-335. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3839(00)00066-1 [14] Aminzadeh A, Narayanan R. Erosion of sediments beneath an oscillating cylinder[J]. Maritime Engineering, 2008, 161(1):33-42. [15] 高伟.海南东方岸外陆架底形变化特征及对海底管线状态的影响[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008. [16] Dyer K R, Huntley D A. The origin, classification and modelling of sand banks and ridges[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1999, 19(10):1285-1330. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00028-X [17] 夏东兴, 刘振夏.潮流脊的形成机制和发育条件[J].海洋学报, 1984, 6(3):361-367. [18] 徐继尚, 李广雪, 曹立华, 等.海底管道综合探测技术及东方1-1管道不稳定因素[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2009, 29(5):47-54. [19] 吴建政, 胡日军, 朱龙海, 等.南海北部海底沙波研究[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 36(6):1019-1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5174.2006.06.033 [20] 庄振业, 曹立华, 刘升发, 等.陆架沙丘(波)活动量级和稳定性标志研究[J].中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 38(6):1001-1007. [21] 庄振业, 林振宏, 周江, 等.陆架沙丘(波)形成发育的环境条件[J].海洋地质动态, 2004, 20(4):5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2004.04.002 [22] 赵焕庭, 王丽荣, 袁家义.琼州海峡成因与时代[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(2):33-40. -
Access History

- Figure 1. Zonal distribution of bedforms in the study area (from reference [3])
- Figure 2. The distribution of sand ridges in the study area
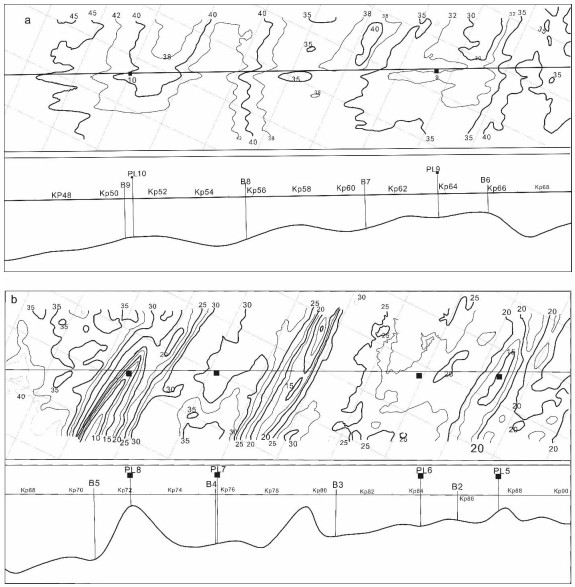
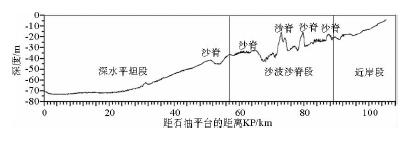
- Figure 3. The bathymetric map and cross sections of the study area (See Fig. 1 for location)
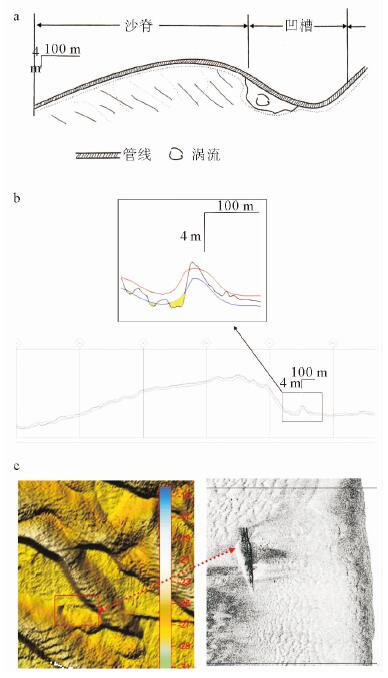
- Figure 4. (a) Lateral flow erosion of sand ridge caused pipe suspension; (b) The steep slope of the sand ridge is eroded by underflow that caused the suspension of the pipe. The black line is the bottom of the sea surface, the red and blue line is the upper and lower edge of the pipe, the yellow part is the suspended pipe; (c) 3D(left) and sonar(right) figures around KP80.2
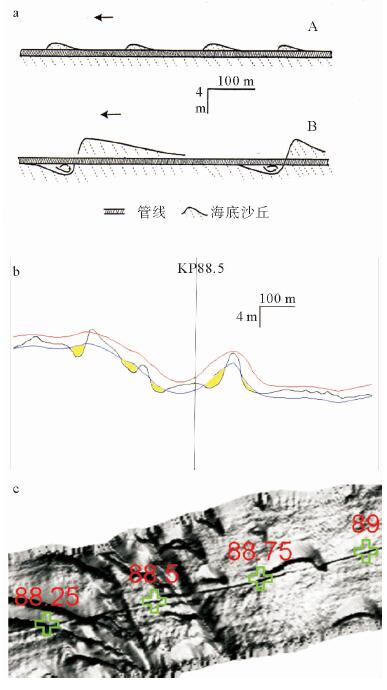
- Figure 5. (a) The sand dunes enlarged during storm surge, and the valleys deepened when the pipe suspended (A. normal weather; B. the storm surge); (b) Sections around KP88.5, the black line is the bottom of the sea surface, the red and blue lines are the upper and lower boundaries of the pipeline, the yellow part is the suspended pipe; (c) The multibeam image around KP88.5, The pipeline passes through the barchan dune area and the crater between sand ridges
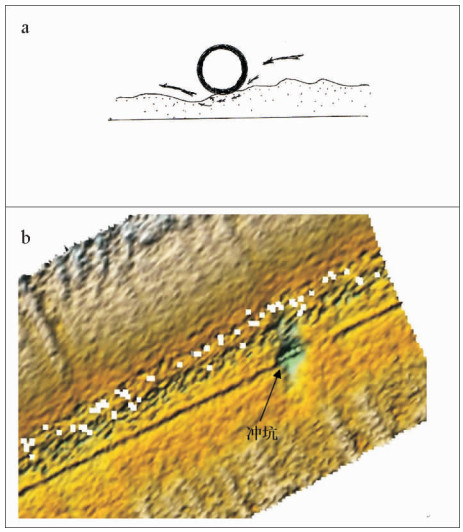
- Figure 6. (a) The schematic diagram of piping erosion effect; (b) The seafloor sonograms of the small sand flow of a circular crater caused by current




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: